Natural Vegetative Strips (NVS) [الفيليبين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Mathias Gurtner
technologies_1133 - الفيليبين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
MERCADO Agustin
a.mercado@cgiar.org / agustin9146@yahoo.com
International Center for Research in Agroforestry ICRAF
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor
أندونيسيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Rondal José
joserondal@yahoo.com
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Bureau of Soils and Water Management SRDC Bldg. Visayas Avenue corner Elliptical Road, Diliman, Quezon City 1101 Metro Manila
الفيليبين
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Garrity Dennis
International Center for Research in Agroforestry ICRAF
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor
أندونيسيا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - الفيليبيناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
26/06/1999
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

LANDCARE - Claveria Landcare Association (CLCA) [الفيليبين]
Associations that help diffuse, at low cost, soil and water conservation technologies among upland farmers to generate income while conserving natural resources.
- جامع المعلومات: Romeo Villamin Labios
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
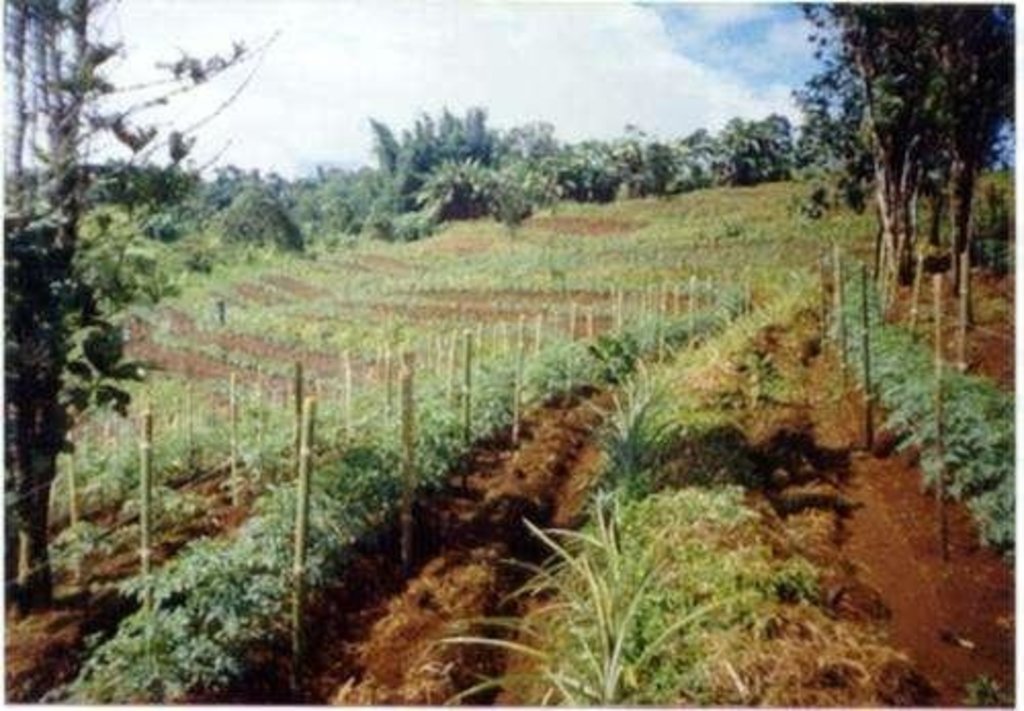
Within individual cropland plots, strips of land are marked out on the contour and left unploughed in order to form permanent, cross-slope barriers of naturally established grasses and herbs.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
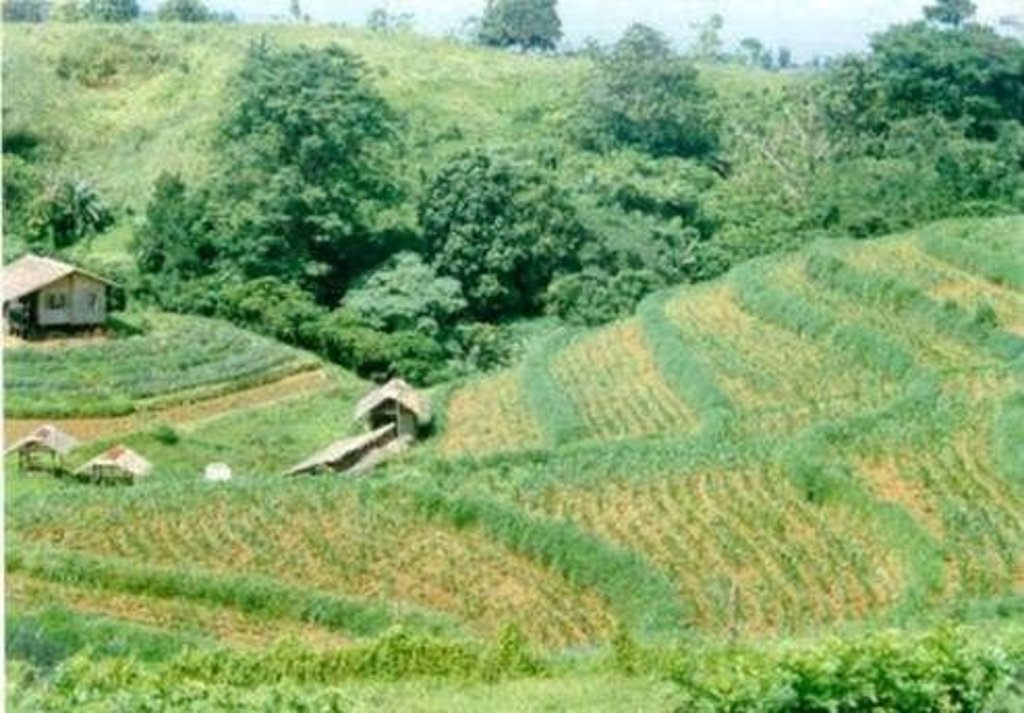
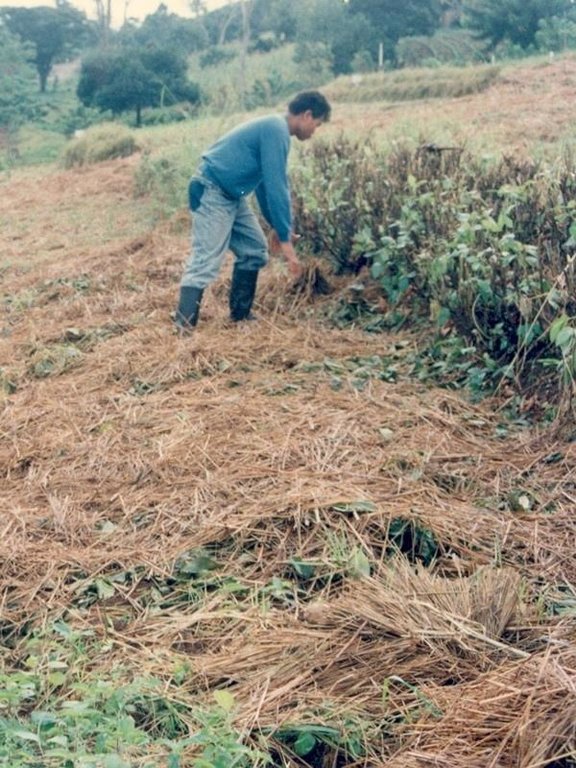
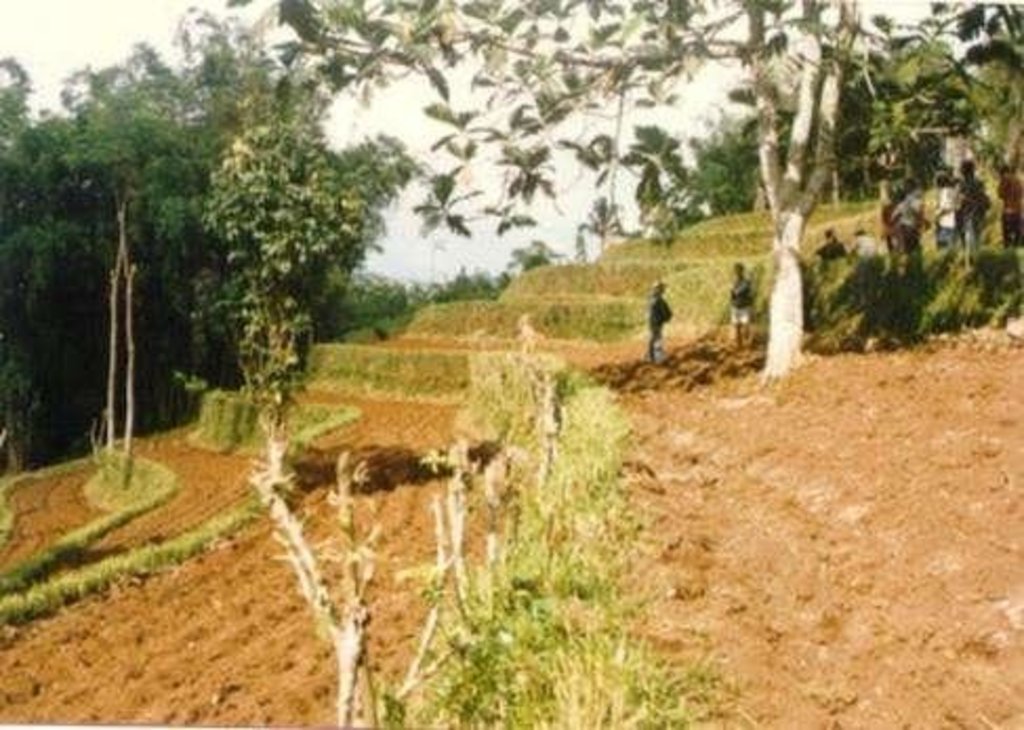
Natural vegetative strips (NVS) are narrow live barriers comprising naturally occurring grasses and herbs. Contour lines are laid out with an A-frame or through the ‘cow's back method’ (a cow is used to walk across the slope: it tends to follow the contour and this is confirmed when its back is seen to be level). The contours are then pegged to serve as an initial guide to ploughing. The 0.3-0.5 m wide strips are left unploughed to allow vegetation to establish. Runoff flowing down the slope during intense rain is slowed, and infiltrates when it reaches the vegetative strips. Eroded soil collects on and above the strips and natural terraces form over time. This levelling is assisted by ploughing along the contour between the NVS - through ‘tillage erosion’ - which also moves soil downslope.
The vegetation on the established NVS needs to be cut back to a height of 5-10 cm: once before planting a crop, and once or twice during the cropping period. The cut material can be incorporated during land preparation, applied to the cropping area as mulch, or used as fodder. This depends on whether the farmer has livestock or not, on personal preference, and on the time of cutting. If the grass is applied as mulch or incorporated, the technology can be considered to be an agronomic, as well as a vegetative, measure.
NVS constitutes a low-cost technique because no planting material is required and only minimal labour is necessary for establishment and maintenance. Some farmers had already practiced the technology for several years before the intervention of the ICRAF (The World Agroforestry Centre) in 1993. ICRAF came to realise that farmers here preferred NVS to the recommended ‘contour barrier hedgerows’ of multipurpose trees- which land users viewed as being too labour intensive. When farmers became organised into ‘Landcare’ groups, NVS began to gain wide acceptance.
Land users appreciate the technique because it effectively controls soil erosion and prevents loss (through surface runoff) of fertilizers applied to the crop. As an option, some farmers plant fruit and timber trees, bananas or pineapples on or above the NVS. This may be during establishment of the contour lines, or later. The trees and other cash perennials provide an additional source of income, at the cost of some shading of the adjacent annual crops.
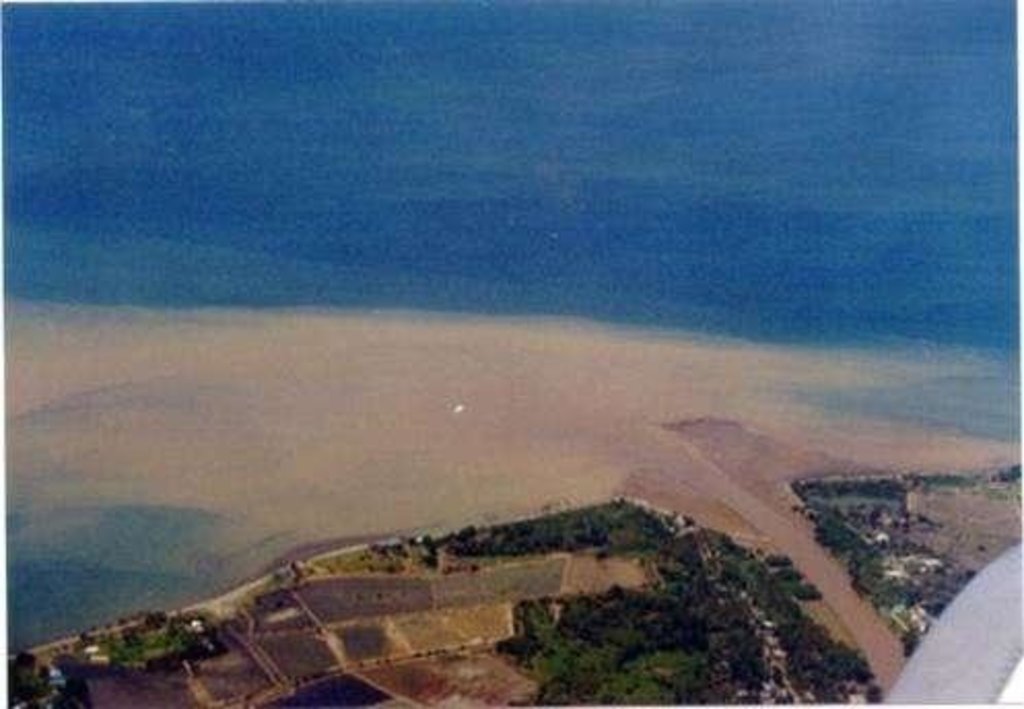
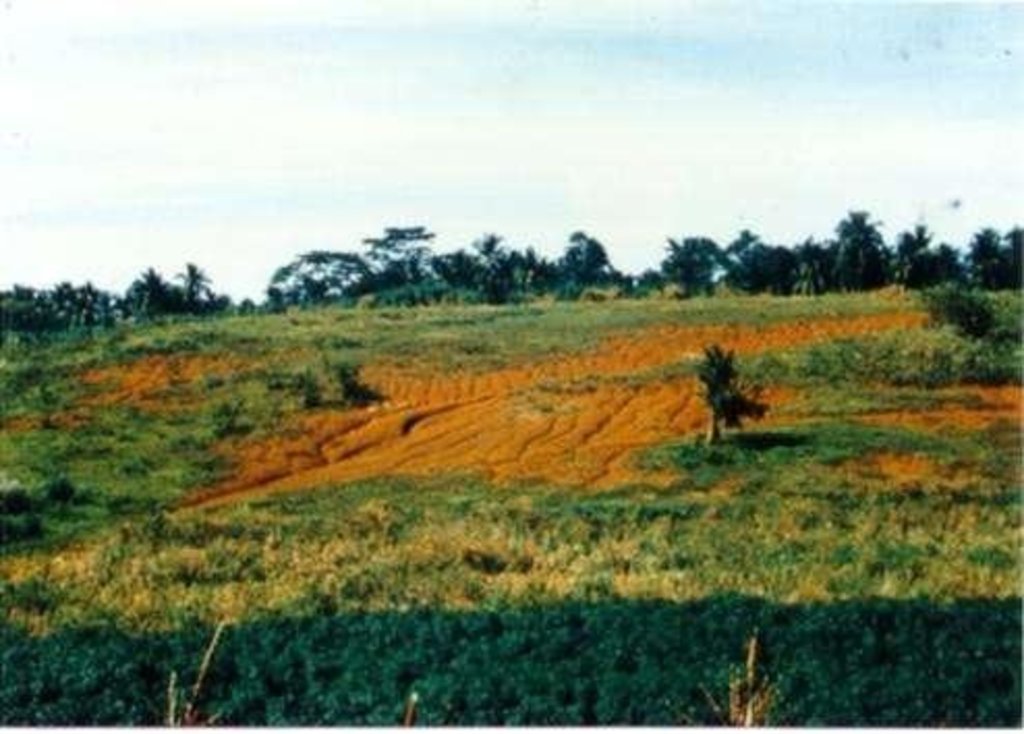
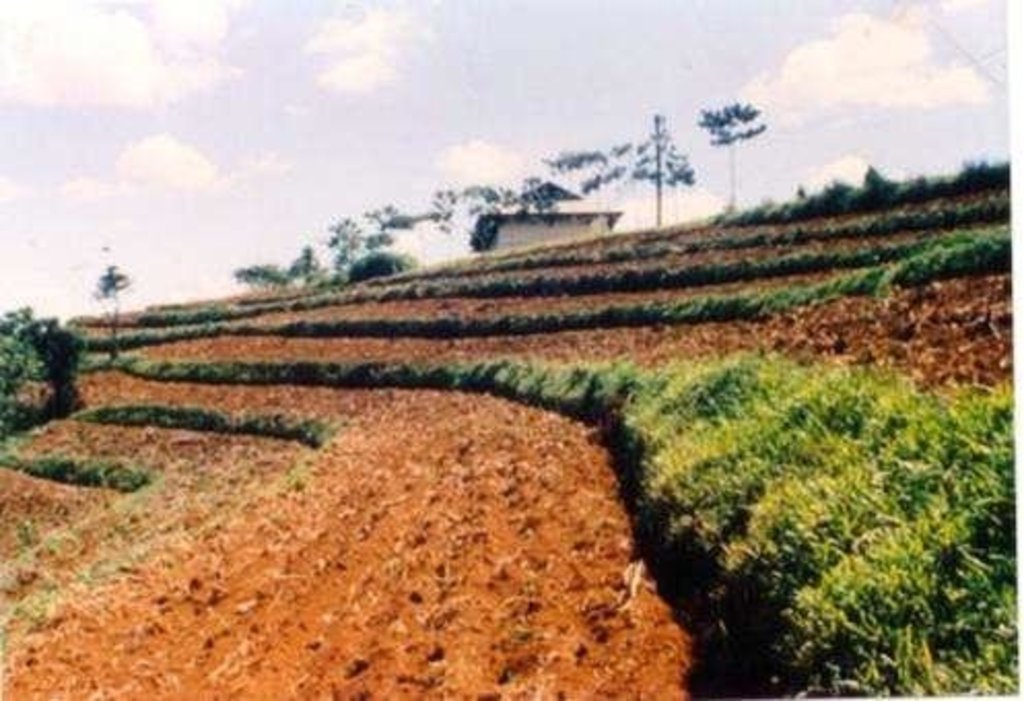
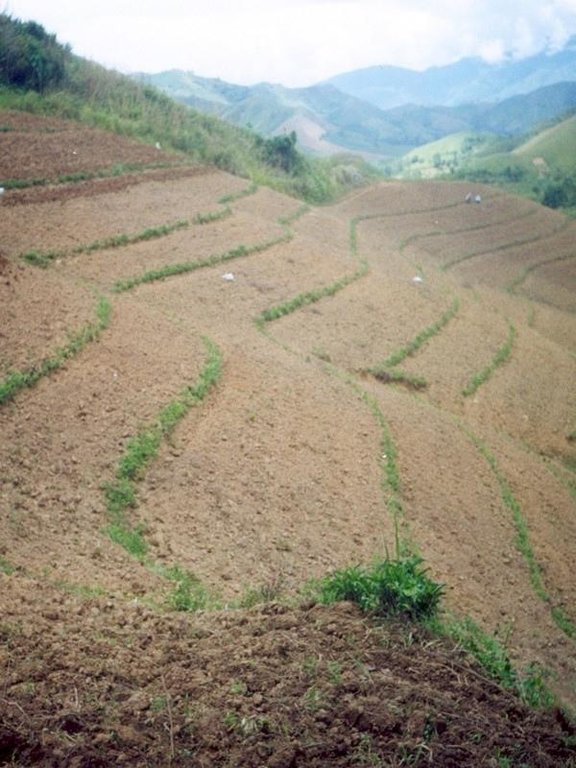
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الفيليبين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Misamis Oriental
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Bukidnon
التعليقات:
The technology has been practiced by a few farmers for the past several years. With the entry of the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) in 1993; farmers became organized and the technology gained wide adherence.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
1993
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
It evolved in the area with some adaptations.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Maize, vegetables; coffee; fruit trees; upland rice
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Loss of topsoil through sheet erosion and rills, leading to rapid soil fertility decline. In turn soil fertility decline results in the need for increasing levels of fertilizer inputs to maintain crop yield. However, these fertilizers are often washed away by surface runoff - a vicious circle.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil productivity decline; need more inputs to maintain crop yield.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period: 240 days (Mar - Dec)
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 110 m2. The technology has been practiced by a few farmers for the past several years. With the entry of the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) in 1993; farmers became organized and the technology gained wide adherence.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة
التعليقات:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (caused massive erosion and loss of productivity), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority (no clear cut policy and support from LGU). Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (over population of livestock, low land ratio), education, access to knowledge and support services (farmers are not fully aware of simple SWC approach), Agricultural causes (unsustainable practice in farming)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
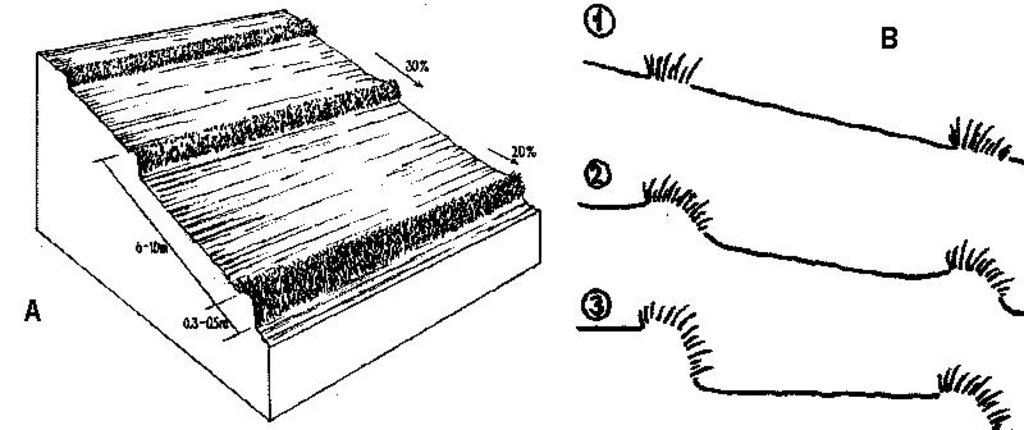
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
A - Spacing of natural vegetative strips depends on the slope.
B - The insert shows the evolution of terraces over time through tillage and soil erosion, leading to accumulation of sediment behind the strips (steps 1-3).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate. Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate.
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, control of dispersed runoff. Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measures:
Mixed cropping / intercropping - Material/ species: annuals/perennials; Remarks: laid out alternately.
Mulching - Material/ species: crop residues; spread on the surface
Legume inter-planting - purpose: for nitrogen fixation
Manure / compost / residues - Material/ species: animal, crop residues
Contour tillage - Material/ species: Contour strips are laid into 6-10 meters apart depending on slope gradient.
Vegetative measures:
Aligned, along contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass, O : other
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Narrow grass barriers
Vegetative material: grass
Number of plants per (ha): dense grass
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-0.7
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia mangium, Eucalyptus deglupta, Gmelina arbarea
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, Durian, Rambutan, Jackfruit
Perennial crops species: Coffee, rubber, pineappe
Grass species: Bamboo, setara, napier, Panicum spp.
Other species: Legumes
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 20%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 ha
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layout of contours with the use of an A-frame (or cow’s back method, see Annexe T3)) placing wooden pegs along the contours. | نباتية | dry season/before land preparation |
| 2. | Seeding (T, F, C) | نباتية | dry season |
| 3. | Transplanting | نباتية | onset of rainy season |
| 4. | Land preparation | نباتية | dry season/before planting |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | animal traction | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | tools | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | stakes (pegs) | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 84,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Initial ploughing along the contour: leaving unploughed strips. | زراعية | onset of rainy season / before each season |
| 2. | Planting | زراعية | onset of rainy season / each cropping season |
| 3. | Mulching | زراعية | dry season / only whensufficient crop residues |
| 4. | Fertilization | زراعية | early vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 5. | Interim cultivation/weeding | زراعية | vegetative stage / each cropping season |
| 6. | Ploughing mulch into the soil during normal land cultivation. | زراعية | |
| 7. | Weeding (T, F, C), Slashing grass | نباتية | rainy season /2 times |
| 8. | Spreading the cut materials evenly in the alleys (between strips) as | نباتية | rainy season /2 times (weeded materials) |
| 9. | Pruning | نباتية | before and during cropping /2 times per cropping |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | 1,0 | 36,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | animal traction | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 | |
| معدات | tools | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 78,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: plough, harrow
Costs of establishing contours and maintenance by slashing are calculated by total length of NVS. This example is from a typical field with an 18% slope: at an NVS spacing of 5 m, the approximate total linear distance for one hectare is 2,000 m. In this example, the farmer has paid for everything him/herself (see section on acceptance/adoption). Note that the establishment cost is more or less equivalent to the cost of standard land preparation by ploughing. When 'enrichment planting’ of the strips is carried out, extra cost for seedlings (of fruit trees for example) and associated labour for planting are incurred.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Slope is the dominant factor in cost calculation. The steeper the slope, the more difficult the mobility is and the more closely-spaced the contours are .
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Rainfall is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soils are developed from fine-grained igeneous rocks. Soil fertility: strongly acid and with high P fixing capacity. Rapid organic matter mineralisation due to high temperature. Soil drainage is generally good except in isolated depressions.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
مستوى المكننة:
- الجر الحيواني
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2; Annual population growth: > 4%
and own 20% of the land (5).
and own 40% of the land (30).
and own 30% of the land (65).
Off-farm income specification: Carpentry, trade, business, labour for neighbouring farms and other labour intensive agricultural activities (e.g. vegetable production)
Market orientation of production system: Upland rice is grown as subsistence. Maize is sold to feed millers.
Level of mechanization: The terrain limits the extensive use of machineries.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Subdivision of inheritance lands. High population growth rate attributed to natural birth and envigoration of lowland population create pressure to farm site.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
area competition
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
biomass as fertilizer (or biomass as mulch)
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
biomass as fertilizer (or biomass as mulch)
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
crop area loss, before NVS evolved to cash perennials or fodder grasses
إدارة الأراضي
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
during establishment
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
biomass was given value
فروقات اقتصادية
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
regular pruning
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
very low inputs required
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
التعليقات/ حدد:
government line agencies and educational institutions
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
negligible socio-cultural conflicts
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
45
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
8
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
partly increased water-logging (negligible)
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
التعليقات/ حدد:
important for sustainability
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
pest sanctuary
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
soil structure
soil fertility
weed infestation due to seed dispersion and grass roots
التعليقات/ حدد:
spreading from the NVS to nearby areas (especially with cogon grass: Imperata cylindrica)
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
no actual measurement
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 90-50%
التعليقات:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support (2000 families)
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology spontaneously (without external material support) (2000 families)
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Factor that helped was the formation of Landcare associations which have benefited their members in various ways. There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption, especially where Landcare associations are in operation.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain |
| Improve soil fertility |
| Prevent soil erosion |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Easy to establish and maintain (How to sustain: Transform farmers associations into cooperative which serve as conduits in marketing. Intensify information and education campaign.) |
| Less competition for space, sunlight, moisture and nutrient. (How to sustain: Ensure continued regular trimming of vegetative strips and use of these as fodder or mulch.) |
| Low labor and external inputs requirement |
|
Effective in reducing soil erosion (by 90%) (How to sustain: Adopt other supportive technologies like mulching, zero tillage/minimum tillage, etc.) |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High initial establishment cost | Subsidy/assistance from government |
| Effect of technology is not readily seen | Education about what long term sustainability means |
| High gestation period for some component of the system | Proper mix of annual and perennial crops |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
|
Effect on yield and income is not readily felt, since reduced erosion is not easily translated into increased income or yield |
Farmers should have supplementary sources of income (eg livestock). Education about what long-term sustainability means. |
| Reduction of productive area by approx 10% |
Optimum fertilization to offset production loss. Nutrients are conserved under NVS and this will result in the reduction of fertilizer requirement after some years. |
|
Creation of a fertility gradient within the alley (soil is lost from the top of the alley and accumulates above the NVS where fertility then concentrates) |
Increased application of fertilizer on the upper part of alley. |
| Overall increase of production value is low | Land users could ask for subsidy/assistance from Government: eg for fertilizers, establishment of nurseries, free seedlings (for higher value fruit trees). |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Managing soil fertility on terraces forming behind vegetative filter strips: An assessment of farmer strategies
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor, INDONESIA
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Crop productivity using forage legumes and grasses as contour hedgerows species in an acid upland soils
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICRAF, P.O. Box 161, Bogor, INDONESIA
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Garrity DP, Stark M and Mercado Jr A: Natural Vegetative Strips: a bioengineering innovation to help transform smallholderconservation. pp 263–270. 2004.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
in Barker DH, Watson AJ, Sombatpanit S, Northcutt B and Maglinao AR Ground and Water Bioengineering for ErosionControl and Slope Stabilisation.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Science Publishers inc. Enfield, USA
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Stark M, Itumay J and Nulla S Assessment of Natural VegetativeContour Strips for Soil Conservation on Shallow Calcareous Soil in the Central Philippines.. 2003.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF), Nairobi, Kenya
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

LANDCARE - Claveria Landcare Association (CLCA) [الفيليبين]
Associations that help diffuse, at low cost, soil and water conservation technologies among upland farmers to generate income while conserving natural resources.
- جامع المعلومات: Romeo Villamin Labios
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية