ប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិដោយប្រើកម្លាំងទឹកហូរសម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងផ្ទះនិងកសិកម្ម [Cambodia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Be Gechkim
- Editors: Navin Chea, SOBEN KIM, Sophea Tim
- Reviewers: Nimul CHUN, Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
បូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិ
technologies_2136 - Cambodia
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
ប្រធានទទួលបន្ទុករួមការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ:
land user:
ប្រុស ហ៊ួ
កសិករ
Cambodia
ភ្នាក់ងារផ្សព្វផ្សាយឃុំនៅសាលាឃុំសោប:
សុភ័ក្រ សុង
សាលាឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Cambodia
ប្រធានការិយាល័យកសិកម្ម រុក្ខាប្រមាញ់ និងនេសាទ ស្រុកសំបូរ:
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Cambodia1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
ឧបករណ៍នេះអាចប្រើដោយមិនត្រូវការម៉ូទ័រ ឬម៉ាស៊ីនអ្វីទាំងអស់ ដោយត្រូវការតែកម្លាំងទឹកហូរប៉ុណ្ណោះ និងអាចប្រើបានច្រើនឆ្នាំមិនចាំបាច់ត្រូវការថែទាំច្រើនទៀតផង។
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
ឧបករណ៍នេះអាចបូមទឹកដោយស្វ័យប្រវត្តិមិនត្រូវការឥន្ធនៈ មិនពិបាកថែទាំ ហើយអាចទាញយកទឹកទៅប្រើប្រាស់នៅរយៈកម្ពស់ខ្ពស់ (អាស្រ័យតាមទំហំទុយោទឹកចេញ) សម្រាប់គ្រួសារ ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ និងស្រោចស្រពដំណាំយ៉ាងងាយស្រួល។
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
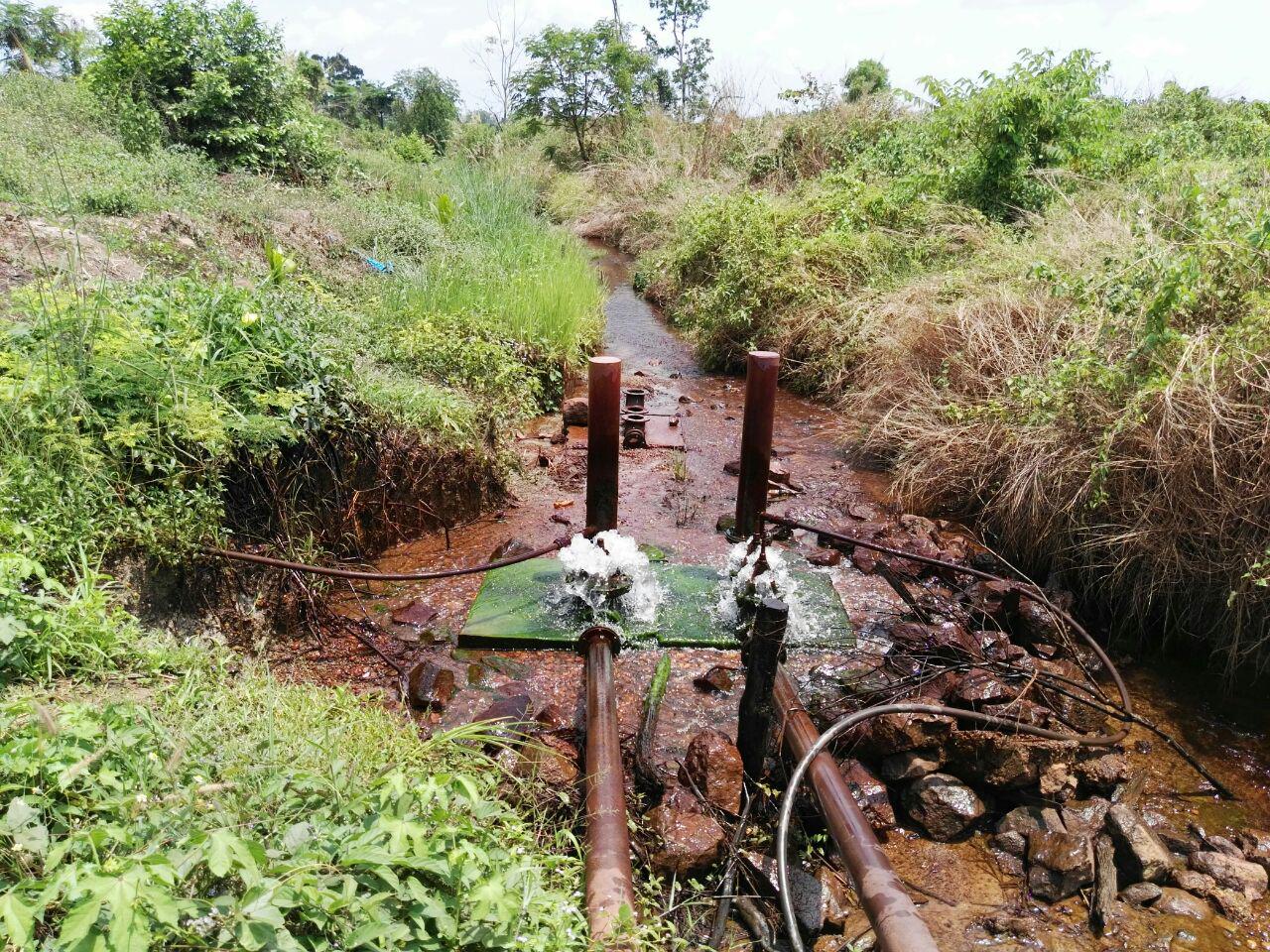
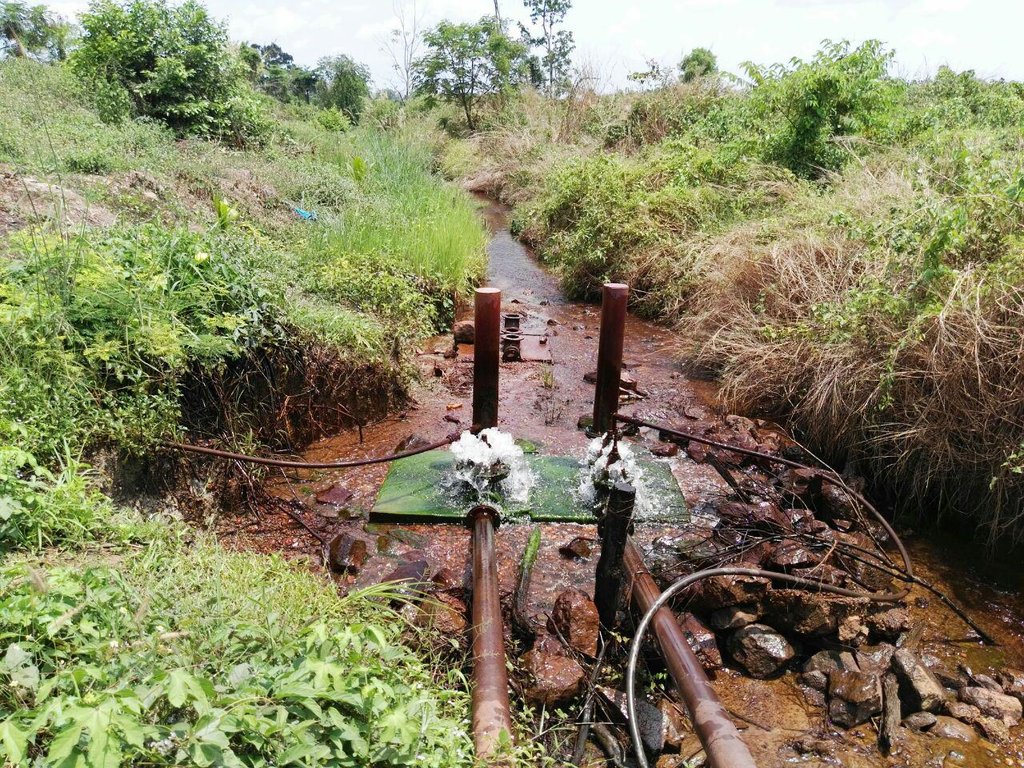
ប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិដើរដោយកម្លាំងទឹកហូរ គឺជាឧបករណ៍បូមទឹក ដែលត្រូវបានគេប្រើប្រាស់ជាច្រើនឆ្នាំមកហើយនៅអឺរ៉ុប និងមួយភាគតូចនៅអាស៊ី តែវាត្រូវបានបាត់បង់ហើយក្រោយមកដោយសារតែតម្រូវការចាំបាច់ព្រោះវាដំណើរការអាស្រ័យតែលើកម្លាំងទឹកហូរ និងមិនត្រូវការការថែទាំច្រើនដែលបណ្តាលឱ្យមានការប្រើប្រាស់បច្ចេកទេសនេះឡើងវិញ (ACF, 2009)។ តាមរយៈការរៀបរាប់បានបង្ហាញថាវាមិនត្រូវការកម្លាំងម៉ាស៊ីន ចំហេះប្រេងឥន្ធនៈ និងពុំចាំបាច់ត្រូវការកម្លាំងពលកម្មច្រើនក្នុងពេលប្រើប្រាស់ ឬការថែទាំនោះទេ។ ដោយឃើញពីអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ខាងលើ កសិករមួយរូបឈ្មោះ ប្រុស ហ៊ួ ដែលរស់នៅក្នុងភូមិសោបក្រោម ឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ បានដំឡើងឧបករណ៍នេះដំបូងគេបង្អស់។ លោកបានមានប្រសាសន៍ថា គាត់ត្រូវចំណាយថ្លៃដើមក្នុងការសាងសង់រហូតដល់ទៅ ១៥០០ ដុល្លារ ដោយអាស្រ័យទៅលើប្រភេទនៃសម្ភារៈឬវត្ថុធាតុដើមសម្រាប់សាងសង់ (គាត់ប្រើប្រភេទបំពង់ដែក និងទុយោសម្រាប់ភ្ជាប់ដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ) ប៉ុន្តែវាមានអាយុកាលប្រើប្រាស់វែងរហូតដល់ទៅ ២០-៣០ឆ្នាំ និងមិនមានផលប៉ះពាល់ដល់បរិស្ថានឡើយ ដោយសារវាមិនមានបំភាយឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់ទៅក្នុងបរិយាកាស។
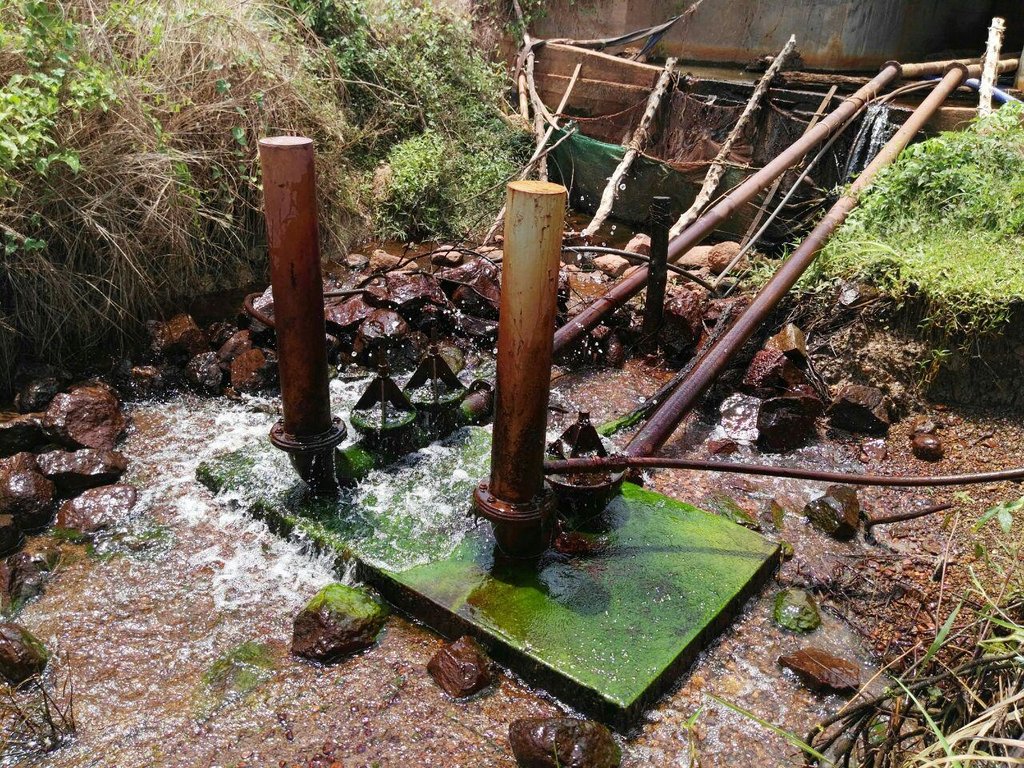
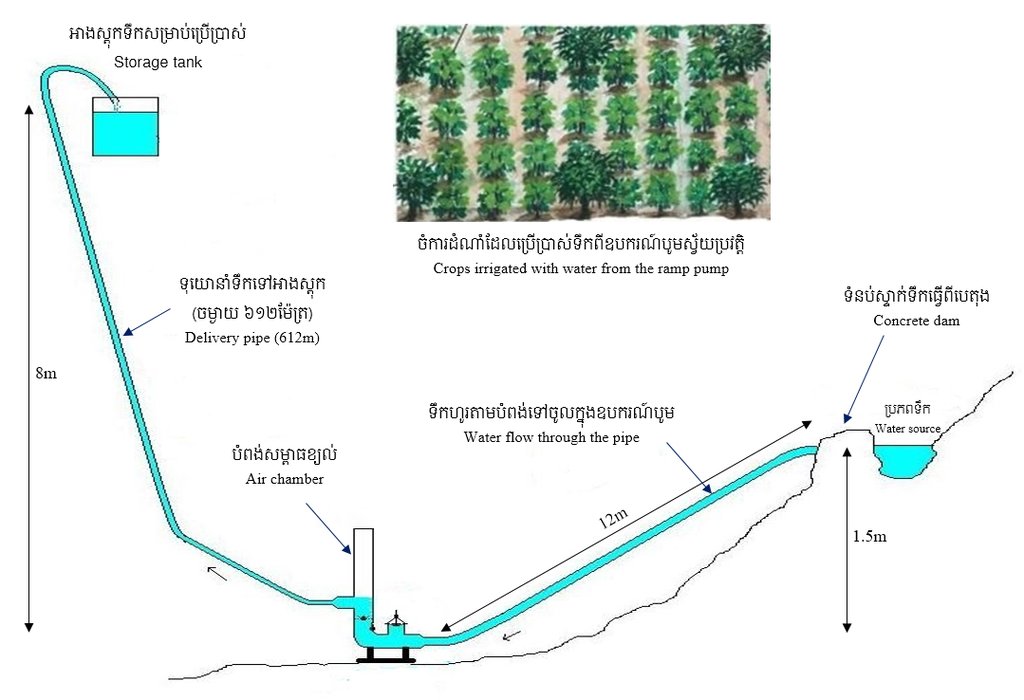
ឧបករណ៍បូមទឹកនេះត្រូវបានដំឡើងនៅទំនប់ស្រែងៀត ជាទីតាំងដែលមានចរន្តទឹកស្ទឹងហូរជាប្រចាំពេញមួយឆ្នាំ។ ចំពោះការដំឡើង កសិករបានសង់ទំនប់ស្ទាក់ទឹកធ្វើពីបេតុង និងចាក់បេតុងធ្វើជាទម្រកល់ឧបករណ៍បូមនៅផ្នែកខាងក្រោមខ្សែទឹកក្នុងរយៈកម្ពស់ ១,៥ម៉ែត្រ ធៀបទៅនឹងចំណុចភ្ជាប់ទុយោពីទំនប់ស្ទាក់ទឹកមក។ កសិករប្រើទុយោដែកមុខកាត់ទំហំ ១១៤មីលីម៉ែត្រ ប្រវែង ១២ម៉ែត្រ (ចំងាយពីចំណុចឧបករណ៍បូមទៅទំនប់ស្ទាក់ទឹក)។ ចេញពីឧបករណ៍បូម គាត់ប្រើទុយោនាំទឹកចេញទំហំមុខកាត់ ៣០មីលីម៉ែត្រ (ទុយោនេះត្រូវតែតូចជាងទុយោ ឬបំពង់នាំទឹកចូលទៅឧបករណ៍បូម) សម្រាប់នាំទឹកទៅកន្លែងប្រើប្រាស់។ ឧបករណ៍បូមនេះដំណើរការដោយកម្លាំងទឹកហូរ ដែលទាញយកទឹកពីទំនប់តាមបំពង់ដែក និងប្រើកម្លាំងសម្ពាធខ្យល់នៃបំពង់រុញទឹកតាមទុយោតូចនាំទឹកទៅកាន់កន្លែងប្រើប្រាស់ ដែលមានចម្ងាយប្រហែល ៦០០ម៉ែត្រ និងកម្ពស់ប្រហែល ៨ម៉ែត្រ។ ឧបករណ៍បូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិនេះមានសមត្ថភាពបូមទឹកបាន ១,៥ម៉ែត្រត្រីគុណ ក្នុងមួយម៉ោង ធ្វើការពេញ ២៤ម៉ោងជារៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃ និងអាចបូមទឹកបានរហូតដល់កម្ពស់ ២០ម៉ែត្រ។
ទឹកដែលបូមបានពីឧបករណ៍ ត្រូវរក្សាទុកក្នុងអាងចំនួន ២ ដែលអាងនីមួយៗមានចំណុះប្រមាណជា ៤,៧ម៉ែត្រត្រីគុណ បរិមាណនេះអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ក្នុងផ្ទះ សម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមមាន់ចំនួន ១០០ក្បាល និងសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពផ្ទៃដីកសិកម្មដល់ទៅ ៥ ហិកតា។ គុណសម្បត្តិមួយទៀតនៃប្រព័ន្ធនេះ គឺមិនមានផលប៉ះពាល់ដល់បរិមាណទឹក ឬធ្វើឱ្យកង្វក់ដល់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមនោះទេ ព្រោះប្រព័ន្ធនេះបានទាញទឹកយកមកប្រើតែប្រហែលជា ២០-៣០%នៃទំនប់ប៉ុណ្ណោះ ចំណែក ៨០-៧០%ទៀត គឺហូរទៅខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមជាធម្មតា កត្តានេះមិនបង្កឱ្យមានជម្លោះដណ្តើមទឹករវាងអ្នកនៅខ្សែទឹកខាងលើ និងអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកនៅខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមនោះទេ។
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
មិនមាន
Name of videographer:
មិនមាន
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Cambodia
Region/ State/ Province:
ភូមិសោបក្រោម ឃុំសោប ស្រុកព្រែកប្រសព្វ ខេត្តក្រចេះ
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
ប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកនេះត្រូវបានដំឡើងនៅលើទំនប់ស្រែងៀតស្ថិតនៅក្នុងភូមិសោបក្រោម ខេត្តក្រចេះ។
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2015
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
- during experiments/ research
- ស្រាវជ្រាវតាមប្រព័ន្ធអ៊ីនធឺណែត
Comments (type of project, etc.):
កសិករបង្កើតឧបករណ៍នេះដោយខ្លួនឯងតាមរយៈការស្វែងយល់បន្ថែមពីប្រព័ន្ធ YouTube។
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
- create beneficial economic impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Waterways, waterbodies, wetlands
- Ponds, dams
Main products/ services:
ទំនប់ទឹកស្រែងៀតមានទឹកទាំងរដូវប្រាំង និងរដូវវស្សា
Comments:
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ: 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់: ដាំដំណាំស្វាយ និងមានដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំជាបន្តបន្ទាប់ដូចជា សណ្តែកកួរ ត្រសក់ សាឡាដ ត្រកួនជាដើម។
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Comments:
ជាធម្មតាប្រើទឹកដែលបានពីប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិ តែនៅពេលមានភ្លៀងធ្លាក់មិនត្រូវការជំនួយពីឧបករណ៍បូមនោះទេ។
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
- water diversion and drainage
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S7: Water harvesting/ supply/ irrigation equipment
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
ដោយប្រើប្រាស់ប្រព័ន្ធនេះអាចទទួលបានទឹកប្រើប្រាស់គ្រប់គ្រាន់ដែលអាចដាំដុះបានតាមទីជម្រាលដើម្បីកាត់បន្ថយការហូរច្រោះ និងស្តារជីជាតិឡើងវិញបានមួយផ្នែកផងដែរ។
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
ទីតាំងដែលអាចឱ្យប្រព័ន្ធដំណើរការបាន គឺត្រូវមានប្រភពទឹកហូរធម្មជាតិដែលមានកម្ពស់យ៉ាងតិច ១,៥ម៉ែត្រ ប្រៀបនឹងទីតាំងដាក់ឧបករណ៍បូម។ បន្ទាប់មកយកទុយោទំហំ ១១៤មីលីម៉ែត្រ តភ្ជាប់ពីទឹកមកបេតុងចំនួន ២ដើម ដែលមានចំងាយប្រវែង ១២ម៉ែត្រ។ សម្រាប់ទុយោដែលត្រូវរាយនៅខាងក្រោមដីទៅតំបន់ដែលប្រើប្រាស់នោះ គឺមានទំហំមុខកាត់ ៣០មីលីម៉ែត្រ។ ចំណែកចម្ងាយពីឧបករណ៍បូមទៅតំបន់ដែលប្រើប្រាស់ គឺប្រវែង ៦១២ម៉ែត្រ ហើយកន្លែងដែលប្រើប្រាស់ទឹកនោះបើធៀបទៅនឹងក្បាលស្នប់បូម គឺមានកម្ពស់ ៨ម៉ែត្រ។ ទុយោបង្ហូរមួយអាចទាញទឹកបាន ១,៥ម៉ែត្រគូប ក្នុងមួយម៉ោង ហើយទឹកអាចបូមបានកម្ពស់រហូតដល់ ២០ម៉ែត្រ។
Author:
កញ្ញា អ៊ុំ សុវណ្ណនី និងកញ្ញា បេ ហ្គេចគីម
Date:
12/04/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
ឧបករណ៍បូមទឹកដោយស្វ័យប្រវត្តិ
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
កន្លែងដំឡើងឧបករណ៍៖ ១ ម៉ែត្រការ៉េ
other/ national currency (specify):
រៀល
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
20000រៀល
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ទិញសម្ភារៈ | រដូវប្រាំង |
| 2. | រៀបចំឧបករណ៍ | រដូវប្រាំង |
| 3. | ដំឡើងឧបករណ៍ | រដូវប្រាំង |
| 4. | រៀបប្រព័ន្ធទឹកសម្រាប់ដាំដំណាំ | រដូវប្រាំង |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ថ្លៃបង្កើតសរុបរួមកម្លាំងពលកម្មដោយខ្លួនឯង និងសម្ភារសម្រាប់បង្កើត | សរុប | 1.0 | 6000000.0 | 6000000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 6000000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1500.0 | |||||
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | បើកប្រើប្រចាំថ្ងៃ | រៀងរាល់ថ្ងៃ |
| 2. | ប្តូរស្បែកក្នុងឧបករណ៍បូម | មួយឆ្នាំម្តង |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ប្តូរស្បែកក្នុងឧបករណ៍បូម | សរុប | 1.0 | 100000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 100000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 25.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
សម្រាប់ការជួសជុល គឺមួយឆ្នាំប្តូរតែស្បែករបស់ឧបករណ៍តែប៉ុណ្ណោះ ហើយចំណាយអស់តែ ២៥ ដុល្លារ។
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ និងទុយោដែលត្រូវប្រើច្រើនដោយសារពីទីតាំងបូមទឹកទៅកន្លែងប្រើប្រាស់ គឺនៅឆ្ងាយ។
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1138.20
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងនៅឆ្នាំ ២០១៥ គឺ ១១៣៨.២ មម ឆ្នាំ ២០១៤ គឺ ១៦៩៦.៥ មម និងឆ្នាំ ២០១៣ គឺ ១៦៦១.៨ មម។
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ក្រសួងធនធានទឹក និងឧតុនិយមឆ្នាំ (២០១៥)
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- high (>3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
ខ្នាតមធ្យមដោយសារគាត់មានដីទំហំ ៣០ហិកតា និងមានអ្នកមានដីច្រើនរហូតដល់ ៥០ហិកតា។
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- communal/ village
Land use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Comments:
ប្រភពទឹកសម្រាប់សាងសង់បច្ចេកទេសនេះ គឺស្ថិតក្នុងតំបន់ដែលប្រើប្រាស់រួមគ្នា តែទឹកដែលបានពីបច្ចេកទេស គឺសម្រាប់ប្រើប្រាស់ឯកជនប៉ុណ្ណោះ។
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
ផលិតកម្មកើនឡើងដោយសារអាចដាំដំណាំបានច្រើនមានទឹកគ្រប់គ្រាន់សម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព។
risk of production failure
Comments/ specify:
អាចគ្រប់គ្រងបានដោយសារមិនខ្វះខាតទឹកប្រើប្រាស់ ហើយមិនត្រូវការកម្លាំងពលកម្មខ្ពស់។
Water availability and quality
water availability for livestock
Comments/ specify:
ឧបករណ៍បូមទឹកដោយស្វ័យប្រវត្តិអាចផ្តល់ទឹកគ្រប់គ្រាន់ជាប្រចាំ និងកម្លាំងពលកម្មតិច។
irrigation water availability
Comments/ specify:
ទឹកអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បានច្រើនជាងមុនដោយស្វ័យប្រវត្តិ។
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
ការប្រើប្រាស់ឧបករណ៍បច្ចេកទេសនេះ គឺជួយកាត់បន្ថយកម្លាំងពលកម្ម ពេលវេលា ថវិកាក្នុងការជួសជុល និងមិនត្រូវការការថែទាំច្រើនទៀតផង។ បច្ចេកទេសនេះក៏បានកាត់បន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់ប្រេងសម្រាប់បូមទឹក ព្រោះប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកនេះដើរដោយកម្លាំងទឹកហូរ។
farm income
Comments/ specify:
ចំណូលកើនឡើងព្រោះថាមិនចំណាយច្រើនសម្រាប់ដំណើរការបូមទឹកនោះទេ ហើយអាចដាំដំណាំបានច្រើនជាងមុន។
diversity of income sources
Comments/ specify:
ពីព្រោះទទួលបានទឹកគ្រប់គ្រាន់សម្រាប់ដាំដំណាំច្រើនមុខជាងមុន។
economic disparities
Comments/ specify:
ទទួលបានចំណូលបន្ថែម ហើយថែមទាំងកាត់បន្ថយចំណាយសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពផងដែរ។
workload
Comments/ specify:
បន្ទុកការងារត្រូវបានថយចុះដោយប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកនេះដំណើរការដោយស្វ័យប្រវត្តិ។
Socio-cultural impacts
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
កសិករបង្កើនចំណេះដឹងតាមរយៈការអនុវត្តផ្ទាល់នៃបច្ចេកទេសបូមទឹកនេះ ហើយគាត់ក៏មានលទ្ធភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ដើម្បីក្លាយជាអ្នកសម្របសម្រួលសម្រាប់កសិករដទៃដែរ។ គាត់បានចែករំលែកចំណេះដឹងរបស់គាត់ជាមួយអ្នកជិតខាងដើម្បីឱ្យពួកគាត់ប្រើប្រាស់បច្ចេកទេសនេះផងដែរ។
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
Comments/ specify:
បរិមាណទឹកមិនត្រូវបានកាត់បន្ថយ ឬកើនឡើងឡើយដោយសារប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកនេះគ្រាន់តែទាញយកទឹកមកប្រើប្រាស់ត្រឹម ២០ ទៅ ៣០ % ប៉ុណ្ណោះ និងមិនបានកាត់ផ្តាច់លំហូរទឹកឡើយ។
excess water drainage
Comments/ specify:
ប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិអាចទាញយកទឹកមកប្រើប្រាស់ជាប្រចាំដោយមិនត្រូវការកម្លាំងពលកម្មឡើយ។
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Comments/ specify:
កសិករផ្សេងៗ និងអ្នកជិតខាងនៅតែអាចទទួលបានទឹកពីទំនប់មកប្រើប្រាស់បានដដែល ដោយសារប្រព័ន្ធនេះបានទាញយកទឹកមកប្រើប្រាស់ត្រឹម ២០ ទៅ ៣០% ទេ។
impact of greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
ដោយមិនបានប្រើប្រាស់ម៉ាស៊ីនផ្សេងៗដែលបំភាយឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់ឡើយ។
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
ទទួលបានប្រយោជន៍ច្រើនដោយសារពីមុនគាត់ត្រូវចំណាយលើការបូមទឹកពីអណ្តូងដែលប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្មច្រើន និងត្រូវចំណាយលើប្រេងផងដែរ ឥឡូវនេះគាត់មានភាពងាយស្រួលច្រើន។
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| បើទោះបីជាចំណាយច្រើនបន្តិចនៅពេលដំបូងតែវានៅតែទទួលបានផលចំណេញច្រើនជាងការប្រើប្រាស់ប្រេងដែលដើរដោយម៉ាស៊ីនសម្រាប់ការទាញយកទឹកមកប្រើប្រាស់ជាប្រចាំដែរ។ |
| ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្មតិចដោយសារវាបូមទឹកដោយស្វ័យប្រវត្តិ |
| ទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពដំណាំ គឺអាចទទួលបានគ្រប់ពេល និងរដូវកាល |
| ទទួលបានចំណូលកើនឡើងដោយបង្កើនការដាំដុះ ដែលទទួលបានទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រពពីប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកស្វ័យប្រវត្តិ។ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយផលប៉ះពាល់ដល់បរិស្ថានដោយមិនបានប្រើប្រាស់ប្រេងសម្រាប់ដំណើរការបូមទឹកឡើយ។ |
| ប្រព័ន្ធបូមទឹកនេះអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានច្រើនឆ្នាំ និងមិនចំណាយច្រើនលើការថែទាំទៀតផង។ |
| ជួយកាត់បន្ថយកម្លាំងពលកម្ម និងពេលវេលាក្នុងការទាញទឹកមកប្រើប្រាស់ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ឧបករណ៍មានតម្លៃថ្លៃទៅលើការសាងសង់ | សន្សំលុយដើម្បីទិញ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
មួយនាក់
- interviews with land users
មួយនាក់
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
៣ នាក់
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
12/04/2017
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
ACF (2009). Hydraulic Ram Pump Systems. From
Available from where? Costs?
https://www.pseau.org/outils/ouvrages/acf_gravity_fed_system_in_rural_areas_6_hydraulic_ram_pump_systems_2009.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Judy of the Woods. Homemade Hydraulic Ram Pump. Retrieved on May 20 2017 from
URL:
http://www.judyofthewoods.net/diy/ram_pump.html
Title/ description:
Hydraulic ram pump 8 inches in Cambodia. Retrieved on May 20 2017 from
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5MiLas_FCfQ
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules