Forest Beekeeping [الكاميرون]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1360 - الكاميرون
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Verina Ingram
Cifor Cameroon
Yaounde
الكاميرون
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: SLM in Practice - Guidelines and Best Practices for Sub-Saharan Africa (SLM in Practice)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CIFOR Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) - الهند1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
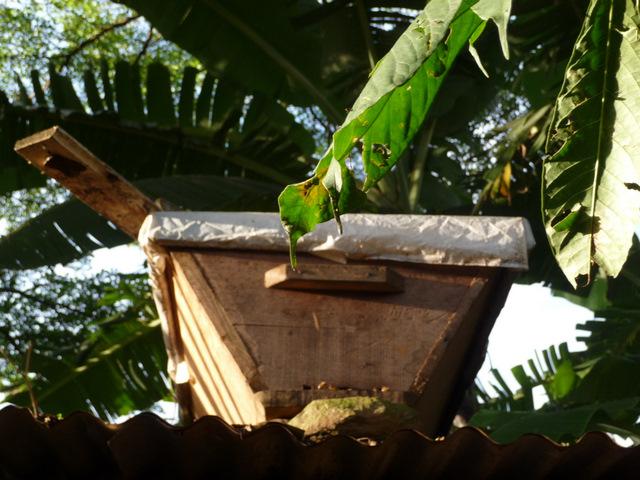
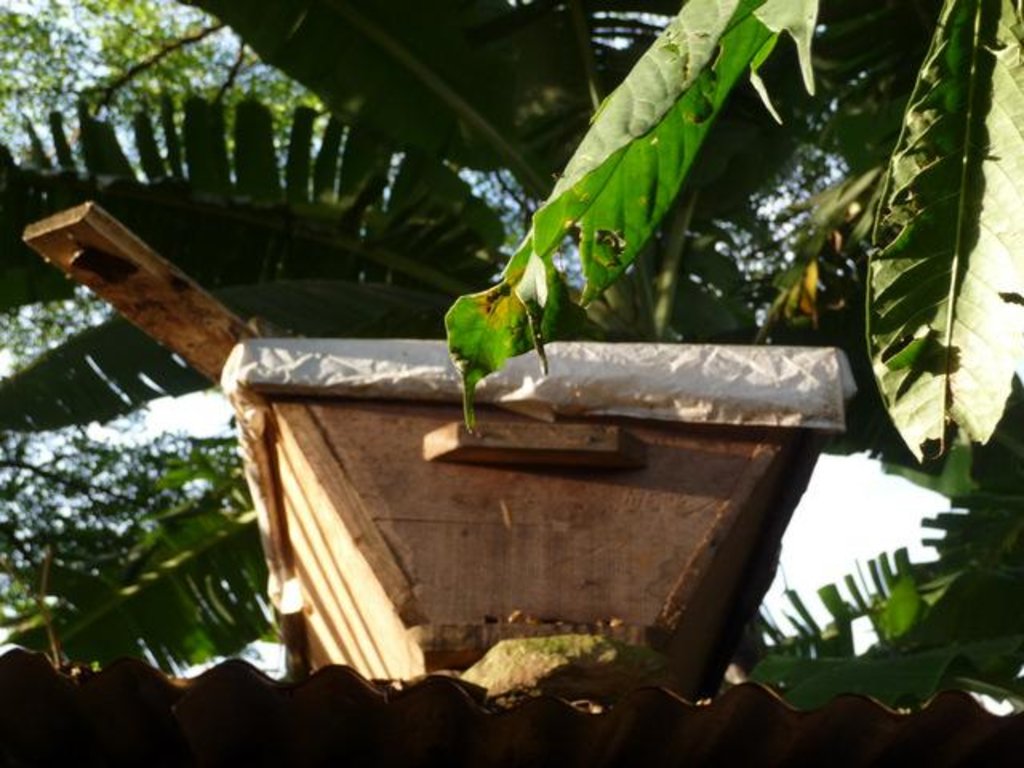
Apiculture (beekeeping) is a traditional practice providing a high number of non-timber forest products.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
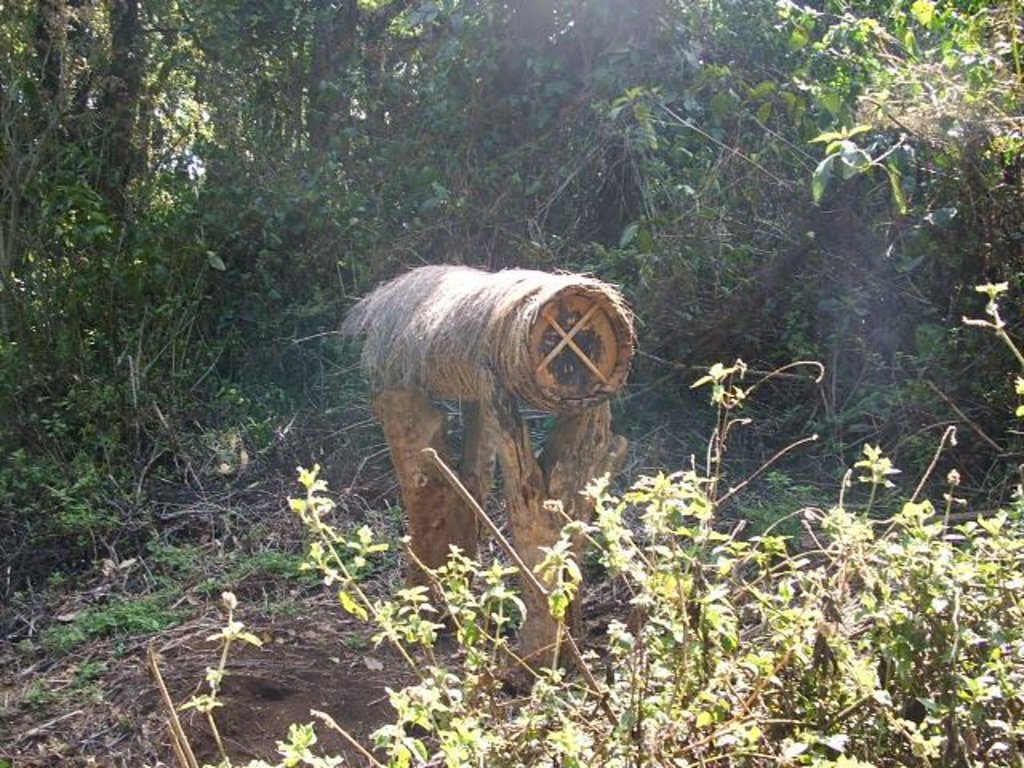
Apiculture (beekeeping) has been traditionally practiced for at least a century in Cameroon; with forest-based apiculture increasing in the last 2 decades. The ancient art of honey hunting, and the more recent apiculture and its products like honey, wax, propolis, bee venom and royal jelly, are examples of non-timber forest products (NTFP). A number of projects were supporting production and marketing, due to the conservation and development benefits of beekeeping. Beekeeping has low establishment costs and requires little land or labour, and by providing a suitable environment for the hives in a favourable location (i.e. forest with a range of melliferous trees and plants and sufficient water available year round) it is possible to sustainably harvest a range of bee products on an annual basis. For processing of the honey, the honeycomb is filtered and honey can be bottled and sold. Higher value is obtained by packaging and labelling. In Cameroon up to 4 US$/kg can be achieved for good quality honey. It can also be sold for industrial use – for example bakeries, sweets. If combs are washed, the resulting honey-water can be made into wine. Wax needs to be melted and cleaned, and can then be sold ‘raw’ for a price of about 2-6 US$/kg, or further processed into candles, soaps and creams. In Cameroon, the consumer market is expanding and a small, niche export market for high quality, certified organic and fair trade wax, honey and propolis, is emerging. The exports to Europe and the US require quality assurance schemes that entail costs, expertise and collaboration between government and beekeepers. The number of hives per bee-farmer can vary considerably from a few up to 150 hives. Approximately 15 hives can be installed per hectare. Beekeepers can be good ‘guardians of the forests’, because they know that the forest provides both forage and water for the bees, and the water and materials needed to make hives and process apiculture products.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الكاميرون
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Mount Oku region, Mountainous forests of Northwest Cameroon
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Bui, Boyo, Mezam and Donga Mantung divisions
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- Sustainable rainforest management
منتجات وخدمات:
- الفواكه والمكسرات
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Deforestation, Overuse of natural ressources
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تربية النحل، واستزراع الأسماك، والدواجن، وتربية الأرانب، وتربية دودة القز، الخ.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M3: التخطيط وفقا للبيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
التعليقات:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: Indirectly deforestation / overuse of natural forests
Layout change according to natural and human environment
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of hives (traditional or modern, depending on skills and availability/ cost of materials) | إدارية | |
| 2. | Place hives on forest trees or on stands, above the level of fires, as well as away from ant and termite colonies | إدارية | |
| 3. | None |
التعليقات:
Establishing activities: extra information Harvesting of honey combs often done at night to minimize disturbance of the bees Comb washing water can be used in honey beer or wine in lidded buckets / basins or bottles or using as fermentation airlock
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| معدات | Smoker | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | |
| معدات | Buckets | ha | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | |
| معدات | Filtering materials | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| معدات | Bottles | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Replacement/repair hive, filte | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 112,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wait for natural colonisation or capture a swarm and transfer to hive | إدارية | |
| 2. | Regular (weekly or monthly) checking of hive conditions to ensure that the colony is not disturbed by pests or damaged through wind/ rain. In drought periods a shallow bucket of water is provided to the bees. Reparation activities if needed. | إدارية | |
| 3. | Harvest honey (as soon as sufficient is available), wax and propolis, using a 'smoker' and clean bucket, leaving brood combs to maintain the colony (usually annually at end of rainy and/or flowering season; depends on location) | إدارية | |
| 4. | Filter honey from combs to separate honey and wax; then bottle and pack | إدارية | |
| 5. | Process wax (e.g. washing comb and boiling in water or solar melting box) and melt into moulds, using a press or centrifuge. | إدارية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Replacement/repair hive, filte | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 65,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: machete, axe, knife
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
2000-2400
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (Mountain forests)
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture: FIne/heavy (lateritic clay)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: small to medium scale, very poor to average level of wealth; individuals, groups cooperative or employee; cooperatives are mainly used for marketing products and/ or buying material
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Relative level of wealth: average, poor, very poor
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
Land ownership: community forest or individual (titled and not titled)
Land use rights: legal form of community management; many people keep bees by the forest edge on their farms, usually on privately owned land
Land ownership: communal / village, individual, not titled, individual, titled
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased income from honey, wax and propolis sales
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Subsistence use and sales of apiculture products e.g. wax / honey / propolis soaps, cosmetic, creams
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Own consumption of honey food and medicine and propolis (medicinal use)
الآثار الايكولوجية
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Conservation of forests and particularly melliferous trees as well as pollination of forests and crops
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Conservation of forests and particularly melliferous trees as well as pollination of forests and crops
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Conservation of forests and particularly melliferous trees as well as pollination of forests and crops
الأنواع المفيدة
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
Pollination
التعليقات/ حدد:
Pollination in area approx 4-6 km from hive
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
التعليقات:
Unknown sensitivity of bees to climatic extremes; resilience of bees is assumed, but changes in honey quality and quantity depending on forage available with changes in forest cover/ structure
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Initial investment in hives often recouped in 2-5 years, depending on level of production
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
4500 households and 100% of the area covered
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
4500 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Established and knowledgeable beekeepers in a community aid dissemination of technology and spontaneous adoption.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Protection of the forest because beekeepers are aware of the benefits they receive from this ecosystem |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Pests destroy hives / eat honey (e.g. honey badgers, ants, termites, civets) | relocate hives, stronger/ different hive construction, regular checks |
| Theft of hives | patrol forest, make agreements in community, locate hives near farms/houses, chain or lock hive. |
| Low production | relocate hives to more forested areas, ensure hive located with < 2 km from water source in dry season |
| Bush fires can destroy hive | agreements with farmers/pastoralists about bush fire patrols in dry season, create fire breaks around hive and support trees |
| Rain can destroy hive | use of metal, sheet, grass, raffia or wood as protective ‘roof’, place in a ‘’bee house’’ of locally constructed materials, or under a simple shelter, and experiment with different designs |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية