Maize strip tillage [سويسرا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Nicole Guedel
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Streifenfrässaat
technologies_1009 - سويسرا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
مستخدم الأرض:
Schneider Markus
+41 (0)62 963 26 26
schneider.agrar-service@gmx.ch
Schneider Agrarservice
Obergasse 20, 4922 Thunstetten, Switzerland
سويسرا
مستخدم الأرض:
Bangerter Roland
+41 (0) 32 384 50 35
rol.bangerter@bluewin.ch
Gisleren, 3266 Wiler bei Seedorf, Switzerland
سويسرا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bangerter-Gisleren - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Schneider Agrar-service - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
30/10/2008
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
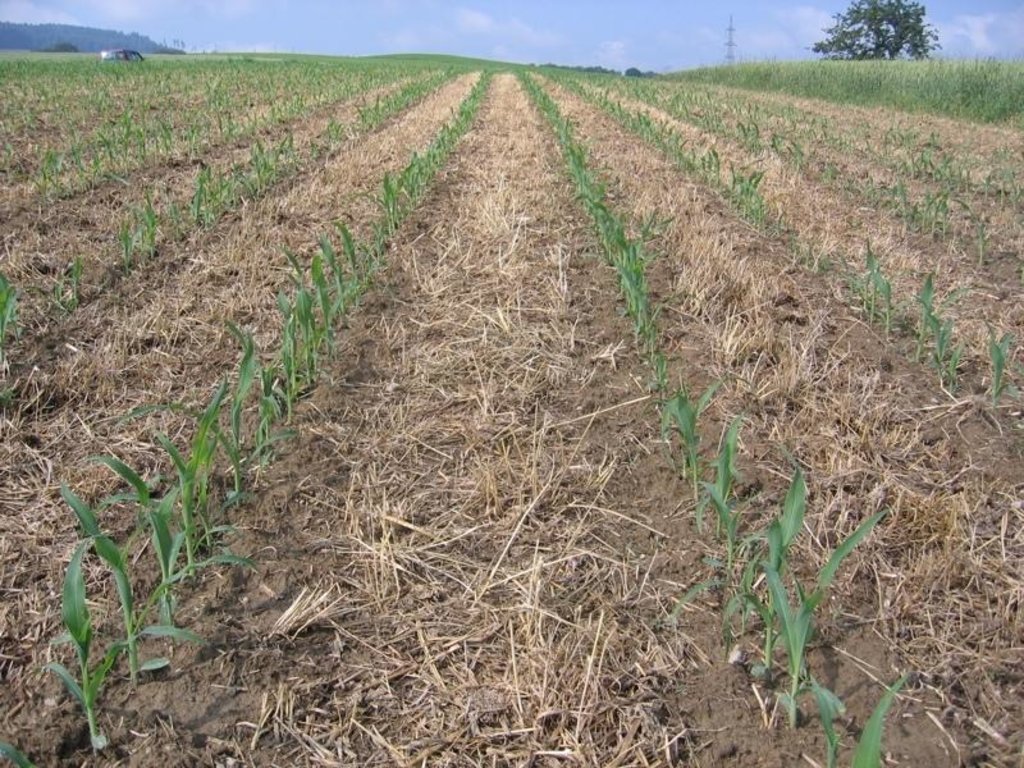
Maize strip tillage is a technology used for corn cultivation. It cultivates only thoses stripes in which the seed is added to.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
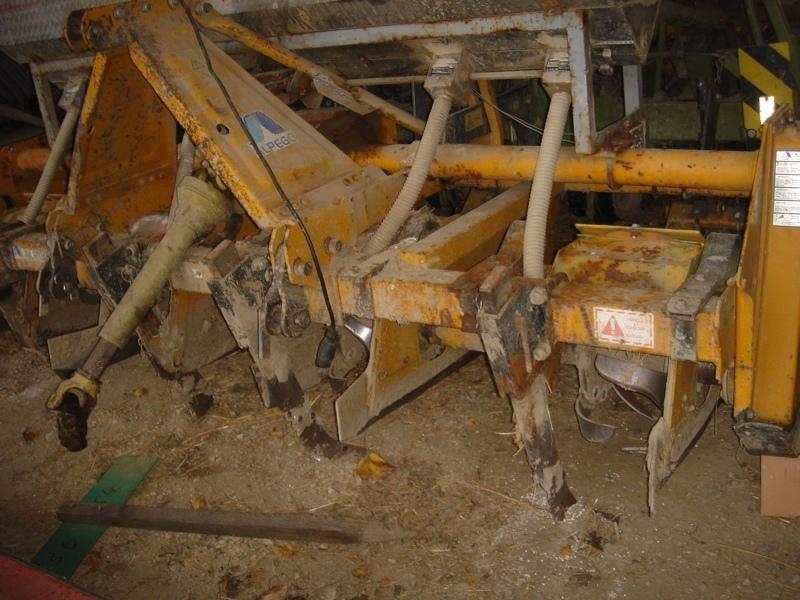
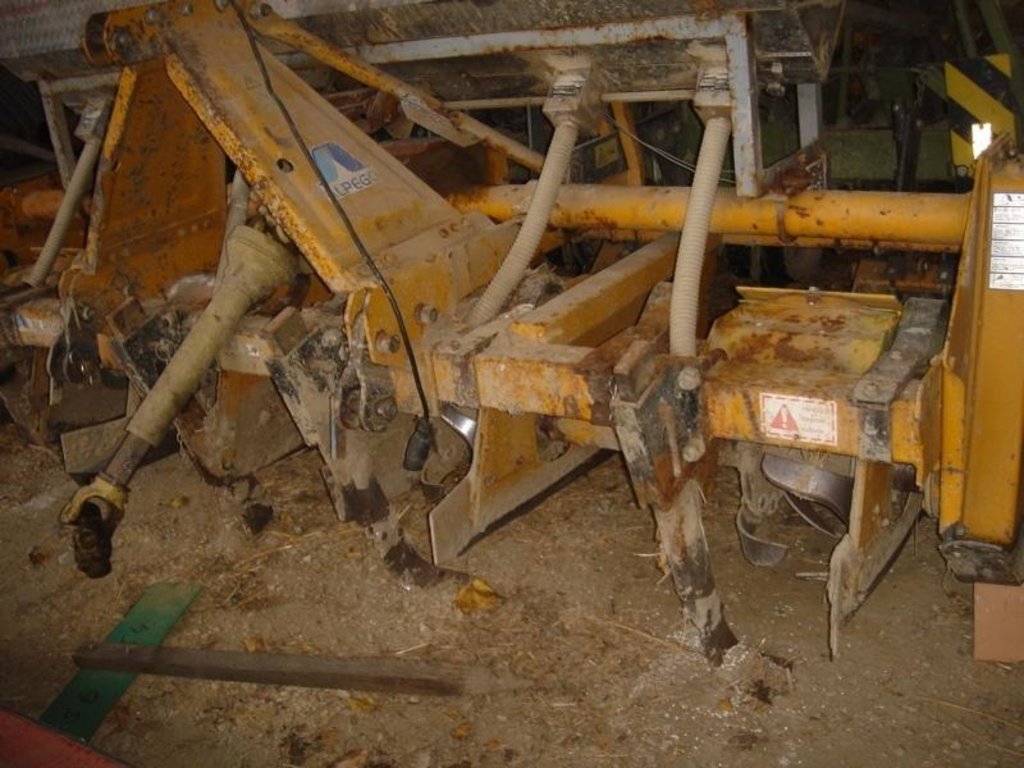
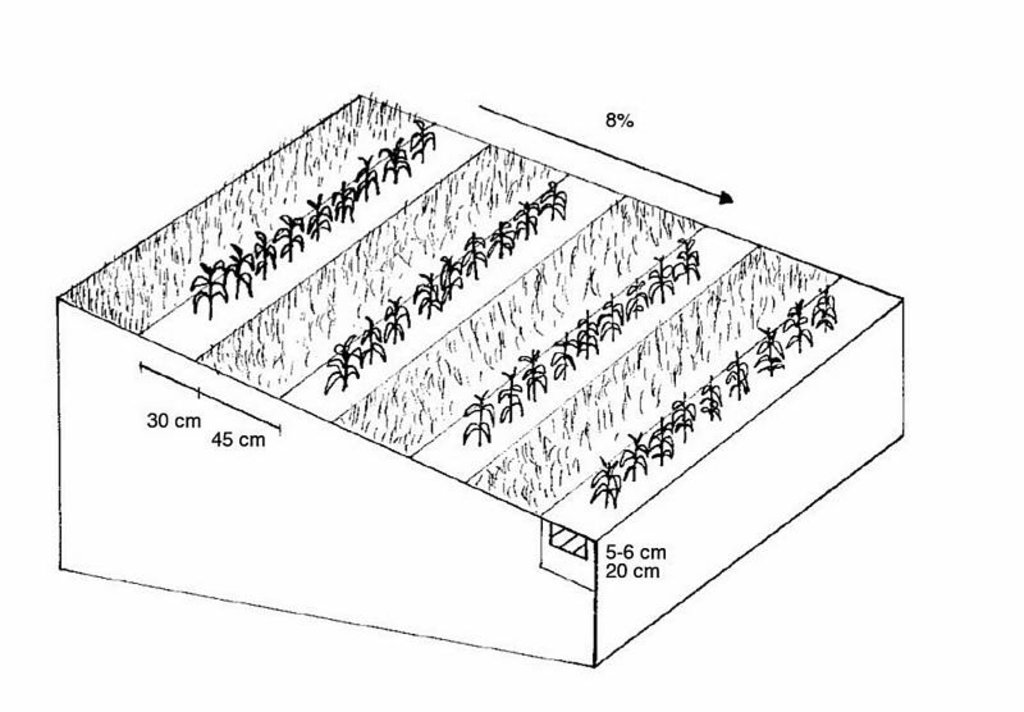
Maize strip tillage is a soil-conservation method used in crop production. First of all the grass in the area needs to be prepared by splattering round-up some 3-10 days prior seeding. Then the actual maize strip tillage machine carves a stripe and the seed are inserted within this 30 cm strip. At the same time fertilizer is added on these cultivated stripes. Between those cultivated stripes the mulch-grass stripes (45cm) are unmechanised and protect the soil by increasing its stability. The work is done within one working unit compared to the traditional technique whereas the farmer needs to drive for each working step separately.
There are some clear ecological advantages using this technology. Like in a minimum tillage system the stability of the soil is enhanced.
Due to these mulch-stripes the matrix of the soil is more complex and therefore the stability is better especially during harvest in September. The interviewed farmer said compaction would occur less and the risk of soil erosion is decreasing. Especially in hilly areas the technology is suitable since soil erosion is a problems when using a plough. Another advantage is the better soil structure due to the mulch stripes and the minimal tillage ensures that the soil is more stable.
A high level of knowledge about the natural environment is a required when adopting this technology. On one hand, the farmer must time the date for seeding adequately to the natural conditions (not too humid). On the other hand, the farmer has to apply Glyphosphat one to three times after the seeding in order to guarantee an optimal growth period for the corn.The interviewed farmer found it problematic to use this amount of Glyphosat and he was not sure about the effects in the water. The timing to start seeding with this technology may be later cause corn is sensitive towards rival plants, low temperatures and humidity. When adopting the technology the farmer needs to have a certain level of knowledge and experience in order to guarantee a sound harvest.
This technology is applied in the village Seedorf (Canton Bern) after the farmers made positive experiences and if they see the economic advantages too. Generally there is only one work step needed for the seeding which lowers the costs compared to the traditional technology with about a third. Furthermore the subsidies of the canton of Berne enables farmers to apply this technology for the first 5 years. In this cycle the areas are usually left with grass first, second cultivated with corn (using maize strip tillage), then sugar beets and after all two years of cereals (wheat and rye) before the cycle starts again.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
سويسرا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Seedorf
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Bern
التعليقات:
27.2 km2 are owned by the farmer whereas he is applying the technology on 5 km2. He said that he is hired as a contract worker and applies the technology on approximately 90 km2
Map
×2.7 إدخال التقنية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
A neighbouring farmer adapted the technology and after the first successful harvest Roland Bangerter bought a machine too some 5 years ago and started apply this technology.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion in hillside areas
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): soil degradation in general
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 90 m2.
27.2 km2 are owned by the farmer whereas he is applying the technology on 5 km2. He said that he is hired as a contract worker and applies the technology on approximately 90 km2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, manure / compost / residues, rotations / fallows, minimum tillage
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (the use of plough increases the danger of soil erosion)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: mulch stripes
Rotations / fallows
Remarks: a cultivation cycle of 5 year is needed
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying a 120 PS tractor | زراعية | |
| 2. | Buying a machine for maize strip tillage | زراعية | |
| 3. | buying a sowing machine | زراعية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | 120 PS tractor | Farm | 1,0 | 126000,0 | 126000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Machine for maize strip tillage | Farm | 1,0 | 165000,0 | 165000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Sowing machine | Farm | 1,0 | 12600,0 | 12600,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 303600,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Adding some round-up on the field one week before technology is applied | زراعية | 1 |
| 2. | Applying technology maize strip tillage | زراعية | 1 |
| 3. | Adding herbicide on the mulch stripes | زراعية | 1-3 |
| 4. | Harvest of corn | زراعية | 1 |
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Prevention of erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain green cover. |
|
Improvement of soil quality (fertility, organic matter, moisture retention, soil structure) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ensure that cover vegetation doesn’t compete with the vines; improve soil properties by applying mentioned agronomic measures. |
|
Contribution to a better balanced and more stable ecosystem (with living space for a wider range of organisms) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Specific management of cover crops (alternating treatment of inter-rows; find solutions to replace application of herbicide). |
| In the long-term economically beneficial because of cutting costs of restoration of soils and fertility loss after heavy erosion events. |
| Possibilities of farm income increase through marketing wine under the ‘vinatura’ label, certifying ecologically produced wine. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| General competition of water and nutrients depending on climate, soil depth and species of cover vegetation | Eliminate/reduce competitive effect of cover vegetation by cutting/mulching vegetation or ripping/ploughing soil. |
| Application of herbicides around vines because of undesirable vegetation in proximity of vine | Find alternative solutions, or minimise application of herbicides. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Güdel N . Boden- und Wasserkonservierung in Schweizer Rebbergen. Ein Beispiel im Rahmen von WOCAT. Unpublisheddiploma thesis.. 2003.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Centre for Development and Environment (CDE), University of Berne
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية