កសិរុក្ខកម្ម-ដំណាំសណ្តែកដីជាមួយស្វាយចន្ទីនៅតំបន់ខ្ពង់រាប [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Navin Chea
- Editors: Sophea Tim, SOBEN KIM
- Reviewers: SO Than, Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
សណ្តែកដី និងស្វាយចន្ទី
technologies_2315 - Cambodia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកគូលែន:
land user:
វីន អ៊ុត
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
Cambodia
មន្ត្រីការិយាល័យកសិម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកជាំក្សាន្ត:
ឆ្លាត ប្រាជ្ញ
ការិយាល័យកសិម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកជាំក្សាន្ត
Cambodia
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
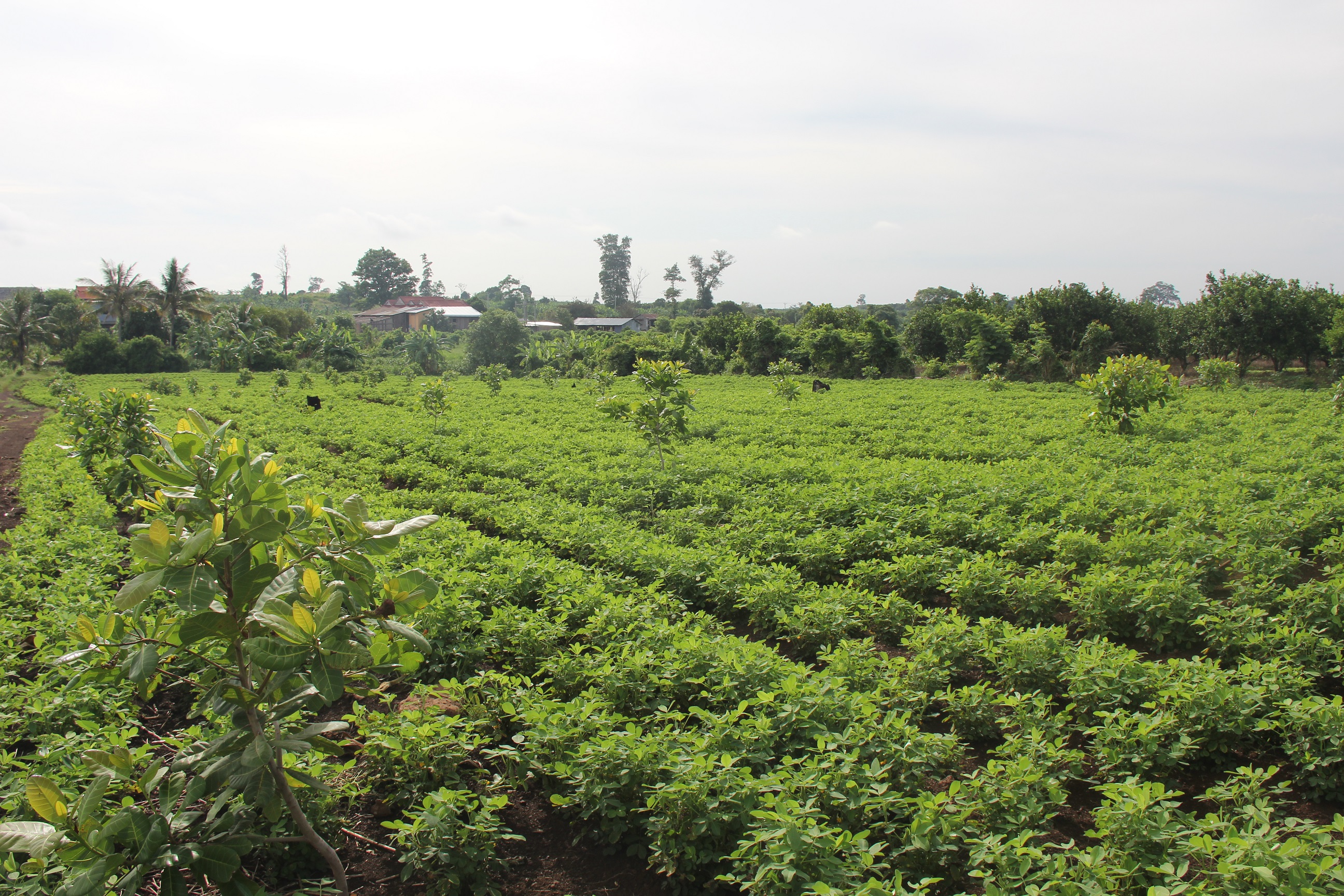
ការដាំដំណាំប្រចាំរដូវ(សណ្តែកដី) ក្នុងចម្ការស្វាយចន្ទីដែលទើបដាំថ្មីមានគោលបំណងដាំបំពេញដីទំនេរចោលនៅចន្លោះដើមស្វាយចន្ទី។ វាជាដំណាំគម្របដីទប់ស្កាត់ការហូរច្រោះ និងបង្កើនជីជាតិដី ម៉្យាងវិញទៀតសណ្តែកដីជាប្រភេទដំណាំមានទីផ្សារ។
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
សណ្តែកដីស្ថិតក្នុងអម្បូរ Leguminosae មានឈ្មោះវិទ្យាសាស្ត្រ Arachishypogaea L.ជាដំណាំដែលសម្បូរទៅដោយសារធាតុមានគុណប្រយោជន៍សំខាន់ៗជាច្រើន។ គ្រាប់សណ្ដែកដីមានផ្ទុកសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹមដូចជា : ប្រូតេអ៊ីន កាល់ស្យូម វីតាមីនបេ និងគ្លុយតាម៉ីនអាស៊ីត ហើយមានជាតិប្រេងយ៉ាងខ្ពស់រហូតដល់ ៤០-៦០ ភាគរយ ។ សណ្តែកដីផ្តល់ទិន្នផលជាមធ្យម០.៧៣តោន/ហិកតា (Cambodian Agricultural Research and Development Institute, 2006) ។ ដំណាំនេះត្រូវបានប្រជាជនកម្ពុជានិយមចូលចិត្តដាំជាលក្ខណៈគ្រួសារ ឬជាចម្ការធំៗ ។
សណ្ដែកដីអាចដុះលូតលាស់នៅលើដីច្រើនប្រភេទ ជាពិសេសដីល្បាប់ខ្សាច់ ដីល្បប់ ដីខ្មៅ ដែលជាប្រភេទដីស្រោះទឹកល្អ ។ សណ្ដែកដីជារុក្ខជាតិត្រូវការពន្លឺពេញ ការខ្វះពន្លឺនាំឱ្យពន្យារពេលក្នុងការលូតលាស់ ។ ដំណាំនេះតម្រូវឱ្យមានទឹកគ្រប់គ្រាន់ក្នុងការដាំដុះ តែវាក៏មិនធន់នឹងភាពដក់ទឹករយៈពេលយូរបានទេ ផ្ទុយទៅវិញបើខ្វះទឹកក៏ជាបញ្ហាដែរ។ រដូវដាំដុះសម្រាប់តំបន់ខ្ពង់រាប គឺចាប់ពីខែមេសា-ឧសភា និងចាប់ពីខែ កញ្ញា-តុលា ដោយឡែកសម្រាប់តំបន់មាត់ទន្លេ គឺដាំនៅរដូវសម្រកចាប់ពីខែវិច្ឆិកាទៅ។ រយៈពេលនៃការប្រមូលផល គឺអាស្រ័យទៅលើពូជរបស់វា។ ពូជរយៈពេលខ្លី អាចប្រមូលផលក្រោយរយៈពេល ៩០-១០០ ថ្ងៃ ពូជរយៈពេលវែង គឺប្រមូលផលនៅរយៈពេលពី ១២០-១៤០ ថ្ងៃ (Agritoday, 2016,Yayo, 2016)។
ចំណែកស្វាយចន្ទីមានឈ្មោះវិទ្យាសាស្ត្រ Anacardiumoccidentale L. ស្ថិតនៅក្នុងគ្រួសារ Anacardiaceae (Royal University of Agriculture, 2006) ។ បច្ចុប្បន្នបណ្ដាប្រទេសមួយចំនួននៅតំបន់ត្រូពិចមានការនិយមដាំស្វាយចន្ទីយ៉ាងច្រើន។ គ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទីមានផ្ទុកសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹមក្នុងកម្រិតខ្ពស់ គឺក្នុងគ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទី ១០០ក្រាម អាចផ្តល់ថាមពលរហូតដល់ ៥០០ កាឡូរី។ ស្វាយចន្ទីអាចប្រមូលផលជាលើកដំបូង គឺនៅអាយុ ៣ ទៅ ៤ឆ្នាំ(ផ្តល់ផលលើកដំបូងបាន ប្រហែល ២,៥០-៣ គីឡូក្រាម នៅក្នុងមួយដើម) នៅអាយុបាន ២ ឆ្នាំក៏អាចប្រមូលផលបានខ្លះដែរក្រាន់តែទិន្នផលទាប ប៉ុន្តែគេអាចទទួលបានទិន្នផលខ្ពស់នៅពេលវាមានអាយុ ៧ ឆ្នាំ ហើយផ្តល់ទិន្នផលថេរក្នុងរយៈពេលវែង គឺរហូតដល់ពេលដែលគេកាប់ដើមចាស់ចោល ហើយដាំសារជាថ្មីដែលមានរយៈពេលប្រហែលជា ២៥ ឆ្នាំ។ នៅក្នុងឆ្នាំ ២០១៧ គ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទីស្រស់មានតម្លៃប្រមាញជា ៨៥០០ រៀល ក្នុងមួយគីឡូក្រាម (Agritoday,2017)។
គោលបំណងសំខាន់ៗនៃការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសដាំសណ្តែកដីនៅចន្លោះដើមស្វាយចន្ទី បានបង្ហាញច្បាស់តាមរយៈការកាត់បន្ថយបានការដុះលូតលាស់របស់ស្មៅចង្រៃរហូតដល់ ៥០ ភាគរយ និងបង្កើនប្រាក់ចំណូលបន្ថែមទៀតផង (MoE,2016)។
លោកស្រីអ៊ុត វីន រស់នៅតំបន់ខ្ពង់រាបក្នុងខេត្តព្រះវិហារ (ប្រទេសកម្ពុជា) គឺជាកសិករមួយរូបដែលអនុវត្តន៍ប្រព័ន្ធកសិរុក្ខកម្ម។ ទីតាំងអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសនោះមានប្រវត្តិជាតំបន់ព្រៃរេចរិល ដំបូងឡើងគាត់បានកាប់ឆ្ការព្រៃនោះយកមកដាំដំណាំឯកវប្បកម្ម (ដំឡូងមី ចេក សណ្ដែកបាយ ឬសណ្ដែកសៀង)។ នៅឆ្នាំ២០១៦ដីនេះត្រូវបានយកមកដាំស្វាយចន្ទីជាមួយនឹងសណ្ដែកដីវិញ។
ប្រព័ន្ធនៃការដាំដំណាំនៅចន្លោះប្រភេទឈើបែបនេះផ្តល់អត្ថប្រយោជន៍ដូចខាងក្រោម៖
១. ការអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសនេះ គឺបង្កើនផលប្រយោជន៍ផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ចយ៉ាងច្រើនដល់កសិករ តាមលទ្ធភាពដីដែលមាន។តាមការអនុវត្តន៍តាមបច្ចេកទេសនេះ ទោះដីរេចរិលក៏អាចយកមកដាំដំណាំបានដែរ ដែលនេះជាការបង្កើនផលដើម្បីធ្វើឱ្យកាន់តែប្រសើរឡើងប្រាក់ចំណូលគ្រួសារ។
២. មុនពេលកសិករទទួលបានទិន្នផលពេញលេញពីដើមស្វាយចន្ទី(ក្រោយអាយុបាន ៣ឆ្នាំ) សណ្តែកដីបានផ្តល់ប្រាក់ចំណូលបានយ៉ាងឆាប់(ទទួលផលក្នុងរយៈពេល ៣ខែ ហើយដាំបាន ០២ ដង នៅក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ)។ នៅក្នុងដីមួយហិកតា សណ្តែកដីអាចផ្តល់ប្រាក់ចំណេញសុទ្ធចំនួន ៣,០០០,០០០ រៀល (តម្លៃលក់បាន ៤០០០ រៀល/គីឡូក្រាម)។
ដោយសារតែសណ្តែដីត្រូវការពន្លឺពេញ ការដាំដំណាំចន្លោះដីទំនេរត្រូវបានបញ្ឈប់ក្រោយពេលស្វាយចន្ទីមានអាយុ ៣ឆ្នាំ នេះដោយសារតែដើមរបស់វាបែកមែកសាខាគ្របជាម្លប់ដែលមិនអំណោយផលសម្រាប់ការដាំដុះសណ្តែកដីបន្តទៀតបាន។
ក្រៅពីអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ដូចរៀបរាប់ខាងលើ ការដាំដំណាំសណ្តែកដីក៏បានជួយបង្កើនជីជាតិដីផងដែរព្រោះវាជាប្រភេទដំណាំដែលប្រព័ន្ធប្ញសរបស់វាមានកំពកដែលបង្កើតឡើងដោយវត្តមាននៃបាក់តេរីសហប្រាណពពួករីហ្សូប្សូម(Rhizobium)ដែលក្រុមនេះមានសមត្ថភាពអាចស្រូប និងចាប់យកអាសូតសេរីពីបរិយាកាសទៅក្នុងដីបាន។ បន្ទាប់ពីប្រមូលផលរួច កាកសំណល់ដើមសណ្តែកដីត្រូវបានភ្ជួរលប់ទៅក្នុងដីក្លាយជាជីសរីរាង្គមួយដ៏ប្រសើរ ដូចនេះវា គឺជាជីស្រស់ដែលជួយកាត់បន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់ជីគីមី។ ការដាំដំណាំសណ្តែកដីមិនឱ្យដីនៅទំនេរចោលនៅឆ្នាំដំបូងនៃការដាំដើមស្វាយចន្ទី ក៏មានសារប្រយោជន៍ណាស់ដែរ ដើម្បីទប់ទល់នឹងការដុះដាលស្មៅចង្រៃ។ មុខងារចុងក្រោយដែលមានសារសំខាន់ដែរនោះគឺ សណ្តែកដី និងស្វាយចន្ទី គឺជាដំណាំដែលទប់ទល់នឹងការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក។
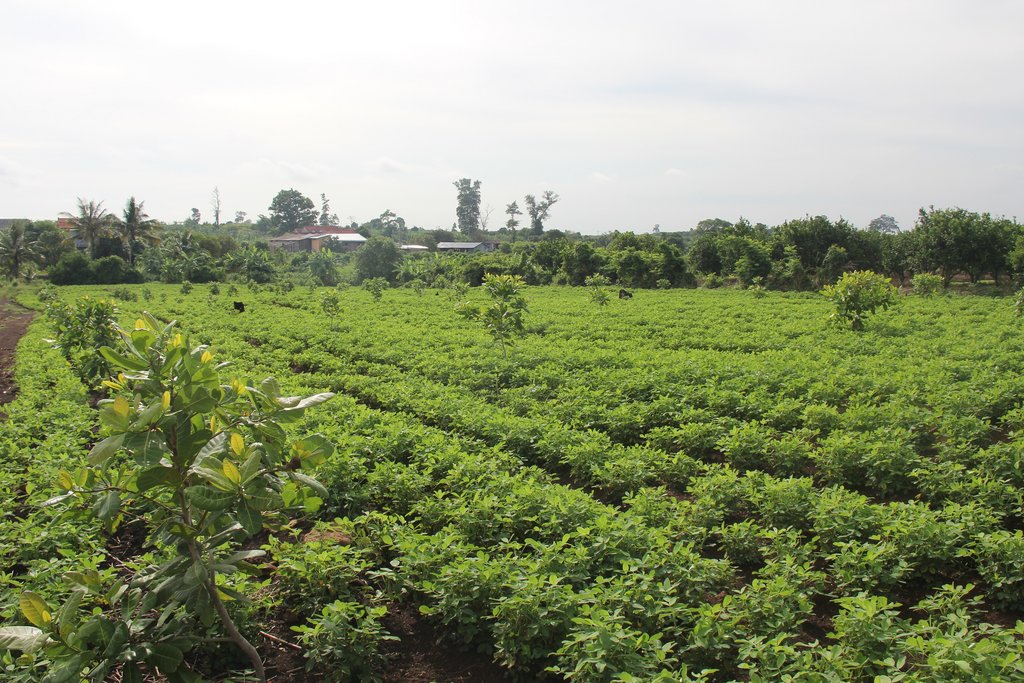
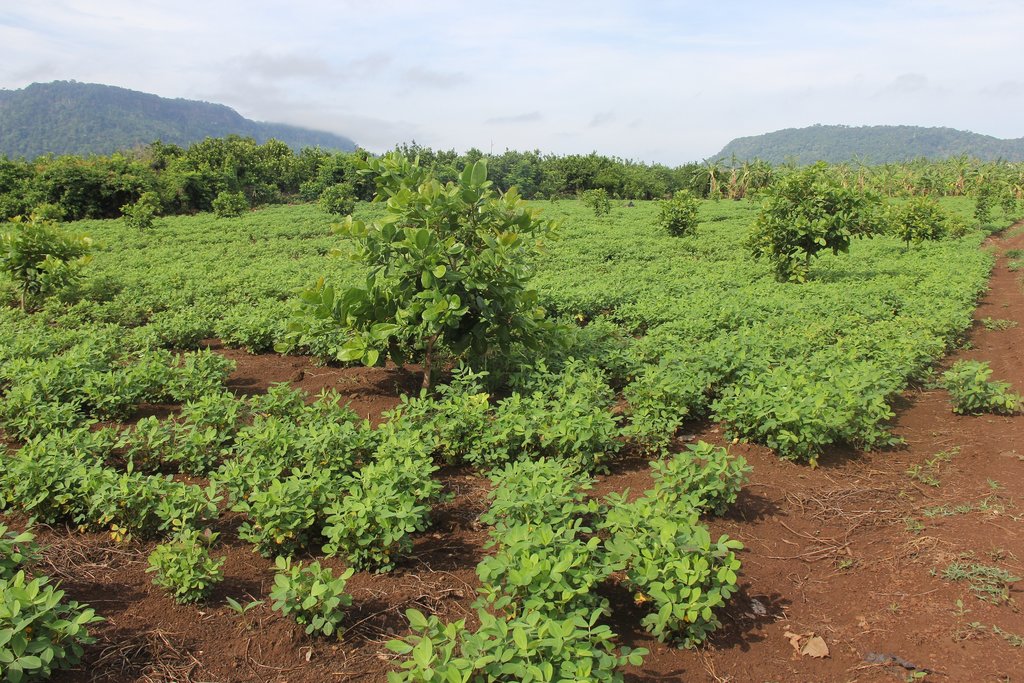
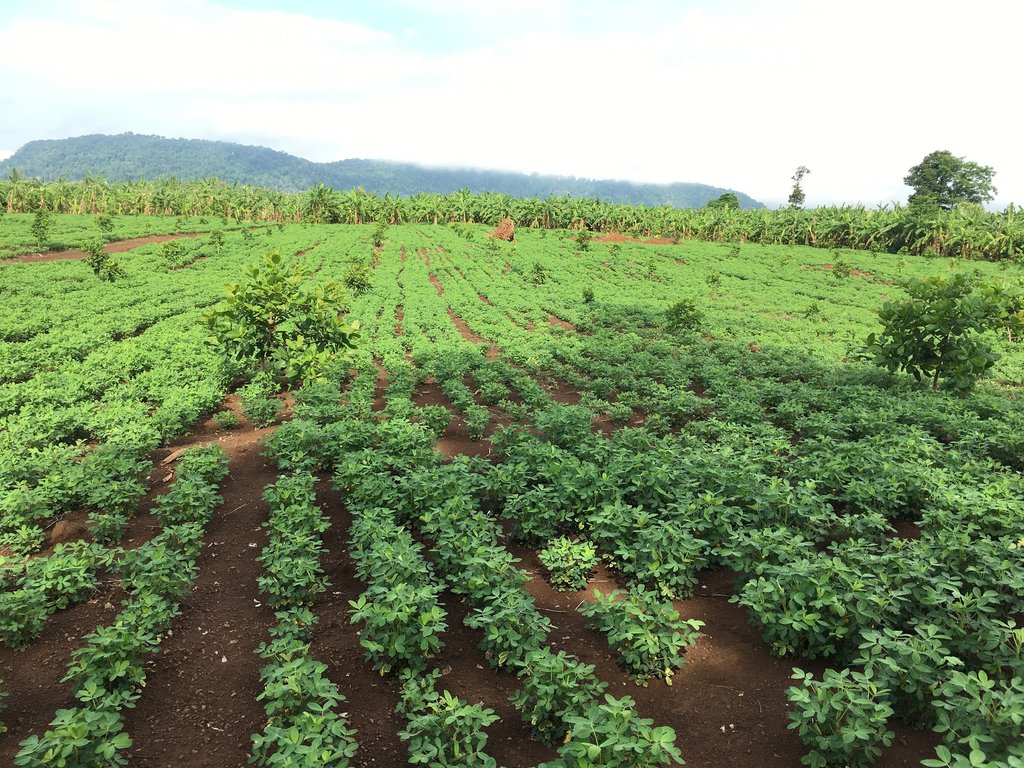
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
ភូមិបេងកោង ឃុំព្រះឃ្លាំង ស្រុកត្បែងមានជ័យ ខេត្តព្រះវិហារ
Further specification of location:
នៅចម្ការចង្ងាយ ០២គីឡូម៉ែត្រពីជើងភ្នំ
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2016
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
Comments (type of project, etc.):
សួរគេខ្លះហើយច្នៃខ្លួនឯងខ្លះ។ ពីមុនធ្លាប់ដាំចេកប៉ុន្តែជួបប្រទះជំងឺ។
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Ja
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- legumes and pulses - beans
- legumes and pulses - soya
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
- root/tuber crops - cassava
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- cashew
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Is intercropping practiced?
Ja

Forest/ woodlands
Products and services:
- Fruits and nuts
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

Other
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
Comments:
បន្ទាប់ពីប្រមូលផលសណ្តែកដីរួច កាកសំណល់របស់វាត្រូវបានភ្ជួរលប់ទៅក្នុងដីដើម្បីធ្វើឱ្យជីជាតិដីប្រសើរឡើងដែលមានសារប្រយោជន៍សម្រាប់ដំណាំស្រូបយក។
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
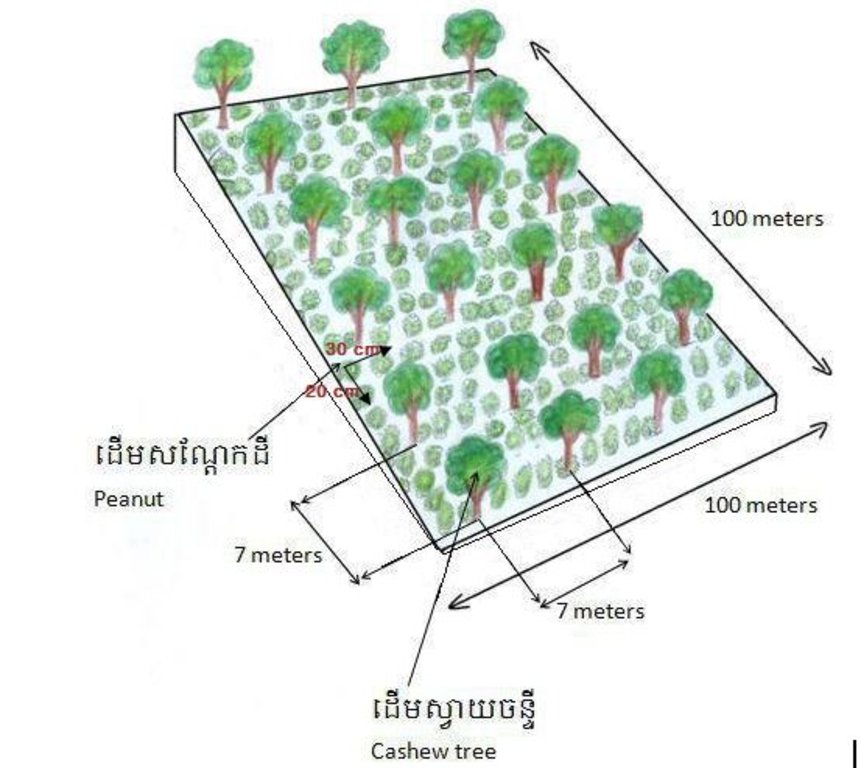
នៅលើផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសមានទំហំ ១០,០០០ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ(ទទឹង ១០០ ម៉ែត្រ បណ្តោយ១០០ ម៉ែត្រ)។ ដើមស្វាយចន្ទីសរុបមានចំនួន ២២០ ដើម ដោយចន្លោះពីដើមមួយទៅដើមមួយទៀតមានប្រវែង ៧ម៉ែត្រ និងចន្លោះជួរស្វាយចន្ទីមានប្រវែង ៧ ម៉ែត្រ។ រណ្តៅជីកដាំស្វាយចន្ទីមានទំហំ ៣០សង់ទីម៉ែត្របួនជ្រុង និងជម្រៅ ៣០ សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ។ សណ្ឋានដីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសនេះមានជម្រាលប្រហែល ១,៥ ទៅ ៣ ដឺក្រេ ចម្ងាយ ២គីឡូម៉ែត្រពីជើងភ្នំ។
ចំណែកសណ្តែកដីធ្វើការបុកដាំដោយមួយរន្ធដាក់ ៣ គ្រាប់សណ្តែកដី ក្នុងជម្រៅ ៣-៤ សង់ទីម៉ែត្រជាជួរ ដែលមានចន្លោះជួរ ៣០សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ និងពីគុម្ពមួយទៅគុម្ពមួយទៀតគឺ២០ សង់ទីម៉ែត្រ។ នៅលើផ្ទៃដី ១០,០០០ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ប្រើគ្រាប់ពូជសណ្តែកដីអស់ ២០០ គីឡូក្រាម។
Author:
កញ្ញា អ៊ុំ សុវន្នី
Date:
05/05/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
១ហិកតា
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
១ ហិកតា=១០០០០ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
other/ national currency (specify):
រៀល
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
20000
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ភ្ជួរដីហាល | ខែមករា-មីនា |
| 2. | ជីករណ្តៅសម្រាប់ដាំកូនស្វាយចន្ទី | ខែកក្កដា |
| 3. | ដាក់ជី | ខែកក្កដា |
| 4. | ដាំសណ្តែកដី | ខែកក្កដា |
Comments:
សណ្តែកដីដាំនៅខែវស្សា ហើយអាស្រ័យតែលើទឹកភ្លៀងទាំងស្រុង មិនមានប្រភពស្រោចស្រពនោះទេ។
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ភ្ជួរដីហាល | ហិកតា | 1.0 | 60000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | បុកដាំសណ្តែកដី | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 40.0 | 20000.0 | 800000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ជីករណ្តៅដាំស្វាយចន្ទី និងដាំកូនស្វាយចន្ទី | រណ្តៅ | 220.0 | 600.0 | 132000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ចបកាប់ | ផ្លែ | 10.0 | 35000.0 | 350000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | កាំបិតធំ | កាំបិត | 5.0 | 50000.0 | 250000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ចបជីក | ចបជីក | 10.0 | 35000.0 | 350000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | កូនស្វាយចន្ទី | ដើម | 220.0 | 3000.0 | 660000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ពូជសណ្តែកដី | គីឡូក្រាម | 200.0 | 4700.0 | 940000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ជីទ្រាប់បាត | គីឡូក្រាម | 25.0 | 3000.0 | 75000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3617000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 904.25 | |||||
Comments:
ប្រើប្រាស់លុយដែលកម្ចីពីមីក្រូហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ។
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | បាញ់ថ្នាំជំនួយចន្ទី (ជំនួយត្រួយ) និងបាញ់ថ្នាំកម្ចាត់សត្វល្អិត | ១ អាទិត្យបាញ់ម្តង |
| 2. | ដាក់ជីតាមគល់របស់ស្វាយចន្ទី | ០៦ ដងក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ |
| 3. | ដកស្មៅនៅតាមគល់ស្វាយចន្ទី | ០៣ ដងក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ |
| 4. | បាញ់ថ្នាំល្បាស់លើសណ្តែកដី(ជំនួយត្រួយ ស្លឹក) | ពេលសណ្តែកដីដុះបាន២០ថ្ងៃ |
| 5. | បាញ់ថ្នាំជំនួយផ្កា និងដើមសណ្តែកដី | ០៣ ដងក្នុងរយៈពេល ០៣ ខែនៃវដ្តដំណាំ |
| 6. | ដកស្មៅតាមដើមសណ្តែកដី | ០២ ដងក្នុងរយៈពេល ០៣ ខែនៃវដ្តដំណាំ |
| 7. | ប្រមូលផលសណ្តែកដី | ០៣ ខែក្រោយពេលដាំ |
| 8. | ប្រមូលផលគ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទី | ក្រោយអាយុបាន ៣ឆ្នាំ |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | បាញ់ថ្នាំជំនួយផ្លែ ស្លឹក និងបាញ់ថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិត (ស្វាយចន្ទី) | ដង | 32.0 | 40000.0 | 1280000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ដាក់ជីតាមគល់ស្វាយចន្ទី | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 36.0 | 20000.0 | 720000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ដកស្មៅតាមគល់ស្វាយចន្ទី | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 45.0 | 20000.0 | 900000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | បាញ់ថ្នាំសណ្តែកដីដើម្បីជំនួយស្លឹក | ដង | 3.0 | 40000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ធុងបាញ់ថ្នាំប្រើដោយម៉ាស៊ីន | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 400000.0 | 400000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ធុងបាញ់ថ្នាំប្រើដោយកម្លាំងដៃសប់ | គ្រឿង | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ថ្នាំជំនួយស្វាយចន្ទី | ប្រអប់ | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ថ្នាំជំនួយដើម ផ្កា (សណ្តែកដី) | ប្រអប់ | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ថ្នាំជំនួយដើមសណ្តែកដី | កញ្ចប់ | 10.0 | 2500.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ទិញតង់សម្រាប់ហាលគ្រាប់សណ្តែកដី | តង់ | 5.0 | 24000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ទិញបាវច្រកគ្រាប់សណ្តែកដី | បាវ | 700.0 | 1000.0 | 700000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | កញ្ឆេដាក់គ្រាប់សណ្តែកដី | កញ្ឆេ | 3.0 | 15000.0 | 45000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | ដកស្មៅតាមដំណាំសណ្តែកដី | ដង | 20.0 | 20000.0 | 400000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | ដកសណ្តែកដី | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 70.0 | 20000.0 | 1400000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | វាយដើមសណ្តែកដីយកគ្រាប់ | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 60.0 | 20000.0 | 1200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | ជួលគេរោយសម្អាតយកគ្រាប់សណ្តែកដី | នាក់-ថ្ងៃ | 10.0 | 20000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | ជួយគេដើររើស ឬបេះគ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទី | គីឡូក្រាម | 1000.0 | 700.0 | 700000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 8305000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2076.25 | |||||
Comments:
ការចំណាយនៃការថែទាំ ចំពោះស្វាយចន្ទី គឺគិតថ្លៃថែទាំក្នុងរយៈពេល ០១ឆ្នាំ រីឯសណ្តែកដីវិញគិតថ្លៃថែទាំងក្នុងរយៈពេល ០៣ខែនៃវដ្តដំណាំ។ ចំពោះស្វាយចន្ទីមិនទាន់ដល់អាយុប្រមូលផលបាននោះទេ ដូចនេះតម្លៃនៃកម្លាំងពលកម្មដើររើស ឬបេះគ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទី គិតនៅពេលដែលស្វាយចន្ទីអាយុបាន ៣ ឬ ៤ឆ្នាំ។ តម្លៃពលកម្មនៃការបេះគ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទី គឺកសិករបានដឹងតម្លៃពីកសិករផ្សេងទៀតដែលទទួលផលរួចហើយ។
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ជាទូទៅចំណាយច្រើនក្នុងការបង្កើត និងថែទាំបច្ចេកទេសនេះ។ ស្វាយចន្ទី ០៣ ឆ្នាំទើបអាចទទួលបានផល ចំណែកសណ្តែកដី ០៣ខែ គឺអាចទទួលបានផល នៅពេលស្វាយចន្ទីទទួលផលជាទូទៅ គឺមិនអាចដាំសណ្តែកដីបន្តបានទៀតទេ។
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1429.30
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងឆ្នាំ 2015 មាន 1429.3 ម.ម ឆ្នាំ 2014 មាន 1647.3 ម.ម។
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឩត្តុនិយម ឆ្នាំ២០១៥
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
ទីតាំងអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេសជាជម្រាលជិតជើងភ្នំ មានចង្ងាយពីជើងភ្នំ ០២គីឡូម៉ែត្រ។
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
ដីស្រទាប់ខាងលើជាដីគ្រួសពណ៌ខ្មៅ ដីស្រទាប់ខាងក្នុងជាដីក្រហម តែអត់មានគ្រួសទេ។
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
< 5 m
Availability of surface water:
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
ពឹងលើទឹកភ្លៀងទាំងស្រុង។
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
អាយុ ៤១ឆ្នាំ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
កសិករនេះមាន៖
ដីដាំស្វាយចន្ទី ១០ ហិកតា
ដីដាំចេក ១៤ ហិកតា
ដីភូមិ ទំហំ ២៨០ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ( ទទឹង ៧ម៉ែត្រ បណ្តោយ ៤០ម៉ែត្) ដីទុកចោលជាដីភូមិ
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
- ពឹងលើទឹកភ្លៀង
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
ពីមុនគាត់ដាំដំណាំតែមួយមុខដូចជាចេក ដំឡូងមី ឬសណ្តែកសៀង តែឥឡូវគាត់ដាំដំណាំ២ មុខជាពិសេសការដាំសណ្តែកដីបាន ២ដងនៅក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ ហើយគាត់ទទួលបានទិន្នផលខ្ពស់។
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
ដំណាំឯកវប្បកម្ម គឺងាយប្រឈមនឹងការកើតនូវជំងឺដែលធ្វើឱ្យដំណាំមានគុណភាពទាប(ឧទាហរណ៍៖ ដំណាំចេកជាញឹកញាប់ជួប្រទះនូវសត្វក្រា ) ដូចនេះការដាំដំណាំ ២ប្រភេទដូចជា ស្វាយចន្ទី និងសណ្តែកដីក៏ជាយន្តការដែលផ្តល់នូវអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ក្នុងការកំណត់នូវចលនា (ឧ. ការកែប្រែសុខុមាកាស/មីក្រូអាកាសធាតុ)។
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
តាមរយៈការអនុវត្តការដាំដំណាំចន្លោះ គឺមានដំណាំថែមមួយប្រភេទទៀតត្រូវបានដាំនៅចន្លោះដើមឈើលើផ្ទៃដីកសិកម្មតែមួយ។
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
គាត់ដាំដំណាំ ២ប្រភេទនៅលើដីតែមួយ។
land management
Comments/ specify:
ការដាំដំណាំចន្លោះអាចជួយបង្ការការសឹករេចរិលដីពីការហូរច្រោះដោយសារទឹក។ លើសពីនេះទៅទឿតវាកាត់បន្ថយការដុះលូតលាស់របស់ស្មៅចង្រៃ។
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
ការដាំដំណាំច្រើនជាងមួយប្រភេទចំណាយជីអស់ច្រើន កម្លាំងពលកម្ម ថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិត។ល។ ប្រសិនប្រៀបធៀបជាមួយដំណាំឯកវប្បកម្ម។
farm income
Comments/ specify:
ស្វាយចន្ទី និងសណ្តែកដីមានទីផ្សារល្អជាងដំណាំចេកផងដែរ។ អាស្រ័យដោយសណ្តែកដីដាំនៅចន្លោះស្វាយចន្ទី ដូចនេះកសិករទទួលបានប្រាក់ចំណូលមុនពេលដែលស្វាយចន្ទីផ្តល់ផល(មុនស្វាយចន្ទីអាយុបាន ៣ឆ្នាំ)។
diversity of income sources
economic disparities
workload
Comments/ specify:
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីត្រូវធ្វើការថែទាំទាំងដំណាំសណ្តែកដី និងស្វាយចន្ទីទៅលើការដាក់ជី បាញ់ថ្នាំកំចាត់សត្វល្អិត ត្រួតពិនិត្យប្រសិនមានជំងឺ ឬសត្វល្អិតកើតឡើងនៅដំណាក់កាលផ្សេងៗនៃការលូតលាស់របស់ដំណាំ។
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
សណ្តែកដីអាចផ្តល់ទិន្នផលនៅក្នុងរយៈពេលខ្លីមុនពេលដែលដើមស្វាយចន្ទីផ្តល់ផល។
health situation
Comments/ specify:
ផ្តល់នូវសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹមច្រើនប្រភេទដែលមកពីផលិផលខុសៗគ្នាដែលមានប្រយោជន៍ដល់សុខភាពរបស់មនុស្ស។
cultural opportunities
Comments/ specify:
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីជាច្រើនបានរៀនសូត្រពីគ្នាទៅវិញទៅមកពីការអនុវត្តន៍ប្រព័ន្ធកសិរុក្ខកម្ម។ ប្រព័ន្ធនេះមានភាពពេញនិយមនៅតំបន់ខ្ពង់រាបក្នុងខេត្តព្រះវិហារ។
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីបានយល់ពីអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ការដាំដំណាំនៅចន្លោះដើមឈើមិនទុកចន្លោះទំនេរ ឬមិនទុកដីដោយមិនមានដំណាំអ្វីសោះ។ ការដាំសណ្តែកដីអាចបង្កាការសឹករេចរិលដីដោយសារទឹក និងបង្កើនជីជាតិដីតាមរយៈកាកសំណល់ដើមសណ្តែកដី។
conflict mitigation
Comments/ specify:
មិនធ្លាប់មានជម្លោះជាមួយកសិករផ្សេងៗនោះទេ។ កសិករនៅតំបន់នោះចេះចែករំលែកចំណេះដឹងឱ្យគ្នាទៅវិញទៅមក។
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
សណ្តែកដី និងដើមស្វាយចន្ទីជាដំណាំជួយគ្របដី កាត់បន្ថយរំហួតទៅក្នុងបរិយាកាស និងរក្សាដីឱ្យមានសំណើម។
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
ដោយសារតែដំណាំសណ្តែកដី គ្របដីនៅចន្លោះស្វាយចន្ទី។
soil compaction
Comments/ specify:
កាកសំណល់សណ្តែកដី គឺជួយឱ្យដីធូរ។
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
កាកសំណល់សណ្តែកដី គឺជាជីស្រស់មួយដ៏ល្អ និងនៅពេលវារលួយវាក្លាយជាសារធាតុសរីរាង្គដែលមានប្រយោជន៍ក្នុងការធ្វើឱ្យដីមានជីជាតិប្រសើរឡើង និងបង្កើនភាវៈរស់នៅក្នុងដី។
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
plant diversity
Comments/ specify:
មានដំណាំច្រើនប្រភេទលើសពីមួយ (សណ្តែកដី និងដើមស្វាយចន្ទី)។
invasive alien species
Comments/ specify:
មានជំងឺដែលមិនស្គាល់ឈ្មោះកើតឡើងលើដំណាំចេកវាធ្វើឱ្យស្លឹកចេកទៅជាពណ៌លឿង។ វាប្រហែលកើតមកពីពពួកវីរុស។
beneficial species
Comments/ specify:
សម្បូរភាវៈរស់នៅក្នុងដីដូចជា៖ ជន្លេន ស្រមោច សត្វកណ្តៀត ។ល។ ដោយសារដីសម្បូរទៅដោយសារធាតុសរីរាង្គដែលកើតពីការរលួយនៃកាកសំណល់សណ្តែកដី។
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
កាត់បន្ថយកត្តាសត្វចង្រៃ និងជំងឺផ្សេងៗនៅលើដំណាំ ដោយសារតែយន្តការដ៏មានអត្ថប្រយោជន៍នៃចលនានៅក្នុងដី និងសុខុមាកាស/មីក្រូអាកាសធាតុ តាមរយៈដាំសណ្តែកដីនៅចន្លោះស្វាយចន្ទី។
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
| seasonal temperature | dry season | increase | moderately |
| annual rainfall | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | decrease | moderately |
Comments:
ភ្លៀងមិនទៀងទាត់ ពេលខ្លះច្រើនពេក ពេលខ្លះរាំង។ សណ្តែកដីត្រូវដាំនៅខែមានភ្លៀងធ្លាក់។
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| ទទួលបានប្រាក់ចំណូលបន្ថែមពីការដាំសណ្តែកដីដែលអាចប្រមូល ផលបានក្រោយដាំដុះរយៈពេល ០៣ខែ |
| ផ្តល់ចំណូលបន្ថែមមុនពេលទទួលផលពីស្វាយចន្ទីសម្រាប់ដោះស្រាយប្រាក់ចំណាយបន្តក្នុងការថែទាំដំណាំ និងជីវភាពប្រចាំថ្ងៃ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ដំណាំសណ្តែកដីជាដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លីអាចប្រមូលផលក្នងរយៈពេល ០៣ខែ |
| ដាំដំណាំនៅចន្លោះដីទំនេរ ជួយដីកុំឱ្យហូរច្រោះដោយសារទឹកទឹកភ្លៀង និងខ្យល់ |
| សណ្តែកដីជាដំណាំជួយឱ្យដីមានជីជាតិនិងជួយឱ្យដីធូរជាងមុនតាមរយៈការភ្ជួរលប់ដើមសណ្តែកដីនៅពេលដែលប្រមូលផលរួចហើយ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ចំណាយកម្លាំងពលកម្មច្រើនក្នុងការថែទាំ(ដង្កូវ) បាញ់ថ្នាំ ជំនួយត្រួយ ផ្កា ជាដើម | ជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្ម |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ការដាំដុះពឹងផ្អែកទៅលើទឹកភ្លៀងទាំងស្រុង | ជីកអណ្តូង ឬជីកស្រះសម្រាប់ស្តុកទឹកដែលបង្ការនូវហានិភ័យដល់ដំណាំពេលរាំងភ្លៀង |
| ដាំដំណាំអាយុកាលខ្លីដូចជាសណ្តែកនៅពេលដែលស្វាយចន្ទីមិនទាន់ធំក្នុងយៈពេល ០៣ ឬ ០៤ ឆ្នាំ ហើយមិនអាចដាំបន្តទៀតបានទេនៅពេលស្វាយចន្ទីលូតលាស់គ្របម្លប់ជិត | ដាំដំណាំមិនត្រូវការពន្លឺព្រះអាទិត្យខ្លាំងដូចជាល្មៀត ឬរំដេងជាដើម។ល។ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
០២ នាក់
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
០៤ នាក់
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
៩
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
05/05/2017
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Cambodian Agricultural Research and Development Institute. (2006). Farmer Notes. Peanut growing technology., Year 5th,.
Available from where? Costs?
Cambodian Agricultural Research and Development Institute. Free of charge
Title, author, year, ISBN:
MoE. (2016). Agroforestry System “ Enhancing Climate Change Resilience of Rural Communities Living in Protected Areas in Cambodia .”
Available from where? Costs?
Ministry of Environment, Cambodia. Free of charge
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Royal University of Agriculture. (2006). cashew tree management. In Khmer.
Available from where? Costs?
Royal University of Agriculture. Mr. Khoun Eang and Mr. Pagnasoley. Free of charge
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Agritoday. (2016). Peanut
URL:
Retrieved October 30, 2017, from http://agritoday.com/techniques/article/1413.html
Title/ description:
Agritoday. (2017). តម្លៃគ្រាប់ស្វាយចន្ទីស្រស់បានកើនឡើងប្រមាណ ៣០ភាគរយ
URL:
Retrieved October 30, 2017, from http://agritoday.com/news/article/2677.html
Title/ description:
Chouk Khmer. (2017). Cashew trees
URL:
Retrieved October 30, 2017, from https://choukhmer.wordpress.com/2010/12/10/cashew-tree/
Title/ description:
Reaksmey Kampuchea Newspaper. (2017). បច្ចេកទេសដាំសណ្តែកដី
URL:
Retrieved October 30, 2017, from http://www.rasmeinews.com/បច្ចេកទេសដាំសណ្តែកដី/
Title/ description:
Saang. (2017). Cashew crop
URL:
Retrieved October 30, 2017, from https://sroksaang.blogspot.com/2015/02/blog-post_20.html
Title/ description:
Yayo. (2016). ការដាំសណ្តែកដីតាមបែបធម្មជាតិ
URL:
Retrieved October 30, 2017, from http://vayofm.com/news/detail/60014.html
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules