ເຕັກນິກການສ້າງໜອງຢູ່ເຂດພື້ນທີ່ຄ້ອຍຊັ້ນ [Lao People's Democratic Republic]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: kang phanvongsa
- Editors: anousit namsena, Bounthanom Bouahom, Pasalath Khounsy
- Reviewers: Oulaytham Lasasimma, Stephanie Jaquet, Nicole Harari
technologies_2920 - Lao People's Democratic Republic
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
ອຳດາງ ແນບ
030 4525791
ບ້ານ ຕັງໂກ, ເມືອງ ສະໝ້ວຍ, ແຂວງ ສາລາວັນ
Lao People's Democratic Republic
land user:
ອຳໂດ ກູ້ສ້ອຍ
020 91278700
ບ້ານ ຕັງໂກ, ເມືອງ ສະໝ້ວຍ, ແຂວງ ສາລາວັນ
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) - Lao People's Democratic Republic1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
07/07/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
ແມ່ນການຫັນປ່ຽນທີ່ດິນທີ່ມີ ນ້ຳລິນໄຫຼຜ່ານ ລົງສູ່ຫ້ວຍ ມາເປັນໜອງເພື່ອເກັບກັກນ້ຳ ແລະ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການຊະລ້າງເທິງໜ້າດິນ
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
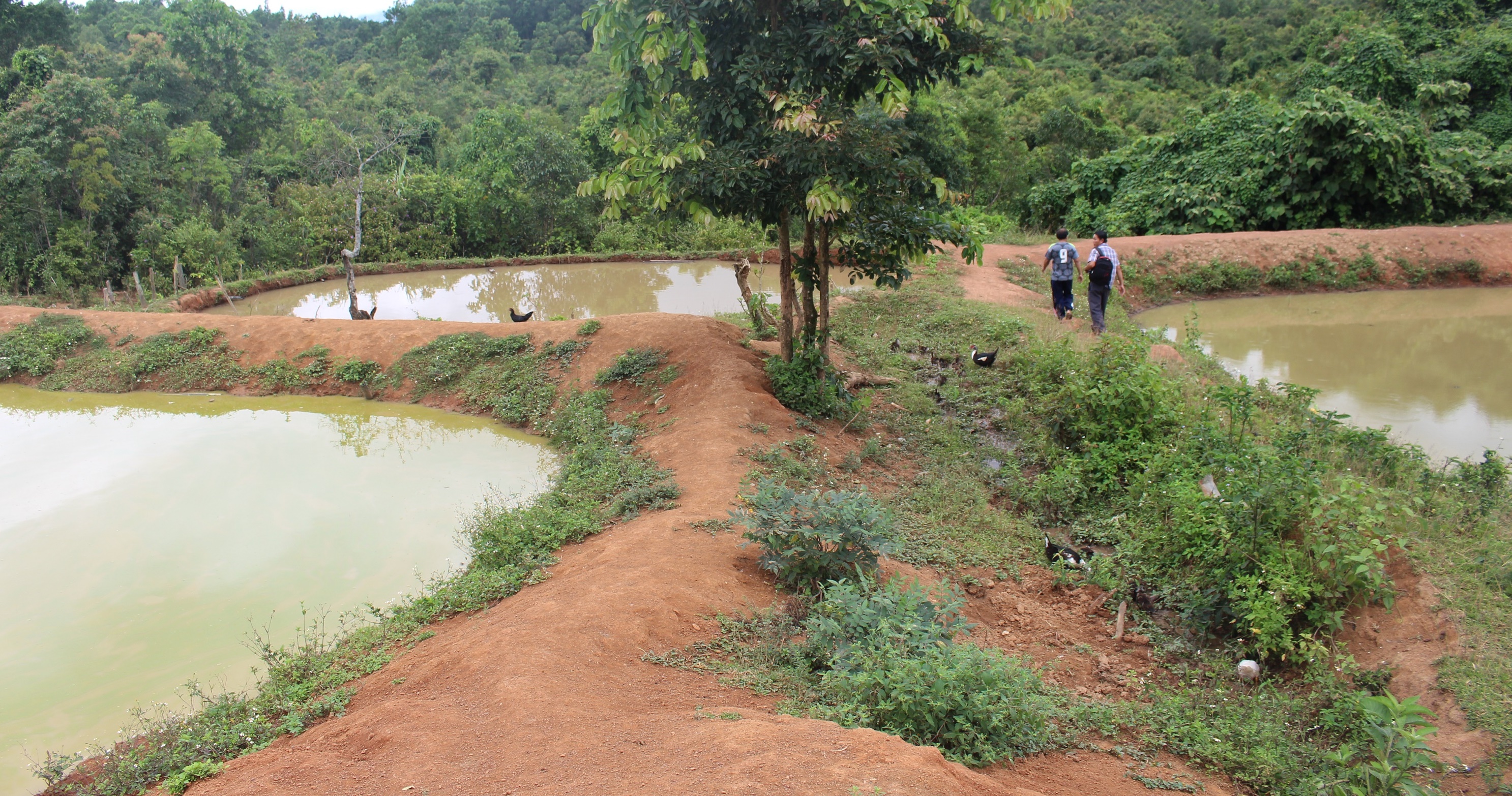
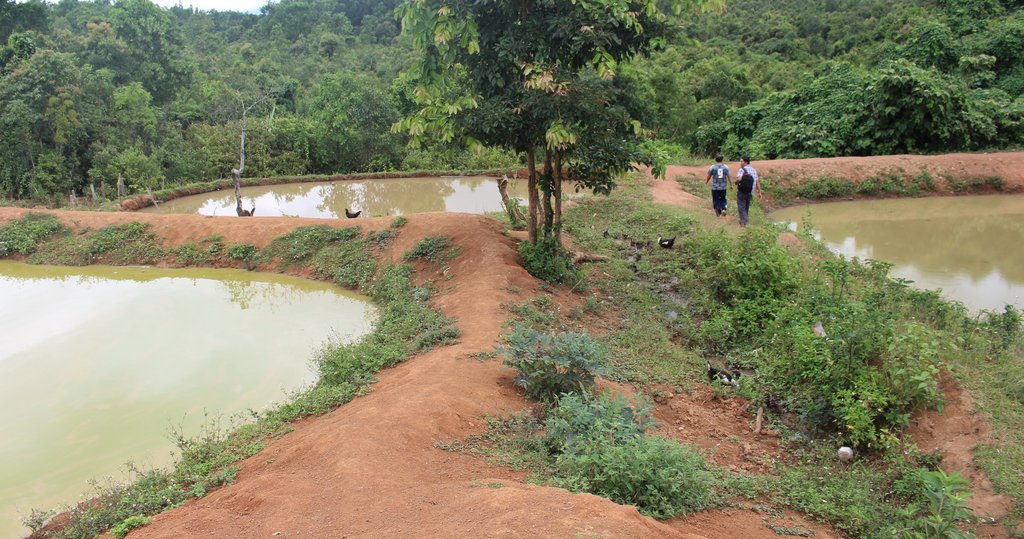
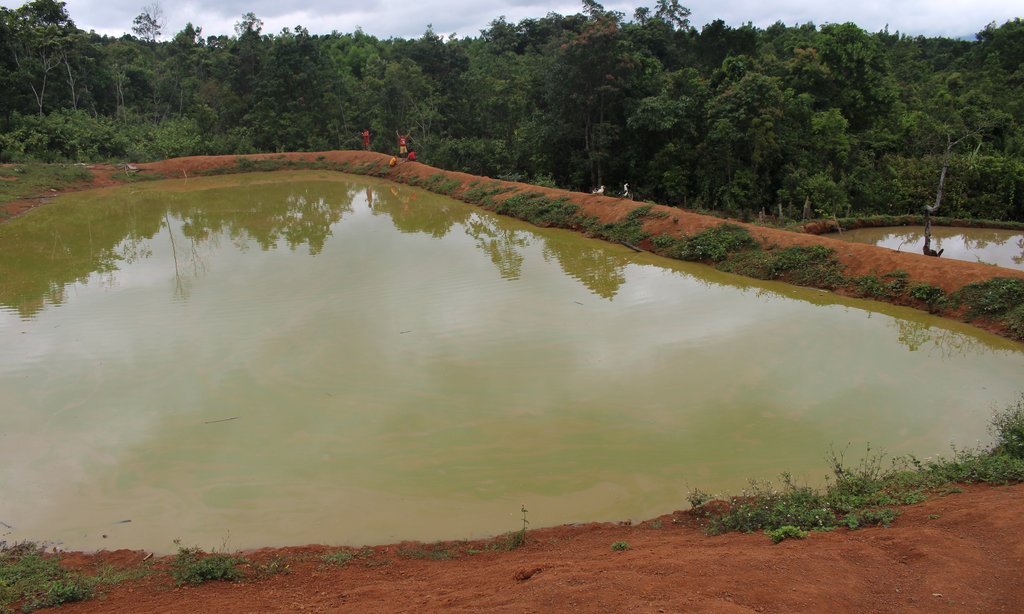
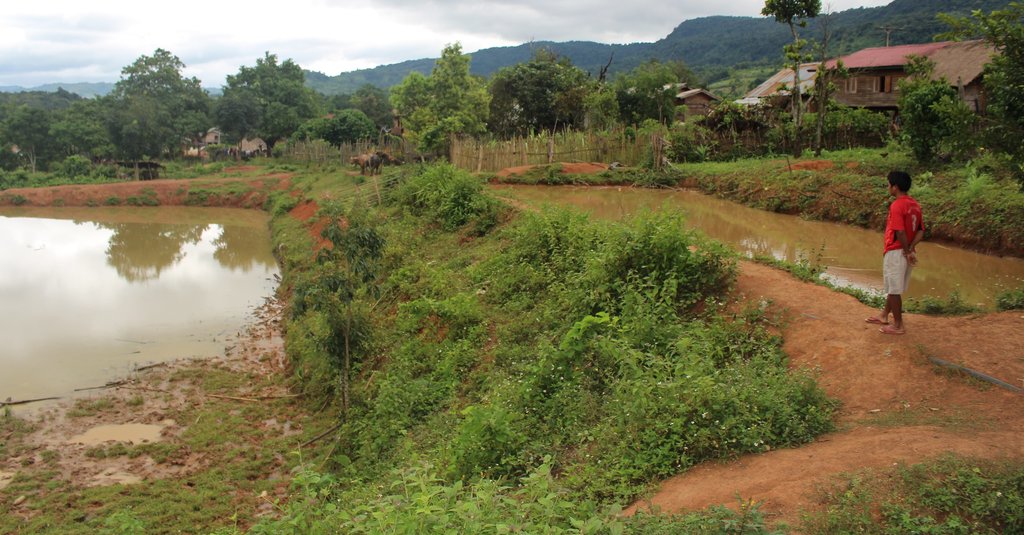
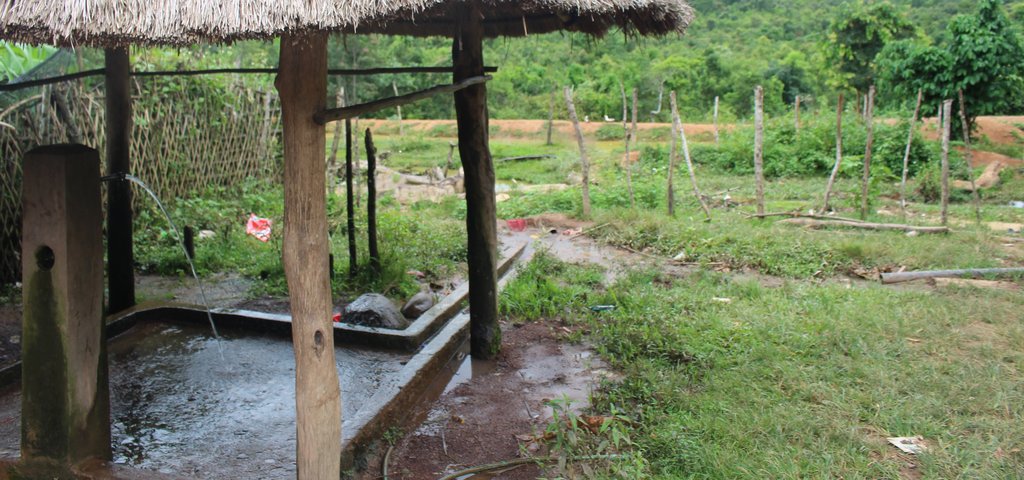
ເຕັກນິກການສ້າງໜອງ ຢູ່ເຂດຄ້ອຍຊັນ ຕີນບ້ານ ເພື່ອເປັນການເກັບກັກນ້ຳໄຫຼ ຈາກຈຸດນ້ຳລິນທີ່ໄຫຼຕະຫຼອດປີລົງສູ່ພື້ນທີ່ດິນດັ່ງກ່າວ ເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນໜຽວ ອຸ້ມນ້ຳ ແລະ ບໍ່ສາມາດເຮັດການຜະລີດປູກຝັງໄດ້. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ທາງໂຄງການ Oxfarm ຈື່ງເຂົ້າມາຊຸກຍູ້ສົ່ງເສີມ ປະຊາຊົນເຮັດໜອງລວມບ້ານ ແລະ ຫຼາຍຄອບຄົວກໍ່ສົນໃຈເຮັດໜອງສ່ວນຕົວ ໃນໄລຍະຕໍ່ມາ.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
ອີງຕາມສະພາບພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ເປັນເຂດຄ້ອຍຊັນ, ໃນລະດູຝົນ ຝົນຕົກແຮງ ເຮັດໃຫ້ນ້ຳໄຫຼເຊາະດິນລົງໄປຕາມຄ້ອຍ ໃນຊ້ວງເດືອນ 7-11 ຂອງທຸກໆປີ, ສົ່ງຜົນເຮັດໃຫ້ ເກີດການສູນເສຍສານອາຫານຂອງດິນ ກໍ່ຄືອິນຊີວັດຖູໃນດິນ. ກ່ອນທີ່ຈະມີການຂຸດໜອງ ພື້ນທີ່
ດັ່ງກ່າວຕ ແມ່ນຕ ເຄີຍມີການປູກໄມ້ຢາງບົງ ແລະ ໄມ້ກິນໝາກຊະນິດຕ່າງໆ ແຕ່ເນ່ືອງຈາກວ່າ ປະຊາຊົນ ຕ້ອງໄດ້ລໍຖ້າ ເປັນເວລາດົນ ເພ່ືອຈະສາມາດເກັບກູ້ຜົນຜະລິດ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ໃນປີ 2004 ທາງໂຄງການ Oxfarm ໄດ້ເຂົ້າມາຊຸກຍຸ້ສົ່ງເສີມ ແລະ ແນະນຳແນວຄວາມຄິດເຕັກນິກ ໃນການຂຸດໜອງລວມບ້ານ ໃຫ້ຊຸມຊົມຈຳນວນ 1 ໜອງ ເນື້ອທີ່ 50 x 40 ແມັດ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຄ້ອຍຊັນ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃກ້ກັບຈຸດທີ່ຕັ້ງບ້ານ ເນ່ືອງຈາກທາງໂຄງການ ເຫັນໄດ້ເຖິງ ຄວາມອາດສາມາດໃນການສ້າງໜອງ ເພາະທາງບ້ານ ມີນ້ຳລິນ ທີ່ໄຫຼຕະຫຼອດປີ ແລະ ບໍ່ເຄີຍບົກແຫ້ງຈັກເທື່ອ ຊື່ງເປັນເງື່ອນໄຂ ທີ່ເອ້ືອຍອຳນວຍ ໃນການສ້າງໜອງ ເພື່ອເກັບກັກນ້ຳໄວ້. ໃນເບື້ອງຕົ້ນ ທາງໂຄງການ ໄດ້ສະໜອງແນວພັນປາຈຳນວນໜ່ືງ (ປານິນ, ປາໃນ, ປາກິນຫຍ້າ). ປະຊາຊົນເຫັນວ່າ ໜອງປາ ແມ່ນມີປະໂຫຍດຫຼາຍຢ່າງ ນອກຈາກກິດຈະກຳການລ້ຽງປາແລ້ວ ຍັງສາມາດນໍຳໃຊ້ນ້ໍຳຈາກໜອງ ເພ່ືອຫົດພືດຜັກສວນຄົວ ແລະ ນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນກິດຈະກຳການລ້ຽງສັດ (ງົວ, ຄວາຍ, ໝູ, ເປັດ), ເປັນກິດຈະກຳ ທີ່ສາມາດຄຸ້ມຄອງບົວລະບັດຮັດສາງ່າຍ ປະຢັດເວລາ ໃນການໄປຫາປາຢູ່ໜອງ ທີ່
ຢູ່ໃກບ້ານ.
ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ປະຊາຊົນ ຈື່ງມີແນວຄິດຢາກສ້າງໜອງເປັນຂອງຕົນເອງ ໂດຍໄດ້ບົດຮຽນຈາກໜອງລວມບ້ານ. ທີ່ມາຊັກຂະຍະພາບ ສາມາດສະໜອງຊີ້ນປາ ໄດ້ປະມານ 200-300 ກິໂລກຣາມ/ປີ ແລະ ເພື່ອຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ ຈາກບັນຫາການນຳໃຊ້ໜອງລວມບ້ານ. ເຊີ່ງກິດຈະກຳການຂຸດໜອງ ກໍ່ມີຂັ້ນຕອນທີ່ບໍ່ຫຍຸ້ງຍາກ, ກ່ອນອື່ນໝົດ ແມ່ນ ປິດທໍ່ນ້ຳລິນ ທີ່ທາງໂຄງການຫຸຼດຜ່ອນຄວາມທຸກຍາກ ໄດ້ມາສ້າງໃຫ້ ເຊີ່ງໄດ້ຕໍ່ມາຈາກເທິງພູ, ແລ້ວກໍ່ໃຊ້ພ້າຖາງຫຍ້າ, ຕັດຕົ້ນໄມ້ ຂຸດເອົາຕໍໄມ້ ແລະ ເສດວັດສະພືດ ທີ່ຖາງອອກໄປໄວ້ນອກພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ຈະຂຸດໜອງ (ເພື່ອຈູດທຳລາຍຕໍ່ໄປ), ບໍລິເວນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ຈະຂຸດໜອງມີເນື້ອທີ່ ປະມານ 30 x 20 ແມັດ. ຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນ, ກໍ່ໃຊ້ຈົກ ແລະ ຊ້ວນ ຂຸດດິນບໍລິເວນເທິງໜ້າຄ້ອຍ ໂດຍການຂຸດເລືກປະມານ 0.5-1 ແມັດ, ແລ້ວນຳເອົາດິນທີ່ຂຸດນັ້ນ ໄປກອງເປັນແຖວ ເພ່ືອເຮັດເປັນຄັນຄູ ຕາມເນື້ອຂອງໜອງທີ່ໄດ້ກຳນົດໄວ້ ລົງໄປຕາມຄ້ອຍ (ໃຫ້ເປັນຮູບສີ່ແຈສາກ) ພ້ອມທັງຕີໃຫ້ແໜ້ນເພ່ືອບ່ໍໃຫ້ນ້ຳຊືມ ແລະ ບ່ໍເຮັດໃຫ້ຄັນຄູໜອງເກີດການເຊາະເຈ່ືອນ, ເຊີ່ງຄັນຄູໜອງມີຄວາມສູງ 1.2 ແມັດ, ໜ້າກວ້າງ 2 ແມັດ ແລະ ຄວາມຊັນ ຈາກຕີນຄັນຄູໜອງຫາ ໜ້າຄັນຄູ (ບ່ອນທີ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ຍ່າງ ເພ່ືອໃຫ້ອາຫານປາ ຫືຼ ປູກຜັກໄດ້) ປະມານ 45% ເພ່ືອຄວາມທົນທານຕ່ໍການເຊາະເຈ່ືອນ ຈາກການດຸດຂອງປາບາງຊະນິດ ຫືຼ ການໄຫຼຂອງນ້ຳ ເພາະວ່າຖ້າຄັນຄູໜອງເປັນແນວສາກ ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນເຈື່ອນໄດ້ງ່າຍ, ພ້ອມກັນນັ້ນ ກໍ່ວາງທໍ່ P100 ຂະໜາດຄວາມຍາວ 4 ແມັດ, ຢູ່ຄັນຄູໜອງເບ້ືອງລຸ່ມ ໃຫ້ໄດ້ລະດັບຄວາມສູງ 1 ແມັດ ຈາກພ້ືນໜອງ ເພື່ອລະບາຍນ້ຳອອກຈາກໜອງ ແລະ ຊ່ວຍບໍ່ໃຫ້ນ້ຳລົ້ນໜອງ ເຊາະຄັນຄູໜອງ). ຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນ, ກໍ່ທຳການປັບໜ້າດິນ ບໍລິເວນພື້ນໜອງໃຫ້ພຽງດີ ໂດຍໃຊ້ຈົກ ແລະ ຊ້ວນ ຂຸດບ່ອນທີ່ ສູງກ່ວາອອກ, ປະໄວ້ປະມານໜື່ງອາທິດ ປະໃຫ້ດິນແໜ້ນດີ ແລ້ວຈິ່ງປ່ອຍນ້ຳເຂົ້າໜອງ ໂດຍການເປີດທໍ່ນ້ຳລິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ປິດໄວ້ໃນເບື້ອງຕົ້ນ.
ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ ຈາກການສ້າງໜອງ ແມ່ນສາມາດເກັບກັກນ້ຳ ທີ່ໄຫຼຖີ້ມ ຈາກນ້ຳລີນ ໂດຍບໍ່ມີປະໂຫຍດ ເພື່ອສາມາດນຳໃຊ້ໃນລະດູແລ້ງ ເປັນຕົ້ນແມ່ນກິດຈະກຳການລ້ຽງປາ, ສາມາດລ້ຽງປາໄດ້ຕະຫຼອດປີ ແລະ ປະກອບສ່ວນເຂົ້າໃນ ການຄ້ຳປະກັນສະບຽງອາຫານ ພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ ແລະ ສາມາດຫຸຼດຜ່ອນການຍາດແຍ່ງກັນ ໃນການໄປຫາປາຢູ່ຫ້ວຍ ທັງເປັນການປະຢັດເວລາໃນການໄປຫາປາ ເຊິ່ງປະຊາຊົນໄດ້ມີການປ່ອຍປາທຸກປີ, ມີນ້ຳສຳລັບກິດຈະກຳລ້ຽງສັດ (ງົວ, ຄວາຍ, ໝູ, ເປັດ), ໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຫົດພືດຜັກສວນຄົວ ແລະ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ສາມາດຫຸຼດຜ່ອນ ການເຊາະເຈ່ືອນຂອງດິນ ເນ່ືອງຈາກ ການຊະລ້າງໜ້າດິນຕາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ ໂດຍການໄຫຼຂອງນ້ຳລິນ ແລະ ນ້ຳຝົນ, ສາມາດສ້າງລາຍຮັຍຈາກການຂາຍປາ ແລະ ມີປາໄວ້ເພ່ືອບໍລິໂພກພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວ.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Region/ State/ Province:
ແຂວງ ສາລາວັນ
Further specification of location:
ບ້ານ ຕັງໂກ, ເມືອງ ສະໝ້ວຍ
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2007
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
ທຳອິດແມ່ນໂຄງການ oxfarm ມາຊ່ວຍ ຂຸດໜອງປາລວມໃຫ້ ຈາກນັ້ນຈິ່ງເກີດມີແນວຄິດຢາກເຮັດ
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial social impact
- ຫຸຼດຜ່ອນຂ້ໍຂັດແຍ່ງໃນການຍາດແຍ່ງກັນຫາປາໃນໜອງລວມ
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Unproductive land
Specify:
ດິນມີນ້ຳລິນໄຫຼລົງຕະຫຼອດປີ ເຮັດໃຫ້ເປັນດິນດາກ ນ້ຳບໍ່ສາມາດຊືມລົງໄປໃນຊັ້ນດິນໄດ້
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
ກ່່ອນເຮັດໜອງ ທີ່ດິນແຕ່ກ່ອນເປັນດິນສ່ວນປູກພືດ ແລະ ໄມ້ກິນໝາກ
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Livestock density (if relevant):
ແບ້ 2 ໂຕ, ໝູ 1ໂຕ, ໄກ່ 10ໂຕ
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
- water harvesting
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S1: Terraces
- S5: Dams, pans, ponds
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- adapt to land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
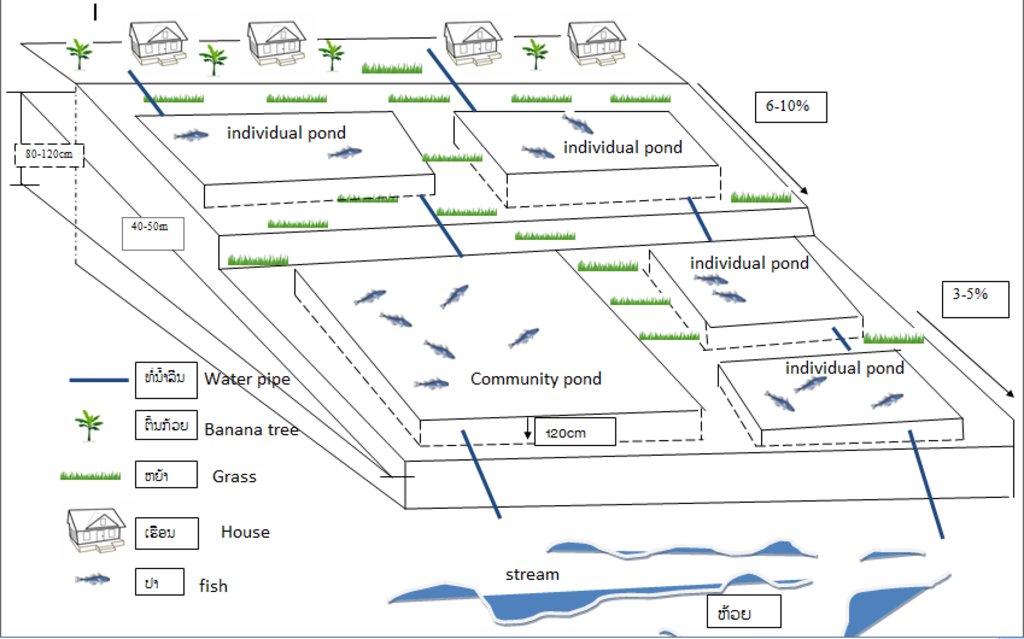
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
-ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປການກໍ່ສ້າງຫນອງໃນຫມູ່ບ້ານ ແມ່ນ ໂຄງສ້າງດຽວກັນຍ້ອນວ່າ ພວກເຂົາເຈົ້າເອົາຕາມແບບຫນອງຂອງຊຸມຊົນ, ແຕ່ໜອງສ່ວນຕົວໄດ້ຖືກຂຸດຄົ້ນນ້ອຍກວ່າ.
- ພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຫນອງຊຸມຊົນແມ່ນ 50 x 30 ແມັດ
- ພື້ນທີ່ຂອງຫນອງບຸກຄົນແມ່ນ 30 x 15 ແມັດ
- ຄວາມສູງຂອງ ຄັນຄູຫນອງແມ່ນ 120 ແມັດ, width 2ແມັດ ຄວາມເລິກຂອງນ້ໍາແມ່ນ 1 ແມັດ
ຄວາມຕ້ອຍມຸມກ່ອນສ້າງໜອງ 10-16% ແລະ ຫຼັງຈາກສ້າງແລ້ວ 3-5%
ອຸປະກອນການກໍ່ສ້າງທີ່ນໍາໃຊ້ປະກອບມີ: ການນໍາໃຊ້ຈົກ ແລະ ຊ້ວນສໍາລັບຂຸດດິນ ເພື່ອສ້າງຄັນຄູໜອງ ຫຼື ປັບພື້ນລຸ່ມຫນອງ. ທໍ່ນ້ໍາປະມານ 80 ແມັດ ຈາກແຫລ່ງນໍ້າໄປຫາຫນອງ ແລະ ໃຊ້ທໍ່ນ້ໍາຂະໜາດ p100 ເພື່ອປ້ອງກັນນໍ້າຖ້ວມ.
ຄວາມຈຸຂອງຫນອງປະມານ 450 ມ3.
ພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດຂອງຫນອງສາມາດຜະລິດປາ ແລະ ຊັບພະຍາກອນສັດນ້ໍາອື່ນຽ ເພື່ອການບໍລິໂພກຕົນເອງ.
ຊະນິດປາທີ່ນໍາໃຊ້ ແມ່ນ ປານິນ, ປາກິນຫຍ້າ, ປາໄນ, ປາປາກ.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
ໜອງສ່ວນຕົວ
Specify volume, length, etc. (if relevant):
30 x 15 ແມັດ
other/ national currency (specify):
ກີບ
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8400.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
35000ກີບ
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ຖາງຫຍ້າທຳຄວາມສະອາດພື້ນທ່ີ່ | Management | ເດືອນ 1-3 ກ່ອນຝົນ |
| 2. | ຮື້ຈູດ | Management | ເດືອນ 1-3 ກ່ອນຝົນ |
| 3. | ຂຸດດິນ ແລະ ປ້ານຄັນຄູໜອງ | Structural | ເດືອນ 1-3 ກ່ອນຝົນ |
| 4. | ວາງທໍ່ຢາງ P100 ແລະ ປ່ອຍນ້ຳເຂົ້າໜອງ | Management | None |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານ | ຄົນ | 180.0 | 35000.0 | 6300000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຈົກ | ດວງ | 4.0 | 50000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຊ້ວຍ | ດວງ | 5.0 | 30000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ພ້າ | ດວງ | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ທໍ່ລະບາຍນ້ຳ p100 | ແມັດ | 80.0 | 15000.0 | 1200000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 7910000.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | ປ່ອຍນ້ຳອອກ | Management | ຫຼັງການເເກັບກ່ຽວ, ທ້າຍລະດູຝົນ |
| 2. | ອະນາໄມພື້ນໜອງ | Management | ຫັຼງການລະບວຍນ້ຳອອກ |
| 3. | ືເສີມຄັນຄູໜອງ | Structural | ກ່ອນລະດູຝົນ |
| 4. | ປ່ອຍນ້ຳເຂົ້າໜອງ | Management |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານລະບາຍນ້ຳອອກ | ຄົນ/ມື້ | 1.0 | 35000.0 | 35000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານອະນາໄມພ້ືໜໜອງ | ຄົນ/ມື້ | 2.0 | 35000.0 | 70000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ແຮງງານເສີມຄັນຄູໜອງ | ຄົນ/ມື້ | 3.0 | 35000.0 | 105000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | None | None | 1.0 | 35000.0 | 35000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຈົກ | ດວງ | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຊ້ວນ | ດວງ | 2.0 | 30000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 405000.0 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ອຸປະກອນທີ່ນຳເຂົ້າ ເຊັ່ນ ຈົກ, ຊ້ວນ, ລາຄາແພງຂື້ນ
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
500.00
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ກົມອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເມືອງສະໝ້ວຍ
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- convex situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
20 ກິໂລກຣາມ
Quantity after SLM:
5 ກິໂລກຣາມ
Comments/ specify:
ເຄີຍປູກຜັກສວນຄົວໃສ່ດິນດັ່ງກ່າວ ແລະ ພາຍຫຼັງສ້າງໜອງ ແລ້ວໄດ້ຍ້າຍ ໄປປູກຢູ່ເຂດອ່ືນ ແລະປະຈຸບັນປະຊາຊົນປູກຜັກໃສ່ແຄມໜອງ ໃນເນື້ອທີ່ຈາໍກັດ
animal production
Quantity before SLM:
200 kg
Quantity after SLM:
300 kg
Comments/ specify:
ມີປາໃຫ້ບໍລິໂພກຫຼາຍຂ້ືນ ແລະ ຫຸຼດຜ່ອນເວລາໃນການໄປຫາປາຢູ່ຫ້ວຍ
production area
Quantity before SLM:
2 ໜານ
Quantity after SLM:
3 ໜານ
Comments/ specify:
ຍ້ອນໄດ້ຍ້າຍພື້ນທີ່ ການປູກຝັງໄປບ່ອນອ່ືນ
Water availability and quality
water availability for livestock
Comments/ specify:
ມີນ້ຳໃຫ້ສັດລ້ຽງກິນພຽງພໍຢູ່ໃກ້ໝູ່ບ້ານ (ຄຸ້ມຄອງງ່າຍ) ກ່ອນຫນ້ານີ້ ສັດຕ້ອງໄປຫາແມ່ນ້ໍາ ຫລື ເພ່ືອດ່ືມນ້ໍາຫັຼງຈາກໄດ້ສ້າງໜອງ ມີນ້ໍາສໍາລັບສັດໃນຫນອງ
Income and costs
workload
Comments/ specify:
ການຫຼຸດລົງໃນການເຮັດວຽກສໍາລັບຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຍ້ອນວ່າເຂົາບໍ່ຈໍາເປັນຕ້ອງໄປຫາປາຢູ່ ໃນຕາມຫ້ວຍໄກຈາກບ້ານ
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
ການປັບປຸງການຜະລິດປາ ແລະ ສາມາດປະກອບສ່ວນເຂົ້າປາ ສໍາລັບການບໍລິໂພກພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວຕະຫຼອດປີ
land use/ water rights
Comments/ specify:
ການປັບປຸງການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ສໍາລັບຫນອງປາທີ່ ຄົວເຮືອນມີຫນອງປາຂອງຕົນເອງ
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
ນາຍບ້ານບໍ່ໄດ້ສະຫນັບສະຫນູນການຄຸ້ມຄອງໜອງຂອງຊຸມຊົນ (ອັນນີ້ເຮັດໃຫ້ປາໝົດໄປ).ຫຼັງຈາກໄດ້ສ້າງໜອງແຕ່ລະບ້ານ,ນາຍບ້ານໄດ້ຊີ້ນໍາການເຮັດວຽກ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຢູ່ໃນຫນອງຂອງຊຸມຊົນ. ອະນຸຍາດໃຫ້ຫາປາໃນລະຫວ່າງງານບຸນໃນຫມູ່ບ້ານ.ໜອງສ່ວນ ບຸກຄົນ ແມ່ນ ຖືກຮັກສາໂດຍເຈົ້າຂອງເອງ
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
ປັບປຸງ ແລະ ຫຸຼດຜ່ອນຄວາມຂັດແຍ້ງ ກັບເພ່ືອນບ້ານກ່ຽວກັບການຫາປາ ເມ່ືອພວກເຂົາດໍາເນີນການໜອງປາຂອງພວກເຂົາເອງ
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
harvesting/ collection of water
Comments/ specify:
ການປັບປຸງການໄຫຼຂອງນ້ໍາດີຂ້ືນ ໂດຍການກ່ໍສ້າງຂອງໜອງປາ
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
animal diversity
Comments/ specify:
ການເພີ່
ມທະວີ ການລ້ຽງສັດນ້ໍາກ່ຽວກັບປະລິມານ ແລະ ຊະນິດພັນເຊັ່ນ : ປູ, ຫອຍ ແລະຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ ດິນສາມາດມີປາຊະນິດ(ປານິນ, ປາໄນ)
habitat diversity
Comments/ specify:
ການຫຸຼດລົງຂອງພືດໃນໜ້າດິນ
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
Comments/ specify:
ການຫຸຼດລົງຂອງການໄຫຼເຊາະເທິງໜ້າດິນ ຍ້ອນຝົນຕົກຫນັກ
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | wet/ rainy season | decrease | well |
| seasonal temperature | dry season | increase | very well |
| annual rainfall | increase | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
| seasonal rainfall | dry season | decrease | not well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
| local hailstorm | moderately |
| local windstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| cold wave | not well |
| drought | not well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| flash flood | not well |
| landslide | moderately |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | moderately |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
5 ຄົວເຮືອນໃນບ້ານ ຕັງໂກ ມີຫນອງປາສ່ວນຕົວຂອງເຂົາເຈົ້າເອງ ແລະ ບາງຄົນແມ່ນໄດ້ລິເລີ່ ມເພື່ອເພີ່ ມຈໍານວນຫນອງປາ ບ່ອນທີ່ ເປັນໄປໄດ້
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 50-90%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
other (specify):
ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມຂັດແຍ່ງ
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
ໃນຕອນເລີ່ມຕົ້ນໃນປີ 2004 ພຽງແຕ່ໜອງໃນຊຸມຊົນໄດ້ຖືກສ້າງຂື້ນ.ຊາວບ້ານຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນກໍ່ເລີ່ມ ກ່ໍສ້າງໜອງແຕ່ລະຄົນ ເພ່ືອຫຸຼດຜ່ອນຄວາມຂັດແຍ່ງ ທາງສັງຄົມທີ່ເກີດຈາກ ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບໜອງໃນຊຸມຊົນ
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| ຍ້ອນວ່າຫນອງສ່ວນບຸກຄົນ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃກ້ກັບເຮືອນ, ມັນກໍ່ງ່າຍສໍາລັບຜູ້ທີ່ໃຊ້ດິນໃນການຫາປາ ແລະຮັກສາທຸກຄັ້ງທີ່ເຂົາເຈົ້າ ຕ້ອງການ. |
| ມີນ້ຳໃນໜອງຕະຫຼອດປີ |
| ມີປາໄວ້ກິນເປັນອາຫານພາຍໃນຄອບຄົວຫຼາຍຂ້ືນ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ຊາວບ້ານຈະສາມາດຜະລິດປາລຸ້ນຕໍ່ໄປໄດ້ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ຝົນຕົກຫຼາຍເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນຄັນຄູໜອງເຊາະເຈ່ືອນ ຢູ່ບໍລິເວນທ່ໍລະບາຍນ້ໍາອອກນ້ຳລົ້ນໜອງ ໃນລະດູຝົນ | |
| ນ້ຳລົ້ນໜອງ ໃນລະດູຝົນ | ເຮັດທໍ່ລະບາຍນ້ຳໃຫ້ໃຫ່ຍຂື້ນ |
|
ດິນຄັນຄູໜອງບ່ໍແໜ້ນ ເນ່ືອງຈາກວ່າໄດ້ໃຊ້ແຮງງານ ໃນການຕໍາດິນ (ແຮງງານຂ້ືນຢຽບ, ໃຊ້ຈົກຕໍາ) |
ເຮັດຄັນຄູ ຄອນກຣີດ |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
|
ປະຊາຊົນ ຍັງຂາດປະສົບການ ແລະ ບໍ່ມີຄວາມຮູ້ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນິກ ໃນການຂຸດໜອງປາ ເພາະຍັງເຮັດຄັນຄູໜອງແຄບສົ່ງຜົນເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນຄັນຄູເຈ່ືອນ ແລະ ຍັງບ່ໍຮູ້ ວິທີການທົດສອບດິນ ກ່ອນຈະຂຸດດິນ |
ຕ້ອງເຮັດຄັນຄູໜອງກວ້າງອອກ ປະມານ 3 ແມັດ ແລະ ຕ້ອງໄດ້ເອົາໃຈໃສ່ ໃນວິທີການຄັດເລືອກພື້ນທີ່ການສັງເກດເບີ່ງດິນກ່ອນຂຸດໜອງ |
| ປະຊາຊົນ ຍັງບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ເຕັກນິກ ວິທີ ການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຂະຫຍາຍ ແນວພັນປາເພາະຍັງໄດ້ຊື່ ແລະ ເປັນການເພີ່ມລາຍຈ່າຍ ໃນການຊ້ືລູກປາມາປ່ອຍ | ຕ້ອງມີການຝຶກອົບຮົມ ໃຫ້ປະຊາຊົນ ຜູ້ທີ່ມີໜອງປາ ໃຫ້ສາມາດຜະລິດແນວພັນປາໄດ້ເອງ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1ຄັ້ງ
- interviews with land users
2 ຄົນ
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules