បច្ចេកទេសដាំត្រប់វែងក្នុងចម្ការក្រូចឆ្មារ [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Be Gechkim
- Editors: Sophea Tim, Navin Chea, Sok Pheak
- Reviewers: SO Than, Ursula Gaemperli
ការដាំដំណាំចម្រុះ
technologies_3153 - Cambodia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
អ៊ឹម សុខុម
(+855) 88 25 35 216 / (+855) 89 69 15 52
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
កសិករ
ភូមិស្វាយស ឃុំខ្នាចរមាស ស្រុកបវេល ខេត្តបាត់ដំបង
Cambodia
មន្ត្រីការិយាល័យផ្សព្វផ្សាយកសិកម្ម នៅការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកថ្មគោល:
តារាភូសា ស៊ីវ
(+855) 12 501 462
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
ការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកថ្មគោល
ភូមិកសិកម្ម ឃុំតាពូង ស្រុកថ្មគោល ខេត្តបាត់ដំបង
Cambodia
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកសង្កែ:
ចន្ថា ឆែម
(+855) 92 571 228
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
ការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកសង្កែ
ភូមិបឹងបេង ឃុំអន្លង់វិល ស្រុកសង្កែ ខេត្តបាត់ដំបង
Cambodia
មន្ត្រីក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រនៅការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកបវេល:
ឡាម ម៉ូត
(+855) 88 375 50 06
មិនមានអ៊ីម៉ែល
ការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកបវេល
ភូមិទំនប់ទឹក ឃុំ បវេល ស្រុកបវេល ខេត្តបាត់ដំបង
Cambodia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
30/06/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
ការដាំដំណាំត្រប់វែងតាមចន្លោះដើមក្រូចឆ្មារដោយប្រើកាកសំណល់ពីបន្ទប់ទឹកជាមួយកាកសំណល់ពីដំណាំផ្សេងៗដើម្បីជំនួយសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹមដល់ដីដោយមិនប្រើប្រាស់ជីគីមី។
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
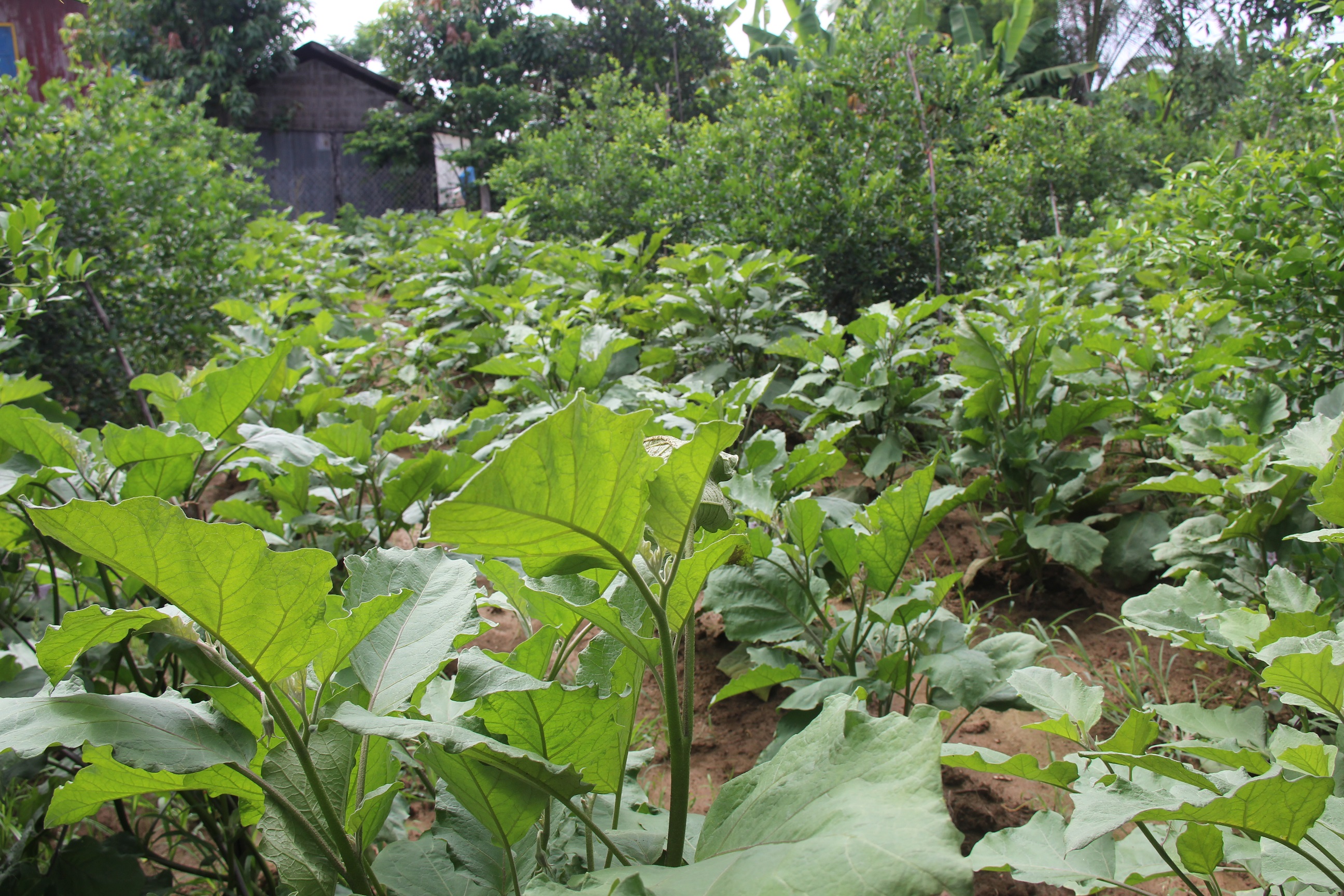
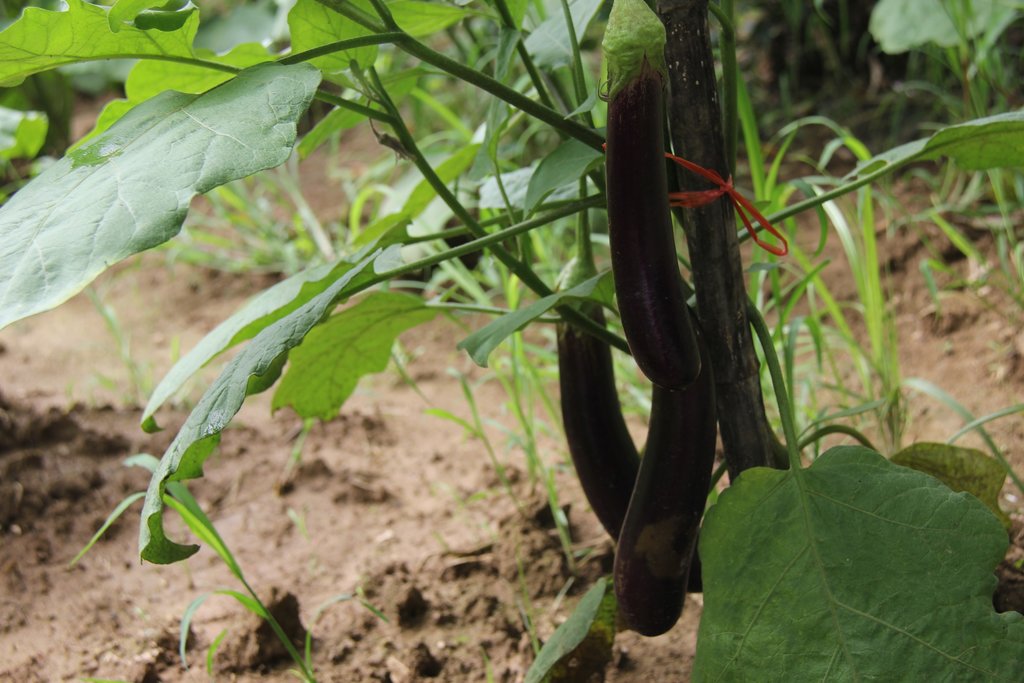
ការដាំដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លី ដូចជាត្រប់វែង ឬដំណាំបន្លែផ្សេងៗទៀតតាមចន្លោះដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង ត្រូវបានគេស្គាល់ថាជាប្រព័ន្ធដំណាំតាមចន្លោះ។ ក្នុងករណីនេះកសិករបានដាំដើមក្រូចឆ្មារដែលជាប្រភេទដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង ដូច្នេះគេក៏អាចចាត់ទុកថាជាប្រព័ន្ធកសិរុក្ខកម្មមួយដែរ។ ហេតុផលសំខាន់មួយដែលកសិករជ្រើសយកការដាំទាំងដំណាំអាយុកាលវែង និងអាយុកាលខ្លីនៅលើផ្ទៃដីតែមួយនោះ គឺដើម្បីប្រើប្រាស់ឱ្យអស់លទ្ធភាពធនធានដីដែលខ្លួនមាន។ ហើយមូលហេតុមួយទៀត គឺដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លីបានផ្តល់ប្រាក់ចំណូលយ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស មុនពេលដែលដំណាំរយៈពេលវែងផ្តល់ផលពេញលេញ។
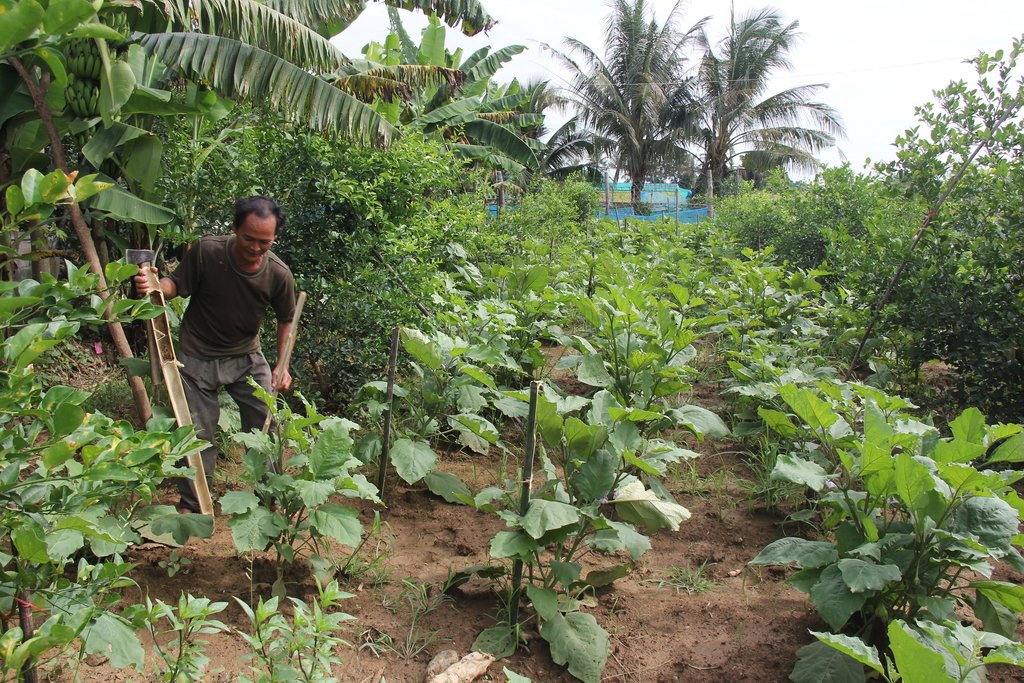
លោក អ៊ឹម សុខុម ជាកសិករដែលរស់នៅក្នុងភូមិស្វាយស ឃុំខ្នាចរមាស ស្រុកបវេល ខេត្តបាត់ដំបងដែលជាខេត្តមួយស្ថិតនៅភាគពាយព្យនៃប្រទេសកម្ពុជា បានប្តូរពីកសិកម្មឯកវប្បកម្មទៅជាប្រព័ន្ធកសិកម្មដំណាំតាមចន្លោះនៅឆ្នាំ ២០១៦។ ក្នុងចំណោមមូលហេតុចម្បងៗដែលបណ្តាលឱ្យមានការផ្លាស់ប្តូរនេះអាចមកពី ដីចម្ការរបស់គាត់ គឺជាដីល្បាប់ជ្រៅ មានកម្រិត pH ស្មើ ៥ មានសារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ខាងលើខ្ពស់ មានវាយនភាពមធ្យម ហើយស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ដែលមានបរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងមធ្យមប្រចាំឆ្នាំ គឺ ១១០០ មម។ លើផ្ទៃដីរាបស្មើ ដែលមានទំហំដីប្រមាណជា ៣២៥,៥ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ (១៨,៣ x ៤៥ ម៉ែត្រ) គាត់បានដាំក្រូចឆ្មារចំនួន ១០ ជួរ (មួយជួរមាន ៤ ដើម) ជាមួយនឹងគម្លាត ៤,៥ x ៤,៥ ម៉ែត្រ។ ក្នុងឆ្នាំទីមួយបន្ទាប់ពីដាំដំណាំក្រូចឆ្មាររួចរាល់ (ក្នុងខែធ្នូ) គាត់បានភ្ជួរ រួចហាលដីតាមចន្លោះកូនក្រូចឆ្មារ បន្ទាប់មកគាត់បានដាំត្រប់វែងដែលមានចន្លោះពី ៨០ ទៅ ១០០ សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ពីដើមមួយទៅដើមមួយ សរុបមាន ៦៤០ ដើម ដាំជា ៤០ ជួរ ក្នុងមួយជួរមាន ១៦ ដើម។
ហេតុដែលកសិករជាច្រើននាក់មានចំណូលចិត្តលើការដាំត្រប់វែងជាដំណាំតាមចន្លោះ ព្រោះវាជាដំណាំដែលអាចប្រមូលផលបានបន្ទាប់ពីដាំបានមួយខែ និងអាចប្រមូលផលបានពេញមួយឆ្នាំ។ ភាពជាក់ស្តែងមួយទៀតដែលកសិករចូលចិត្តនោះ គឺដោយសារវាងាយដាំ ហើយមិនប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្មច្រើន។ ទោះជាបែបនេះក៏ដោយក៏ទិន្នផលរបស់វា ប្រែប្រួលទៅតាមការថែទាំផងដែរ ដូចជា គេត្រូវកាត់ស្លឹកចាស់ៗចេញ នៅពេលដែលវាចេញផ្កាតិចទៅៗ (General Directorate of Agriculture, 2012)។ បន្ទាប់ដំណាំត្រប់វែងកសិករក៏អាចផ្លាស់ប្តូរទៅដាំដំណាំបន្លែផ្សេងៗទៀតតាមចំណង់ចំណូលចិត្តរបស់គាត់ផងដែរ។ ម្យ៉ាងវិញទៀតដំណាំក្រូចឆ្មារត្រូវចំណាយពេល ៣ ឆ្នាំមុនពេលផ្តល់ផល ហើយវានឹងផ្តល់ផលក្នុងរយៈពេល ៨ ទៅ ១០ ឆ្នាំបន្តទៀត។ ពេលខ្លះវាអាចផ្តល់ផលពេញមួយឆ្នាំ ប៉ុន្តែត្រូវផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកឱ្យបានគ្រប់គ្រាន់ចាប់ពីពេលចេញផ្ការហូតដល់ពេលប្រមូលផល។ ជារួមក្នុងអំឡុងពេលរង់ចាំក្រូចឆ្មារផ្តល់ផលបានពេញលេញ ត្រប់វែង គឺជាដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លីដែលផ្តល់ផលជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ដើម្បីធានាឱ្យមានប្រាក់ចំណូលជាប្រចាំ។ លើសពីនេះ គុណសម្បត្តិនៃការដាំដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លីតាមចន្លោះដើមក្រូចឆ្មារ បង្កើតបានជាគម្របដី កាត់បន្ថយការដុះដាលនៃស្មៅចង្រៃ ហើយបង្កលក្ខណៈងាយស្រួលក្នុងការគ្រប់គ្រងដី។
ទន្ទឹមនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់លំហរដីអស់លទ្ធភាព បច្ចេកទេសនេះក៏បាន រក្សា និងបង្កើនគុណភាពដីតាមរយៈការប្រើប្រាស់កាកសំណល់ពីបន្ទប់ទឹក ដោយយកទឹកដែលបង្ហូរចេញពីអាងស្តុកកាកលាមក/ទឹកមូត្រ ដែលបានបំបែកធាតុរលាយសព្វ (គ្មានក្លិនស្អុយ) មកប្រើផងដែរ។ រីឯការប្រើប្រាស់ជី គឺក្នុងមួយគុម្ពចាក់ទឹកជីនោះប្រមាណជា ៣០០ ទៅ ៤០០ មីលីលីត្រ បន្ទាប់មកស្រោចទឹកបន្ថែមដូចធម្មតា។ ការដាក់ជីធ្វើឡើងសារជាថ្មីនៅពេលដើមត្រប់ស្បើយផ្លែ ក្រៅពីនេះសំណល់រុក្ខជាតិក្រោយពេលប្រមូលផលរួច ត្រូវបានគរទុកជាគម្របដីនៅចន្លោះដើមក្រូចឆ្មារ សម្រាប់ផ្តល់ជីជាតិបន្ថែមជំនួសឱ្យការប្រើប្រាស់ជីគីមីហើយរក្សាសំណើមដីបានទៀតផង។
ក្រោយពីចាប់ផ្តើមអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដំណាំតាមចន្លោះរួមផ្សំនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់កាកសំណល់សរីរាង្គបានមួយរយៈមក អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីយល់ដឹងពីតម្រូវការក្នុងការថែទាំ គឺជាប្រការសំខាន់ដើម្បីទទួលបានផលប្រយោជន៍យូរអង្វែងពីក្រូចឆ្មារ និងផលប្រយោជន៍ចំពោះមុខពីដំណាំរយៈពេលខ្លី ឧទាហរណ៍ការស្រោចស្រពដំណាំត្រប់វែងដែលដាំតាមចន្លោះ និងការស្រោចស្រពក្រូចឆ្មារគួរតែធ្វើឱ្យបានជាប្រចាំដើម្បីរក្សាផលិតភាពរបស់វា។ បើប្រៀបធៀប ការដាំដំណាំតែមួយមុខ (ដូចជា ពោត ឬអំពៅ) ជាមួយនឹង ការដាំដំណាំតាមចន្លោះនេះ គេសង្កេតឃើញថា កសិករទទួលបានប្រាក់ចំណូលកាន់តែល្អប្រសើរ និងមានស្ថេរភាពជាង (ជាក់ស្តែងក្នុងទីតាំងនេះ គឺពីមុនមកគេដាំអំពៅ)។
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
មិនមាន
Name of videographer:
មិនមាន
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
ភូមិស្វាយស ឃុំខ្នាចរមាស ស្រុកបវេល ខេត្តបាត់ដំបង
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2016
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
Comments (type of project, etc.):
អាចទទួលបានចំណូលជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ហើយកាត់បន្ថយការចំណាយលើជី ឬប្រើប្រាស់ប្លាស្ទិក។
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agroforestry
Main products/ services:
ដំណាំត្រប់វែង និងក្រូចឆ្មារ
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
ជាដីដាំអំពៅ
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
ប្រើទឹកអណ្តូង
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
ដំាដំណាំផ្សេងៗបន្តគ្នាបន្ទាប់ពីដំណាំត្រប់នៅចន្លោះក្រូចឆ្មារ
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
- integrated soil fertility management
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

vegetative measures
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

biological degradation
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
បច្ចេកទេសនេះកសិករដាំលើផ្ទៃដី ៨២៣,៥ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ (១៨,៣ ម៉ែត្រ × ៤៥ម៉ែត្រ) ដែលមានក្រូចឆ្មារចំនួន ១០ជួរ និង ១ជួរមាន ៤ដើម (សរុប ៤០ ដើម)។ ចន្លោះក្រូចឆ្មារ ៤,៥ × ៤,៥ម៉ែត្រ ដែលត្រូវជីករណ្តៅដាំ ជម្រៅ ២០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ទំហំ ១៥សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ដែលកូនក្រូចឆ្មារបានមកពីការផ្ស៊ាំមែកក្រូចឆ្មារដោយខ្លួនឯង។ រីឯត្រប់វែងមានចន្លោះដើម ៨០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ ទៅ ១ម៉ែត្រ ដែលមាន ៤០ ជួរ ស្ថិតនៅចន្លោះក្រូចឆ្មារ ហើយ ១ ជួរមានចំនួន ១៦ ដើម និងសរុបទាំងអស់មាន ៦៤០ ដើម ហើយនៅជុំវិញដីទាំងមូលមានដាំចេក និងទៀបទៀតផង។ ម៉្យាងវិញទៀតបច្ចេកទេសនេះក៏បាន រក្សា និងបង្កើនគុណភាពដីតាមរយៈការប្រើប្រាស់កាកសំណល់ពីបន្ទប់ទឹក ដោយយកទឹកដែលបង្ហូរចេញពីអាងស្តុកកាកលាមក/ទឹកមូត្រ ដែលបានបំបែកធាតុរលាយសព្វ (គ្មានក្លិនស្អុយ) មកប្រើផងដែរ។
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
៨២៣,៥ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
other/ national currency (specify):
រៀល
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
២០០០០រៀល
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | កាប់ដីហាល | Agronomic | ខែ តុលា |
| 2. | ផ្ស៊ាំក្រូចឆ្មារ | Vegetative | ខែ តុលា |
| 3. | ដាំក្រូចឆ្មារ | Vegetative | ខែ វិច្ឆិកា |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | កាប់ដីហាល | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 6.0 | 20000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ផ្ស៊ាំក្រូចឆ្មារ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | កាប់រណ្តៅដាំក្រូច | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ម៉ូទ័រ និងបុកអណ្តូង | ឈុត | 1.0 | 750000.0 | 750000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ចបកាប់ | ចប | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ចបជីក | គូ | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | បង្គី | គូ | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | កូនក្រូចឆ្មារ | ដើម | 36.0 | 5000.0 | 180000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ពូជត្រប់វែង | កញ្ចប់ | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ធុងស្រោច | គូ | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ទុយោ | ម៉ែត្រ | 40.0 | 12000.0 | 480000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 1790000.0 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | សាបត្រប់វែង | Vegetative | ខែវិច្ឆិកា |
| 2. | កាប់ដីហាល | Agronomic | ខែធ្នូ |
| 3. | ដាំត្រប់វែង | Agronomic | ខែធ្នូ |
| 4. | ស្រោចទឹកក្រូចឆ្មារ | Management | ស្រោចតែខែប្រាំងទេ |
| 5. | បាញ់ថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិត | Agronomic | នៅពេលមានសត្វល្អិតបានបាញ់ |
| 6. | ដាក់ជីបានពីកាកសំណល់បន្ទប់ទឹក (ក្រូចឆ្មារ) | Agronomic | ២ដងក្នុង ១ ឆ្នាំ |
| 7. | ស្រោចទឹកត្រប់វែង | Management | ៣ថ្ងៃ ទៅ ៧ថ្ងៃ ស្រោចទឹកម្តង |
| 8. | ដាក់ជីបានពីកាកសំណល់បន្ទប់ទឹក (ត្រប់វែង) | Agronomic | នៅពេលត្រប់អន់ផ្លែ ឬស្លឹកត្រប់មានសញ្ញាខុសប្រក្រតីដូចជាស្លឹកលឿងជាដើម |
| 9. | បាញ់ថ្នាំលើត្រប់វែង | Agronomic | ២ ដងក្នុង ១ សប្តាហ៍ |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | សាបកូនត្រប់វែង និងដាំត្រប់វែង | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 2.5 | 20000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ស្រោចទឹកក្រូចឆ្មារ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 26.0 | 20000.0 | 520000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | បាញ់ថ្នាំ | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 78.75 | 20000.0 | 1575000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ដាក់ជី | នាក់/ថ្ងៃ | 3.0 | 20000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ពូជត្រប់វែង | កញ្ចប់ | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ថ្នាំបណ្តេញសត្វល្អិត (ដង្កូវ) | ដប | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ថ្នាំបណ្តេញសត្វល្អិត (ចៃ) | ដប | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 2405000.0 | |||||
Comments:
ត្រប់វែងបន្ទាប់ពីដាំបាន ១,៥ ខែអាចចាប់ផ្តើមប្រមូលផល ហើយអាចប្រមូលផលបានរហូតដល់ ១ឆ្នាំ បើថែទាំបានល្អ។
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ការប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិតជាពិសេសចំពោះដំណាំត្រប់វែង។
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1102.02
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ ២០១៥ មាន ១១០២.០២ មម ឆ្នាំ ២០១៤ មាន ៨៧៨.១៣ មម និងឆ្នាំ ២០១៣ មាន ១៣៩៣ មម។
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឧតុនិយម (២០១៥)
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
ដីល្បាប់ដែលមាន pH = ៥
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
មិនមាន
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
កសិករអាយុ ៥៣ ឆ្នាំ។
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
ដីដាំដំណាំ ១៨,៣ម៉ែត្រ×៤៥ម៉ែត្រ = ៨២៣,៥ម៉ែត្រការេ និង ដីប្អូន ៤០ម៉ែត្រ×៤០ម៉ែត្រ= ១៦០០ម៉ែត្រការេ។
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
Comments:
មានអណ្តូងសម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងគ្រួសារផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន។
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំកើនឡើងដោយសារកាលពីមុនគាត់ដាំតែមួយមុខដំណាំ តែឥលូវគាត់មានដាំដំណាំនៅចន្លោះដំណាំរយៈពេលវែងបន្ថែមទៀត។
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
គុណភាពដំណាំល្អជាងមុនពីព្រោះគាត់ប្រើកាកសំណល់ពីបន្ទប់ទឹកជាមួយកាកសំណល់ពីដំណាំផ្សេងៗជំនួសជីគីមី។
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
គាត់មានដាំដំណាំចាប់ពី ២ មុខឡើងទៅ ដូចនេះបើមានមួយមុខណាមានបញ្ហាគាត់អាចទទួលបានចំណូលពីដំណាំមុខផ្សេងទៀតជំនួស។
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
បច្ចុប្បន្នគាត់ដាំដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទជាងមុន
production area
Comments/ specify:
ផលិតកម្មកើនឡើងតិចតួចដោយសារគាត់បានប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលតែមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពជាងមុន។
land management
Comments/ specify:
គាត់ដាំដំណាំបន្លែជាមួយដំណាំអាយុកាលវែងដោយប្រើកាកសំណល់ចេញពីបន្ទប់ទឹក។
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
កាលពីមុនគាត់ដាំដំណាំដោយប្រើតែជីគីមីទេ
farm income
Comments/ specify:
មានដាំដំណាំជាច្រើនមុន (បន្លែ) នៅចន្លោះក្រូចឆ្មារជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ ដែលជួយបង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូល។
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
កាលពីមុនមានតែដំណាំក្រូចឆ្មារប៉ុណ្ណោះដែលទទួលផល ប៉ុន្តែបច្ចុប្បន្នគាត់អាចទទួលបានប្រាក់ចំណូលពីដំណាំដែលនៅចន្លោះបន្ថែមទៀត។
economic disparities
Comments/ specify:
ចំណូលរបស់កសិករបានកើនឡើង ដូច្នេះហើយស្ថានភាពសេដ្ឋកិច្ចរបស់គាត់ក៏បានប្រសើរឡើងដែរ។
workload
Comments/ specify:
គាត់មានការងារច្រើនជាងមុនបន្តិចតែមិនសូវពិបាកដូចមុនទេ
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
បច្ចុប្បន្នគាត់ទទួលបានចំណូលជាប្រចាំពីដំណាំទាំងនោះ
health situation
Comments/ specify:
ល្អជាងមុនដោយប្រើតែជីកាកសំណល់ពីបន្ទប់ទឹកលាយជាមួយកាកសំណល់ពីដំណាំផ្សេងៗជំនួសជីគីមី។
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
អំឡុងពេលឆ្នាំដំបូងនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ គាត់បានរៀនអំពីវិធីដោះស្រាយ និងការថែទាំដំណាំត្រប់វែងបានយ៉ាងច្រើន។
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
evaporation
Comments/ specify:
ដីមានដំណាំជាប់រហូតដែលធ្វើឱ្យរំហួតត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយច្រើន។
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
សំណើមដីល្អជាងមុនដោយសារមានដំណាំធ្វើជាគម្របដីជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ (ម្លប់ពីស្លឹក)។
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
គម្របដីកើនឡើងដោយសារការដាំដំណាំបន្តបន្ទាប់នៅចន្លោះដំណាំក្រូចឆ្មារ។
soil crusting/ sealing
Comments/ specify:
ការប្រើកាកសំណល់បង្គន់ដែលបំបែកធាតុរលាយសព្វល្អ និងកាកសំណល់ត្រប់វែងបានកាត់បន្ថយដីប្រេះនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើបានយ៉ាងល្អ។
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
ដីហាប់ត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយដោយសារការប្រើប្រាស់កាកសំណល់ពីបង្គន់ និងលាយជាមួយកាកសំណល់ដំណាំជំនួសជីគីមី។
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គកើនឡើងក៏ដោយសារការប្រើប្រាស់កាកសំណល់ដែលចេញពីអាងស្តុកលាមក និងសំណល់ពីដំណាំផ្សេងៗ។
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
មានដាំដំណាំជាប្រចាំបន្ទាប់ពីប្រមូលផល
plant diversity
Comments/ specify:
ប្រភេទដំណាំត្រូវបានផ្លាស់ប្តូរជាប្រចាំ
invasive alien species
Comments/ specify:
ការកើនឡើងនៃគម្របរុក្ខជាតិដោយសារការដាំដំណាំ បានជួយគ្រប់គ្រងស្មៅបានល្អ ហើយប្រភេទសត្វរាតត្បាតក៏ត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយខ្លះៗដែរ។
beneficial species
Comments/ specify:
ពពួកជន្លេនកើតមានច្រើននៅពេលដែលគាត់ប្រើប្រាស់កាកសំណល់ពីបង្គន់ជំនួសជីគីមី។
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
ករណីទីមួយដំណាំត្រប់វែងត្រូវការការការពារខ្លាំងពីសត្វល្អិត និងជំងឺ ព្រោះវាងាយទទួលរងនូវការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិតចង្រៃ។ ម៉្យាងវិញទៀតក្លិននៃក្រូចឆ្មារអាចរារាំងការបំផ្លាញពីសត្វល្អិតចង្រៃ ហើយដើមឈើក៏អាចទាក់ទាញសត្វស្លាបដែលស៊ីសត្វល្អិតផងដែរ។
Climate and disaster risk reduction
micro-climate
Comments/ specify:
ម្លប់នៃដើមឈើ កម្ពស់ខុសៗគ្នានៃដំណាំ និងដង់ស៊ីតេនៃដំណាំខ្ពស់ៗដែលនៅជុំវិញទីតាំងបច្ចេកទេស (ដំណាំចេក) បានជះឥទ្ធិពលដល់មីក្រូអាកាសធាតុដើម្បីឱ្យល្អប្រសើរឡើង (របាំងខ្យល់ និងតុល្យភាពកម្តៅ)។
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
Comments regarding impact assessment:
មិនមានផលប៉ះពាល់ដល់បរិវេណខាងក្រៅគួរឱ្យកត់សម្គាល់ទេ។
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | very well |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 90-100%
Comments:
មិនមានអ្នកចង់ធ្វើតាមទេ
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| ចំណេញដីដោយនៅក្នុងទំហំដីដដែលអាចដាំបានច្រើនមុខ ដែលអាចផ្តល់ផលបានបន្តគ្នា។ |
| ងាយស្រួលក្នុងការថែទាំ ដោយមិនបាច់ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្មបន្ថែម ព្រោះការថែទាំ ឬស្រោចទឹកត្រប់វែង គឺក្រូចឆ្មារក៏បានទទួលការថែទាំ និងសំណើមដែរ។ |
| បច្ចេកទេសនេះអាចធន់ទៅនឹងកម្តៅ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ជួយជីជាតិដោយប្តូរប្រភេទដំណាំ និងប្រើកាកសំណល់ពីបន្ទប់ទឹក |
| អាចកាត់បន្ថយការចំណាយលើការប្រើប្រាស់ជីគីមី |
| ជួយរក្សាសំណើមដី និងបន្ថយកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងការថែទាំ និងស្រោចស្រព |
| កាត់បន្ថយស្មៅចង្រៃដោយមានដំណាំគម្របដីជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| មានបញ្ហាជំងឺ និងសត្វល្អិត | ប្រើប្រាស់ថ្នាំស្របតាមបច្ចេកទេស |
| ខ្វះបច្ចេកទេសធ្វើថ្នាំការពារ និងកំចាត់ពីសត្វល្អិតដែលផ្សំឡើងពីរុក្ខជាតិ | អាចផ្តល់ជាបច្ចេកទេសតាមរយៈសៀវភៅ ឬមានការបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបន្ថែម។ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1 នាក់
- interviews with land users
1 នាក់
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
3 នាក់
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
General Directorate of Agriculture (2012) Vegetable techniques. Retrieved on Aug 2017 from
URL:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B41jxuufJz2-Y1c1bHpNb2ZpMm8/view
Title/ description:
My Agriculture Information Bank (2015) Inter Cropping and Its Advantages. My Agriculture Information Bank. Retrieved on July 25 2017 from
URL:
http://www.agriinfo.in/?page=topic&superid=1&topicid=492
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules