Bio-fermentation technology for soil improvement [Thailand]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Kukiat SOITONG
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Num Mak She Wa Parp
technologies_4233 - Thailand
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
ผู้รวบรวม:
ดุรงค์กาญจน์ นายสาโรช
สถานีพัฒนาที่ดินปราจีนบุรี สำนักงานพัฒนาที่ดินเขต 2 กรมพัฒนาที่ดิน
Thailand
land user:
สนลอย นางวันเพ็ญ
เกษตรกร และหมอดินอาสาประจำจังหวัดปราจีนบุรี กรมพัฒนาที่ดิน
Thailand
SLM specialist:
สนลอย นางวันเพ็ญ
เกษตรกร และหมอดินอาสาประจำจังหวัดปราจีนบุรี กรมพัฒนาที่ดิน
Thailand
SLM specialist:
สนลอย นางวันเพ็ญ
เกษตรกร และหมอดินอาสาประจำจังหวัดปราจีนบุรี กรมพัฒนาที่ดิน
Thailand
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
การใช้เทคโนโลยีชีวภาพในพื้นที่ดินค่อนข้างเป็นทราย เสื่อมโทรม ช่วยปรับปรุงโครงสร้างดิน เพิ่มจุลินทรีย์ในดิน ทำให้ดินร่วนซุย ช่วยลดการใช้สารเคมี และช่วยรักษาสิ่งแวดล้อม
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Bio-fermentation technology for soil improvement is an alternative technology that helps to restore degraded land from intensive land usage which lack of soil improvement to get back to be the soil productivity that can provide effective production.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
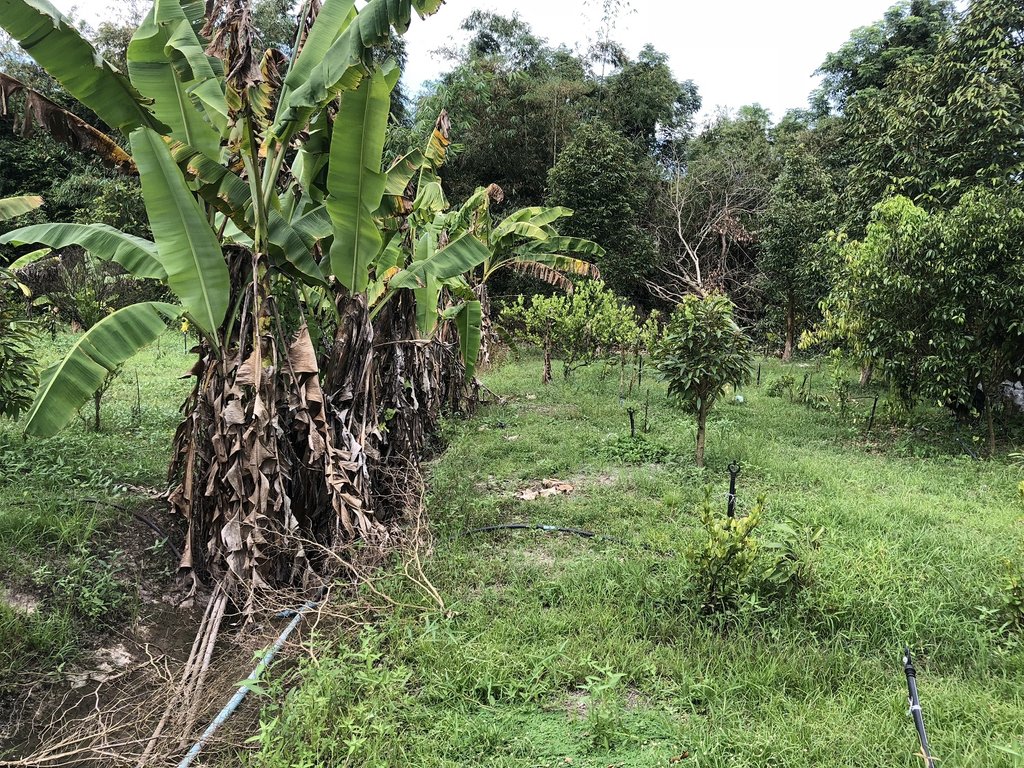
The area has chemical and physical degradation problems. The area is the lowland. The soil is quite sandy. The soil structure is poor which the draining system is quite bad. The organic matter, soil nutrients and soil fertility is low.
Farmers use the land to grow rice but have the low rice yield. Farmers have changed their rice fields to grow their crops instead.
Which changing the area from the normal rice field by digging the ditch for 1 meter wide on growing area, 1 meter wide for the drain and 0.80 meters deep)that grow durian, banana, lime, vegetable (Climbing Wattle)
The weed management by using chemicals and chemical fertilizers in the high rate continuously to make the soil degrade or dense and grow the ineffective crops.
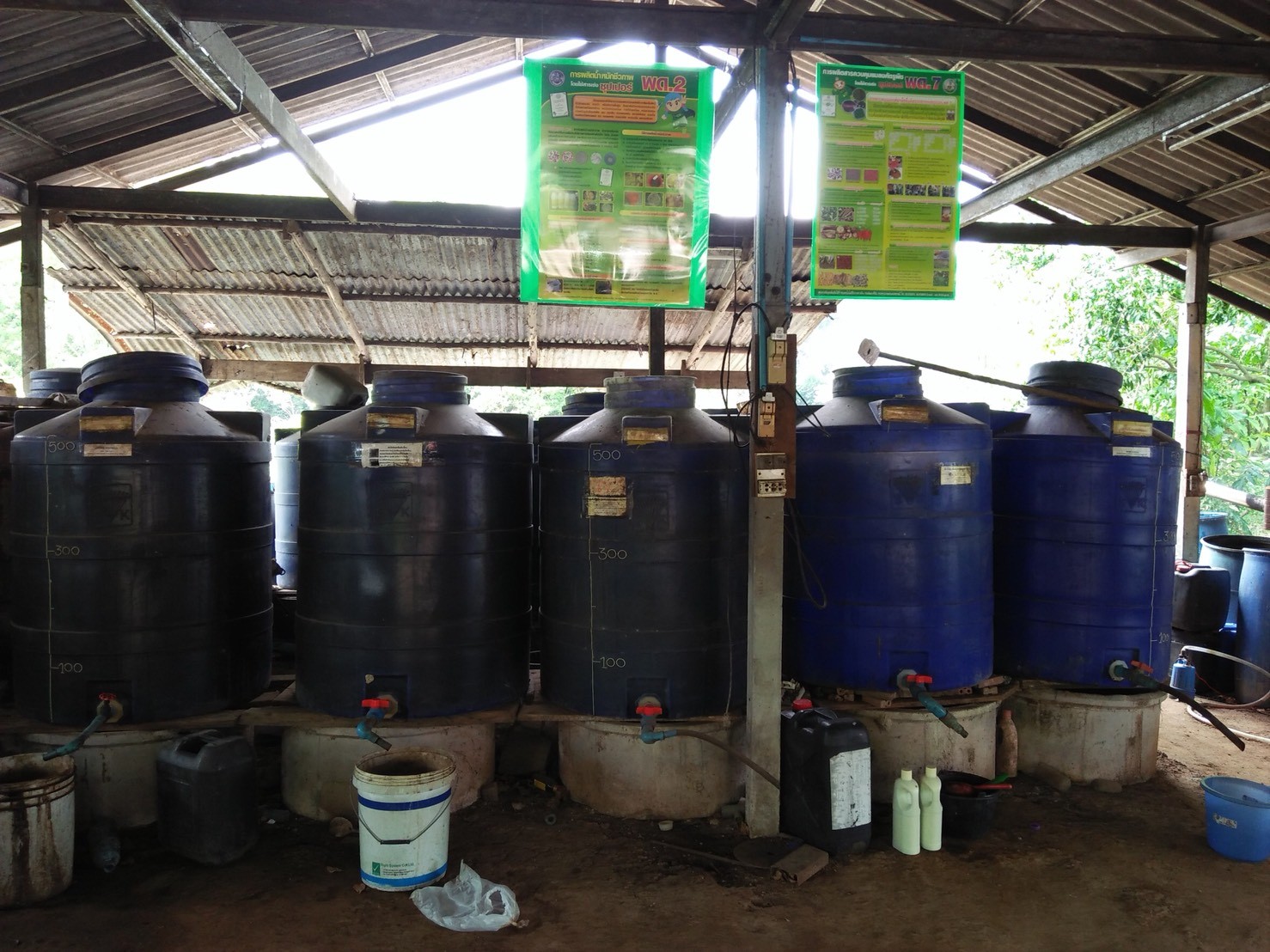
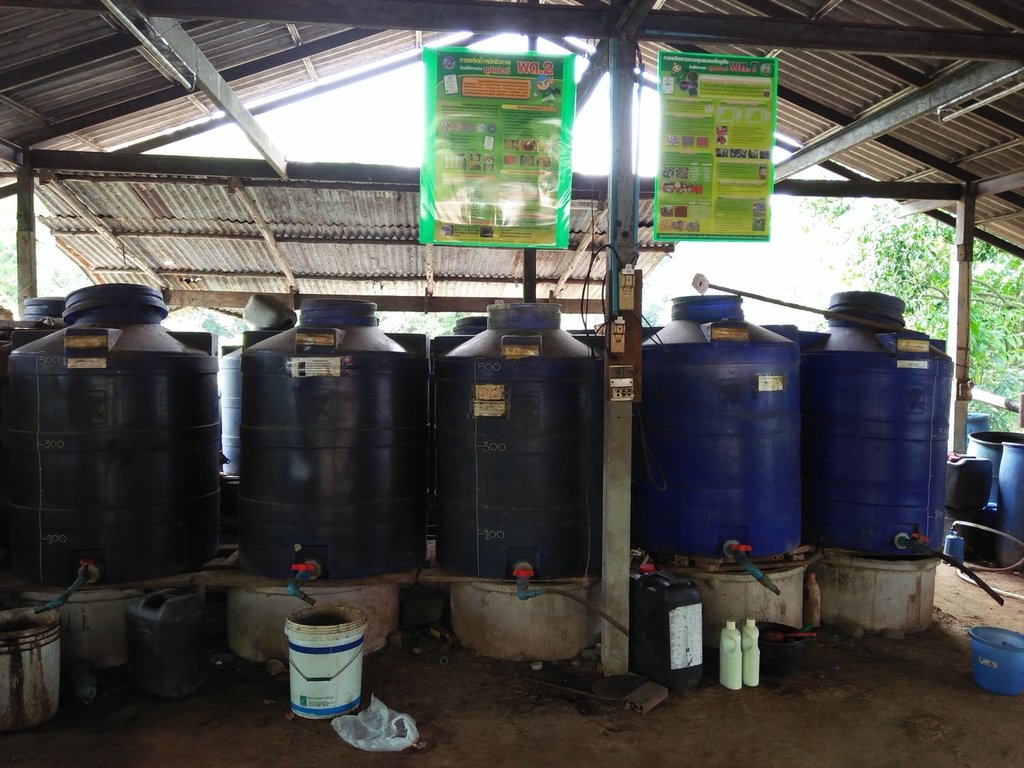
Bio-fermentation technology for soil improvement consists of the production of 3 types of biological fermentation and the usage of 3 types of biological fermentation as follows:
1. Product Processions of bio-fermented water
The methods of the 3 types bio-fermented producing are as follows.
1.1 Production of bio-fermented from the fish fraction by using the Microbial Activators from LDD.
1.2. Production of photosynthetic microorganisms
1.3 Production of Bio-Fermented Water from rice flour water
2. How to use the bio-fermentation to improve the soil
Mix the three bio-nutrients at a rate of 1: 1: 1 per 200 litters of water and spray or pour on the ground every 3 days or use sprinkler system by releasing the bio-fermented water mix with water for 10 minutes followed and wash it with water for 3 minutes for 3 years (at the beginning of the growing season).
The usage of Bio-fermentation technology to improve the soil has the objective is to restore the degradation of agricultural land for a long term and using the high rate of chemical fertilizers continuously to be able to do the farm effectively.
The usage of Bio-fermentation technology to improve the soil has the important activities to do are following:
1. Product Processions of Bio-fermentation Solution
The methods of the 3 types bio-fermented producing are as follows.
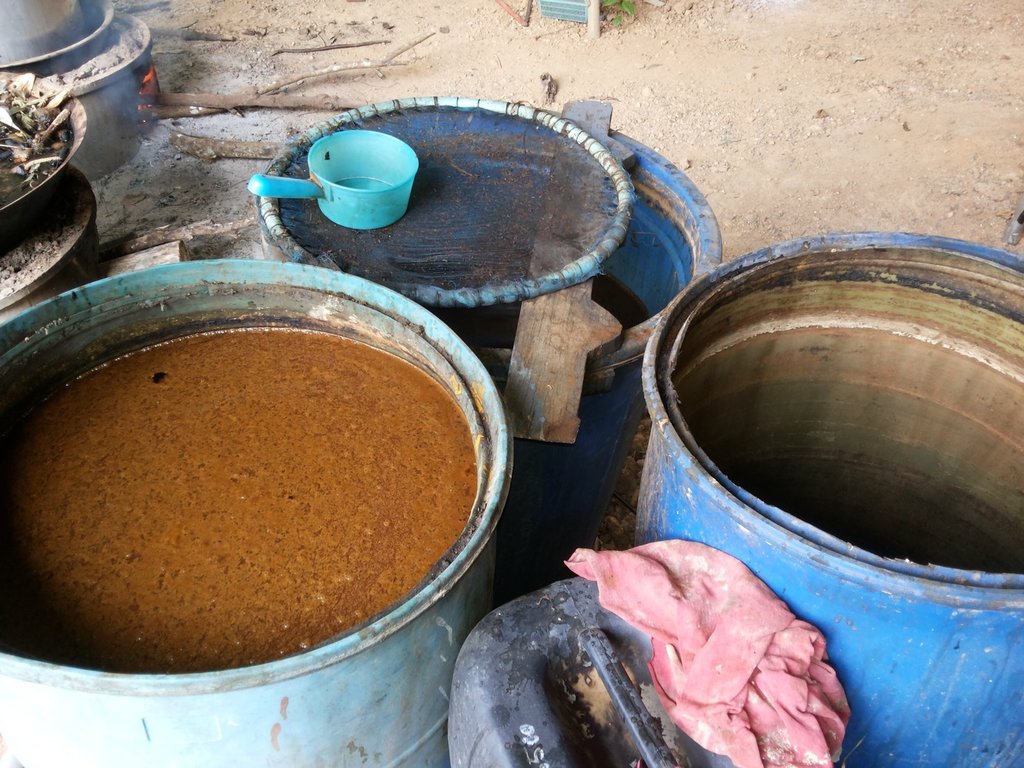
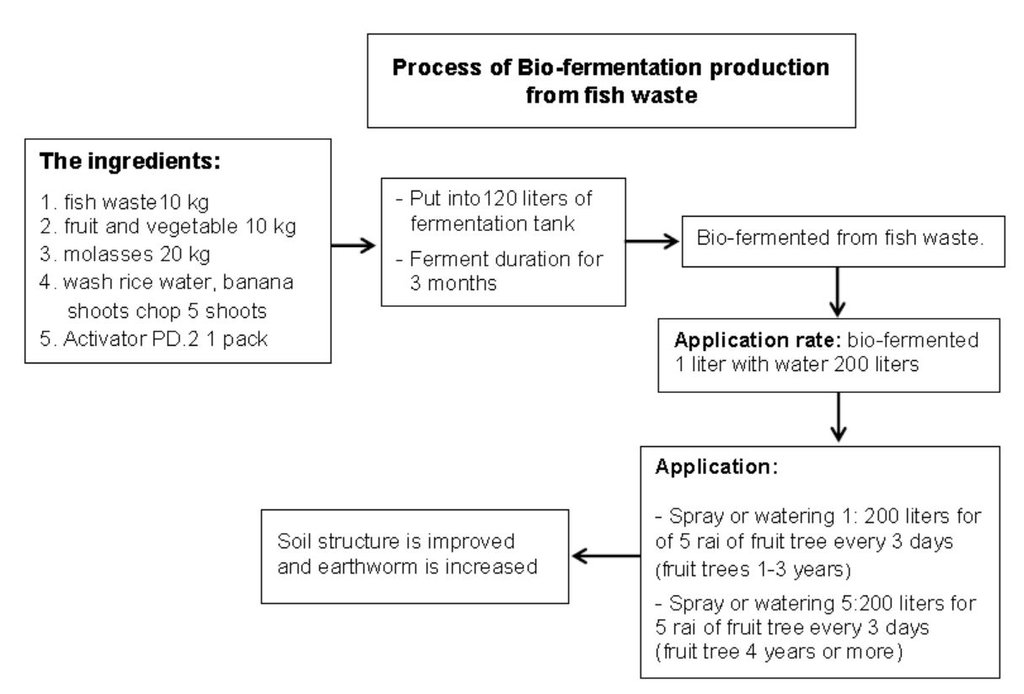
1.1 Production of bio-fermented from the fish fraction by using the Microbial Activators PD2 by using the fish fraction about 10 kilograms, the fruit and vegetable fraction about 10 kilograms, molasses about 20 kilograms, the rice flour water or the banana fraction about 5 spire and the Microbial Activators PD 1 packet to mix everything in the tank size 120 litters for 3 months.
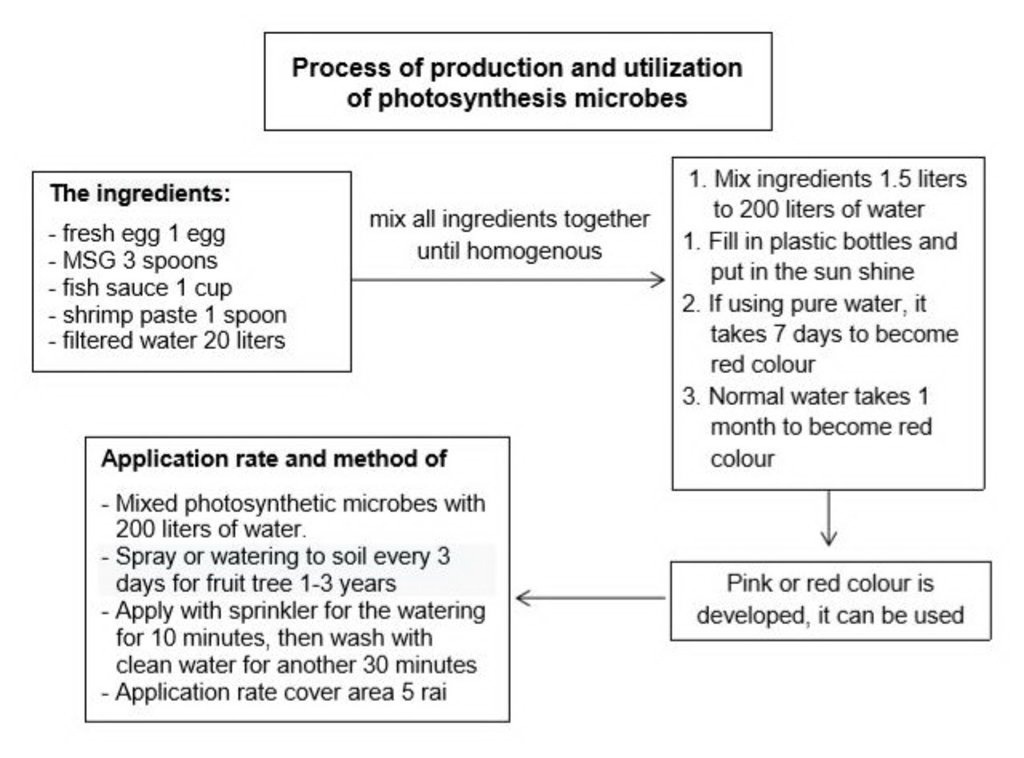
1.2. Production of photosynthetic microorganisms made by 5 eggs, 3 tablespoons of MSG, 1 tablespoon of fish sauce, 1 tablespoon of filtered water and 20 liters of pure water mixed in a homogeneous mixture at the rate of 1.5 liters per 200 liters of water for 7 days and it will be red (in case of using the pure water) and 1 month (in case of using clear water).
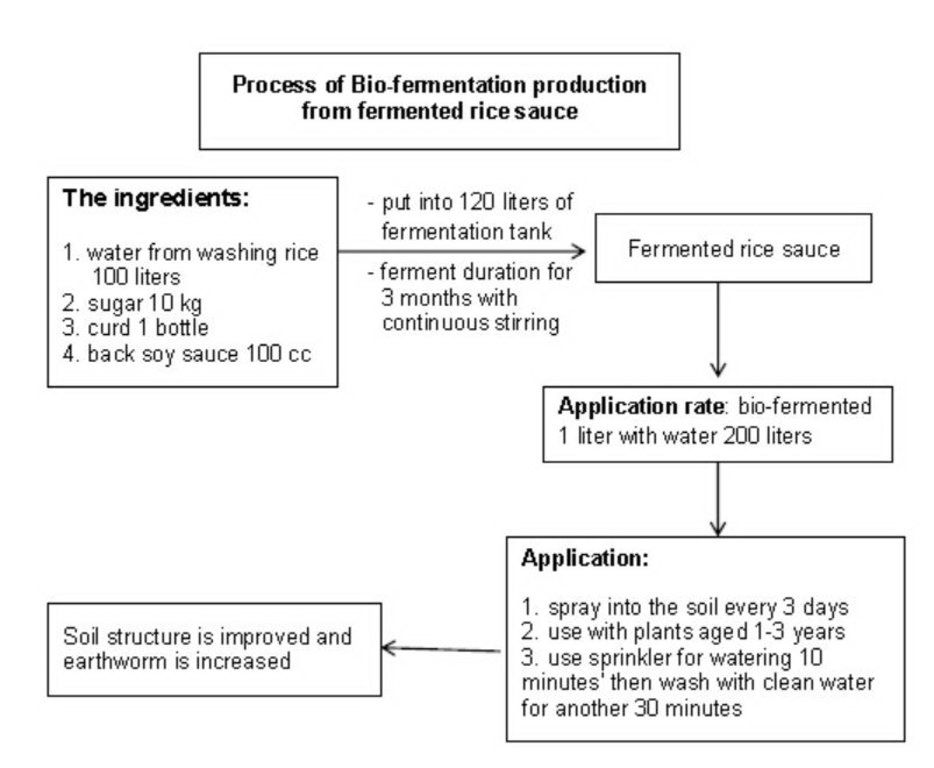
1.3 Production of bio-fermented solution from using 100 liter of rice flour water, 10 kilogram of sugar, 1 yakult bottle (curd) and 10 milliliters of fermented soy sauce in a 120 liters pot size fermentation tank for 3 months
2. The using steps of bio-fermented solution to improve the soil to improve the soil in the crop land for the different periods of cultivation as follows.
2.1. The early stage before the production period (1-3 years)
Mix the three types ofBio-fermentation solution at a rate of 1: 1: 1 per 200 litters of water and spray or pour on the ground every 3 days or use sprinkler system to release the bio-fermented water for 10 minutes and use the clear water later for 30 minutes
2.2 The yield period (more than 4 years)
To dissolve the bio-fermented which from the fish for 5 liters: 200 liters of water and spray or pour on the ground every 3 days or use sprinkler system to release the bio-fermented water for 10 minutes, followed by 30 minutes of the clear water.
1. Make the soil more fertile, organic matter and microorganisms in soil (earthworm). The benefits of nutrients in the soil increase. It can grow durian which can be sold at high prices (180 baht / tree).
2. Reduce the plant production costs due to using the waste materials from the land to be the fermentation materials. The farmers have increased income, lives are not dependent on themselves and the using the biotechnology does not have an impact on the environment.
1. This technology is the knowledge that is derived from experiential / practical experiments in the area of farmer prototype technology users which can see the real results from using it.
2. The methods / procedures are not complicated.
3. It is easy to use, not difficult mosquitoes.
4. There are multichannel technology has been released that the farmers can access it easily.
1. This technology (bio-fermentation / bio-extract) does not have any nutritional status checking which cannot be shown the quantity.
2. Farmers generally lack of the motivation to do and use.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
การใช้เทคโนโลยีชีวภาพเพื่อการพัฒนาที่ดิน
Date:
07/03/2018
Name of videographer:
กรมพัฒนาที่ดิน
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Thailand
Region/ State/ Province:
ภาคตะวันออก/จังหวัดปราจีนบุรี
Further specification of location:
62/1 หมู่ 5 ตำบลไม้เค็ด อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดปราจีนบุรี
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
1997
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- preserve/ improve biodiversity
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
- การปลูกพืชผสมผสาน
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 2
Specify:
-
Comments:
-
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Comments:
-
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
-
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- integrated soil fertility management
- integrated pest and disease management (incl. organic agriculture)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

other measures
Specify:
others การผลิตและการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ
Comments:
มีการทำเกษตรแบบผสมผสานทั้งไม้ผลและพืชผักสวนครัว
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction

biological degradation
- Bl: loss of soil life
Comments:
เกิดจากการใช้ปุ๋ยเคมีมากเกินความจำเป็น เกินความต้องการของพืชต่อเนื่อง เป็นระยะเวลานาน ทำให้ดินเสื่อมโทรม
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
Comments:
การใช้ปุ๋ยเคมีต่อเนื่องเป็นระยะเวลานาน ทำให้สมบัติทางเคมีและชีวภาพของดิน เสื่อมโทรมลง จำเป็นต้องได้รับการฟื้นฟู
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
1.กระบวนการผลิต น้ำหมักชีวภาพ
วิธีการผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพ 3 สูตร มีดังนี้
1.1 การผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพจากเศษปลาด้วยสารเร่ง พด 2 ผลิตโดยใช้ เศษปลา 10 กก. เศษผัก/ผลไม้ 10 กก. กากน้ำตาล 20 กก. น้ำซาวข้าว/หน่อกล้วยสับ 5 หน่อ และสารเร่ง พด.2 1 ซอง หมักในถังหมักขนาด 120 ลิตร นาน 3 เดือน
2. วิธีการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพเพื่อปรับปรุงบำรุงดิน
ให้นำน้ำหมักชีวภาพทั้งสามสูตรผสมกันในอัตรา1:1:1 ต่อน้ำ200 ลิตร ฉีดพ่นหรือรดลงดินทุกๆ 3 วัน หรือใช้ระบบสปริงเกอร์ โดยปล่อยน้ำหมักชีวภาพไปกับน้ำ 10 นาที ตามด้วยการล้างด้วยน้ำเปล่าอีก 30 นาที เป็นเวลา 3 ปี (ช่วงเริ่มต้นของการปลูกปลูกไม้ผล
Author:
นายสาโรช ดุรงค์กาญจน์
Date:
02/10/2018
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
1.2.การผลิตจุลินทรีย์สังเคราะห์แสง ผลิตโดยใช้ส่วนผลมไข่ไก่ ผงชูรส 3 ช้อนโต๊ะ น้ำปลา 1 แก้ว กะปิ 1 ช้อนโต๊ะ และน้ำกรองสะอาด 20 ลิตร ผสมจนเป็นเนื้อเดียวกัน ผสมนำในอัตรา 1.5 ลิตร ต่อน้ำ 200 ลิตร กรอกใส่ขวดพลาสติกใส วางตากแดด ใช้เวลา 7 วัน จะเกิดสีแดง (ในกรณีที่ใช้น้ำบริสุทธิ์) และใช้เวลา 1 เดือน (ในกรณีใช้น้ำประปาทั่วไป)
2. วิธีการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพเพื่อปรับปรุงบำรุงดิน
ให้นำน้ำหมักชีวภาพทั้งสามสูตรผสมกันในอัตรา1:1:1 ต่อน้ำ200 ลิตร ฉีดพ่นหรือรดลงดินทุกๆ 3 วัน หรือใช้ระบบสปริงเกอร์ โดยปล่อยน้ำหมักชีวภาพไปกับน้ำ 10 นาที ตามด้วยการล้างด้วยน้ำเปล่าอีก 30 นาที เป็นเวลา 3 ปี (ช่วงเริ่มต้นของการปลูกปลูกไม้ผล
Author:
นายสาโรช ดุรงค์กาญจน์
Date:
02/10/2018
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
1.3 การผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพจาก น้ำซาวข้าว ผลิตโดยใช้ น้ำซาวข้าว 100 ลิตร น้ำตาลทราย 10 กก. ยาคูลท์ 1 ขวด และซีอิ๊วดำ 10 มล. หมักในถังหมักขนาด 120 ลิตร นาน 3 เดือน
2. วิธีการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพเพื่อปรับปรุงบำรุงดิน
ให้นำน้ำหมักชีวภาพทั้งสามสูตรผสมกันในอัตรา1:1:1 ต่อน้ำ200 ลิตร ฉีดพ่นหรือรดลงดินทุกๆ 3 วัน หรือใช้ระบบสปริงเกอร์ โดยปล่อยน้ำหมักชีวภาพไปกับน้ำ 10 นาที ตามด้วยการล้างด้วยน้ำเปล่าอีก 30 นาที เป็นเวลา 3 ปี (ช่วงเริ่มต้นของการปลูกปลูกไม้ผล
Author:
นายสาโรช ดุรงค์กาญจน์
Date:
02/10/2018
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
1.3 การผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพจาก น้ำซาวข้าว ผลิตโดยใช้ น้ำซาวข้าว 100 ลิตร น้ำตาลทราย 10 กก. ยาคูลท์ 1 ขวด และซีอิ๊วดำ 10 มล. หมักในถังหมักขนาด 120 ลิตร นาน 3 เดือน
2. วิธีการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพเพื่อปรับปรุงบำรุงดิน
ให้นำน้ำหมักชีวภาพทั้งสามสูตรผสมกันในอัตรา1:1:1 ต่อน้ำ200 ลิตร ฉีดพ่นหรือรดลงดินทุกๆ 3 วัน หรือใช้ระบบสปริงเกอร์ โดยปล่อยน้ำหมักชีวภาพไปกับน้ำ 10 นาที ตามด้วยการล้างด้วยน้ำเปล่าอีก 30 นาที เป็นเวลา 3 ปี (ช่วงเริ่มต้นของการปลูกปลูกไม้ผล
Author:
นายสาโรช ดุรงค์กาญจน์
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
1 ไร่
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
-
other/ national currency (specify):
Thai Baht
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
32.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
แรงงานต่อวันคือ 300 บาท
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | กระบวนการผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพ | - |
| 2. | วิธีการใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ | - |
Comments:
เป็นการใช้เทคโนโลยีระหว่างการบำรุงและดูแลไม้ผลก่อนเก็บเกี่ยวผลผลิต
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | จ้างผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพพด.2,จุลินทรีย์สังเคราะห์แสงน้ำหมักชีวภาพน้ำซาวข้าว | คน | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ต่อท่อน้ำสปริงเกอร์ | คน | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ท่อน้ำและข้อต่อ | ตัว | 50.0 | 40.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ปั๊มน้ำ | ปั๊ม | 1.0 | 8000.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ถังหมัก | ใบ | 3.0 | 500.0 | 1500.0 | 80.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | กากน้ำตาล | ลิตร | 120.0 | 12.0 | 1440.0 | 80.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | เศษปลา/เศษผักผลไม้Waste | กิโลกรัม | 40.0 | 10.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ผงชูรส/กะปิ/ไข่/Yakult/ซีอิ๋ว/น้ำตาลทราย | - | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | สารเร่วพด2 | ซอง | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 14654.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 457.94 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
สถานีพัฒนาที่ดินปราจีนบุรี
Comments:
สถานีพัฒนาที่ดินสนับสนุนปัจจัยการผลิต ได้แก่ ถังหมัก กากน้ำตาล และเชื้อจุลินทรีย์สารเร่ง พด.2
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. การใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ | สัปดาห์ละ1ครั้ง |
| 2. | 2. การผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพ | 3 เดือน/ครั้ง |
Comments:
เป็นการดูแลรักษาเครื่องมือ เช่น ข้อต่อ หัวฉีด ไม่ให้อุดตัน
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | จ้างผลิตน้ำหมักชีวภาพพด.2,จุลินทรีย์สังเคราะห์แสง,น้ำหมักชีวภาพน้ำซาวข้าว | คน | 4.0 | 300.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | ท่อน้ำและข้อต่อ | ตัว | 50.0 | 40.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | กากน้ำตาล | ลิตร | 120.0 | 12.0 | 1440.0 | 80.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | เศษปลา/เศษผักผลไม้Waste | กิโลกรัม | 40.0 | 10.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | ผงชูรส/กะปิ/ไข่/Yakult/ซีอิ๋ว/น้ำตาลทราย | กิโลกรัม | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | สารเร่วพด2 | ซอง | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 5154.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 161.06 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
-
Comments:
เป็นค่ารักษาซ่อมแซมในกรณีที่ชำรุดเสียหาย
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ราคาวัตถุดิบในการผลิคน้ำหมักชีวภาพ เช่นกากน้ำตาล
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
-
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
-
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
-
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
Comments and further specifications on topography:
-
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
-
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Ja
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
คุณภาพน้ำดีสามารถนำมาใช้ทางการเกษตรได้ แต่ยังไม่เหมาะสำหรับการดื่มกินต้องได้รับบำบัดก่อนจึงจะนำมาบริโภคได้
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
เนื่องจากมีการปลูกพืชหลายชนิด เช่น ทุเรียน ลองกอง ส้มโอ มะนาว ถั่ว ชะอม ทำให้มีความหลากหลายทางพันธุกรรมพืชสูง ส่วนแหล่งที่อยู่อาศัยมีไม่มากทำให้มีความหลากหลายในระดับปานกลาง
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- elderly
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
-
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
เนื่องจากเป็นการประเมินราคาที่ดินในเขตเมือง
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Specify:
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำเป็นแบบเปิดเนื่องจากเป็นประปาของชุมชนไม่มีระเบียบว่าอย่างไรแต่เสียค่าใช้จ่ายตามปริมาณใช้จริงและส่วนใหญ่การใช้น้ำในพื้นที่มาจากบ่อของตนเองเป็นหลัก
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
Comments:
-
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Quantity before SLM:
10
Quantity after SLM:
30
Comments/ specify:
ผลทุเรียนเพิ่มขึ้น
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
-
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
ปัจจัยบางอย่างนามาใช้ในปีถัดไปได้ เช่น ถังหมัก
farm income
Comments/ specify:
รายได้จากการจำหน่ายต้นพันธุ์ และผลทุเรียน
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
ดีขึ้นสามารถพึ่งพาตนเองได้
health situation
land use/ water rights
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
สถาบันครอบครัว
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
ดินมีอินทรีย์วัตถุเพิ่มขึ้น โครงสร้างดินดีขึ้น
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quality
Comments/ specify:
ลดการปนเปื้อนเนื่องจากเป็นการใช้สารอินทรีย์ ลดการใช้สารเคมี
surface runoff
groundwater table/ aquifer
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
มีหญ้าปกคลุมมีไส้เดือน
soil loss
soil crusting/ sealing
Comments/ specify:
ดินร่วนซุยขึ้น
soil compaction
nutrient cycling/ recharge
acidity
Quantity before SLM:
4.0-4.5
Quantity after SLM:
5.5-6.0
Comments/ specify:
pH เพิ่มขึ้น
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
plant diversity
beneficial species
Comments/ specify:
ไส้เดือนเพิ่มขึ้น
pest/ disease control
Comments/ specify:
ลดลง
Climate and disaster risk reduction
flood impacts
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
groundwater/ river pollution
Comments/ specify:
ลดลงเนื่องจากลดการใช้สารเคมี
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | summer | increase | not well |
| annual rainfall | increase | moderately | |
| seasonal rainfall | wet/ rainy season | increase | not well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| flash flood | moderately |
Comments:
ปีนี้ฝนประจำปีมาเร็วขึ้นทำให้ผลไม้ติดผลลดลงเนื่องจากฝนตกลงมาช่วงออกดอก
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
very positive
Comments:
คิดเห็น การทำน้ำหมักและการวางระบบกระจายน้ำในแปลงจะเป็นการลงทุนในปีแรกที่สูงแต่ในปีถัดไปค่าใช้จ่ายจะลดลงเพราะไม่ได้ซื้อเพิ่ม เช่น ถังหมัก ท่อน้ำ ปั๊มน้ำ มีแต่ค่าดูแลรักษาเวลาชำรุด เสียหาย เช่น ท่อน้ำแตก อุดตัน และมีระยะเวลาการใช้ ประมาณ 4-5 ปี
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
เฉพาะอำเภอเมือง จังหวัดปราจีนบุรี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
ประมาณจากจำนวนผู้ได้รับการถ่ายทอดเทคโนโลยีที่เข้ามาศึกษาที่ศูนย์เรียนรู้
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
If yes, indicate to which changing conditions it was adapted:
- changing markets
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
ความต้องการสินค้าเกษตรปลอดภัยหรือเกษตรอินทรีย์มีเพิ่มขึ้น ทำให้เทคโนโลยีสามารถปรับตัวให้เข้ากับสภาพการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่เกิดขึ้นได้
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| มีองค์ความรู้จากผู้ปฏิบัติจริง/เห็นผลจริง |
| เทคโนโลยีนี้เผยแพร่หลายช่องทาง |
| มีสถานที่และอุปกรณ์พร้อมในการเผยแพร่ |
| มีองค์ความรู้จากผู้ปฏิบัติจริง/เห็นผลจริง |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| วิธีการ/ขั้นตอนการผลิตไม่ยุ่งยากซับซ้อน |
| วิธีการใช้ นำไปใช้ได้ง่าย สะดวกไม่ยุงยาก |
| - |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| ไม่ทราบปริมาณธาตุอาหารพืชในน้ำหมัก | ให้มีกาตรวจวิเคราะห์ |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| เกษตรกรยังขาดแรงจูงใจในการทำ | ให้เกษตรกรเห็นว่าลดต้นทุนได้อย่างไร ส่งผลดีต่อพืชอย่างไร |
|
การใช้เทคโนโลยีนี้ เเกษตรกรที่จะปฏิบัติตามต้องมีความเชื่อมั่น ขยันและอดทน...เนื่องจากต้องใช้เวล าในการพิสูจน์ให้เก็นผลจากการใช้ |
รัฐและเกษตรกรต้องร่วมมือกันสร้างความเชื่อมั่นให้แก่เกษตรกร ด้วยการให้ความรู้ และเผยแพร่ |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
5 ราย
- interviews with land users
5 ราย
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
10/10/2018
Comments:
-
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
-
Available from where? Costs?
-
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
-
URL:
-
7.4 General comments
-
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules