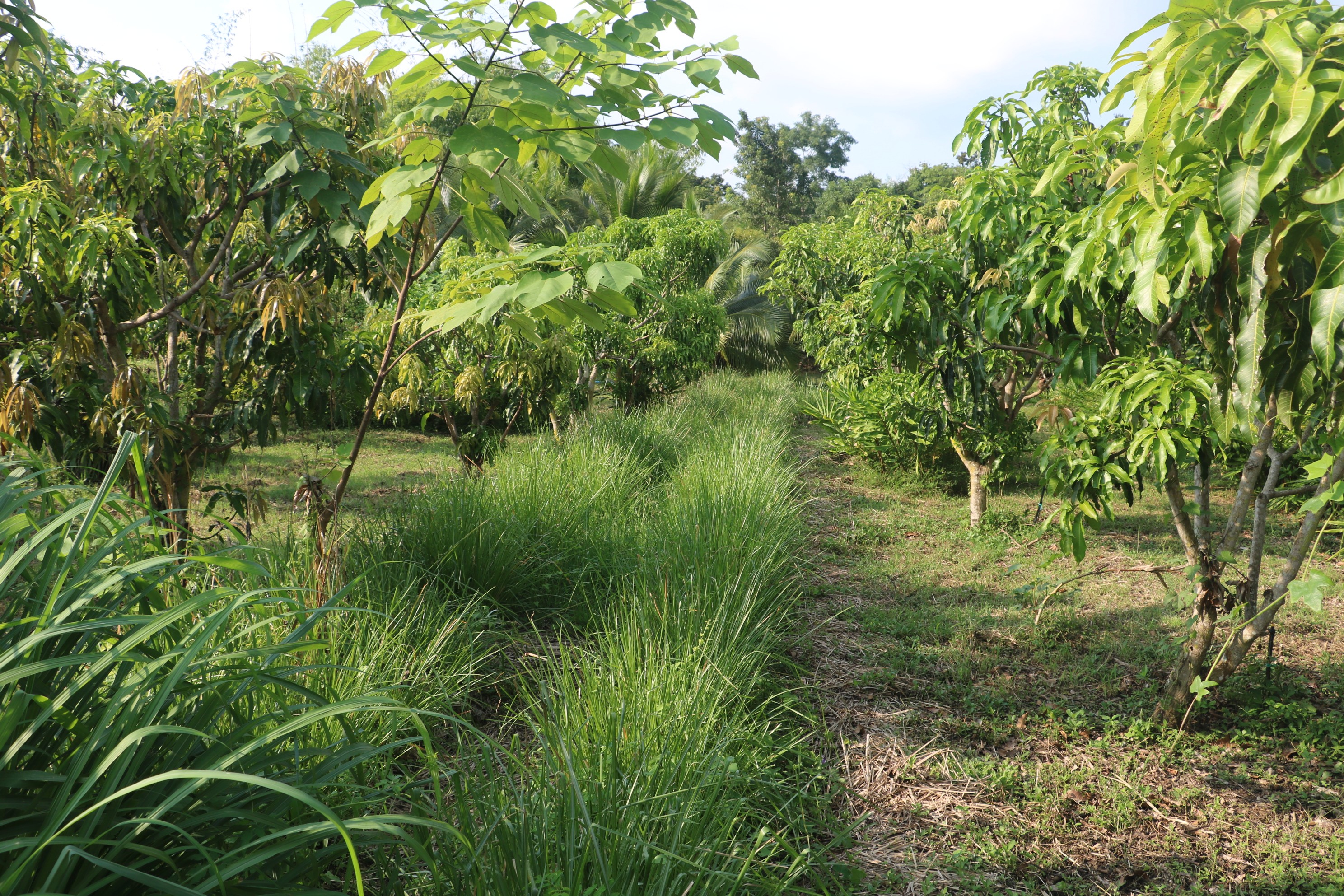
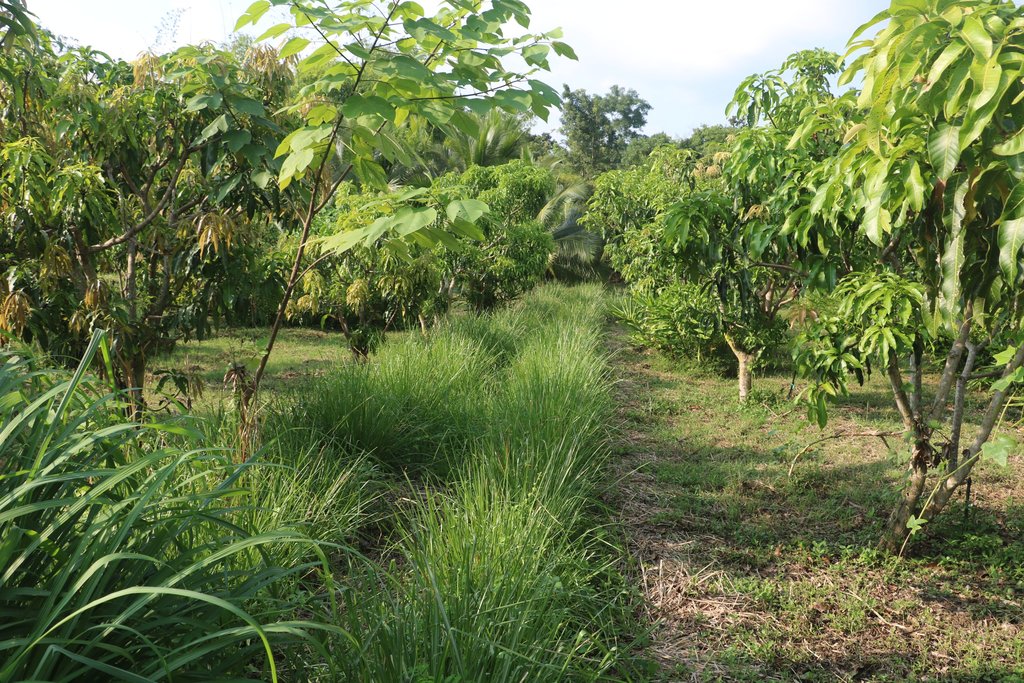
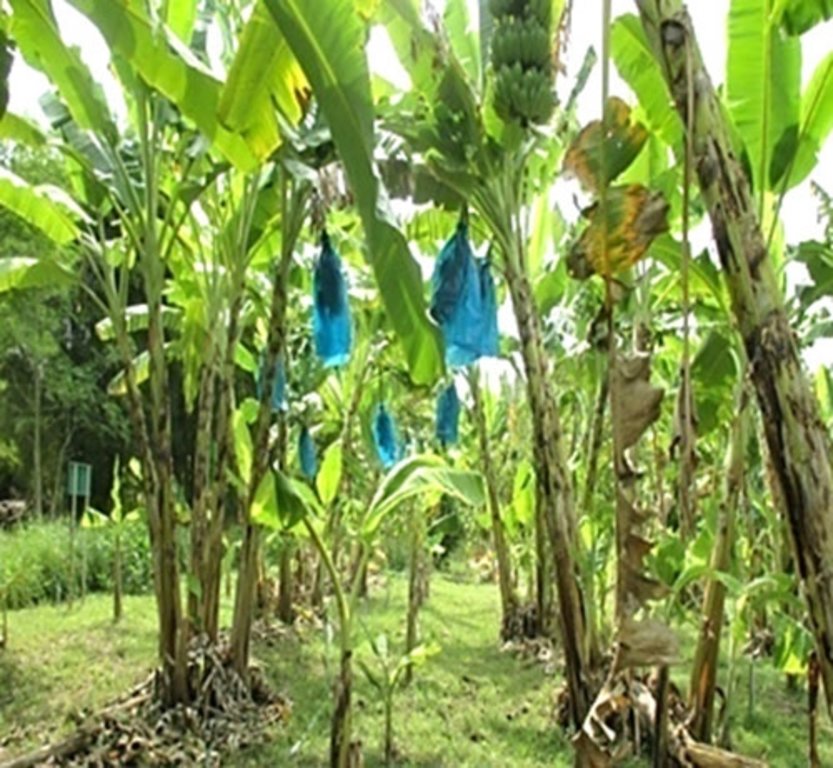
เกษตรอินทรีย์บนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา Organic Farm on Moderate Hillside Slope [Thailand]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Kukiat SOITONG
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
-
technologies_4242 - Thailand
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
land user:
มงคลกาญจนคุณ นายพัฒน์พงษ์
-
Thailand
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Ja
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
Nee
Comments:
เกษตรกรสามารถประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยีได้ด้วยตนเอง
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

กลุ่มเกษตรธรรมชาติสัมพันธ์ [Thailand]
กลุ่มเกษตรธรรมชาติสัมพันธ์ เป็นการรวมกลุ่มของเกษตรกรที่ดำเนินการทำเกษตรอินทรีย์บนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา โดยได้จัดให้มีศูนย์ถ่ายทอดด้านเกษตรอินทรีย เพื่อเป็นแหล่งศึกษา เรียนรู้ร่วมกัน
- Compiler: Kukiat SOITONG
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
เกษตรอินทรีย์บนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา เป็นการจัดการพื้นที่ ดินและน้ำ ให้สามารถผลิตสินค้าทางการเกษตรที่ปลอดภัยได้อย่างยั่งยืน
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
(1)เทคโนโลยีนำไปใช้ที่ไหน(สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
พื้นที่ทำการเกษตร ที่เป็นที่ลาดเชิงเขา ดินมีลักษณะเป็นดินร่วนปนกรวด ง่ายต่อการชะล้างพังทลาย และยังขาดมาตรการอนุรักษ์ดินและน้ำ ทำให้ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ของดินลดลง มีการทำการเกษตรเชิงเดี่ยว ได้แก่ การปลูกข้าวโพดเลี้ยงสัตว์ ที่มีการใช้ปัจจัยการผลิตและใช้เงินลงทุนมาก เช่น ปุ๋ยเคมี สารกำจัดศัตรูพืชและวัชพืช อย่างต่อเนื่องเป็นระยะเวลานาน ทำให้เกิดสารพิษตกค้างในผลผลิต เป็นอันตรายต่อสุขภาพ
)(2) อะไรคือลักษณะหรือองค์ประกอบที่สำคัญของเทคโนโลยี
องค์ประกอบที่สำคัญของเทคโนโลยีระบบเกษตรอินทรียบนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา
1.สร้างความอุดมสมบูรณ์ให้กับดิน ด้วยการใช้พืชปุ๋ยสด(ปอเทือง สลับกับถั่วพร้า)และการใช้ ปุ๋ยหมัก
2.การจัดการพื้นที่ โดย ปลูกหญ้าแฝก บนที่ลาดเชิงเขา เพื่อชะลอการไหลของน้ำ และแบ่งพื้นที่ทำการเกษตรตามความลาดชัน
3. สร้างแหล่งน้ำในพื้นที่ เช่น ขุดสระน้ำ หรือ ขุดบ่อบาดาล
4. การจัดทำ Buffer Zone
5. การจัดการ โรคและแมลง ด้วยสารชีวภัณฑ์
6. กำจัดวัชพืช ด้วยวิธีการตัดหญ้าคลุมดิน
(3)อะไรคือจุดประสงค์หรือหน้าที่ของเทคโนโลยี
จุดประสงค์ของ เทคโนโลยีระบบเกษตรอินทรียบนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา
1 เพื่อฟื้นฟูความอุดมสมบูรณ์ของดิน สร้างสมดุลให้กับระบบนิเวศน์ และเพิ่มความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
2. เพื่อลดต้นทุนการผลิตและเพิ่มรายได้
3. เพื่อให้มีสุขภาพดีขึ้น
(4)กิจกรรมที่สำคัญหรือปัจจัยการผลิตที่จำเป็นในการจัดตั้งหรือบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี
ขั้นตอนการปฏิบัติในการจัดทำระบบเกษตรอินทรียบนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา
1.สร้างความอุดมสมบูรณ์ให้กับดิน
1.1 ปลูกพืชปุ๋ยสด โดยใช้ปอเทือง สลับกับถั่วพร้า ปลูก 6 ครั้งต่อปี ต่อเนื่อง 2 ปี
1.1.1 การปลูกปอเทือง
ใช้วิธีการปลูกแบบหว่าน ใช้เมล็ดประมาณ 5 กิโลกรัม/ไร่ แล้วทำการคราดกลบตื้นๆ หลังการปลูกแล้ว ประมาณ 50 -60 วัน หลังเมล็ดงอก ปอเทืองจะเริ่มออกดอก แล้วทำการไถกลบ หลังจากนั้น ใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ พด. 2 (หมักจากผักและผลไม้) ฉีดพ่นให้ทั่วแปลง อัตรา 5 ลิตรต่อไร่ผสมน้ำ 100 ลิตร แล้วปล่อยให้ย่อยสลายประมาณ 12 -15 วัน
1.1.2 วิธีการปลูกถั่วพร้า
ใช้วิธีการปลูกแบบโรยเป็นแถว โดยใช้เมล็ดโรยลงในแถว ซึ่งมีระยะระหว่างแถว 75 – 100เซนติเมตร เมื่อโรยเมล็ดลงในแถวแล้วกลบเมล็ดด้วยดินบาง ๆ ในอัตรา 5 - 8 กิโลกรัมต่อไร่ หลังการปลูกแล้ว ประมาณ 50 -60 วัน หลังเมล็ดงอก ถั่วพร้าจะเริ่มออกดอก แล้วทำการไถกลบ หลังจากนั้น ใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ พด. 2 (หมักจากผักและผลไม้) ฉีดพ่นให้ทั่วแปลง อัตรา 5 ลิตรต่อไร่ผสมน้ำ 100 ลิตร แล้วปล่อยให้ย่อยสลายประมาณ 12 -15 วัน
1.2 ใช้ปุ๋ยหมักจากวัสดุเหลือใช้ในฟาร์ม และใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ
2. การจัดการพื้นที่
2.1 ปลูกหญ้าแฝก บนที่ลาดเชิงเขา เพื่อชะลอการไหลของน้ำ ดักตะกอนดิน และเป็นการควบคุมแมลงศัตรูพืช
2.2 ให้จัดการพื้นที่และปลูกพืชตามความลาดชัน เป็น 2 ระดับคือ
-ที่ลาดเชิงเขา ปลูกไผ่ ไม้ผล ป่าใช้สอย
-ที่ราบ ปลูกกล้วย มะละกอ พืชผักสวนครัว ฝรั่ง สมุนไพร ไม้ผล
3. สร้างแหล่งน้ำในพื้นที่ โดยขุดสระน้ำ และขุดบ่อบาดาล เพื่อใช้ในการอุปโภค และทำการเกษตรครอบคลุมพื้นที่ 34 ไร่ โดยการใช้ระบบสปริงเกอร์ และให้น้ำตามความลาดชันของพื้นที่ นอกจากนี้ มีการให้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ ผ่านระบบสปริงเกอร์
4. การจัดทำ Buffer Zone โดยปลูกไผ่ ป่าไม้ใช้สอย และขึงสแลนสูง 2.50 เมตร ในด้านที่ไม่สามารถปลูกต้นไม้ได้ เพื่อป้องกันสารเคมีที่ปลิวมาจากด้านข้าง
5. การจัดการ โรคและแมลง ใช้สารชีวภัณฑ์ เช่น น้ำหมักชีวภาพ พ.ด 7
6. กำจัดวัชพืช ด้วยวิธีการตัดหญ้าคลุมดิน เพื่อรักษาความชื้นในดินและเพิ่มอินทรยวัตถุให้แก่ดิน
7 การจัดทำบัญชีฟาร์ม เพื่อให้ทราบต้นทุน กำไร-ขาดทุน ในการบริหารและจัดการฟาร์ม
5)ประโยชน์ที่ได้รับหรือผลกระทบของเทคโนโลยีคืออะไรบ้าง
1 พื้นที่ที่ทำการเกษตรมีความอุดมสมบูรณ์มากขึ้น
2 สามารถลดต้นทุนการผลิตได้
3 ผลผลิตทางการเกษตรที่ได้มีความปลอดภัย ไม่มีสารพิษตกค้าง ทำให้ขายผลผลิตได้ราคาดีขึ้น
4. ทำให้สุขภาพของเกษตรกร ดีขึ้น
3)โอกาส
3.1 ทำให้เกิดความร่วมมือของผู้ผลิตกับหน่วยงานต่างๆ รวมทั้งภาครัฐที่เข้ามาร่วมสนับสนุน
3.2 มีโอกาสได้รับการรับรองมาตรฐานสินค้า ทำให้เป็นที่ต้องการของตลาด
3.3 รัฐมีนโยบายสนันสนุนด้านเกษตรอินทรีย์ ทำให้เกิดความร่วมมือของภาครัฐและเกษตรกร สร้างเสริมขีดความสามารถในการแข่งขันได้มากขึ้น
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
-
Location:
-
Name of videographer:
-
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Thailand
Region/ State/ Province:
กาญจนบุรี
Further specification of location:
บ้านทุ่งนา ม.4 ต.หนองเป็ด อ.ศรีสวัสดิ์ จ.กาญจนบุรี
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
-
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2004
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
กรมส่งเสริมการเกษตร
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
- มะม่วง มะละกอ มะพร้าว ฝรั่ง เงาะ ไผ่

Grazing land
Comments:
-
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Comments:
-
3.4 Water supply
other (e.g. post-flooding):
- บ่อบาดาล
Comments:
-
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- windbreak/ shelterbelt
- integrated crop-livestock management
- integrated soil fertility management
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
Comments:
-
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

chemical soil deterioration
- Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)

biological degradation
- Bq: quantity/ biomass decline
Comments:
-
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
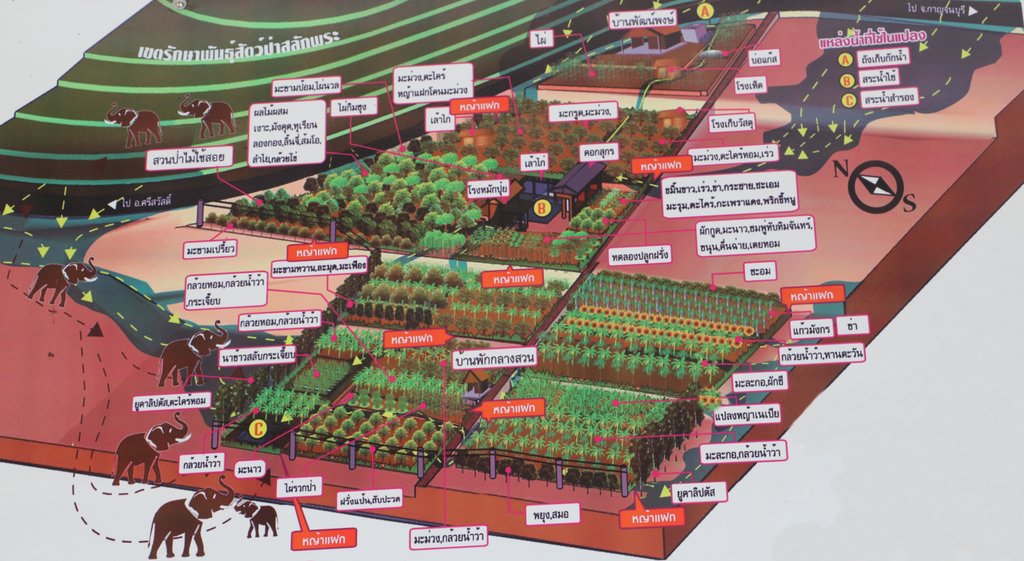
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
พื้นที่การเกษตร ขนาด 39 ไร่ ทิศเหนือติดเขตรักษาพรรณสัตว์ป่าสลักพระ ทิศใต้ติดถนน
ขั้นตอนการปฏิบัติในการจัดทำระบบเกษตรอินทรียบนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา
2.สร้างความอุดมสมบูรณ์ให้กับดิน
1.1 ปลูกพืชปุ๋ยสด โดยใช้ปอเทือง สลับกับถั่วพร้า ปลูก 6 ครั้งต่อปี ต่อเนื่อง 2 ปี
1.1.1 การปลูกปอเทือง
ใช้วิธีการปลูกแบบหว่าน ใช้เมล็ดประมาณ 5 กิโลกรัม/ไร่ แล้วทำการคราดกลบตื้นๆ หลังการปลูกแล้ว ประมาณ 50 -60 วัน หลังเมล็ดงอก ปอเทืองจะเริ่มออกดอก แล้วทำการไถกลบ หลังจากนั้น ใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ พด. 2 (หมักจากผักและผลไม้) ฉีดพ่นให้ทั่วแปลง อัตรา 5 ลิตรต่อไร่ผสมน้ำ 100 ลิตร แล้วปล่อยให้ย่อยสลายประมาณ 12 -15 วัน
1.1.2 วิธีการปลูกถั่วพร้า
ใช้วิธีการปลูกแบบโรยเป็นแถว โดยใช้เมล็ดโรยลงในแถว ซึ่งมีระยะระหว่างแถว 75 – 100เซนติเมตร เมื่อโรยเมล็ดลงในแถวแล้วกลบเมล็ดด้วยดินบาง ๆ ในอัตรา 5 - 8 กิโลกรัมต่อไร่ หลังการปลูกแล้ว ประมาณ 50 -60 วัน หลังเมล็ดงอก ถั่วพร้าจะเริ่มออกดอก แล้วทำการไถกลบ หลังจากนั้น ใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ พด. 2 (หมักจากผักและผลไม้) ฉีดพ่นให้ทั่วแปลง อัตรา 5 ลิตรต่อไร่ผสมน้ำ 100 ลิตร แล้วปล่อยให้ย่อยสลายประมาณ 12 -15 วัน
1.2 ใช้ปุ๋ยหมักจากวัสดุเหลือใช้ในฟาร์ม และใช้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ
2. การจัดการพื้นที่
2.1 ปลูกหญ้าแฝก บนที่ลาดเชิงเขา เพื่อชะลอการไหลของน้ำ ดักตะกอนดิน และเป็นการควบคุมแมลงศัตรูพืช
2.2 ให้จัดการพื้นที่และปลูกพืชตามความลาดชัน เป็น 2 ระดับคือ
-ที่ลาดเชิงเขา ปลูกไผ่ ไม้ผล ป่าใช้สอย
-ที่ราบ ปลูกกล้วย มะละกอ พืชผักสวนครัว ฝรั่ง สมุนไพร ไม้ผล
3. สร้างแหล่งน้ำในพื้นที่ โดยขุดสระน้ำ และขุดบ่อบาดาล เพื่อใช้ในการอุปโภค และทำการเกษตรครอบคลุมพื้นที่ 34 ไร่ โดยการใช้ระบบสปริงเกอร์ และให้น้ำตามความลาดชันของพื้นที่ นอกจากนี้ มีการให้น้ำหมักชีวภาพ ผ่านระบบสปริงเกอร์
4. การจัดทำ Buffer Zone โดยปลูกไผ่ ป่าไม้ใช้สอย และขึงสแลนสูง 2.50 เมตร ในด้านที่ไม่สามารถปลูกต้นไม้ได้ เพื่อป้องกันสารเคมีที่ปลิวมาจากด้านข้าง
5. การจัดการ โรคและแมลง ใช้สารชีวภัณฑ์ เช่น น้ำหมักชีวภาพ พ.ด 7
6. กำจัดวัชพืช ด้วยวิธีการตัดหญ้าคลุมดิน เพื่อรักษาความชื้นในดินและเพิ่มอินทรยวัตถุให้แก่ดิน
7 การจัดทำบัญชีฟาร์ม เพื่อให้ทราบต้นทุน กำไร-ขาดทุน ในการบริหารและจัดการฟาร์ม
Author:
-
Date:
2016
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
39 ไร่
other/ national currency (specify):
Thai Baht
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
32.0
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
300บาท
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ปรับปรุง | ก่อนปลูก |
| 2. | ระบบน้ำ | ฤดูแล้ง |
| 3. | การกำจัดวัชพืช | ระหว่างปลูก |
| 4. | การกำจัดศัตรูพืช | ระหว่างปลูก |
| 5. | แนวกันชน | ฤดูฝน |
| 6. | การใช้หญ้าแฝก | ฤดูฝน |
| 7. | การทำบัญชีฟาร์ม | ตลอดปี |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | 1.1การปลูกปอเทือง | ครั้ง | 2.0 | 900.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 1.2สับกลบปอเทือง | ครั้ง | 2.0 | 900.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 1.3ฉีดน้ำหมักชีวภาพ | ครั้ง | 2.0 | 900.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 1.4ใส่ปุ๋ยหมัก | ครั้ง | 1.0 | 1800.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | 1.5ใส่ปูนโดโลไมท์ | ครั้ง | 1.0 | 1600.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | 2.ใส่ปุ๋ยหมักปรับปรุงดิน | ครั้ง | 1.0 | 9000.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | 3.กำจัดวัชพืช | ครั้ง | 8.0 | 9600.0 | 76800.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | 4.กำจัดศัตรูพืช | ครั้ง | 24.0 | 600.0 | 14400.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | 5.ใช้ตาข่ายพรางแสงเป็นแนวกันชน | ม้วน | 2.0 | 600.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | 6.ปลูกต้นไม้เป็นแนวกันชน | ครั้ง | 2.0 | 600.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | 7.ดูแลรักษาตัดแต่งหญ้าแฝก | ครั้ง | 8.0 | 900.0 | 7200.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | อุปกรณ์ต่อบ่อบาดาล | บ่อ | 3.0 | 30000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ตาข่ายพรางแสง | ม้วน | 2.0 | 1700.0 | 3400.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ค่าเมล็ดพันธุ์ปอเทือง | กก. | 63.0 | 33.0 | 2079.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | ค่าต้นไม้ปลูกแนวกันชน | ต้น | 100.0 | 10.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | พันธุ์กล้าหญ้าแฝก | กล้า | 150000.0 | 0.73 | 109500.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | 1.การปรับปรุงพื้นที่ทำการเกษตร | |||||
| Fertilizers and biocides | 1.1น้ำหมักชีวภาพ | ลิตร | 50.0 | 20.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | 1.2โดโลไมท์ | กก. | 4200.0 | 4.0 | 16800.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | 2.ปุ๋ยหมักปรับปรุงดิน | กก. | 5500.0 | 4.0 | 22000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | 3.สารไล่แมลง | ลิตร | 50.0 | 30.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 1.การปจัดการพื้นที่ทำการเกษตร | |||||
| Other | 1.1ค่าไถพื้นที่ | ไร่ | 21.0 | 500.0 | 10500.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 2.บ่อบาดาล | บ่อ | 3.0 | 70000.0 | 210000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 586379.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 18324.34 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
-
Comments:
-
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. ระบบน้ำ | 2 ครั้งต่อปี ก่อน-หลังฤดูฝน |
| 2. | 2.การกำจัดวัชพืช | 12 ครั้งต่อปี ระหว่างฤดูปลูกพืช |
| 3. | 3. การกำจัดศัตรูพืช | 12 ครั้งต่อปีระหว่างฤดูปลูกพืช |
| 4. | 4.แนวกันชน | 2 ครั้งต่อปี ก่อนและหลังฤดูปลูก |
| 5. | 5.การใช้หญ้าแฝก | 12 ครั้งต่อปี ระหว่างฤดูปลูก |
Comments:
-
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | 1.ค่ากำจัดวัชพืชในแปลง | ครั้ง | 8.0 | 1200.0 | 9600.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 2.ค่ากำจัดศัตรูพืช | ครั้ง | 24.0 | 600.0 | 14400.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 3.ค่าซ่อมแซมแนวกันชน | ครั้ง | 6.0 | 300.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | 4.ค่าตัดแต่งแนวหญ้าแฝก | ครั้ง | 8.0 | 900.0 | 7200.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | 1.ค่าไฟฟ้าเกี่ยวกับระบบน้ำ | เดือน | 12.0 | 500.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 39000.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1218.75 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
-
Comments:
-
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
ค่าสาธารณูปโภค1.ค่าไฟฟ้า 2. ค่าเจาะบ่อบาดาลพร้อมวางระบบน้ำ 3. ค่าแรงงานและขนส่ง
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
1600.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
เป็นพื้นที่เงาฝน (rain shadow) ทำให้มีฝนตกน้อย อากาศร้อนจัดในฤดูร้อน และหนาวจัดในฤดูหนาว โดยมีอุณหภูมิสูงสุดประมาณ 44-45 องศาเซล-เซียสในเดือนเมษายน อุณหภูมิต่ำสุดในเดือนธันวาคมประมาณ 8-9 องศาเซลเซียส และอุณหภูมิเฉลี่ยประมาณ 27 องศาเซล-เซียส ช่วงฤดูฝนเริ่มตกจากกลางเดือนเมษายน และสิ้นสุดในช่วงกลางเดือนตุลาคม
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
-
Agro-climatic zone
- humid
-
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
Comments and further specifications on topography:
พื้นที่ส่วนใหญ่เป็นที่ราบบนภูเขา ติดอ่างเก็บน้ำเขื่อนศรีนครินทร์ สภาพภูมิประเทศเป็นภูเขาหินปูนและหินตะกอนเป็นส่วนใหญ่ ระดับความสูง สูงสุดประมาณ 1,100 เมตร จากระดับน้ำทะเลปานกลาง โดยมีความสูงเฉลี่ยประมาณ 400 เมตร
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
Is water salinity a problem?
Nee
Is flooding of the area occurring?
Nee
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
-
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
-
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
-
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- large-scale
Comments:
-
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
Specify:
-
Comments:
-
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
Comments:
-
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
-
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
-
animal production
Comments/ specify:
-
product diversity
Comments/ specify:
-
land management
Comments/ specify:
-
Water availability and quality
drinking water quality
Comments/ specify:
-
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
Comments/ specify:
-
farm income
Comments/ specify:
-
diversity of income sources
workload
Comments/ specify:
-
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Comments/ specify:
-
health situation
Comments/ specify:
-
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
-
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Comments/ specify:
-
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
-
soil loss
Comments/ specify:
-
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Comments/ specify:
-
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
-
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
plant diversity
Comments/ specify:
-
Climate and disaster risk reduction
drought impacts
Comments/ specify:
-
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
Comments/ specify:
-
fire risk
Comments/ specify:
-
wind velocity
Comments/ specify:
-
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
-
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream siltation
Comments/ specify:
-
groundwater/ river pollution
Comments/ specify:
-
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
-
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
-
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | decrease | moderately | |
| seasonal temperature | decrease | moderately | |
| annual rainfall | moderately | ||
| seasonal rainfall | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | moderately |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
| forest fire | moderately |
Biological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| epidemic diseases | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| extended growing period | not well |
| reduced growing period | well |
Comments:
-
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
neutral/ balanced
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
-
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
10 ครัวเรือน
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
-
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
Ja
other (specify):
ปรับเปลี่ยนเรื่องค่าใช้จ่ายต้องประหยัดมากขึ้น ต้องมีความละเอียดมากขึ้น (สังเกตมากขึ้น)
Specify adaptation of the Technology (design, material/ species, etc.):
ปรับลดการใช้พลังงานโดยการใช้โซล่าร์เซลล์ในการใช้น้ำบาดาล
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| 1.1 พื้นที่ที่ทำการเกษตรมีความอุดมสมบูรณ์มากขึ้น |
| 1.2 สามารถลดต้นทุนการผลิตได้ |
| 1.3 ผลผลิตทางการเกษตรที่ได้มีความปลอดภัยไม่มีสารพิษตกค้าง |
| 2.1 ขายผลผลิตได้ราคาดีขึ้น |
| 2.2 ทำให้สุขภาพร่างกายแข็งแรง |
| 2.3 เป็นพื้นที่ที่สามารถส่งผลผลิตสู่ตลาดอย่างง่าย เส้นทางคมนาคมสะดวก |
| 2.4 เกษตรกรได้รับความรู้และมีประสบการณ์ในการทำการเกษตรดีกว่าเกษตรกรรายอื่นๆ |
| 3.1 มีการร่วมมือของผู้ผลิตกับหน่วยงานต่างๆ รวมทั้งภาครัฐที่เข้ามาร่วมสนับสนุน |
| 3.2 ได้รับตราสัญลักษณ์รับรองมาตรฐานสินค้าทำให้ผู้บริโภคเชื่อมั่นเป็นที่ต้องการของตลาด |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| 1)ได้มีนโยบายของภาครัฐที่ช่วยสนันสนุนด้านการเกษตรอินทรีย์ |
| 2)ได้มีการร่วมมือของภาครัฐและผู้ผลิตทำให้สามารถแข่งขันได้มากขึ้น |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| 1.1 ต้องใช้เวลาเพิ่มมากขึ้นในการทำการเกษตรแบบระบบอินทรีย์ | 1.1 หานวัตรกรรมและเทคโนโลยีต่างๆเข้ามาช่วย |
| 1.2 ต้องทำแนวกันชนแปลงตัวเองเพิ่มมากขึ้นเพื่อป้องกันสารพิษของแปลงเพื่อนบ้าน | 1.2 ต้องมีการออกกฏหมายคุ้มครองสำหรับการทำเกษตรอินทรีย์ |
| 2.1 ต้องเสียเวลานานและมีหลายขั้นตอนในการขอใบรับรองมาตรฐานเกษตรอินทรีย์ | 2.1 ให้หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องปรับหลักเกณฑ์ทำให้เหมาะสม |
| 2.2 ต้องใช้เวลาและแรงงานพร้อมจัดหาวัสดุในการทำปุ๋ยอิทรีย์ใช้เอง | 2.2 หาวัสดุในพื้นที่นำมาใช้เพื่อลดต้นทุนการผลิต |
| 3.1 ผู้บริโภคยังสับสนไม่รู้ว่าเกษตรอินทรีย์คืออะไร | 3.1 ให้ความรู้เผยแพร่ประชาสัมพันธ์ให้มากขึ้น |
| 3.2อุปสรรคเรื่องของราคา เนื่องจากมีต้นทุนสูง | 3.2 ให้หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องช่วยประชาสัมพันธ์และหาตลาดรองรับ |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| 1)เกษตรกรยังขาดการวางแผนในเรื่องของการใช้ที่ดินอย่างเป็นระบบ | 1.ให้ความรู้และข้อมูลต่างๆมากขึ้น |
| 2.เกษตรกรยังขาดความรู้ความเข้าใจในเรื่องของการปรับปรุงบำรุงดิน | 2.ให้หน่วยงานหรือผู้ที่เกี่ยวข้องให้ความรู้ที่ครอบคลุมรอบด้าน |
| 3)เกษตรกรยังขาดความเข้าใจในเรื่องของความต่อเนื่องของการผลิตและการตลาด | 3. ให้เรียนรู้ในเรื่องของการผลิตและการตลาดให้รู้ทันเหตุการณ์ |
| 4)การกำหนดราคายังเป็นปัญหาใหญ่เนื่องจากมีการผันผวนของราคราอยู่มาก | 4.ให้ภาครัฐหรือหน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องช่วยกำกับดูแลอย่างแท้จริง |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
-
Available from where? Costs?
-
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
-
7.4 General comments
-
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

กลุ่มเกษตรธรรมชาติสัมพันธ์ [Thailand]
กลุ่มเกษตรธรรมชาติสัมพันธ์ เป็นการรวมกลุ่มของเกษตรกรที่ดำเนินการทำเกษตรอินทรีย์บนพื้นที่ลาดเชิงเขา โดยได้จัดให้มีศูนย์ถ่ายทอดด้านเกษตรอินทรีย เพื่อเป็นแหล่งศึกษา เรียนรู้ร่วมกัน
- Compiler: Kukiat SOITONG
Modules
No modules