Pilancón [Ecuador]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Pablo Caza
- Editor: Carlos Samaniego
- Reviewers: Giacomo Morelli, Nicole Harari, Johanna Jacobi
Pilancón
technologies_3276 - Ecuador
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Ecuador
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministerio de Ambiente y Agua Ecuador (MAAE) - EcuadorName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministerio de Agricultura y Ganadería Ecuador (MAG) - EcuadorName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Organización de la Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura Ecuador (FAO Ecuador) - Ecuador1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
20/11/2019
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
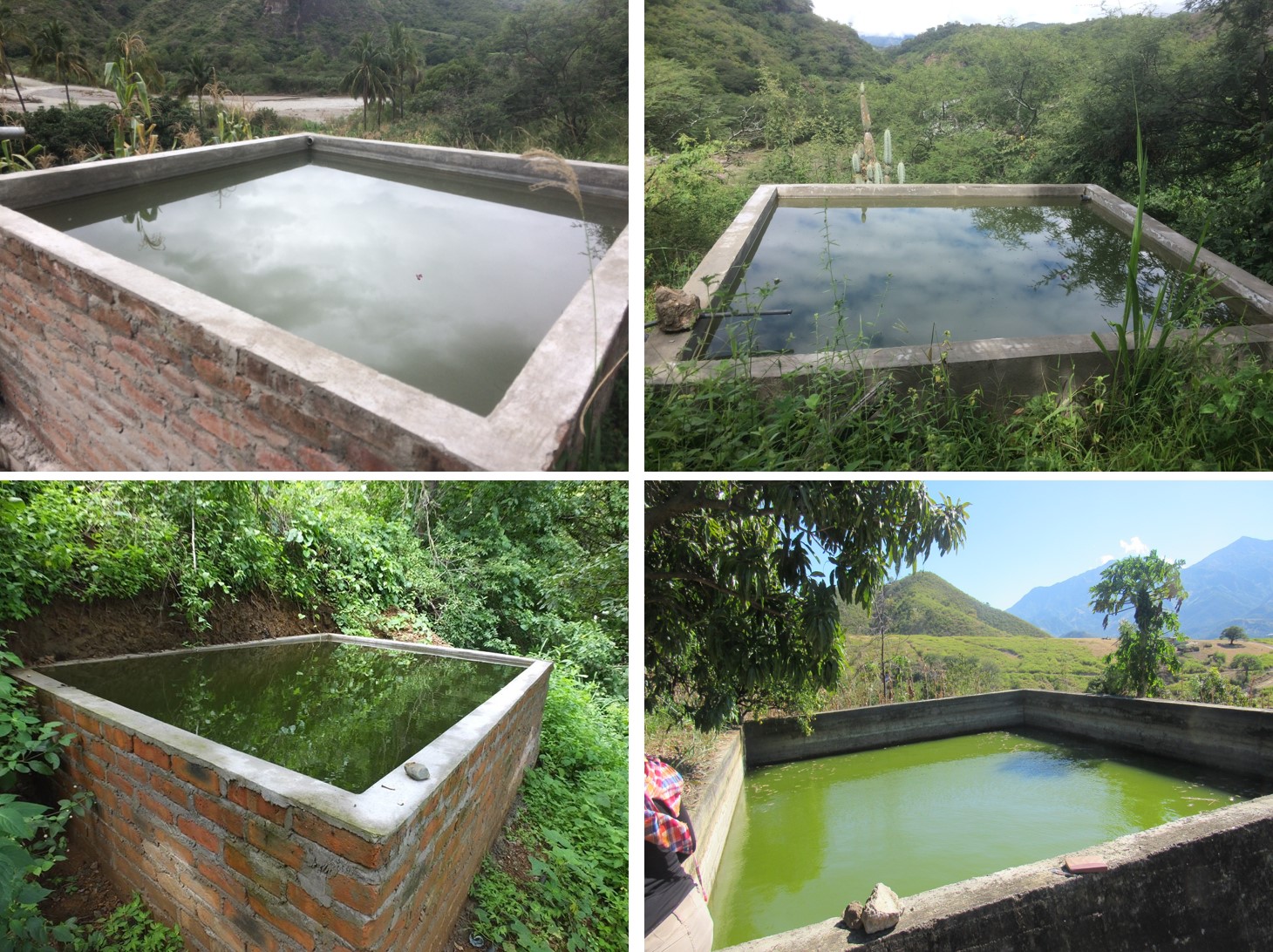
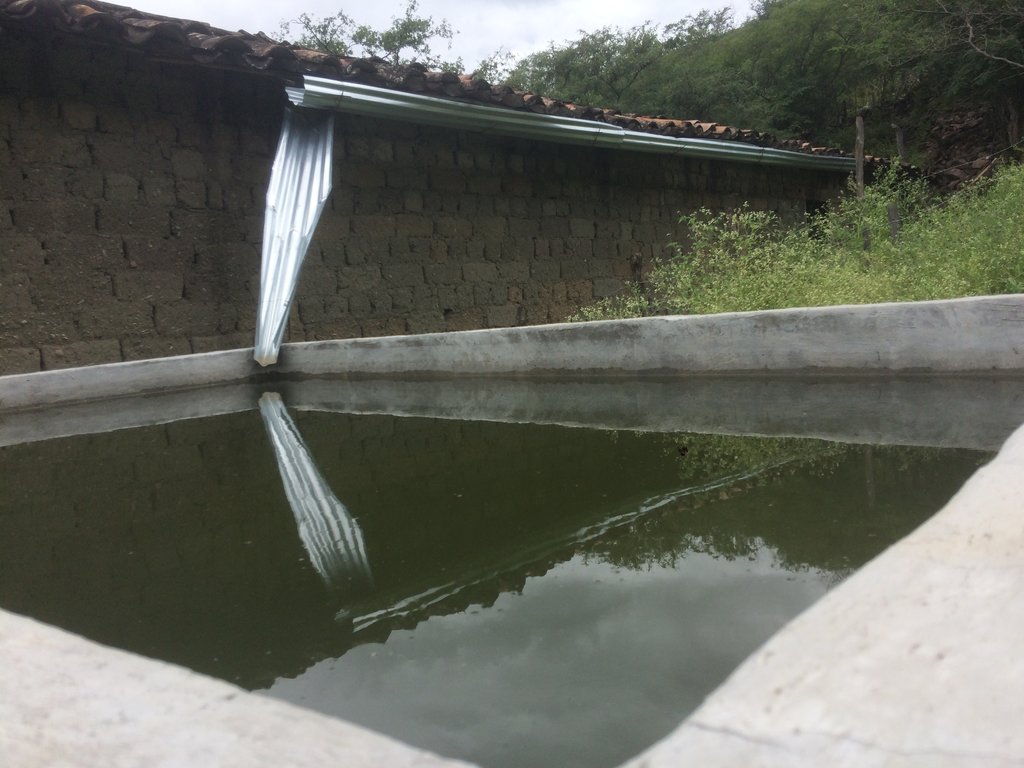
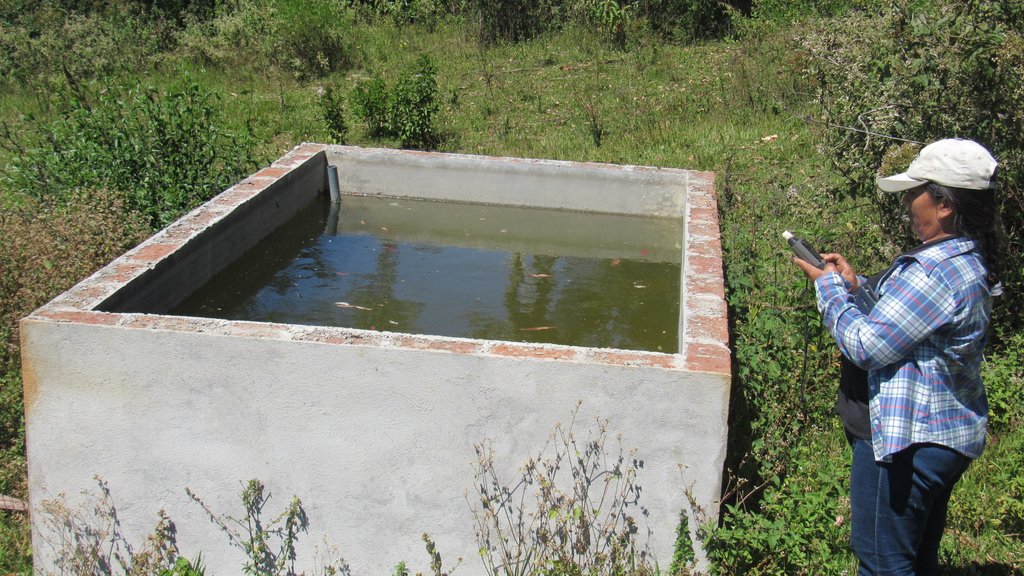
El Pilancón es un micro-reservorio para almacenar agua ya sea de lluvia y quebradas, y es utilizado para el riego de los cultivos de áreas pequeñas.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Es una estructura formada con hierro, cemento, piedra y ladrillo. Es semejante a un reservorio con la particularidad de estar sobre el nivel del suelo. El volumen de almacenamiento es de 12 m3 en promedio. El agua almacenada es utilizada para los abrevaderos del ganado y para el riego por aspersión o gravedad de los cultivos agrícolas y pastos. El diseño y construcción adecuados de los pilancones son indispensables para asegurar el éxito de estas obras, además de hacerlos más fáciles de cuidar, más seguros y económicos. Es ideal considerar en los aspectos constructivos del reservorio el punto más alto de la finca, de modo que el agua pueda llegar desde este punto hasta cualquier lugar de la propiedad. Sin embargo, no siempre es posible tener las condiciones adecuadas para lograr lo anterior. Si la estructura solo puede ubicarse en un punto muy bajo, será necesario considerar la implementación de bombeo. La selección del sitio adecuado es clave para el éxito del reservorio. Debe tomarse en cuenta la topografía del terreno, la textura del suelo, el destino donde se usará el agua y la disponibilidad de la fuente de agua. Este tipo de reservorio es muy similar al excavado, con la diferencia que el nivel del agua se puede llevar por encima del suelo, mediante la construcción de paredes, principalmente de concreto. Se recomienda para zonas donde otros materiales de construcción no se encuentren disponibles.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Ecuador
Region/ State/ Province:
Cantón Paltas, Provincia de Loja
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- create beneficial economic impact
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping

Waterways, waterbodies, wetlands
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- home gardens
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Hp: decline of surface water quality
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
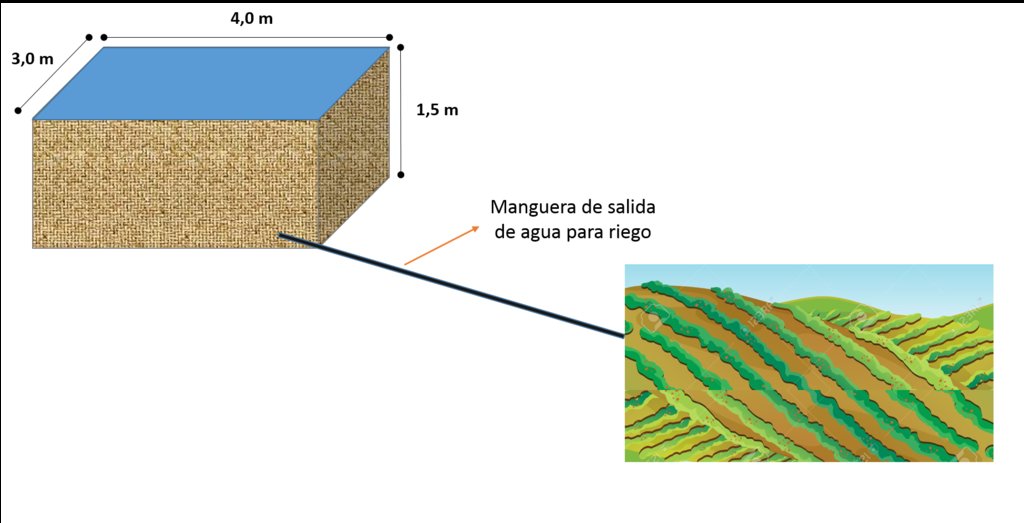
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Los pilancones generalmente se construyen de 3 m de ancho por 4 m de largo y 1,5 m de alto lo que da una capacidad de 18 m3 de almacenamiento de agua con una tubería de salida en el extremo bajo de 2" para su distribución.
Es necesario elaborar una base y pilares de hormigón y luego pegar los ladrillos para evitar resquebrajamiento debido a que los suelos donde existen arcillas expansivas someten a la estructura a constantes presiones que sumados al peso del agua almacenada rompen las paredes en corto tiempo.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Limpieza de terreno | Agronomic | None |
| 2. | Transporte de materiales | Structural | None |
| 3. | Preparación de materiales | Structural | None |
| 4. | Construcción del pilancón | Structural | None |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Limpieza de terreno | jornal | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Transporte de materiales | jornal | 2.0 | 15.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Preparación de materiales | jornal | 2.0 | 15.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Construcción del pilancón | jornal | 4.0 | 15.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | Cemento | quintal | 20.0 | 8.0 | 160.0 | 20.0 |
| Construction material | Arena | m3 | 2.0 | 13.0 | 26.0 | 20.0 |
| Construction material | Piedras | m3 | 0.5 | 24.0 | 12.0 | 20.0 |
| Construction material | Hierro | varilla | 1.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 20.0 |
| Construction material | None | None | 400.0 | 0.25 | 100.0 | |
| Construction material | None | None | 1.5 | 15.0 | 22.5 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 471.5 | |||||
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Other measures | None |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | None | None | 0.3 | 15.0 | 4.5 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 4.5 | |||||
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
El costo del material de construcción es el que más contribuye al costo total de la tecnología.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
- arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
- elderly
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- leased
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
crop quality
fodder production
production area
Water availability and quality
water availability for livestock
irrigation water availability
Income and costs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
health situation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
harvesting/ collection of water
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
Comments regarding impact assessment:
La tecnología no produce ningún tipo de impacto fuera del sitio de implementación.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| cold wave | very well |
| drought | very well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| landslide | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
Mejora la disponibilidad de agua para los abrevaderos del ganado y para el riego por aspersión o gravedad de los cultivos agrícolas y pastos |
| Fácil de cuidar, segura y económica |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Es necesario la disponibilidad de material para su construcción. | |
| No es recomendable en parcelas con superficie plana | |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules