Zai or tassa planting pits [النيجر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Dieter Nill
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, Nina Lauterburg, Fabian Ottiger
Zaï - Tassa (French)
technologies_1219 - النيجر
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
ألمانيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mamadou Abdou Sani
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP)/GIZ
Niamey
النيجر
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Misereor - ألمانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/07/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Zai planting pits are designed to collect rainwater and to conserve nutrients in order to improve crop production and food security.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
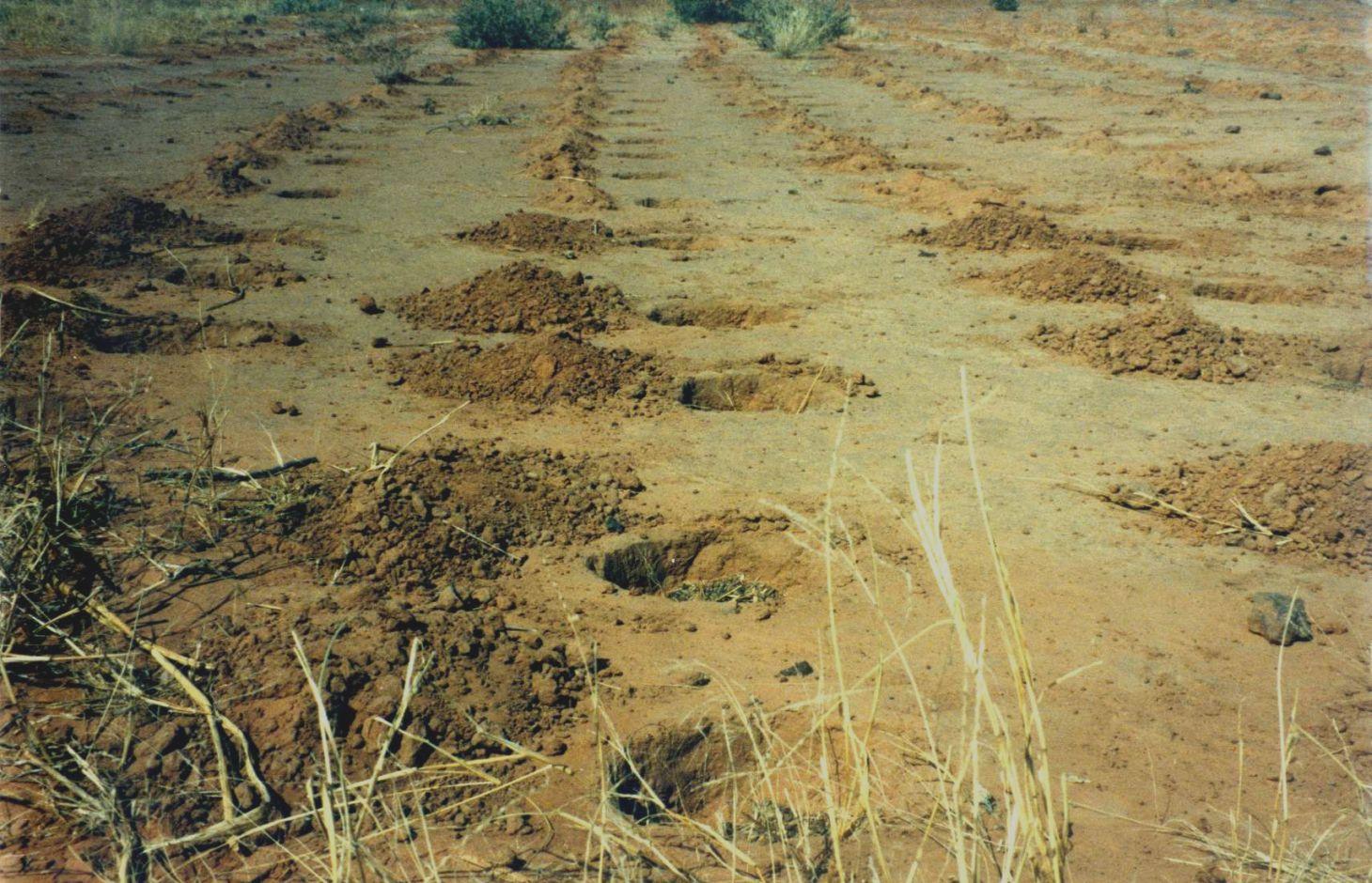
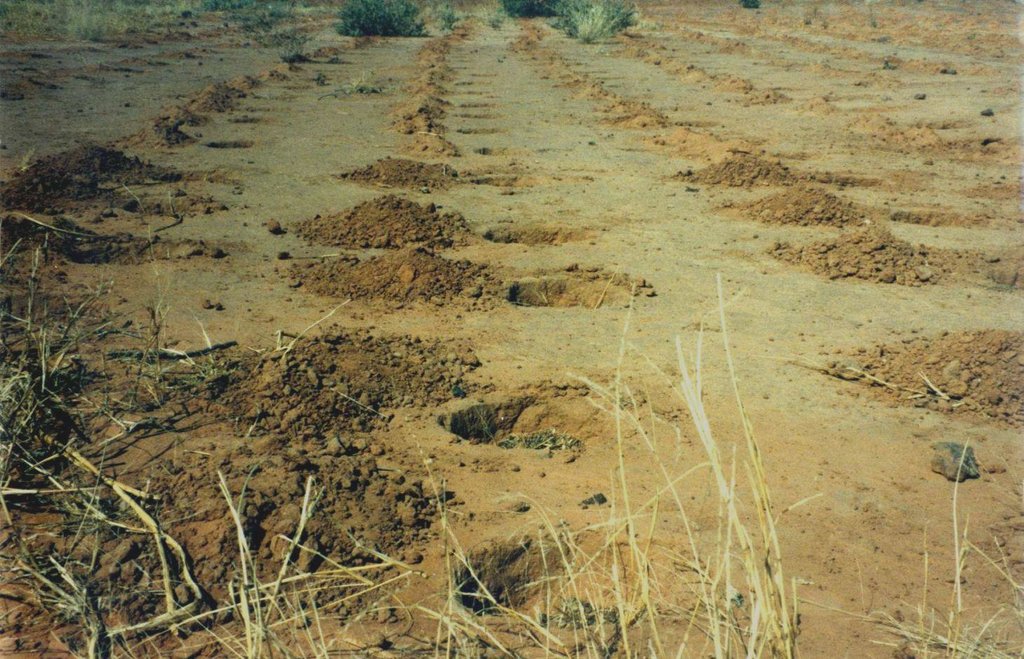
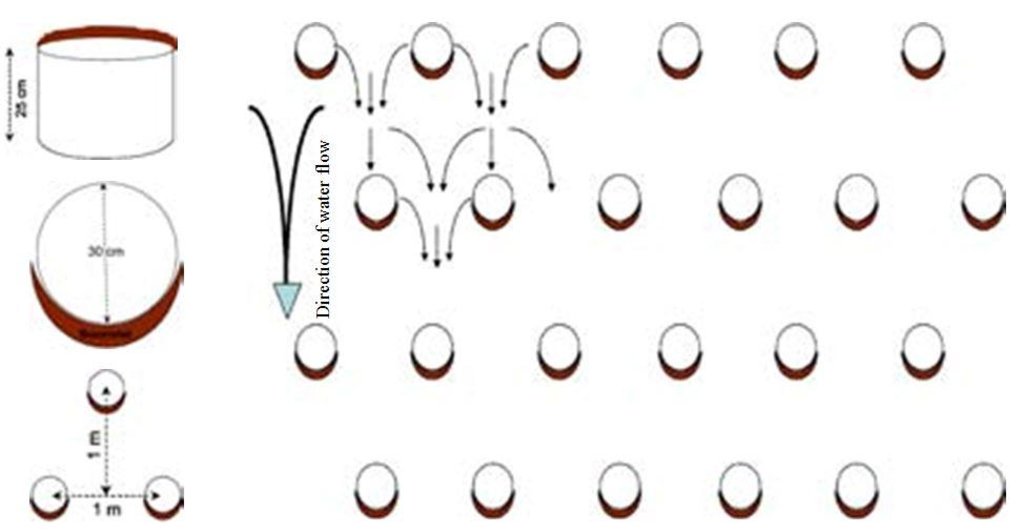
Zai or tassa planting pits are an old farming technique rediscovered after the great drought of 1973/74 and later perfected by development partners working with the farmers. It involves digging planting pits with a diameter of at least 30 to 40 cm and 10 to 15 cm deep. They are spaced 70 to 80 cm apart, resulting in around 10,000 pits per hectare. Staggered rows of holes are dug perpendicularly to the slope. The earth dug out of the hole is piled up to form a small ridge around the rim, which captures water. A couple of handfuls of organic fertiliser or compost are put into each pit. They are normally made in the dry season before the first rains start. However, it is recommended that the pits be made immediately after the rainy season, when the soil is still moist and the weather is not too hot. If the pits are in place early in the dry season, they act as traps during the windy period in February and March, retaining rich dust carried by the harmattan and wind-blown organic matter. At least 3 tonnes of compost per hectare is recommended.
Purpose of the Technology: The arrangement of the pits in staggered rows ensures the most efficient collection of rainwater and slows the flow of water over the surface. The zai technique concentrates and conserves nutrients and water near the roots of the plants grown in them. The application of organic fertiliser directly around the plants is an economical use of a factor of production to which most farmers have limited access. It also reactivates biological activity, increases fertility and loosens the soil.
As zai planting pits restore degraded, uncultivated land, they lessen the pressure to clear other land for farming. They also reduce the vulnerability of plants during dry spells and droughts, ensuring crop production and improving food security.
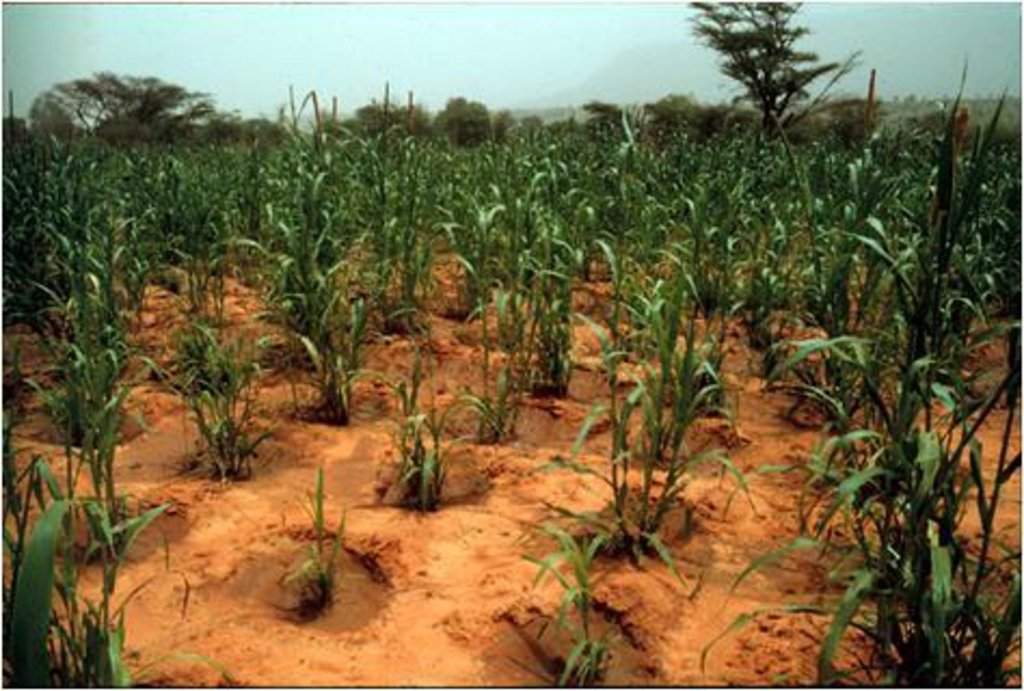
Plots with zai planting pits (with fertiliser) average yields of 409 kg of millet grain per hectare, compared to 195 kg per hectare registered on control plots. Millet yields can therefore be doubled with this technique.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The zai technique requires high labour input. It is estimated that between 40 and 60 man-days per hectare are required, depending on the density of the pits. There is a mechanised system for making the holes, using a special animal-drawn plough, which considerably reduces the number of man-days required to 7 per hectare.
If the pits are prepared each year or once every two years (using the same pits or making new ones in the spaces between the old ones), soil fertility is restored and the crop cycle can be resumed. The application of organic fertiliser in sufficient quantities enables the plot to be cultivated sustainably. After five years, it can be farmed in the normal way.
Covering extensive areas with zai planting pits requires a high level of community mobilisation and effective organisation and logistics. Apart from this, the technique is very simple to implement and easily mastered by the farmers.
Natural / human environment: Zai planting pits are used on marginal or degraded land that is no longer cultivated, such as low-gradient pediments and land with encrusted soil in areas with rainfall levels of less than 800 mm a year. They are not recommended for sandy soils, as they are not stable when dug in this type of soil, or for valley bottoms, where they risk being flooded. Zai planting pits are particularly useful in areas where land use pressure is high, as they permit the rehabilitation of unproductive land for farming.
From the point of view of climate change adaptation, zai planting pits are particularly useful in areas with erratic or low rainfall, as they prevent the loss of water. As the fertiliser is placed inside the pits, it is not washed away by heavy rain.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيجر
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Niger
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
- قطع الأشجار الكلي
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الفواكه والمكسرات
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Major cash crop: Ground nut
Major food crop: Millet
Major other crops: Sorghum, cow pea and mangos
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion, fertility decline, aridification, loss of limited rainwater by runoff
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
Type of grazing land: Extensive grazing: Nomadism, semi-nomadism/pastoralism. Intensive grazing: Cut-and-carry/zero grazing and improved pasture
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة

التدابير البنيوية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
It involves digging planting pits with a diameter of at least 30 to 40 cm and 10 to 15 cm deep. They are spaced 70 to 80 cm apart, resulting in around 10,000 pits per hectare. Staggered rows of holes are dug perpendicularly to the slope. The earth dug out of the hole is piled up to form a small ridge around the rim, which captures water. A couple of handfuls of organic fertiliser or compost are put into each pit.
Location: Niger
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 0.7-0.8
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.15
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3-0.4
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
CFA Franc
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | marking out the rows perpendicular to the slope | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 2. | digging pits in staggered rows | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 3. | forming a ridge on the downhill side | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 4. | A couple of handfuls of organic fertiliser or compost are put into each pit | زراعية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | 1,0 | 16,3 | 16,3 | ||
| العمالة | transport and planting trees | 1,0 | 12,3 | 12,3 | ||
| معدات | machine use | 1,0 | 23,6 | 23,6 | ||
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 52,2 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | the pits are prepared each year or once every two years (using the same pits or making new ones in the spaces between the old ones | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 2. | applying organic fertiliser every two years (1 to 2 hand-fuls per pit, amounting to around 3 tonnes per hectare). | زراعية |
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour: 40 to 60 man-days per hectare
• marking out the rows perpendicular to the slope
• digging pits in staggered rows
• forming a ridge on the downhill side
• applying organic fertiliser every two years (1 to 2 handfuls per pit, amounting to around 3 tonnes per hectare).
Other costs: transportation of 30 cartloads of manure.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture: Fine to medium (sandy to clayey loams)
Soil fertility: Very low to medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low and medium (ranked 2)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply, Most households crop for subsistence, mainly for small agropastoralists ), mixed (subsistence/commercial, crop surplus is sold on market, medium agropastoralists) and commercial market (Some vegetable growing, pastoralists)
Level of mechanization: Menual work (ranked 1) and animal traction (ranked 2, ox, donkey)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
التعليقات:
traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
خطر فشل الإنتاج
منطقة الإنتاج
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Plots with zai planting pits (with fertiliser) average yields of 409 kg of millet grain per hectare, compared to 195 kg per hectare registered on control plots. Millet yields can therefore be doubled with this technique. They also reduce the vulnerability of plants during dry spells and droughts, ensuring crop production and improving food security.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Waterlogging in planting pits after heavy rains
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The arrangement of the pits in staggered rows ensures the most efficient collection of rainwater and slows the flow of water over the surface. The zai technique concentrates and conserves nutrients and water near the roots of the plants grown in them. |
| Zai planting pits are particularly useful in areas where land use pressure is high, as they permit the rehabilitation of unproductive land for farming. Therefore they lessen the pressure to clear other land for farming. |
| They also reduce the vulnerability of plants during dry spells and droughts, ensuring crop production and im- proving food security. |
| It permits a rational use of fertiliser. When fertiliser is spread on the surface of a plot without zai planting pits, it can be washed away by runoff. |
| very simple to implement and easily mastered by the farmers |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The zai technique requires high labour input. | |
| Zai planting pits are not recommended for light soils, as they fill in too quickly |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية