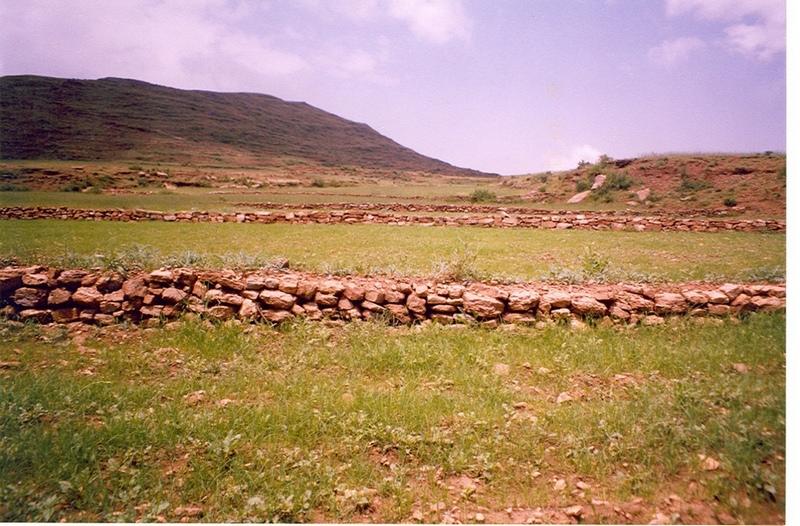
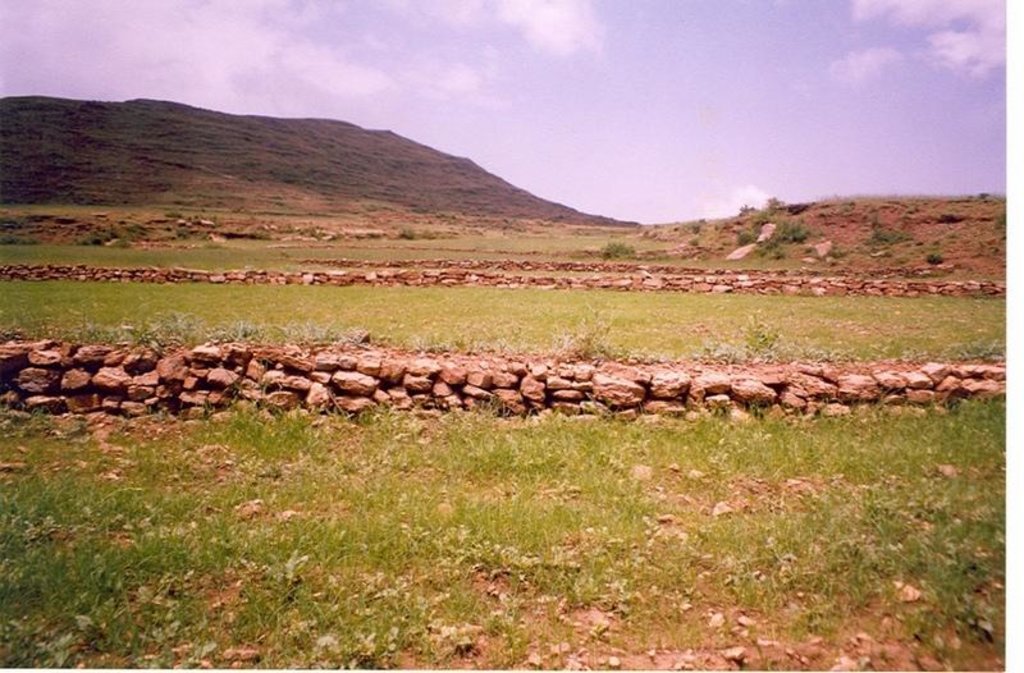
Stone faced soil bund of Tigray [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Emni Getsu hamed zala
technologies_980 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Tesfaye Tadele
S/Samre office of Agriculture and Natural Resources
埃塞俄比亚
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Stone walls placed downslope in an inclined manner having embankment of soil on upstream along the contour line having tieridge.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Description: Along the contour 30 cm width and 420 cm depth of foundation is excavated and stones are cplaced upto a height of 0.5-0.75 with 1 m width and 30 cm top width. On the uper side embankment soil is added and a basin with 5-10 m tie is excavated. Purpose: To reduce soil erosion, shorten slope length and retain soil moisture. Establishment/Maintenance: Integrate with biological SWC activities, Farmers maintain Environment: Enhance vegetation growth, improve micro-climate, decrease land degradation
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Tigray
有关地点的进一步说明:
Woreda
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 327.53 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷类 - 高粱
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
- teff, horse bean
- Leucanea, sasbanea
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Teff and sun flower

牧场
- Free grazing
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, deforestation, overgrazing, decline of fertility, low moisture holding capacity
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low productivity, low rainfall, soil erosion, deforestation
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
Water supply: post-flooding
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Teff and sun flower
Remarks: direct sowing
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 1000/ha
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 15-20
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-1
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucanea, sasbanea
Grass species: local grasses
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3.00%
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 60-80m
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.1m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5m
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-0.75mm
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60-80m
Construction material (earth): none clay and sandy soils
Construction material (stone): medium sized stone
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Birr
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.6
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.88
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seedling production | Dec-June |
| 2. | Pitting | May |
| 3. | Planting | July |
| 4. | Survey & layout | January |
| 5. | Fundation excavation | February-April |
| 6. | Stone collection | February-April |
| 7. | Construction and digging the basin and put the soil at the upper side of the bund | February-April |
| 8. | Forming farmers groups | |
| 9. | Discussion among group members | |
| 10. | Plan of activities | |
| 11. | Implementation of measures | |
| 12. | Guarding |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 33.75 | 33.75 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Person days | ha | 1.0 | 66.9 | 66.9 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 229.45 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 26.68 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Contour plowing | April-may / 3 times |
| 2. | Enrichment planting | August /annual |
| 3. | Weeding and cultivating | September /annual |
| 4. | Stone collection | January/annual |
| 5. | Construction | January/annual |
| 6. | Planting/replanting | |
| 7. | Implementing water harvesting measures |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 10.9 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1.27 | |||||
注释:
Length of structure and number of seedlings
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
steep slope, transport for construction materials (stone), dry soils (land), shallow soils.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1000-2500 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Also mountain- and hill slopes
Slopes on average: Also hilly and moderate
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture: Also medium (ranked 2) and fine/heavy (ranked 3)
Soil fertility is low-medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good-poor
Soil water storage capacity is low-high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land.
15% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Employed as daily labourer for weeding, plowing and harvesting.
Market orientation is subsistence (the area is drought prone and production is very low)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
0.5-1ha for both grazing and cropland per household. Average land holding size is 0.5 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
200 kg
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Space taken by structure is small
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
If proper placing of stone not followed
其它生态影响
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
Enriching ground water
Risk of damage on properties if the structure breaks
Waterlogging
注释/具体说明:
in clay soils during wet seasons it is high
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
decreasing siltation of dam and cultivated area
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
98328 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Especially the maintenance of the structure is done by individuals holding the land
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increase production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cut and carry, area closure, Integrating physical SWC measures with biological SWC measures. |
|
Availability of water near byareas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Water harvesting structures and practices |
|
Animal feed increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting fodder trees and grasses |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It conserves soil How can they be sustained / enhanced? The work has to be continued in organized way. |
|
It conserves moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Include contour cultivation and other methods enhancing the soil moisture build up. |
|
Increase production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integration of biological measures use of manure and other fertility improving measures. |
|
Enhancing spring development How can they be sustained / enhanced? Practice more water retaining measures upslopes |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It reduces cultivated land | Make the land productive by integrating with biological SWC measures, planting grass on the bund |
| It creates problem in farm activities | Design the structure in such a way that it can not create problem for farming. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It takes land | By integrating with biological measures make the land productive. |
| In some places hinder farm operation | Increase width of cultivable strips |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块