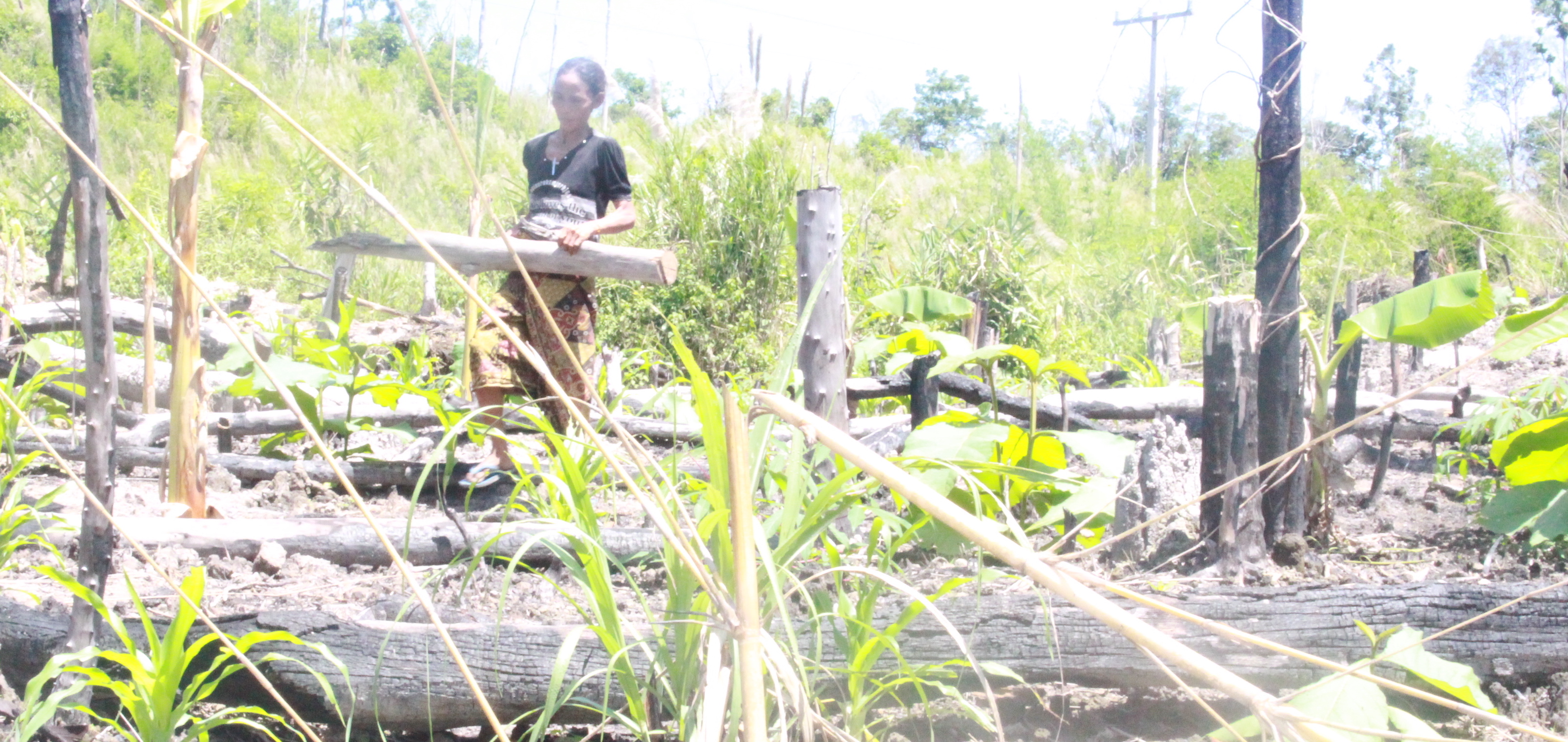
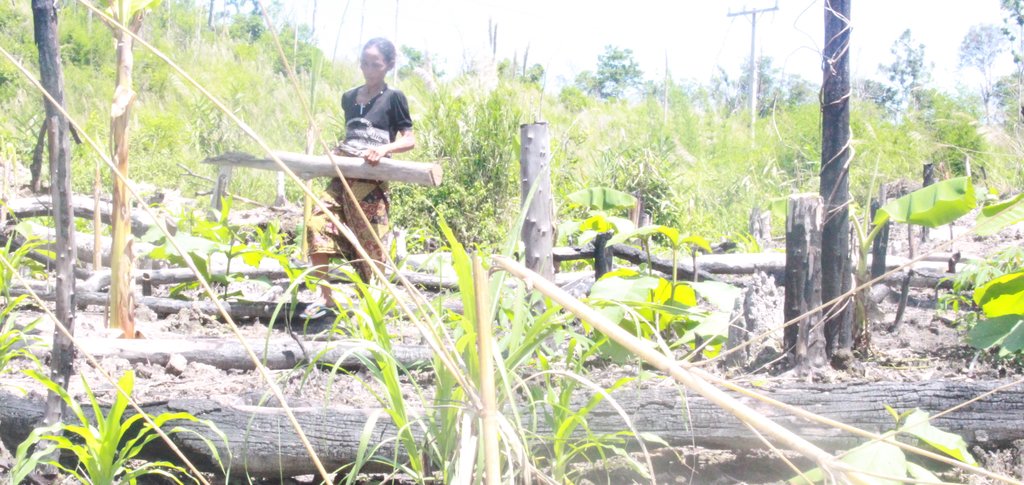
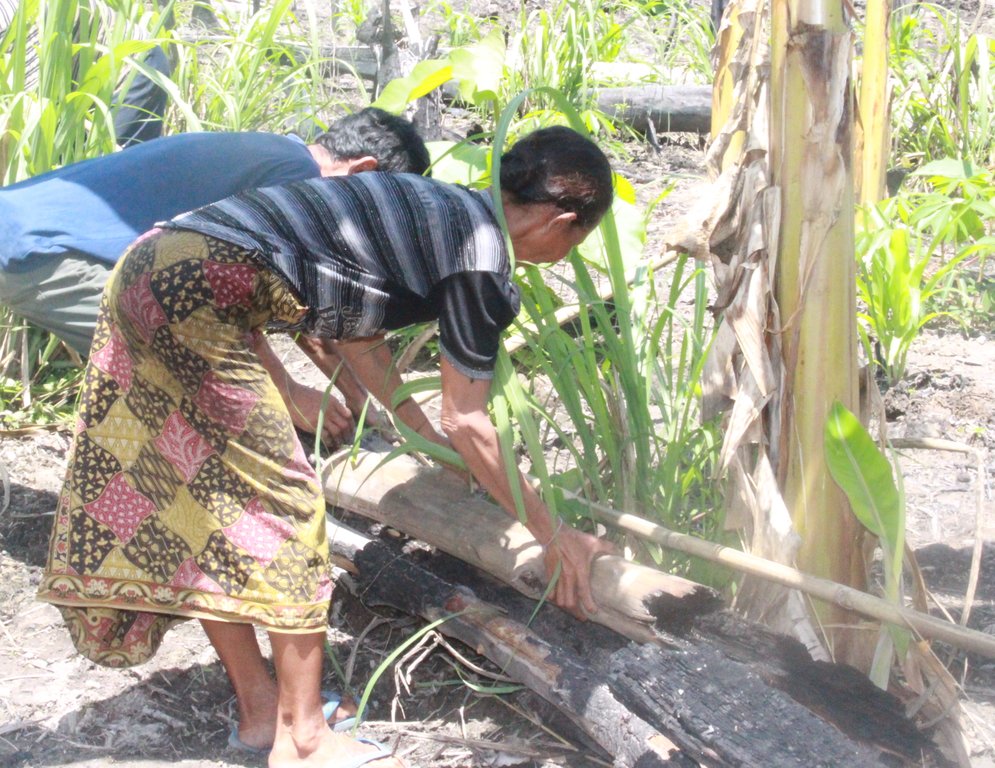
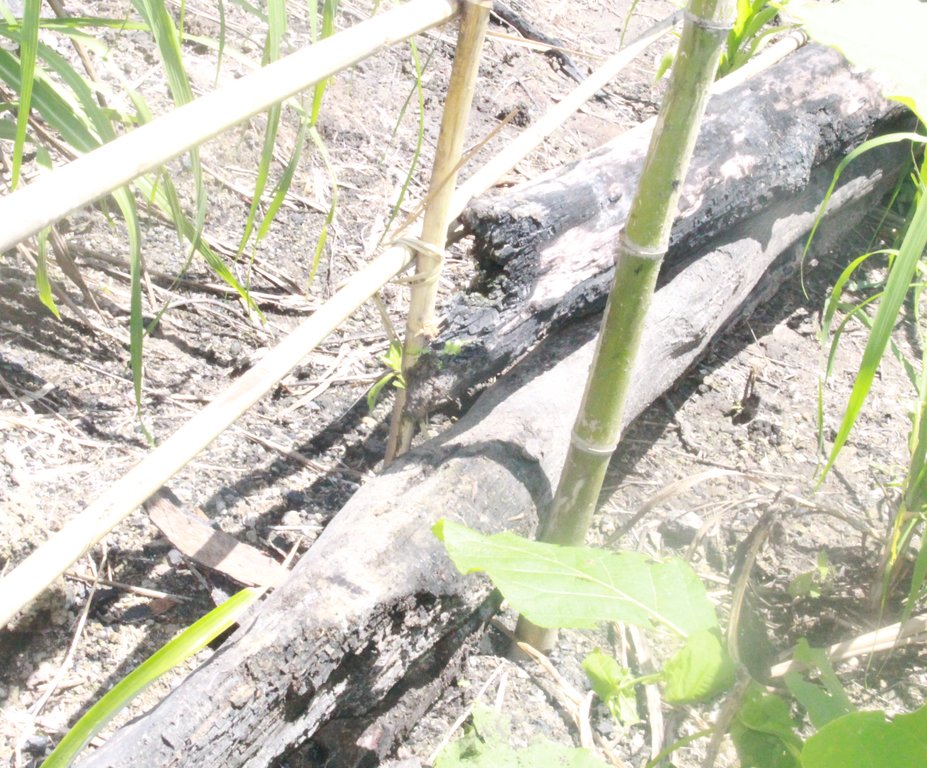
ເຕັກນີກ ເອົາໄມ້ທ່ອນ ມາກັ້ນເປັນຮົ້ວ ປ້ອງກັນໜ້າດີນ ບໍ່ໃຫ້ດີນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ແລະ ຮັກສາ ຄວາມສົມບູນຂອງດິນ [Lao People's Democratic Republic]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: kang phanvongsa
- Editors: Vardsana Buavanxay, Bounthanom Bouahom
- Reviewers: Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_2279 - Lao People's Democratic Republic
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
land user:
ທ່ານ. ບູນເລີດ
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) - Lao People's Democratic Republic1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
ແລວໄມ້ທ່ອນ ເພື່ອຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ການຊະລ້າງ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ ໃນລະດູຝົນ
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
ກິດຈະກາໍ ການຖາງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່ ແບບໝູນວຽນ ແມ່ນ ເປັນອາຊີບຫຼັກ ຂອງຊາວກະສິກອນ, ໃນເຂດພູດອຍ ທີ່ເຄີຍປະຕິບັດກັນມາ ໄດ້ຫຼາຍລຸ້ນຄົນແລ້ວ. ອີງຕາມລັກສະນະພູມສັນຖານ ເປັນເຂດຄ້ອຍຊັນ ທີ່ເປັນຂໍ້ຈາໍກັດ ໃຫ້ການຜະລິດກະສິກາໍ ແລະ ພາຍຫຼັງ ການບຸກເບີກພື້ນທີ່ທາໍການຜະລີດ ໂດຍການຈຸດປ່າ ຖາງໄຮ່ໃນເຂດຄ້ອຍຊັນ ຊື່ງມັນໄດ້ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ການນາໍໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ເປັນຕົ້ນ ແມ່ນ ໃນລະດູຝົນ ເຊີ່ງຝົນຈະເລີ່ມຕົກ ແຕ່ເດືອນ 5-1 ; ບາງເດືອນ ຝົນກໍ່ຕົກແຮງ ໂດຍສະເພາະ ໃນຊ່ວງເດືອນ 9-10 ເຮັດໃຫ້ດິນ ໄຫຼລົງຮ່ອງພູ ເຮັດໃຫ້ຕະກອນ ແລະ ອິນຊີວັດຖຸເທິງໜ້າດິນ ໄຫຼເຊາະລ້າງ ລົງຮ່ອງນາໍ້ ຂ້າງທາງ ເສດໄມ້ ທັບຖົມເຄື່ອງປູກຂອງຝັງ, ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດມີ ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນດີ ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ໃນປີ 2015 ຜູ້ນຳໄຊ້ທີ່ດີນ ຈີ່ງມີແນວຄວາມຄິດ ຕ້ອງການ ຢາກສ້າງແລວກັນດີນເຊາະໄຫຼ ຂອງນ້ຳຝົນ ທີ່ໄຫຼມາແຕ່ເທີງພູ ທັງເປັນການຮັກສາ, ກະຈາຍ ທາດອາຫານ ຕາມໜ້າດີນ ຢູ່ພື້ນທີ່ລຸ່ມຕີນພູ ໂດຍການຄົ້ນຄິດ ຊອກຫາວິທີ ເອົາໄມ້ທ່ອນ ທີ່ຊອກຫາໄດ້ ຈາກທຳມະຊາດ (ເປັນໄມ້ແຫ້ງ ທີ່ ໄດ້ຈາກການຕຸດໄຮ່) ມີຄວາມຍາວ ປະມານ 4-5 ແມັດ/ທ່ອນ, ມີເສັ້ນຜ່າ ສູນກາງ ປະມານ 15-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ ເອົາມາວາງລຽນກັນ ໄວ້ຮ່ອງນ້ຳ ບ່ອນທີ່ເຄີຍຖືກນາໍ້ໄຫຼເຊາະ ຕາມພື້ນທີ່ ການ ຜະລິດ ໃຫ້ໄດ້ຄວາມສູງຈາກພື້ນດິນ ປະມານ 1 ແມັດ.
ຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນ, ກໍ່ໃຊ້ໄມ້ໄຜ່ ທີ່ມີຄວາມ ຍາວ ປະມານ 1.5 ແມັດ, ມີຂະໝາດ ເສັ້ນຜ່າສູນກາງ ປະມານ 10 ຊັງຕີແມັດ ມາເຮັດເປັນຫັຼກຄາ້ໍ ເພ່ືອບ່ໍໃຫ້ ໄມ້ທ່ອນ ທີ່ເອົາມາ ລຽນລາໍນັ້ນ ລົ້ມລົງ ໂດຍການ ນາໍທ່ອນໄມ້ໃຜ່ ຝັງລົງດິນ ປະມານ 50 ຊັງຕີແມັດ ໂດຍການໃຊ້ເຊືອກມັດ. ການເຮັດເຕັກນີກ ດັ່ງ ກ່າວ ແມ່ນ ເລີ່ມຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ພາຍຫຼັງ ສໍາເລັດການ ສັກເຂົ້າໄຮ່ ໂດຍເລືອກເຮັດໃສ່ ບ່ອນພູ ທີ່ມີຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ 20-25% ເປັນບ່ອນ ທີ່ມີຮ່ອງນໍ້າ ໄຫຼເຊາະລົງມາ ຊື່ງໂດຍລວມແລ້ວ ປະຊາຊົນ ຈະນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກນິກນິ້ ປະມານ 2-3 ຈຸດ ພາຍໃນເນື້ອທີ່ ການຜະລິດທັງໝົດ. ຜົນທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບ ຈາກການເຮັດ ເຕັກນິກ ດັ່ງກ່າວນີ້ ແມ່ນ ສາມາດ ຫຸຼດຜ່ອນຄວາມແຮງ ຂອງການໄຫຼເຊາະ ຂອງນໍ້າ ແລະ ສາມາດ ກະຈາຍຕະກອນດິນ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ອອກຈາກ ພື້ນທີ່ທາໍການຜະລິດ ເພາະວ່າ ເມື່ອນ້ຳໄຫຼມາ ຈະມາຕ່ຳໃສ່ໄມ້ກັ້ນ ແລະ ໄຫຼອອກ ທາງດ້ານຂ້າງຂອງໄມ້ກັ້ນ. ສົມທຽບ ກ່ອນ ແລະ ຫຼັງ ການນຳໃຊ້ ເຕັກນີກນີ້້ ເຫັນວ່າ ກ່ອນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກນິກ ໄດ້ຜົນຜະລິດເຂົ້າ ປະມານ 1.5 ໂຕນ/ຮຕ ພາຍຫຼັງ ນຳໃຊ້ເຕັກນິກນີ້ ຜົນຜະລິດເຂົ້າ ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ປະມານ 2 ໂຕນ/ຮຕ ເນ່ືອງຈາກ ການສູນເສຍດີນຫຸຼດລົງ ອີນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດີນເພີ້ມຂື້ນ ເພາະການທັບຖົມຂອງຕະກອນ ແລະ ເສດຊາກພືດ ທີ່ໄຫຼມາຕາມນ້ຳເຮັດໃຫ້ຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ ຖືກເພີ່ມພູນໃຫ້ເປັນຊັ້ນໜາຂື້ນ, ເມື່ອເສດຊາກພືດເຫຼົ່ານັ້ນ ເນົ່າເປ່ືອຍ ຫືຼ ຖືກຍ່ອຍສະຫຼາຍ ໂດຍສິ່ງທີ່ ມີຊີວິດໃນດິນ (ຂີ້ກະເດືອນ, ບົ້ງກື) ຈະເປັນການປັບປຸງດິນ ໃນບໍລິເວນນັ້ນ ໃຫ້ອຸດົມສົມບູນຂື້ນ.
ຈຸດດີ: ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການໄຫຼຂອງຕະກອນດິນ, ການເພີ່ມຂອງອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນພື້ນດິນ (ເຮັດໃຫ້ຊັ້ນດິນໜາຂື້ນ), ກະຈາຍທາດອາຫານໃນພືີ່ນທີ່ກະສິກໍາ ແລະ ຕົ້ນທືນຕ່ຳ.
ຈຸດອ່ອນ: ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີນີ້ ແມ່ນ ບໍ່ຖາວອນ ແລະ ຂ້ອນຂ້າງອ່ອນໄຫວ, ດັ່ງນັ້ນຈິ່ງຕ້ອງມີການສ້ອມແປງ ແລະ ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາປະຈໍາປີ. ຖ້າໂຄງສ້າງເກົ່າຫຼາຍ ຈະຕ້ອງໄດ້ຮັບການຍົກລະດັບ, ມັນຈະຕ້ອງໃຊ້ຄຸນນະພາບທີ່ດີກວ່າເກົ່່າເຊັ່ນ ເຊືອກ ແລະ ເສົາຊີມັງ. ຢ່າງໃດກໍຕາມ, ປະຊາຊົນສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ຍັງ ໃຊ້ອຸປະກອນທີ່ມີ ຢູ່ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ ເຊື່ງມີຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ກໍ່ຄືກັບປະສິດທິຜົນຂອງມັນ.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Region/ State/ Province:
ເມືອງພູວົງ ແຂວງ ອັດຕະປື
Further specification of location:
ບ້ານ ວົງວິໄລ ເໜືອ
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
ເຕັກນີກນີ: ແມ່ນ ປະຕິບັດຢູ່ສະເພາະແຕ່ຈຸດທີ່ເປັນຮ່ອງນ້ຳໄຫຼ ທີ່ເກີດຈາກຝົນຕົກ
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2015
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- reduce risk of disasters
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - rice (upland)
- root/tuber crops - cassava
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- sugar cane
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences
- S11: Others
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wo: offsite degradation effects
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
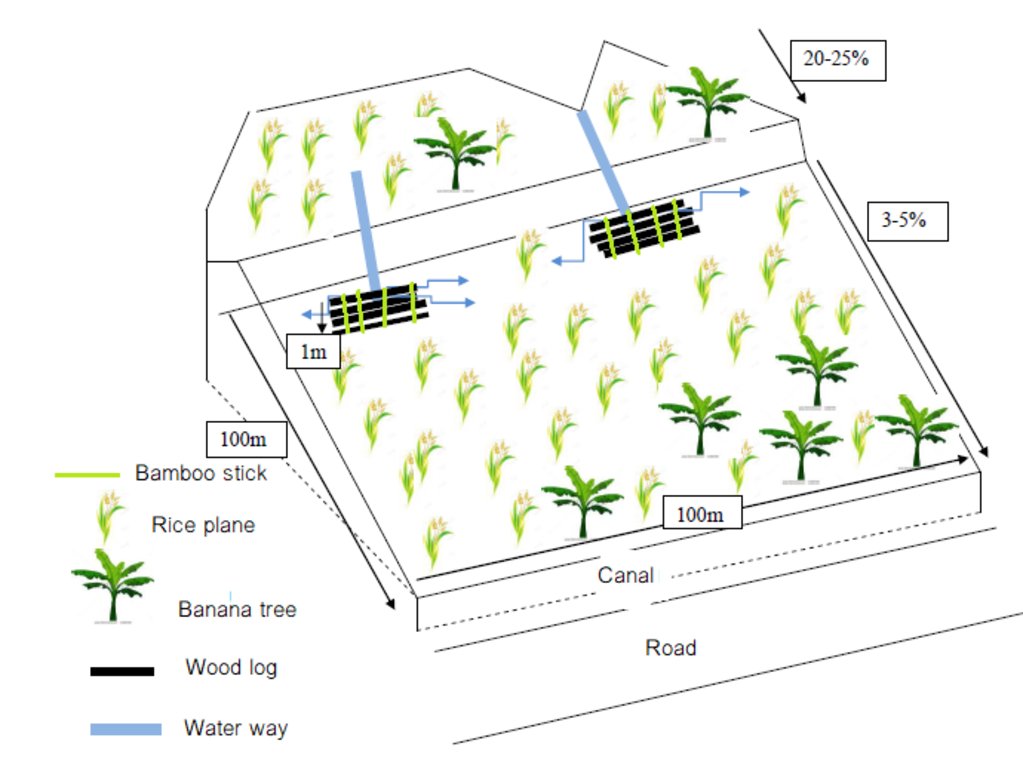
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
ເຕັກນິກນີ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ມີຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
ສິ່ງກີດຂວາງໄມ້ທ່ອນ ໄມ້ຖືກສ້າງຂື້ນດ້ວຍຄວາມສູງ 1 ແມັດຈາກຫນ້າດິນ.
ຄວາມຍາວຂອງໄມ້ທ່ອນ ແມ່ນ ປະມານ 4-5 ແມັດ.
ຄວາມເລິກຂອງໄມ້ໄຜ່ ລົງໄປໃນດິນ ແມ່ນ 50 ຊັງຕີແມັດ
ເຕັກນິກນີ້ ແມ່ນ ປະຕິບັດ ຢູ່ດ້ານເທິງຂອງໄຮ່ ທີ່ມີຄວາມຊັນ 20-25%, ບ່ອນທີ່ນ້ໍາຈາກທໍາມະຊາດ ໄຫຼເປັນຮ່ອງຈາມໜ້າດີນ.
Author:
ນາງ ວາດສະໜາ
Date:
18/05/2017
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
2 ຮາວກັ້ນ
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
ກວ້າງ 4-5 ແມັດ / ສູງ 1 ແມັດ (ສຳລັບ 1 ຮາວ)
other/ national currency (specify):
ກີບ
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8000.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
50000ກີບ
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ເກັບໄມ້ທ່ອນ ແລະ ໄມ້ໄຜ່ | ຫຼັງເກັບກ່ຽວ |
| 2. | ຝັງເສົາມ້ໄຜ່ | |
| 3. | ຈັດລຽງໄມ້ທ່ອນ |
Comments:
ເອົາວາງໃສ່ບ່ອນທີ່ເປັນຮ່ອງນ້ໍາ ເພື່ອຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການໄຫລຂອງນ້ໍາ
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານ | ຄົນ | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຈົກ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຊ້ວນ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຄ້ອນຕີ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ໄມ້ທ່ອນ | ລຳ | 10.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Plant material | ໄມ້ໃຜ່ | ລຳ | 10.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 195000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 24.38 | |||||
Comments:
ກ່ຽວກັບວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ: ໄມ້ໄຜ່ ແລະ ໄມ້ທ່ອນ ແມ່ນໃຊ້ໄມ້ທີ່ເສດເຫຼືອ ທີ່ຖືກເກັບຈາກອ້ອມຂ້າງ
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ສ້ອມແປງ ເອົາໄມ້ມາເສີມໃສ່ | ເດືອນລະເທື່ອ |
Comments:
ການນໍາໃຊ້ວັດສະດຸທີ່ຍັງເຫຼືອ ສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | ແຮງງານ | ຄົນ | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ຟ້າ | ດວງ | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ສຽມ | ດວງ | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ໄມ້ທ່ອນ | ທ່ອນ | 10.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Construction material | ໄມ້ໃຜ່ | ລຳ | 10.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 170000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 21.25 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ຊ້ວນ,ຈົກ,ເຫັຼກຕະປູ,ພ້າແມ່ນຫາຊື້ຈາກທອ້ງຕະຫຼາດ ຊາວກະສີກອນຊື້ເອງ
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
2500.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
ປະລີມານນຳ້ຝົນ ລະຫວ່າງເດືອນ 9 ແມ່ນຝົນຕົກຫຼາຍ, ຫຼາຍສຸດ ແມ່ນ ເດືອນ 6 - 9 ແລະ ໜ້ອຍສຸດ ແມ່ນ ເດືອນ 11- 4
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
ຫ້ອງການຊັບພະຍາກອນທຳມະຊາດເມືອງພູວົງ
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
ອຸນຫະພູມສະເລ່ຍ ປະຈຳປີ 26,2 ອົງສາ
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- children
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
1,5 ໂຕນ/ຮຕ
Quantity after SLM:
2ໂຕນ/ຮຕ
Comments/ specify:
ການເພີ່ມຂື້ນຂອງສານອິນຊີຈາກການສະສົມຂອງຫນ້າດິນ
production area
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນທີ່ຊາວກະສິກອນຈະສູນເສຍພື້ນທີ່ຫຼາຍຍ້ອນຊ່ອງທາງນ້ໍາໃນພື້ນທີ່ການປູກຝັງ; ຫຼັງຈາກທີ່ມີບັນດາອຸປະສັກໄມ້ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກສ້າງຂື້ນແລ້ວ, ພື້ນດິນໄດ້ເພີ່ມຂື້ນໂດຍການສະສົມຂອງດິນ
Income and costs
farm income
Comments/ specify:
ການໄຫລວຽນຂອງນ້ໍາໃນພື້ນທີ່ການຜະລິດທີ່ຜ່ານມາເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດຜົນເສຍຫາຍຕໍ່ການປູກພືດແລະໃນການຫຼຸດລົງຜົນຜະລິດພືດ
workload
Comments/ specify:
ການຕິດຕັ້ງສິ່ງກີດຂວາງໄມ້ເພື່ອຂະຫຍາຍພື້ນທີ່ການປູກຝັງຕ້ອງໃຊ້ແຮງງານຫຼາຍ
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ ໄດ້ຮັບການປັບປຸງຍ້ອນວ່າຊາວກະສິກອນໄດ້ຮັບຜົນຜະລິດຫຼາຍກວ່າ ແລະ ສາມາດຂາຍເຖິງຕະຫຼາດທ້ອງຖິ່ນ
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Comments/ specify:
ນ້ໍາ ແລະ ດິນທີ່ຖືກທໍາລາຍລຸດລົງໃນເວລາທີ່ສຳເລັດ ແລວກີດຂວາງ ແລະ ນ້ໍາແມ່ນມຸ້ງໄປຂ້າງຫນື່ງ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນເທິງພື້ນດິນ ແມ່ນ ມີຜົນກະທົບໜ້ອຍລົງ.
Soil
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນທີ່ຈະມີຫຼາຍໆຊັ້ນດິນໂດຍການລ້າງນ້ໍາໃນພື້ນດິນກໍ່ຖືກສູນເສຍ. ຫຼັງຈາກການຕິດຕັ້ງອຸປະກອນກີດກັນ ນ້ໍາມີການປ່ຽນແປງ ແລະ ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ແລະການຕົກຕະກອນຕາມຮ່ອງຂ້າງທາງ
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
Comments/ specify:
ສິ່ງກີດຂວາງຂອງໄມ້ທ່ອນສາມາດແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຊີວະມວນ ແລະ ຊິ້ນສ່ວນຂອງພືດ ແລະ ຝຸ່ນຊີວະພາບໄປສູ່ພື້ນທີ່ການຜະລິດ (ເພີ່ມຂື້ນຂອງດິນຟ້າ)
Climate and disaster risk reduction
landslides/ debris flows
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນທີ່ຈະມີຝົນຕົກຢ່າງຫຼວງຫຼາຍເຮັດໃຫ້ມີການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຂອງດິນ (ລະດູແລ້ງແລະລະດູແລ້ງລະຫວ່າງແຖວ) ໃນລະດູຝົນ
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນ ໄຫຼຜ່ານເສັ້ນທາງຂອງເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ. ຫຼັງຈາກການຕິດຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ທາງນ້ໍາໄດ້ປ່ຽນແປງໄປສູ່ເຂດບ້ານໂດຍບໍ່ມີການກໍ່ໃຫ້ເກີດຄວາມເສຍຫາຍຢູ່.
ດີນເຈື່ອນລົງສູ່ຮ່ອງຂ້າງທາງ
Comments/ specify:
ກ່ອນ ມີການເຊາະເຈື່ອນໂດຍກົງ. ຫຼັງຈາກຕິດຕັ້ງ ຮົ້ວກີດຂວາງ ຕະກອນດິນ ສ່ວນຫຼາຍ ແມ່ນ ຍັງຫຼົງເຫຼືອຢູ່ຈາມໄຮ່
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | wet/ rainy season | increase | very well |
| annual rainfall | increase | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extreme winter conditions | well |
| drought | moderately |
| forest fire | moderately |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| landslide | moderately |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extended growing period | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Nee
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| ຂໍ້ດີໃນການ ນຳໄຊ້ເຕັກນີກນີ້ ປ້ອງກັນບໍໃຫ້ເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ,ຜົນຜະລິດໃດ້ຮັບ ໜາກຜົນ |
| ບູກຄົນໃດ ກໍ່ສາມາດເຮັດໄດ້ງາ່ຍໆ |
| ບໍໄດ້ໄຊ້ຕົ້ນທືນ ,ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນຜະລິດສູງ ສາມາດກູ້ມຕົນເອງ |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| ສາມາດກະຈາຍຕະກອນດີນທີ່ໄຫຼມາຕາມກະແສນ້ຳ ໄປທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່ ການຜະລິດ |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ຂອງສະຖານທີ່ເຫລົ່ານີ້ບໍ່ຖາວອນ ແລະ ມີຄວາມສ່ຽງທີ່ຕ້ອງການສ້ອມແປງທຸກໆປີ | ມັນອາດຈະຕ້ອງການຄຸນນະພາບທີ່ດີກວ່າ ເຊັ່ນເສົາ ຄອນກຣີດ |
| ການສະສົມມີບາງບ່ອນ, ກໍ່ຍັງເກີດການຊະລ້າງເຫລືອຢູ່ | ຕ້ອງສ້າງຫຼາຍໆຈຸດ |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ປະຊາຊົນຍັງໃຊ້ອຸປະກອນ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນທີ່ ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງການໄຫຼ ທີ່ຖືກທໍາລາຍເຊັ່ນດຽວກັນກັບປະສິດທິຜົນຂອງມັນ. | ມັນອາດຈະຕ້ອງມີການຕິດຕັ້ງສະຖານທີ່ແບບນີ້ໃນຫລາຍໆສະຖານທີ່ຕາມແຄມ ຂື້ນຢູ່ກັບຄວາມຊັນຂອງດິນ. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
1 ສະຖານທີ່
- interviews with land users
1 ຄົນ
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
18/05/2017
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules