Капелное орощение с использованием полиэтиленовой плёнки [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
technologies_1037 - Tajikistan
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Капелное орощение с использованием полиэтиленовой плёнки: Maart 20, 2017 (inactive)
- Капелное орощение с использованием полиэтиленовой плёнки: Julie 22, 2017 (inactive)
- Капелное орощение с использованием полиэтиленовой плёнки: Aug. 21, 2019 (inactive)
- Капелное орощение с использованием полиэтиленовой плёнки: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
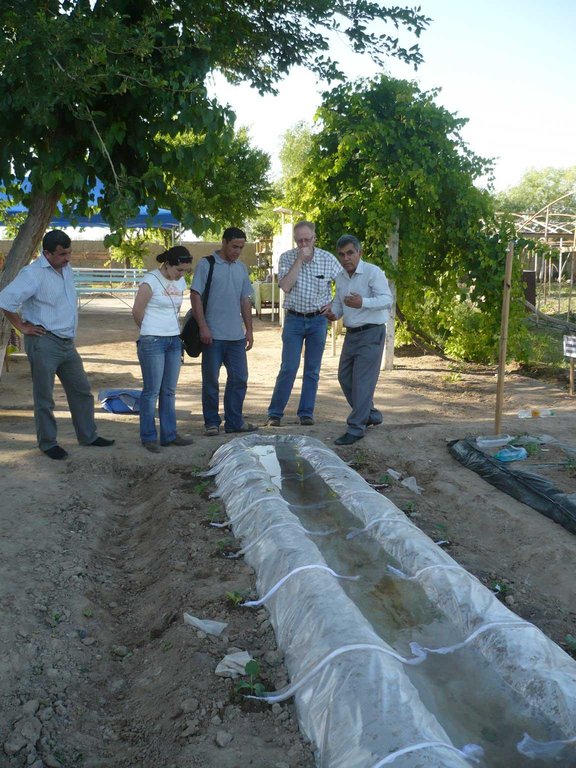
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kyrgyzstan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
03/05/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Капельное орошение с использованием полиэтиленовой плёнки в условиях закрытого и открытого грунта
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
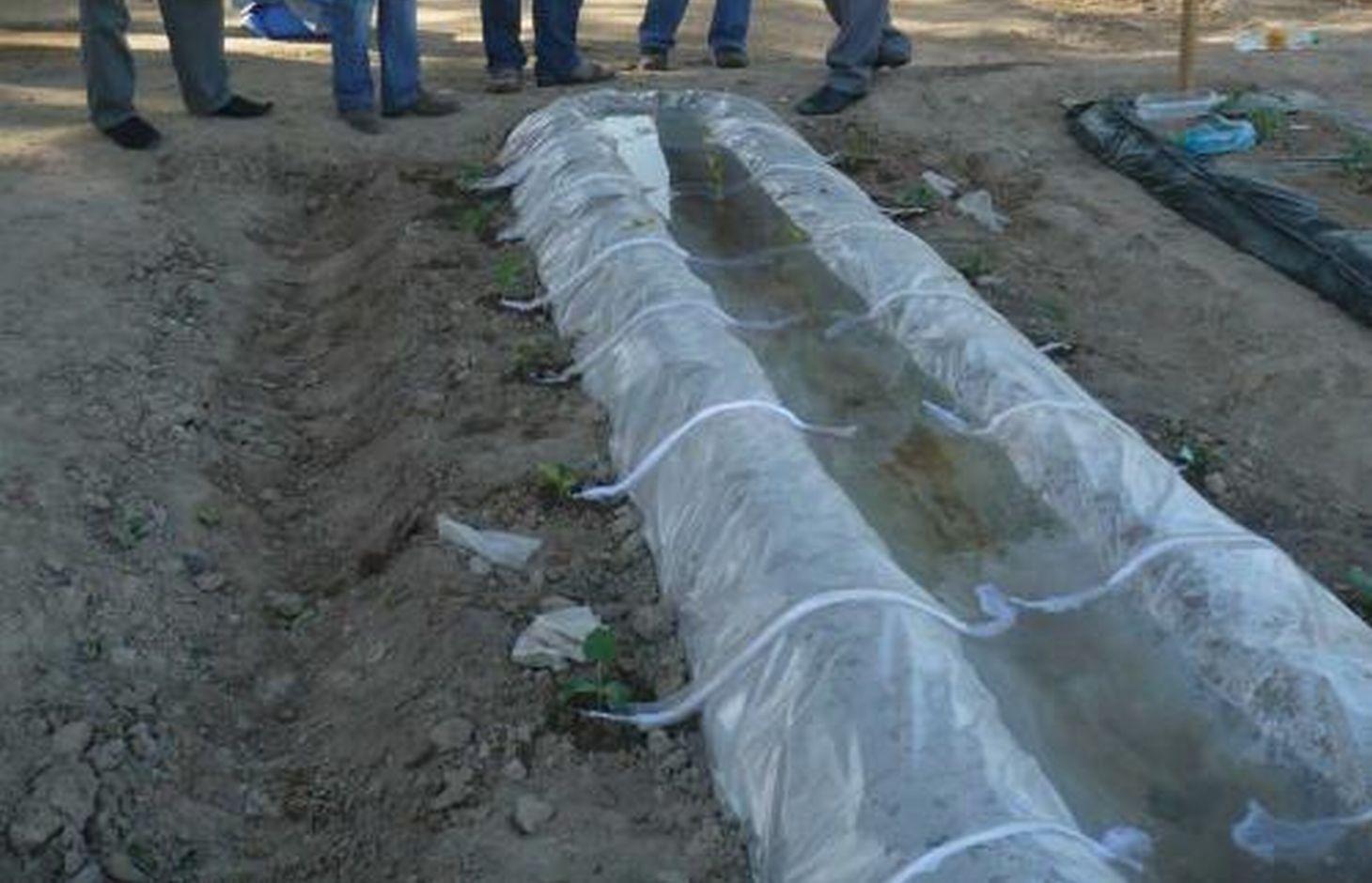
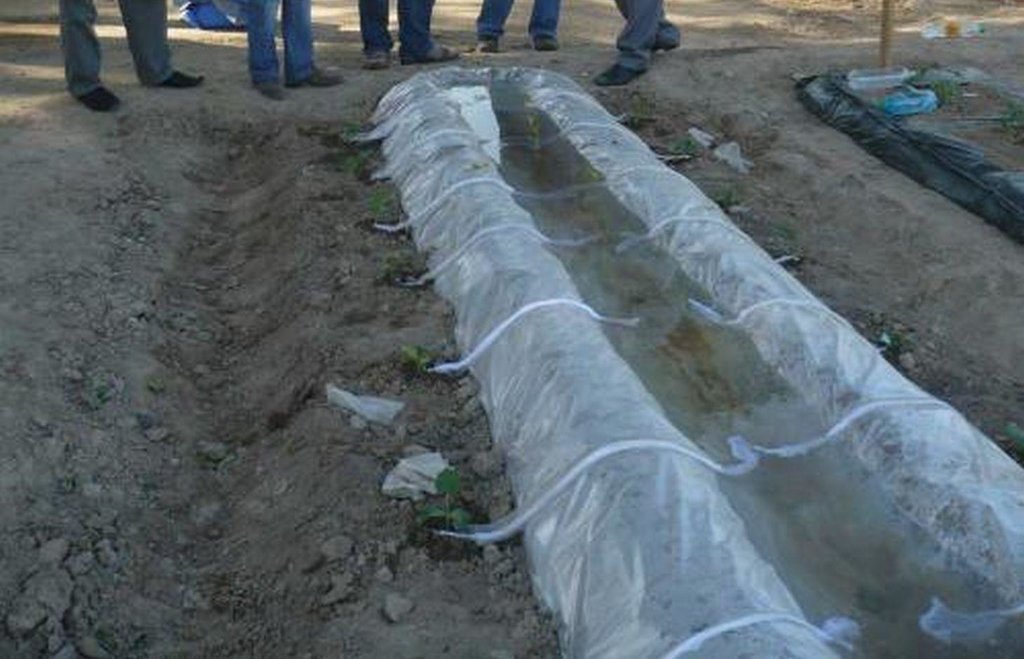
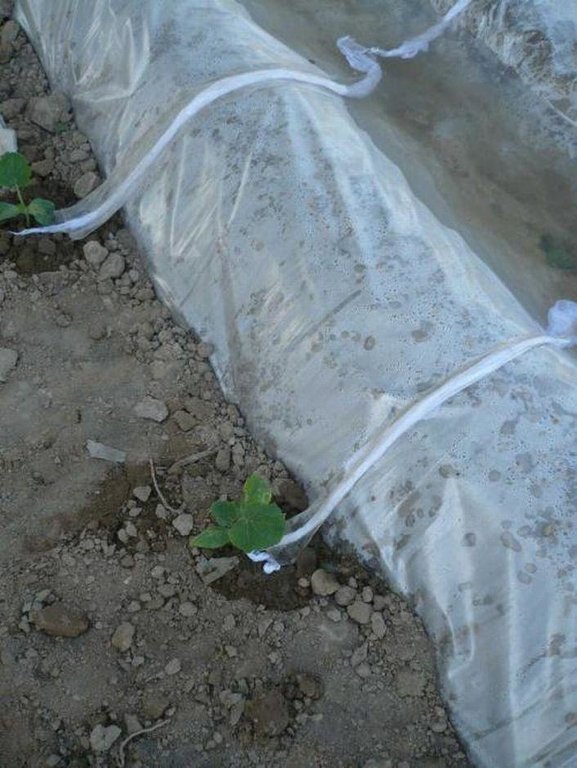
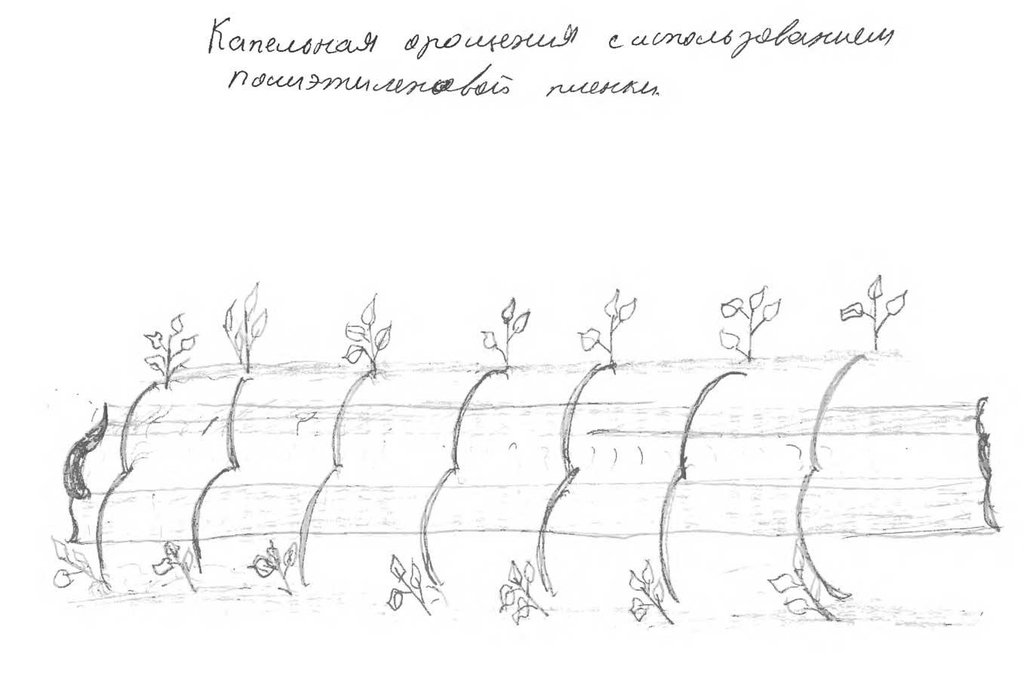
Выращивание хлопка занимает много воды, а на частных земельных участках воды часто не достаточно и народ придумал эту технологию. Воду для полива растений можно запасти в бункерах и затем использовать для капельного орошения или капельного орошения с использованием полиэтиленовой пленки. Этот метод используется в экстремальных условиях дифицита воды в основном для выращивания овощных культур.Пленка расстилается на грядках – она является экраном для воды. Сверху пленка может накрываться полиэтиленовым «покрывалом». Устройство по конструкции может напоминать небольшой бассейн или «грелку». С помощью тряпичных или марлевых шнуров обеспечивается подвод воды к каждому растению. В этом случае питательная среда полностью поглащается растением. Исключается смыв верхного слоя почвы.
Purpose of the Technology: В южных районах Хатлона вода является дефицитом в основном поглощается на хлопковых плантациях. Землепользователи запасали воду в бункерах используя проточную воду и дождевые осадки, а затем использовали эту воду для подачи на грядки с помощью описываемой технологии. Основная цель этой технологии- более экономное использование воды, уменьшение испарения влаги в почве, предотвращение эррозии почв. Технология используется для получения урожаев овощных и бахчевых культур.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Производиться вспашка, чизелевание, делается грядка, производиться посадка культур, растеляется полиэтиленовая плёнка, заполняется водой. Перед каждой рассадой натягивается шнурок от воды для капельного орошения. Постепенно через шнур вымачивается вода и капает под каждым растением. Для создания этой технологии необходимо приобрести полиэтиленовую пленку и тряпочный шнур.
Natural / human environment: Эта технология может быть использована для выращивания культур в условиях экстремального климата, засолённых почв, непредсказуемой погоды и дефицита воды.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Таджикистан
Further specification of location:
Хатлон. Н.Хусравский район
Map
×2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Эта технология используется с 2007 г.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Проблема связанная с ирригационной водой и засолённостью почвы.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Проблема связанная с ирригационной водой и засолённостью почвы.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
Water supply: полностью орошаемое, полностью орошаемое
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 120
Longest growing period from month to month: февраль-май
Second longest growing period in days: 180
Second longest growing period from month to month: июнь-ноябрь
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
Приусадебное хозяйство
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A6: Others

management measures
- M4: Major change in timing of activities
Comments:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: management measures
Type of agronomic measures: ранняя посадка, сменное возделывание культур, большее сохранение раст. покрова, мульчирование, сидерат, посадка бобовых в междурядьях, навоз / компост / остатки
Type of vegetative measures: урегулированный: -контур
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cs: salinization/ alkalinization

physical soil deterioration
- Pk: slaking and crusting
- Pi: soil sealing

water degradation
- Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Вв (Wt): потеря верхнего слоя почвы / поверхностная эрозия, Хс (Cs): засоление / осолонцевание, Дк (Hq): снижение качества грунтовых вод
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Фк (Pk): уплотнение и образование коры
Main causes of degradation: управление землеи, управление с/х культурами (однолетние, многолетние, деревья/кустарники), засуха
Secondary causes of degradation: изменение температуры, наличие работы
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
С двух сторон грядки посажены рассады овощных культур, на грядке растеленна полиетиленовая пленка и заполнена водой. Перед каждым растением натянут шнур- один конец в воде, а другой у корня растения. Шнур постоянно втягивает воду и поддаёт её растению.
Location: Таджикистан. Хатлонский обл. р-н. Н.Хусравский
Date: 3 май 2011г.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: высокий
Technical knowledge required for land users: низкий
Main technical functions: повышение / поддержание сохранения воды в почве, сбор воды / повышение водоснабжения
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: Др: другие
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.35
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.7
Trees/ shrubs species: помидоры, огурцы, перец
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 3%
Structural measure: посадка на ровной земле
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.35
Spacing between structures (m): 0.35
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 35
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.7
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Change of land use type: изменение поливного метода
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
сомони
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4.5
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
10.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Пленка | Vegetative |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 2.0 | 20.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | None | None | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | None | None | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | None | None | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 497.0 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | посадка рассады или семенной посев (помидоры, огурцы, перец) | Agronomic | весной |
| 2. | Подготовка почвы | Agronomic | весной |
| 3. | Арго уход | Vegetative | март июнь |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 2.0 | 20.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 2.0 | 20.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 25.0 | 20.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | None | None | 4.0 | 15.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | None | None | 50.0 | 0.5 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | None | None | 500.0 | 0.4 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 865.0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Засоленная почва
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial, commercial/ market
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
risk of production failure
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
harvesting/ collection of water
excess water drainage
evaporation
Soil
soil crusting/ sealing
nutrient cycling/ recharge
salinity
Climate and disaster risk reduction
drought impacts
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
| local windstorm | not well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Данная технология широко не распространена
Comments on spontaneous adoption: пока только на одной ферме
Comments on adoption trend: дорабатывается
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Данная технология капельного орошения недорогая |
|
Достигается больше урожайности How can they be sustained / enhanced? Данная технология помогает сохранять плодородие почвы и сокращать размыв питательных веществ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Данная технология капельного орошения недорогая |
|
Может быть использована в парниках и при экстремальных климатических условиях How can they be sustained / enhanced? Может быть развита в изменяющихся климатических условиях |
|
При сокращении объемов воды, используемых для орошения, технология помогает сохранять воду How can they be sustained / enhanced? Вода доступна в период роста культуры |
|
Так как технология не трудоемкая, то легко может быть использована How can they be sustained / enhanced? Технология не трудоемкая |
| Технология выгодна в экологическом отношении, так как предотвращает деградацию почвы |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Не пригодна для использования на открытых участках с высокими температурами | Применяется только на пригодных участках |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Не пригодна для использования на открытых участках с высокими температурами | Применяется только на пригодных участках |
| Технология может быть использована только в солончаках | Будет разрабатываться для других видов культур |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules