Agronomic & vegetative rehabilitation [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Restoration, rehabilitation, reclamation
technologies_975 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
Land user participation with research [南非]
Land user participation with researchers to improve existing and develop new technologies
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Combinations; cultivation & vegetative
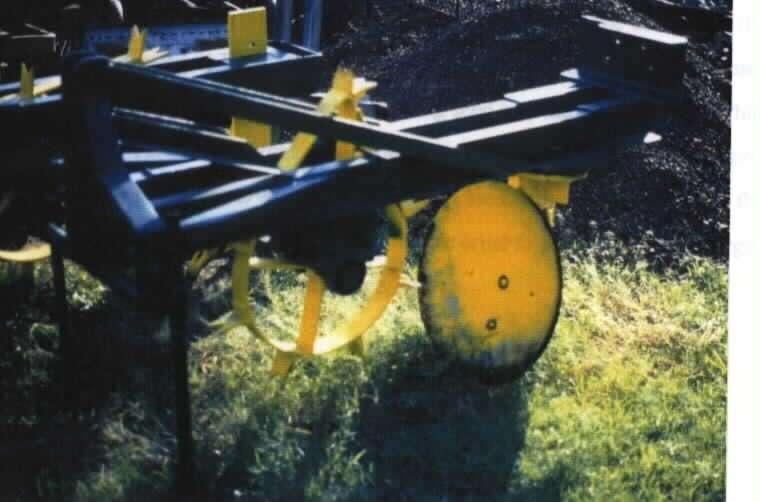
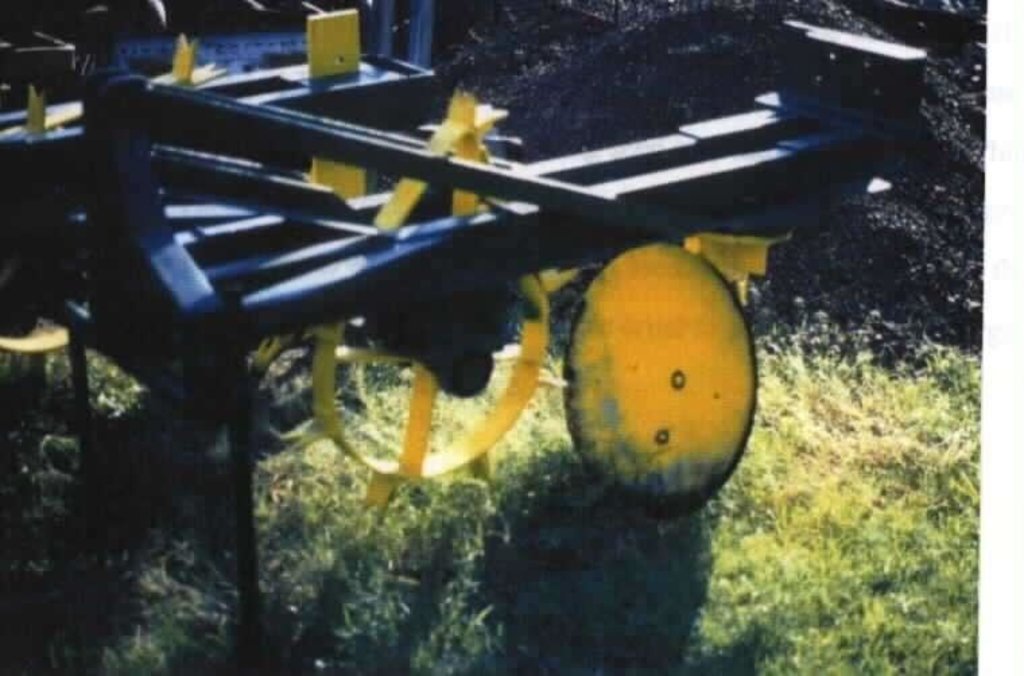
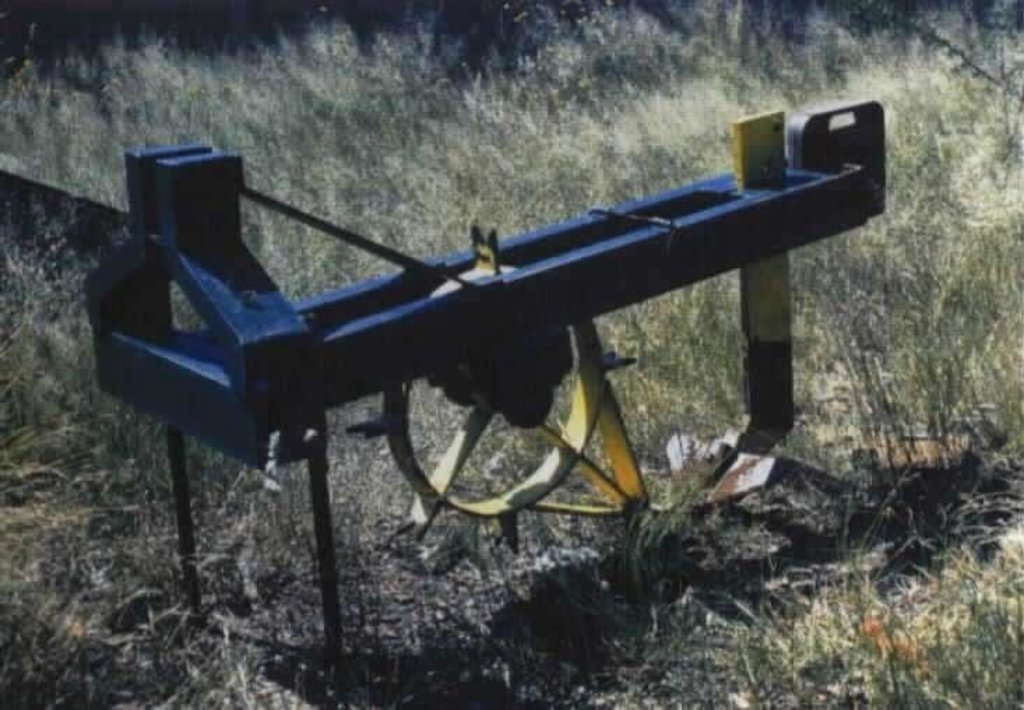
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The purpose of the rehabilitation includes an increase in production potential, vegetative cover and density, biodiversity, fodder for grazing and palatable grass species.
To establish this technology, cultivation of the denuded areas was done by dyker plough. Oversowing with a grass-seed mixture followed. The seeds (indigenous) were purchased from a seed-company. If woody encroachment species are available, place the branches on the cultivated area. No maintenance is necessary; the area is left as it is for 3 years with no grazing if possible (no grazing for cattle, but for game some grazing-areas are partly covered by branches no grazing).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
North West Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Zeerust (Eastern parts)
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
20.0
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 km2.
Commercial owned farmland - game and cattle farming
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Land owners & agriculturist - extension
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 林牧业

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
- 经营牧场

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Bush encroachment, bare denuded land - open spaces
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Not productive for grazing land
Erosion
Low grass cover
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Ranching: Yes
Other grazingland: intensive grazing land
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection, recreation / tourism
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Constraints of recreation
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施

管理措施
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, management measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: contour tillage
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, poverty / wealth (Lack of captial - Not enough money to implement rehabilitation - higher inflation)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Climate), land tenure (Land subdivision - Land properties get smaller & less cost effective), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Also rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measure: overseeding
Material/ species: Indigenous species
Quantity/ density: 5kg/ha
Remarks: In hollows made by cultivation
Agronomic measure: branches
Material/ species: From encroachment species (woody)
Vegetative measure: sowing by hand
Vegetative material: O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 5kg/ha
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5m
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Grass species: seed
Change of land use practices / intensity level
Major change in timing of activities: Different grazing patterns for animals to avoid treated area
Control / change of species composition: Use different animals e.g. game
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
6.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
8.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dyker plough making hollows | Beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Sowing of perennial grass seeds (in hollows, waiting for rain) | Beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Fences | At beginning of project |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Ploughing and sowing | persons/day | 60.0 | 8.0 | 480.0 | |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 100.0 | 14.0 | 1400.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 100.0 | 40.0 | 4000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5880.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 980.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dyker plough cultivation on contours | Start of growing season / |
| 2. | Chopping of woody branches of encroaching species | Start of growing season / |
| 3. | Bush packing on cultivated area | Beginning of season /1st season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor & dyker plough implement
This costs are calculated for 100 ha
No additional fencing material costs.
Old fences used to enclose the treated area.
(+ R 4000 /km fencing costs if new (normal) fence is needed. For game fence R4000 for 300m)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
No subsidies
Very labour intensive
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very low - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low - low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
2% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
17% of the land users are poor.
30% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Commercial
10-50% Communal, poor. Commercial - < 10%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
- commercial
- commercial
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Keep 3 years from grazing
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
经济差异
工作量
其它社会经济效应
input constraints
initial costs
注释/具体说明:
Labour intensive, must have a tractor & implement or hire
社会文化影响
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
From extension worker
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
70
SLM之后的数量:
20
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
其它生态影响
soil erosion locally
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Better vegetative cover, better water infiltration, less siltation of dams used for watering live stock
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
注释/具体说明:
August - wind high, higher vegetation cover & density
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
50 percent of the area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers (land users) are more aware about land degradation and want to do something about it.
More in media
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increase grazing capacity, more fodder How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good & controlled management |
|
Better & more income: meat, funds How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good & controlled management |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Decrease bush encroachment and invasion of woody species How can they be sustained / enhanced? New growth of species must be controlled |
|
Increase vegetation cover & density How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep out grazing |
|
Increase soil moisture & infiltration rate How can they be sustained / enhanced? Deep cultivation, cover by twigs/branches |
|
Increase seed bank for whole area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Let the grasses sown - reproductive & make seed so that seed can be distributed by wind or animals |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Low cost/benefit rates in short term | Keep it up and don't get discouraged -see advantages over the long term |
| Need tractor & implements | Hire implements from Agriculture of other land users |
| Must have knowledge about the SWC technology | Ask technical & support by Agricultural extension or researches or other land users |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Van der Merwe, JPA. MSc thesis. 1995.Soil conservation booklet
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Potchefstroom University
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil conservation booklet
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Land user participation with research [南非]
Land user participation with researchers to improve existing and develop new technologies
- 编制者: Klaus Kellner
模块
无模块