Plantation forestière [Morocco]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Mohamed Sabir
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Donia Mühlematter, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Nicole Harari, Valentin Zuercher
Reboisement
technologies_3232 - Morocco
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royaume du Maroc, Haut Commissariat aux Eaux et Forêts et à la Lutte Contre la Désertification (Royaume du Maroc) - Morocco1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
17/01/2017
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches

Reconstitution et réhabilitation des écosystèmes forestiers. [Morocco]
La reconstitution et la réhabilitation des forêts répondent aux objectifs et missions des gestionnaires visant la pérennité des peuplements forestiers. Dans cet objectif les écosystèmes tenderont vers l'équilibre tout en offrant les biens et services optimaux.
- Compiler: Mohamed Sabir
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
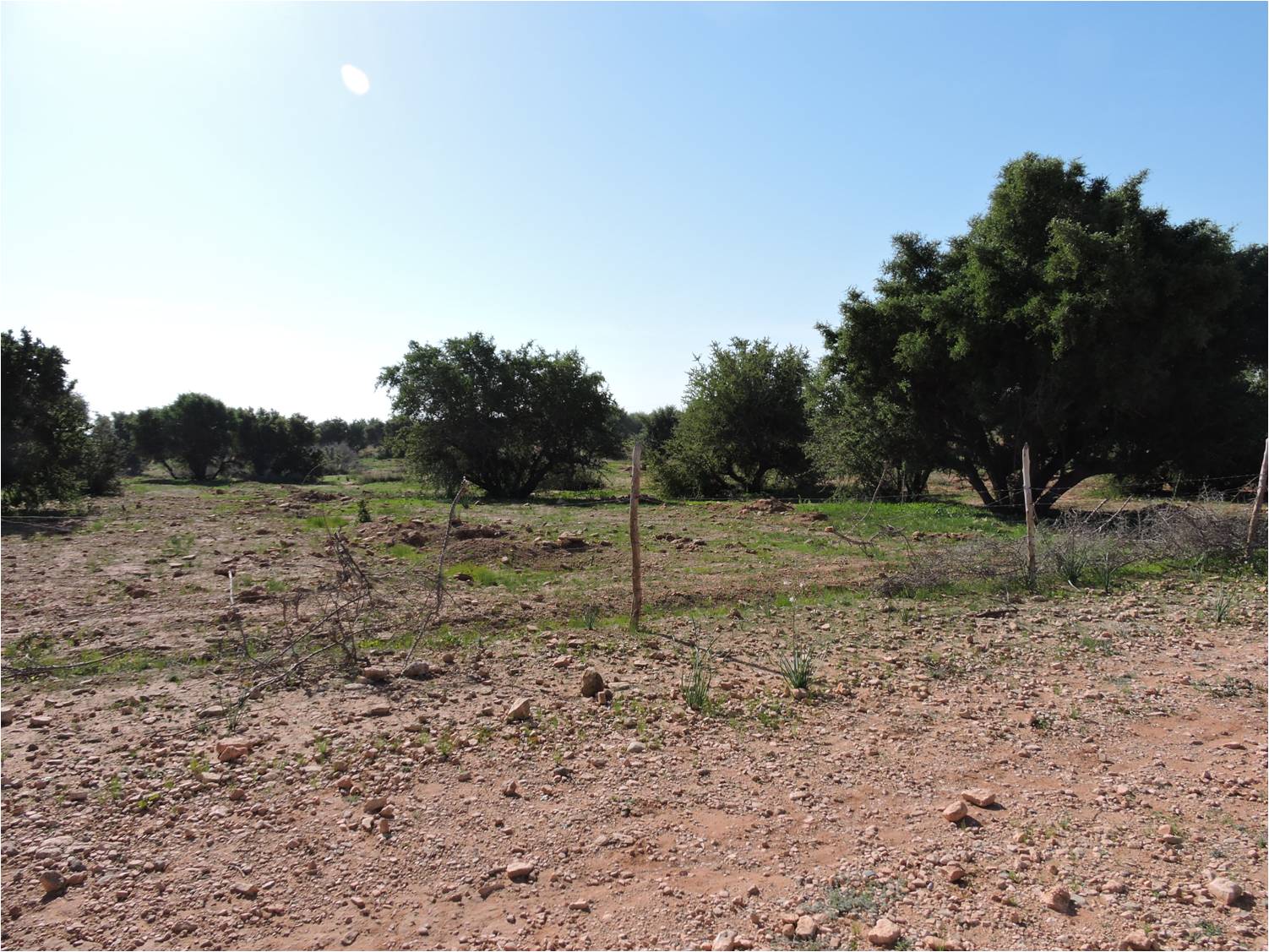
Il s'agit de planter des jeunes plants d'espèces forestières locales (arganier) mais aussi des espèces adaptées aux conditions écologiques concernées (exemple Pinus halepensis).
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Augmentation de la densité des peuplements d'arganier ouverts et dégradés par des jeunes plants issus de pépinière forestière.
les principales opérations :
- Ouverture de potets de 60*60*60cm à raison de 200 plants/ha.
- Rebouchage des troues.
- Plantation des plants.
- Arrosage (15 fois aux besoins).
- Regarnis la deuxième année.
- Désherbage / binage durant 2 ans.
- Compensation du droit de parcours jusqu'à la défensabilité des plants (10 à 12 ans).
Les opérations de plantations commencent par l'attribution des périmètres à planter par adjucation. Après l'ordre de service, l'adjudicataire commence l'installation de la clôture en fil barbelé supporté par piquets en bois ou en fer selon les termes du CPS. Ensuite, on procède à l'ouverture des potets manuellement selon les TDRs du CPS qui sont dans la zone de 60x60x60cm. Après réception des potets l'adjucataire procède au rebouchage des potets et puis à la plantation des jeunes plants livrés par les pepinières dont la qualité a fait l'objet aussi de validation.
L'adjucataire est appelé aussi à réaliser des arrosages (10 à 15) selon les termes du CPS et la réception définitive des périmètres a lieu après 18 mois qui vientde passer à 24 mois.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Morocco
Region/ State/ Province:
Région Souss Massa, Commune d'Amskroud
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2015
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
- through projects/ external interventions
- Convention HCEFLCD-ANDZOA
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Projets décinnaux de reconstitution des forêts menés par l'état.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
- mitigate climate change and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Forest/ woodlands
Tree plantation, afforestation:
- Monoculture local variety
Products and services:
- Grazing/ browsing
Comments:
Les périmètres de reboisement sont interdits à tout usage.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- natural and semi-natural forest management
- forest plantation management
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 km2
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Surpâturage, surexploitation des ressources ligneuses.
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
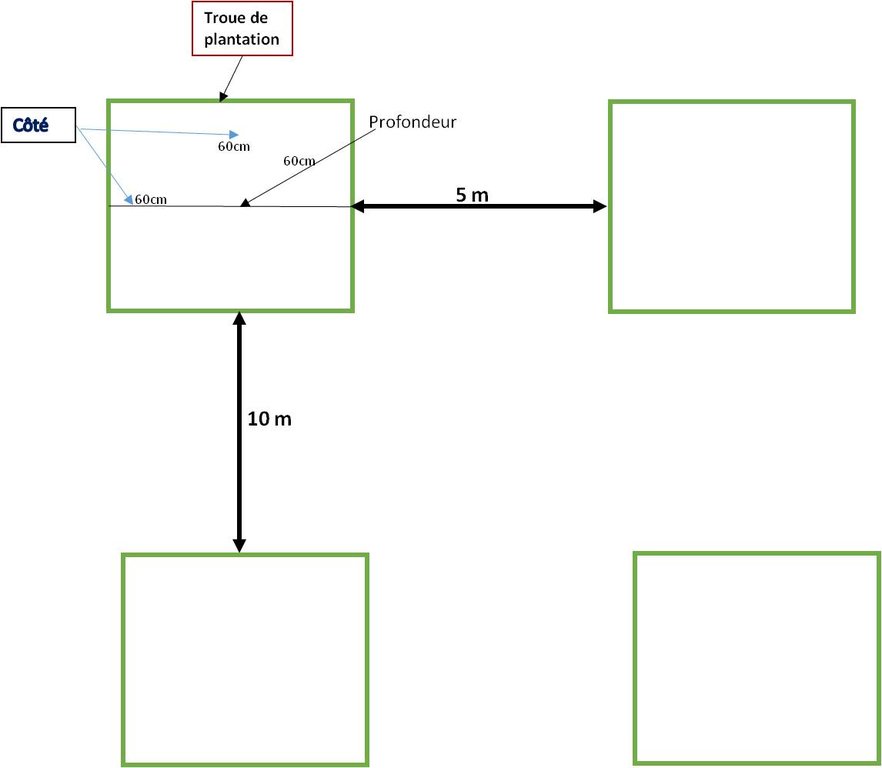
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
- Potes de : 60*60*60 cm
- Densité 200 plants/ha
- Plants de 5 à 7 mois en pépinière regarnis après la première année.
- Entretien des plants (déserbage).
- Arrosages (jusqu'à 15 fois).
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
100 ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare:
1 hectare
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
9.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
70 dh
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clôture | Structural | Septembre |
| 2. | Ouverture des potes | Structural | Octobre |
| 3. | Rebouchage des trous et compost | Structural | Novembre |
| 4. | Acheminement des plants | Structural | Novembre |
| 5. | Plantations | Vegetative | Novembre/Décembre |
| 6. | Regarnis | Vegetative | |
| 7. | Entretiens des plants | Agronomic | |
| 8. | Arrosages | Agronomic |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Ouverture des potets | potet | 20000.0 | 1.0 | 20000.0 | |
| Labour | Rebouchage des plantations | potet | 20000.0 | 1.0 | 20000.0 | |
| Equipment | Clôture | ml | 160.0 | 1000.0 | 160000.0 | |
| Plant material | Acheminement des plants | Plant | 20000.0 | 0.1 | 2000.0 | |
| Plant material | Regarnis | Plan | 5000.0 | 0.1 | 500.0 | |
| Other | Arrosage | Plant | 20000.0 | 3.0 | 60000.0 | |
| Other | Entretiens | Plan | 20000.0 | 0.1 | 2000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 264500.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
L'état.
Comments:
La technologie totalement prise complétement par l'état.
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Arrosage (durant 2 ans) | Agronomic | Juillet - Août - Septembre |
| 2. | Binage et désherbage (durant 2 ans) | Agronomic | Mars - Avril |
| 3. | Regamis | Vegetative | Février à septembre durant la 2ème année |
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Compensation de la mise en défens | ha | 100.0 | 25.0 | 2500.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 2500.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
L'état.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
150.00
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Ja
Regularity:
episodically
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
La technologie exclue actuellement les utilisations des terres habituelles jusqu'à la défensabilité.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
L'utilisation de l'espace est communae pour la communauté usagère.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
fodder quality
wood production
Comments/ specify:
Attendre la réussite de la technologie.
forest/ woodland quality
non-wood forest production
land management
Water availability and quality
drinking water availability
drinking water quality
water availability for livestock
water quality for livestock
Income and costs
diversity of income sources
Socio-cultural impacts
land use/ water rights
community institutions
national institutions
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Quantity before SLM:
Importante
Quantity after SLM:
Faible
Comments/ specify:
Avec la réusssite de la plantation.
groundwater table/ aquifer
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
Quantity before SLM:
Claire
Quantity after SLM:
Améliorée
Comments/ specify:
Au fur et à mesure avec l'age des plants.
soil loss
soil crusting/ sealing
soil compaction
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
Amélioration progressive.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
Amélioration progressive.
biomass/ above ground C
plant diversity
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
drought impacts
impacts of cyclones, rain storms
Comments/ specify:
Réduit avec le couvert végétal.
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
downstream flooding
Comments/ specify:
Réduit avec le couvert végétal.
downstream siltation
wind transported sediments
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| seasonal temperature | spring | decrease | moderately |
| seasonal rainfall | spring | decrease | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | moderately |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
C'est la communauté qui accepte la technologie.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 50-90%
Comments:
Technologie appliquée par les services de l'état.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
Augmenter les conditions de réussite des plantations.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Usagers sont peu favorables en raison de l'exclusion du droit de pâturage en zone plantée. |
| L'état doit assurer des alternatifs ou des mesures plus interressantes à la compensation des ressources fouragères tirés des zones reboisées. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Technologie nécessaire pour la reconstitution et la durabilité des forêts d'arganier en particulier. |
| Développer l'approche participative avec les usgaers. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Contraignante pour les activités des usagers. | Concertation et encouragements des usagers. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Difficultés de réussir la technologie. | Implication et faire adhérer les usagers pour la mise en place de la technologie. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
Plusieurs visites et enquêtes socio - économiques.
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
Plusieurs personnes.
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
Dans le cadre des travaux de recherche encadrés.
Documents de recherche et études.
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Reconstitution et réhabilitation des écosystèmes forestiers. [Morocco]
La reconstitution et la réhabilitation des forêts répondent aux objectifs et missions des gestionnaires visant la pérennité des peuplements forestiers. Dans cet objectif les écosystèmes tenderont vers l'équilibre tout en offrant les biens et services optimaux.
- Compiler: Mohamed Sabir
Modules
No modules