Spontaneous spread [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Ceris A. Jones
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2627 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mwaniki JM
mwanikijm2002@yahoo.com
Ministry of Agriculture/Soil and Water Conservation Branch
Embu
كينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development of Kenya (MoA) - كينيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Agronomica - المملكة المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Système agroforestier à Grevillea [كينيا]
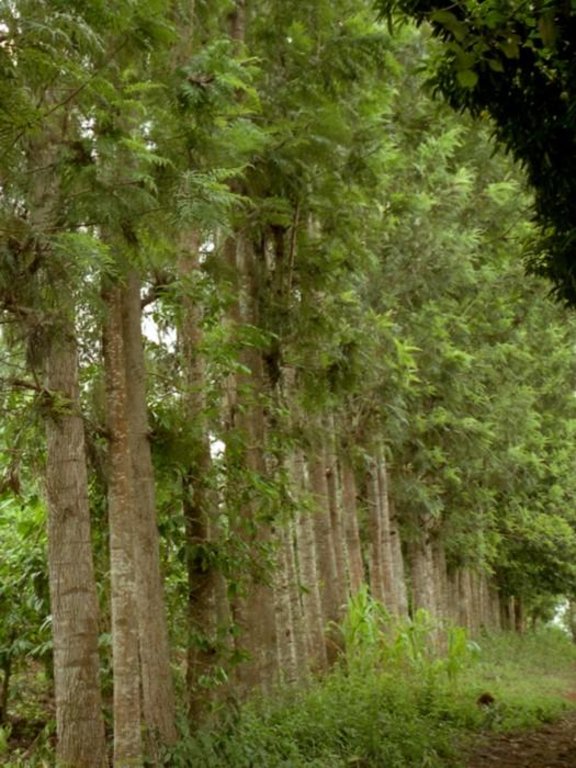
Les arbres de Grevillea robusta à usage multiples sont plantés le long les limites des champs, sur les talus des terraces et des fois dispersés dans les champs.
- جامع المعلومات: Ceris A. Jones
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
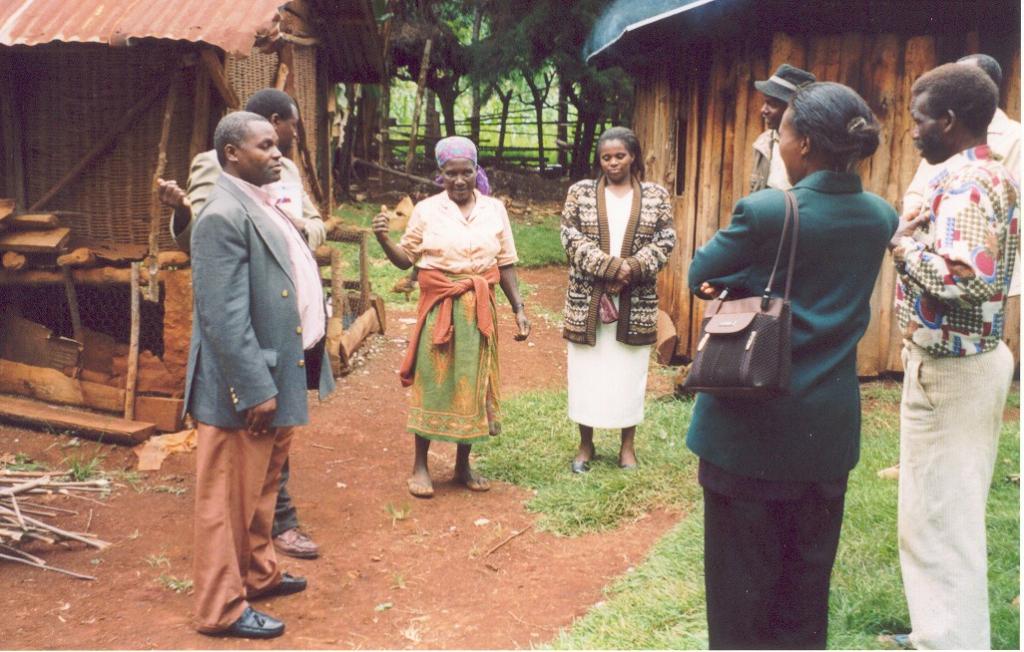
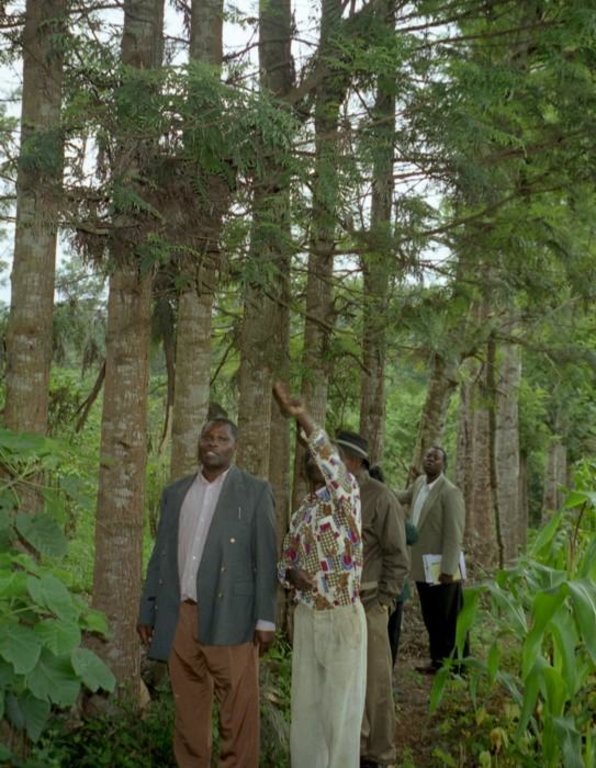
Spontaneous land users' initiative to meet household needs - especially firewood and timber - through planting Grevillea robusta trees as part of an agroforestry system.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
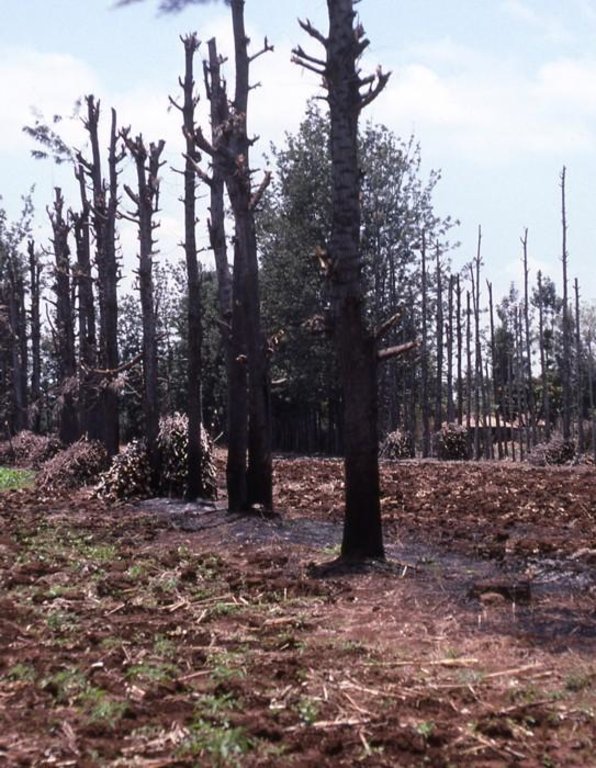
Aims / objectives: Grevillea robusta is a well-known shade tree, used in coffee and tea plantations in East Africa since the early part of the 20th century. While it originates from Australia, it was brought over from India and Sri Lanka by European settlers. Smallholder farmers in the highlands of Kenya noted that there was little or no competition between grevillea and neighbouring crops. Indeed this is one of the reasons it was so successful as a shade tree amongst plantation crops. Responding to the local lack of timber and firewood, due to the expansion of farmland into previously forested areas, smallholders took to planting grevillea, especially as a boundary tree, from the 1970s onwards. While the immediate effect of grevillea planting was to satisfy those needs for wood, the tree also helps in various ways to conserve land and improve the soil. This too was probably a reason for its spontaneous spread.
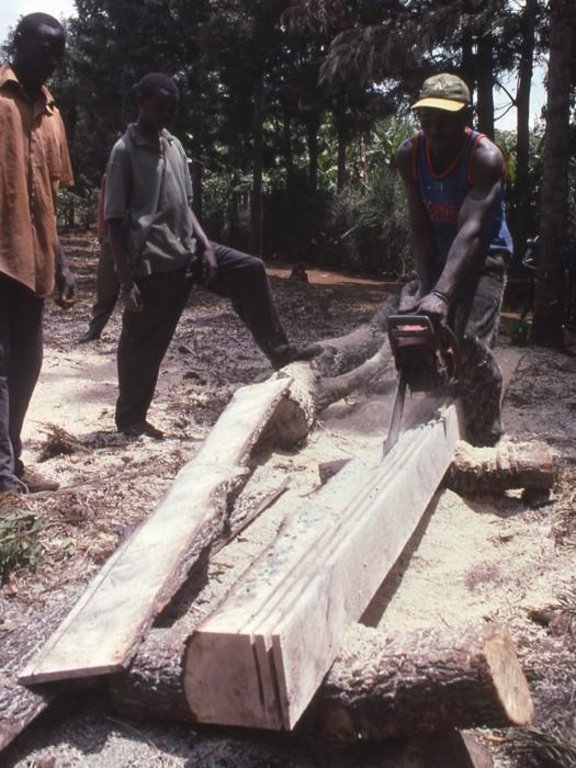
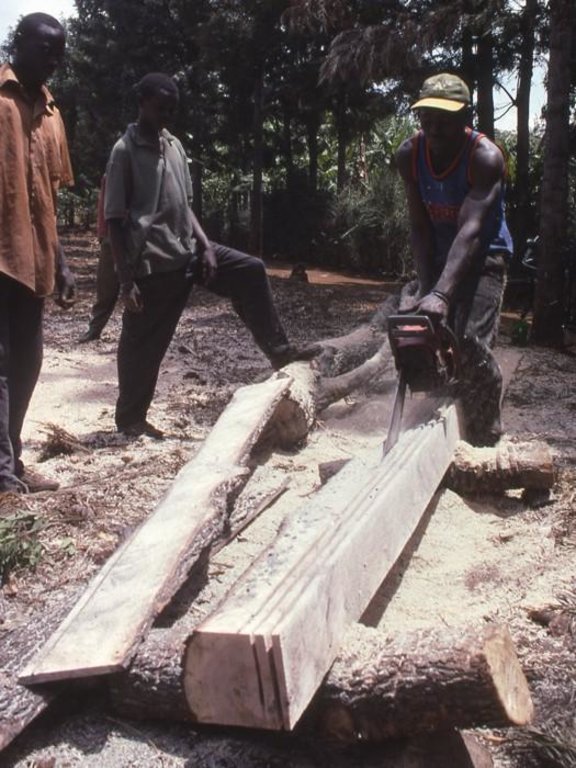
Methods: Because planting of grevillea requires few resources other than tools, even poor land users can readily adopt the technology. Although seedlings can be bought from local Government, NGO or private nurseries, it is also possible to collect ‘wildings’ (naturally generated seedlings) and plant these at minimal cost. The management of grevillea trees, once established, is important to their performance in the field, but the skills of thinning, and pollarding (pruning side branches for use) can be easily learned from neighbours. The success of the spontaneous spread of grevillea, basically through farmer-to-farmer exchange of knowledge, demonstrates that tree planting is not something that has always to be ‘pushed’ by outside agencies. Where smallholders perceive a need for trees and tree products - and an appropriate species is available - they will respond positively. However there is still an important ‘pulling’ role to be played by the Ministry of Agriculture’s extension agents and NGOs, especially through support for tree nurseries and for training to establish private tree nurseries.
2.3 صور عن النهج
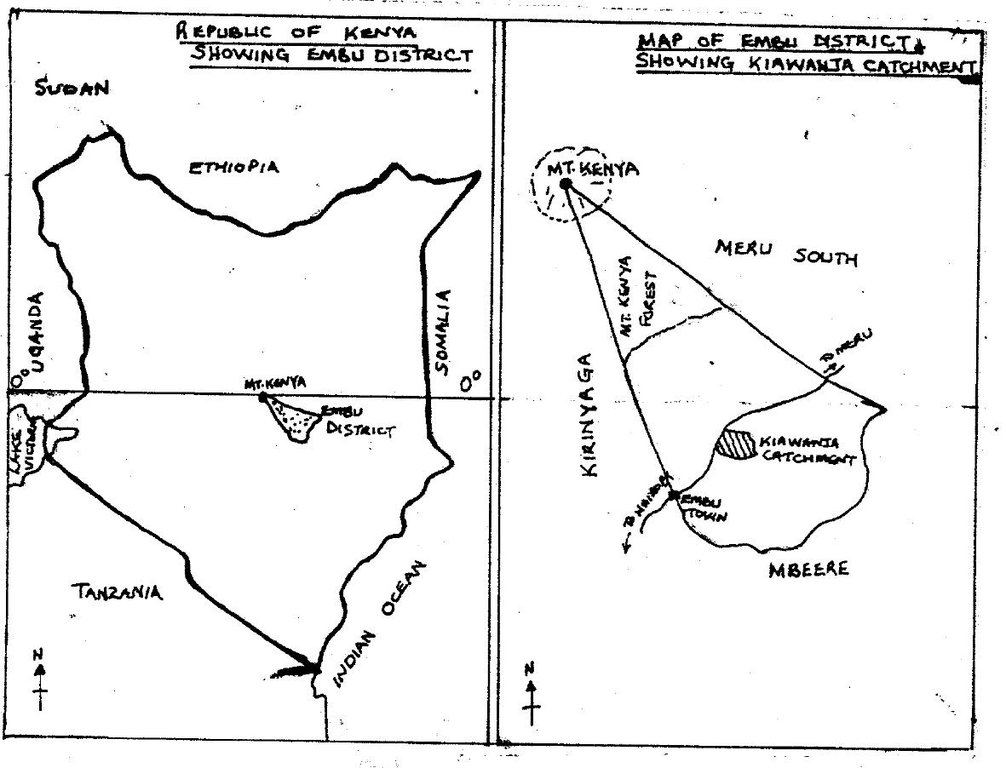
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Eastern Province
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
1971
2.7 نوع النهج
- تقليدي/أصلي
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Fencing, farm boundary marking, ornamental value, fuel wood supply, building materials provision)
- improve availability of tree products (fuelwood and wood for construction). - demarcate own land easily and cheaply (after land registration). - reduce land degradation. - increase land productivity. - improve household income
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - shortage of fuelwood and building materials, environmental degradation. - need for farm boundary marking. - lack of simple, widely applicable agroforestry recommendations
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
المعايير والقيم الاجتماعية /الثقافية/ الدينية
- معيق
Gender bias - women not expected to plant trees
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Although not directly related to this approach, intensive campaigns were conducted (by government and NGO's) to encourage gender balance with respect to tree planting
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
Shortage of tree seedlings and sourced from long distance
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Setting up of individual on-farm tree nurseries and collection of wildlings
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: Private land ownership has given farmers confidence to invest the land, and has also been a direct stimulus through the need to mark plot boundaries
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- معيق
Shortage of tree seedlings and sourced from long distance
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Setting up of individual on-farm tree nurseries and collection of wildlings.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
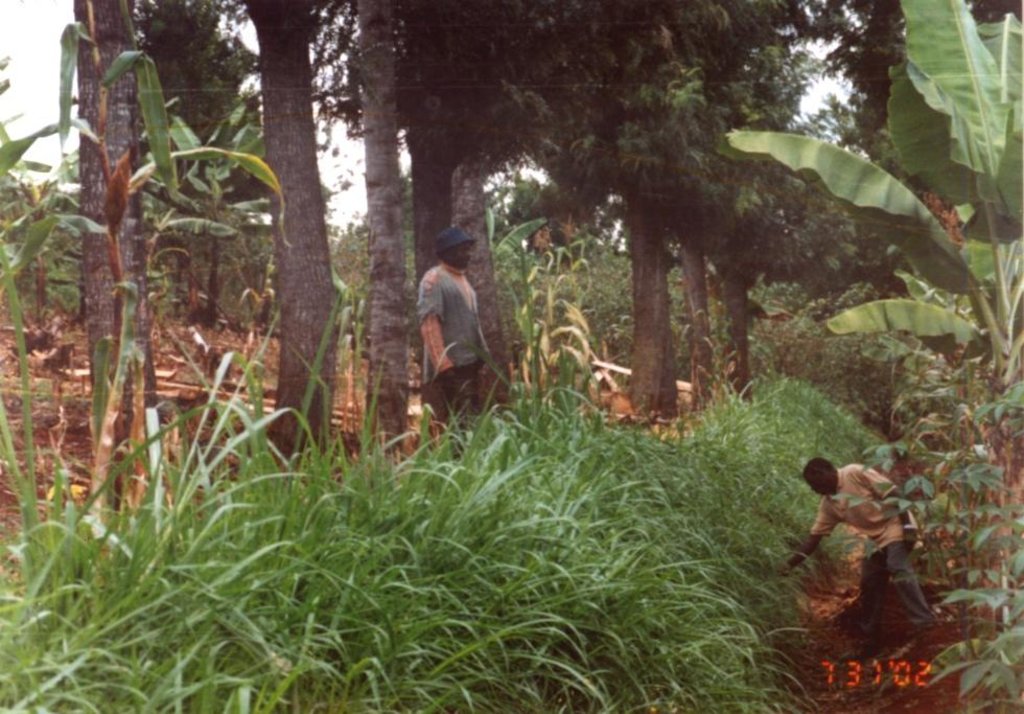
Working land users were mainly men (It was traditionally the role of men to plant trees. This is however changing ie other groups - women and youth - are now planting trees.)
Land users identified, purchased and planted their species of choice. However, at the same time, Grevillea seedlings were available at institutional (Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources) nurseries.
Traditionally men purchased, collected and planted trees. The men had greater access to and control of decisions on planting. The technology requires few resources, so that even poor land users have easily been able to decide to buy seedlings or collect wildlings and plant
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | التعبئة الذاتية | innovative individuals planting grevillea |
| التخطيط | التعبئة الذاتية | informal, individual plans |
| التنفيذ | التعبئة الذاتية | |
| الرصد/التقييم | سلبي | ad hoc observations by MoA; |
| Research | غير موجود | no activities |
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- مستخدمو الأراضي وحدهم (المبادرة الذاتية)
اشرح:
Land user-driven initiative by shortages/problems
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up). The land user decided on when and how to plant the trees.
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
المواضيع المغطاة:
Some demonstrations of benefits of tree planting by Government at provincial agricultural shows.
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
وصف/تعليقات:
Key elements: Informal farmer-to-farmer exchange of ideas and skills. Additionally, on national tree planting days, the government hands out seedlings. Grevillea planting has been encouraged during national campaigns (involving the Ministry of Agriculture, the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources, and NGOs) to encourage soil and w; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: other: individual land users 2) Advisory service was carried out through: other: individual land users
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; There is collaboration between Government extension service and KARI (Kenya Agricultural Research Institute) to further promote the technology
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- لا
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
technical aspects were ad hoc
economic / production aspects were ad hoc
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: None
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - Sponsored national tree planting days): 10.0%; other (Individual land user): 90.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
كلا
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- زراعة
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| بذور | ممول جزئيا | Individual land user. However, labour input was minimal |
إذا كان العمل من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي مدخلاً جوهريًا، فهل كان:
- تطوعي
التعليقات:
Individual land user. However, labour input was minimal
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
better soil and water management, increase in soil organic matter levels, nutrient pumping and reduced soil erosion.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Other extension programmes are utilising individual initiative as an entry point
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، صف كيف:
As land users developed this approach they can continue activities without support.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Strong land user 'ownership' of the approach. |
| Adaptability, flexibilityand simplicity since it is user driven |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Incentives not necessary |
| Valuable lessons from a farmer-driven success for development agencies that promote tree planting and agroforestry systems. |
| Very low inputs (resources) required. However there is still an important 'pulling' role to be played by the Ministry of Agriculture's extension agents and NGOs (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: More support for individual and government tree nurseries.) |
| Self-driven initiative (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: MoA extension staff and land users to encourage other farmers to be self-reliant.) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Lack of other stakeholders input | Encourage and inform land users on where to seek additional information consultations with SWC extensionists |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Adoption rates under such approaches depend on the number and efforts of innovators to stimulate others | SWC extensionists (Ministry and NGOs) to undertake more community mobilisation and awareness raising. |
| Approach is dependent on social cohesiveness for dissemination | promote more farmer interaction at community level |
| Poor collaboration and insitutional linkages | Encourage and create forums where stakeholders can share experiences and inform land users about where to seek additional information and assistance. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
NjiruN.N et al. 1998. PRA report of Kiawanja catchmentSee 'Grevillea agroforestry system' case study (QT KEN16) for technical references
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Nembure district
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Système agroforestier à Grevillea [كينيا]
Les arbres de Grevillea robusta à usage multiples sont plantés le long les limites des champs, sur les talus des terraces et des fois dispersés dans les champs.
- جامع المعلومات: Ceris A. Jones
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية