Defensivo de piedra tipo "acantilado" [Bolivia, Plurinational State of]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Marco Loma
- Editor: Consuelo Aranda
- Reviewers: Johanna Jacobi, Alexandra Gavilano
Enrocado
technologies_514 - Bolivia, Plurinational State of
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
05/03/2014
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
Es una tecnología rustica no complicada que sirve para proteger suelos cultivables
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
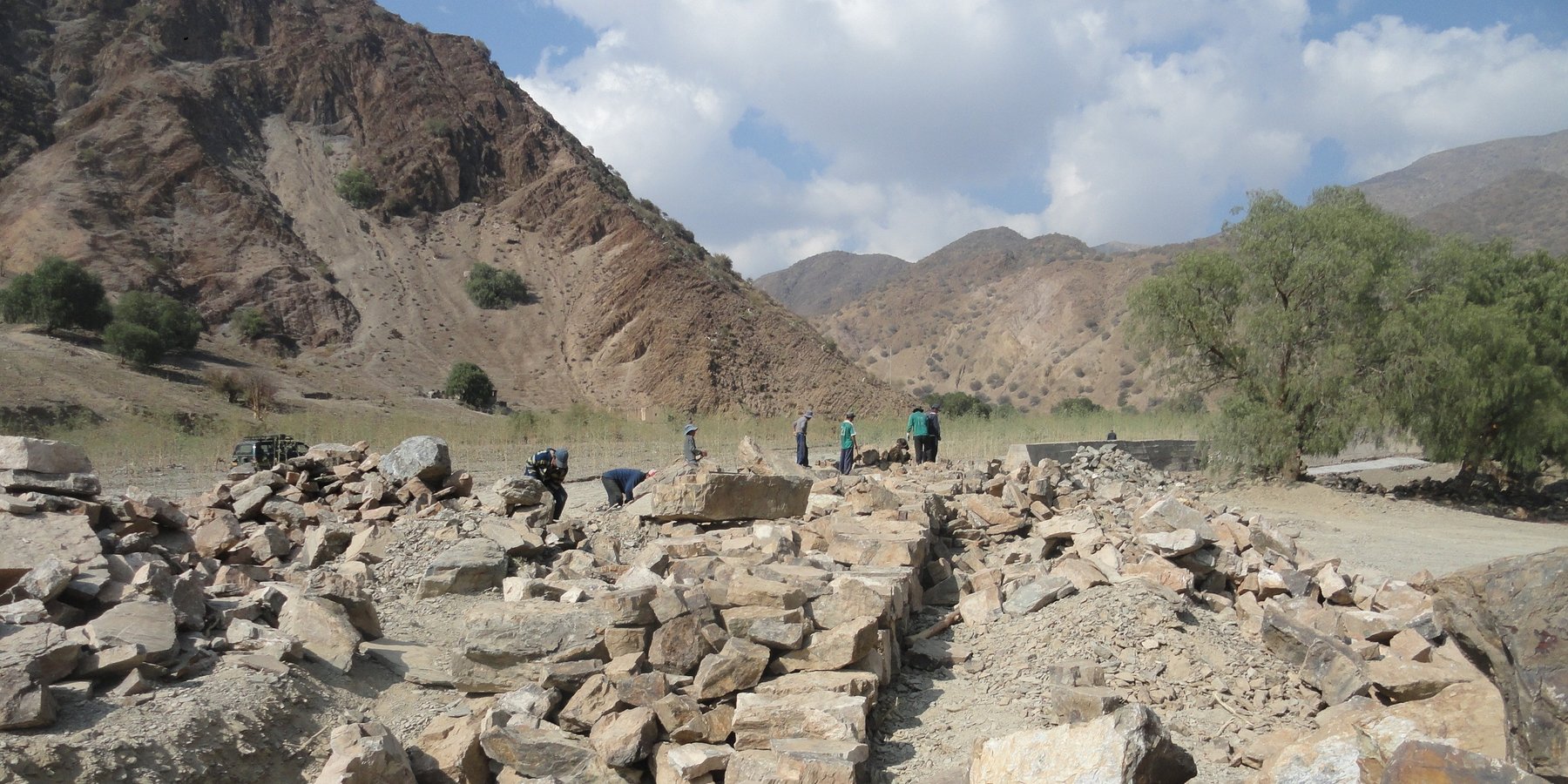
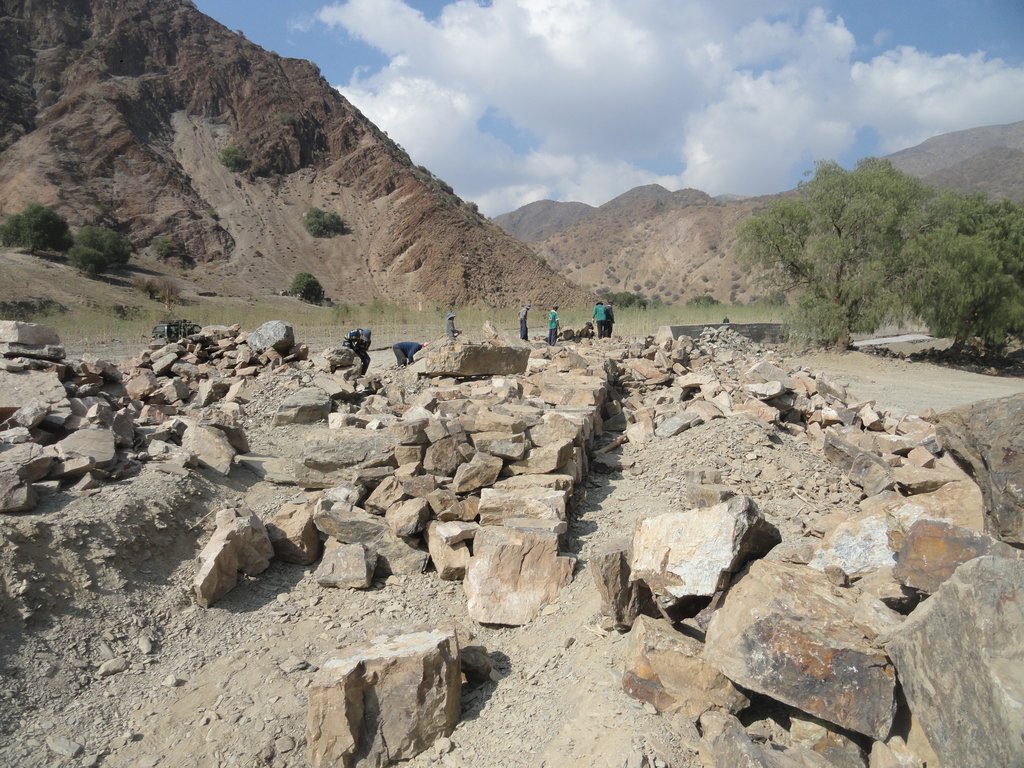
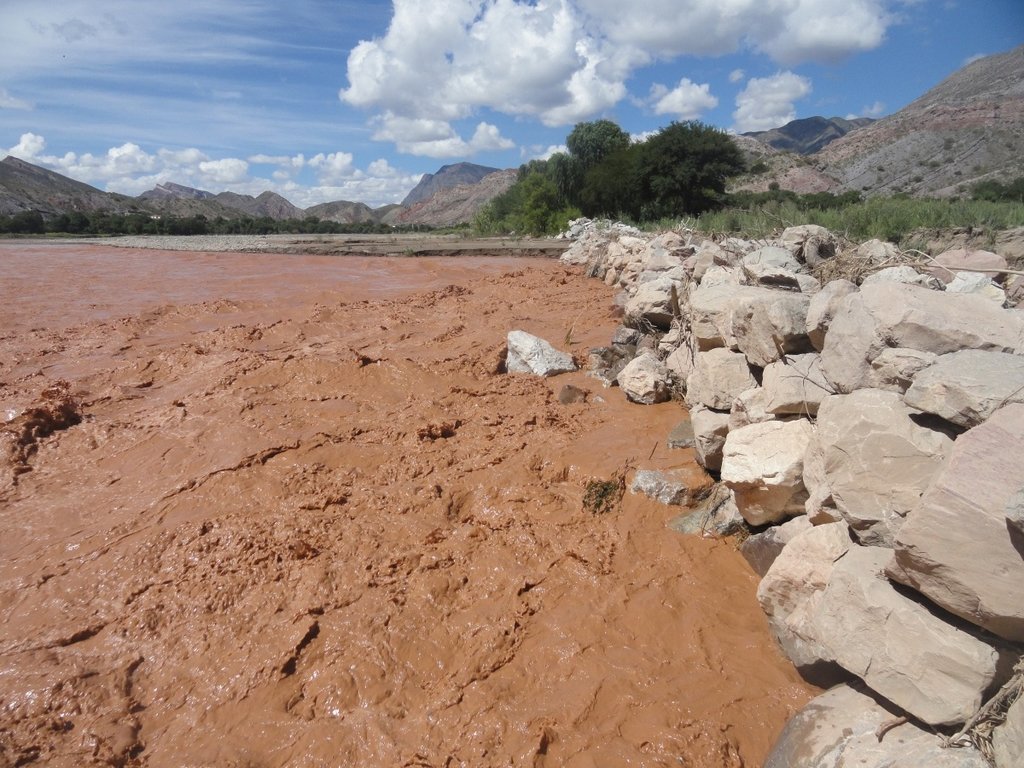
Defensivos flexibles y rústicos, se emplean para proteger terrenos de cultivo frente a amenazas de riadas y erosión lateral. Esta conformada de rocas de gran diámetro con altura y espesor variable que puede ser complementada con plantación de árboles.
Su resistencia y flexibilidad permite que no se deforme fácilmente ante fuertes eventos de crecidas de agua.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
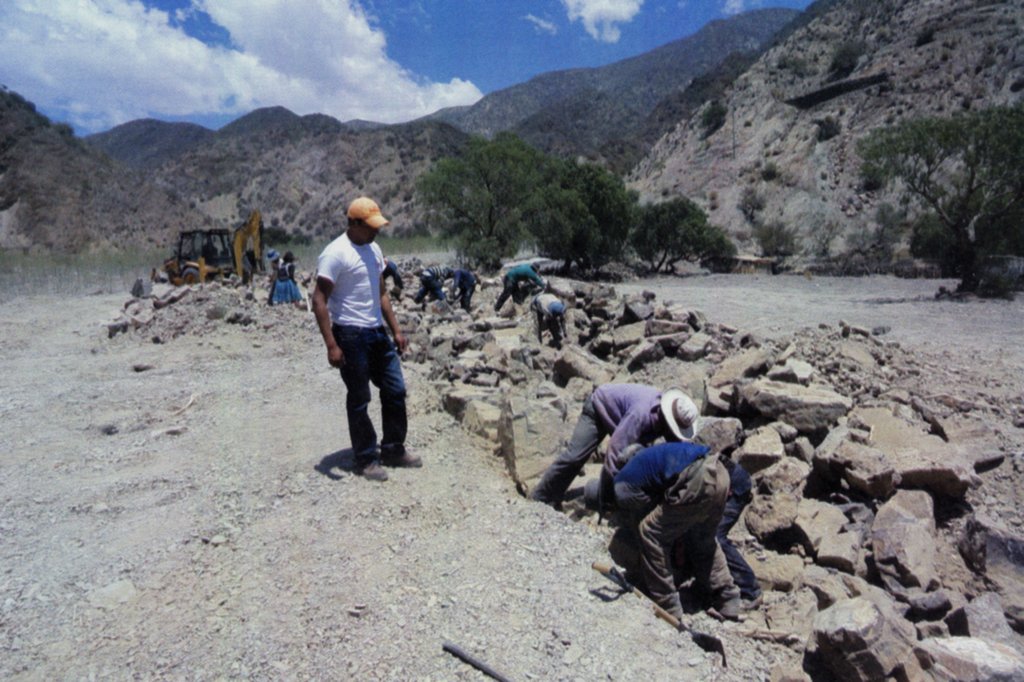
Esta tecnología es muy tradicional en la zona y se la ha recuperado de la experiencia de los comunarios. La tecnología puede, preferentemente, aplicarse en entornos naturales con amenazas de inundaciones dinámicas y en los márgenes de ríos. Son defensivos flexibles y rústicos que se emplean para proteger terrenos de cultivos. Esta conformado de rocas de altura y espesor variable, negus requerimiento. Se aplican paralelos al cauce del río y al pie de terreno a protegerse. Entre los insumos a usar son: piedras de gran tamaño, retroexcavadora para movimientos de tierra para la nivelación y fundación, picos, palas, barrenas y palancas; volquetes para traslado de la piedra.
Vida útil de 10 años del defensivo, disminución de costos de rehabilitación, disminución de costos de afectación por inundaciones a viviendas y terrenos de cultivo.Su tecnología es apropiada y de bajo costo usando materiales locales y costos bajos de operación y mantenimiento.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Bolivia, Plurinational State of
Region/ State/ Province:
Provincia Sud Chichas;
Further specification of location:
Comunidades Colchas e Ichupampa.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2013
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Se discutió con las comunidades el mejor sistema que resistía las inundaciones en la zona y se eligió el acantilado como la mas duradera, por experiencias previas en otras zonas de la región.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Papa, maiz, frutales durazno
Comments:
Al garantizar la seguridad ante las inundaciones se asegura la venta de productos frutales y hortalizas, así como el autoconsumo.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Son cultivos anuales como el maiz y la papa; asi como el durazno. Normalmente maiz y papa se siembra entre septiembre y noviembre y la cosecha del durazno en los mese de febrero y marzo.
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea)
- ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
La tecnología se aplica en lugares puntuales e inundables especialmente en zonas de meandros
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences
Comments:
Los defensivos tipo acantilado son en esencia medidas estructurales para prevenir efectos de inundaciones en zonas de cultivo y en algunos casos en zonas de viviendas.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wr: riverbank erosion
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
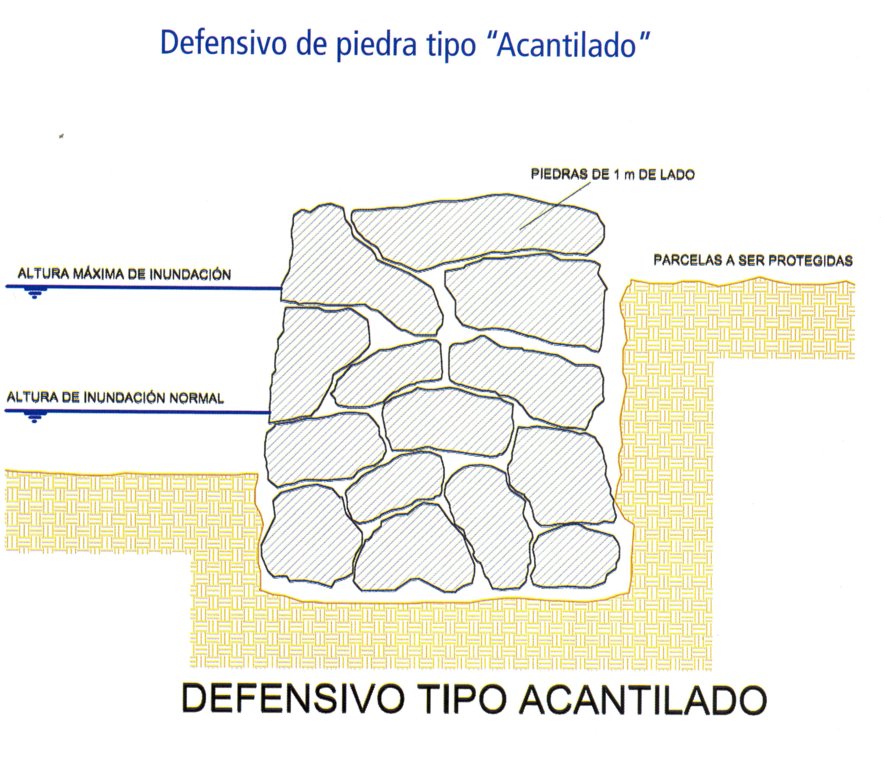
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Para un defensivo de 100 m de longitud y 3 m de altura se utiliza:
Retroexcavadora 10 hrs.
Cargador frontal 50 hrs.
Volqueta de 12 m3 noventa viajes.
900 m3 de piedra.
80 jornales de mano de obra no calificada.
14 jornales de operador.
Forestación deseable con 67 plantines por cada 100 m de longitud colocado en la parte posterior del defensivo.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
10 ha.
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
20 USD/dia
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Other measures | None |
| 2. | None | Structural | None |
| 3. | None | Structural | None |
| 4. | None | Structural | None |
| 5. | None | Other measures | None |
| 6. | None | Structural | None |
| 7. | None | Structural | None |
| 8. | None | Structural | None |
| 9. | None | Vegetative | None |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | no calificada | dia | 80.0 | 12.0 | 960.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | calificada | dia | 14.0 | 25.0 | 350.0 | |
| Equipment | retroexcavadora | hora | 60.0 | 30.0 | 1800.0 | |
| Equipment | volqueta | m3 | 1080.0 | 4.5 | 4860.0 | |
| Construction material | piedra | m3 | 900.0 | 3.0 | 2700.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | herramientas menores | global | 1.0 | 450.0 | 450.0 | |
| Other | plantines | unidad | 67.0 | 2.0 | 134.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 11254.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
El Proyecto reducción del riesgo de desastres financió el proyecto y la comunidad dio la mano de obra y el acopio de materiales.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Distancia y tiempo donde a la que se encuentra el banco de materiales, específicamente las piedras o rocas.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
320.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
Las lluvias mas intensas se producen entre los meses de diciembre - enero y febrero
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Vitichi y Tupiza
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
El clima en la zona es sub humeda con tenedencia a semi arida.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Ja
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
- Semi-nomadic
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Los usuarios son productores campesinos de la región.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
Toda el área pertenece a los usuarios.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
Entre 40 y 60% de la producción perdida
Quantity after SLM:
Sin pérdida de la producción
Comments/ specify:
No se dispone del datos más exactos.
risk of production failure
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Ecological impacts
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
Quantity before SLM:
2 veces al año
Quantity after SLM:
ninguna
Comments/ specify:
La zona protegida ya no ha sufrido inundaciones
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
Comments regarding impact assessment:
No se genera ningún impacto negativo, ya que el rol del muro es de encauzamiento. Se reafirma que la tecnología es apta para la zona.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| seasonal temperature | summer | increase | well |
| seasonal rainfall | summer | increase | very well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | well |
| flash flood | very well |
Comments:
La tecnología esta siendo implementada en la zona toda vez que los eventos extremos exacerbados por el cambio climático están concentrando las precipitaciones y por ende las inundaciones. Ante esa situación la tecnología ha demostrado tener una buena respuesta
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
Se puede señalar que los beneficios con relación a los costos son positivos, toda vez que la tecnología puede resistir inundaciones fuertes e inclusive resitir el arrastres de algunos materiales.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
10 a 20 familias
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| La tecnología no es complicada en su implementación, permite en la zona garantizar la protección de cultivos y lo más importante es que es bastante resistente en el tiempo, en comparación a otro tipo de tecnologías. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| La dependencia del tipo de material como las rocas de gran tamaño, condiciona la viabilidad del proyecto. | Buscar previamente bancos de prestamos que existan en la zona. |
| Mover las piedras de gran tamaño genera la dependencia de maquinaria. | Contar con recursos y hacer acuerdos previos con municipios para contar con la maquinaria |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
reunión con usuarios
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
Dos reportes relativos a la tecnología utilizada y aplicada
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Tipología de obras de infraestructura para aumentar la resiliencia del sector agropecuario Experiencias prácticas de Reducción del Riesgo de Desastres (RRD)
URL:
http://www.rrd.com.bo/wp-content/uploads/2015/publi_fases/fase_03/14tipologiah1.pdf
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules