stone bund [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Eva Ludi
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
erkan (amharic), cab (amharic)
technologies_1389 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Overseas Development Institute (ODI) - المملكة المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
26/04/1999
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
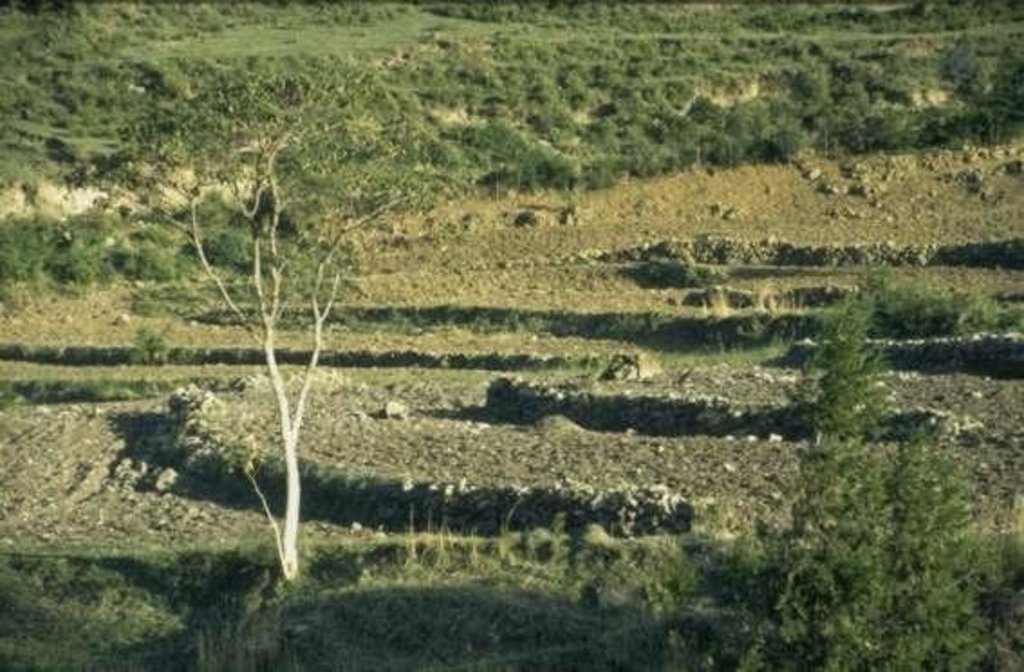
stone terrace more or less along the contour, combined with artificial waterways and traditional ditches to drain excess water, and heightened field borders
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
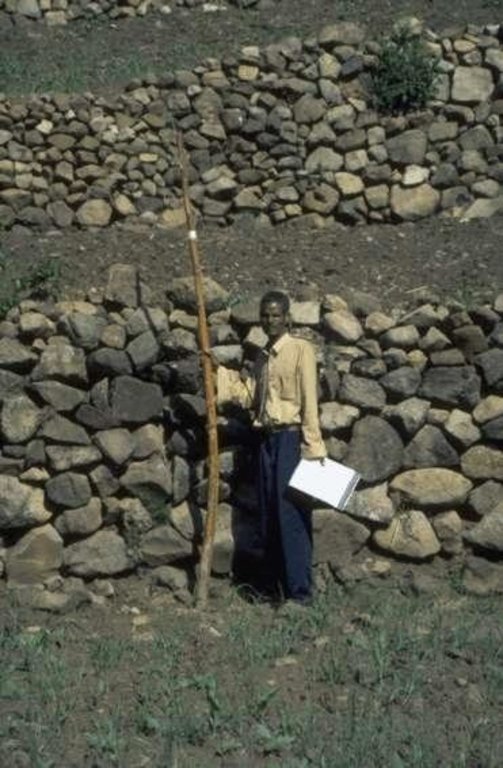
stone bunds, height 0.5 m to 2.5 m, base width 1m to 1.5 m, top width 0.2 m to 1 m (top width mainly below 0.5 m). stones are piled very carefully to form stable terraces, masonry-like, stable drystone walls. In some cases, gesho (local hop, Rhamnus prinoides) is planted above the stone terrace. Bisana (Croton macrostachytus) is planted below the stone bund or along raised field borders. Stone bunds vary in height depending on the slope angle to reach, if possible, flat terraces behind the bund. Bunds are maintained regularly and if necessary bunds are raised. The technology is applied since generations in this area. Farmers continue to build bunds on new plots. A factor favouring the construction and maintenance of bunds - compared with many areas of the Ethiopian Highlans - is that the land distribution of 1996/97 was not carried out in Mesobit & Gedeba.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
North Shewa
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
No historical record
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): continuous cultivation and overgrazing due to high population pressure; declining soil fertility, which is only partially made up with increased inputs; pests
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): continuous cropping and overgrazing due to high population pressure, change of climate, pests
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - DecSecond longest growing period from month to month: Feb - May
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
- تحويل المياه والصرف
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
التعليقات:
Technology known since generations. Knowledge passed down from father to son. One person mentioned the year 1906 EC (1913 gregor. calendar) as the time when SWC started to be applied on a bigger scale in the area. Area of application: unknown. Information given below is for Mesobit and Gedeba KA only (ca 500 ha).
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- الحواجز والضفاف
- S3: الخنادق المتدرجة ،والقنوات، والممرات المائية
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, improvement of soil structure
Trees/ shrubs species: bisana (croton macrostachytus), accacia
Perennial crops species: gesho (rhamnus prinoides)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Construction material (earth): fills up trench behind bund to form level terrace, if soil is moved to build terrace, soil is distri
Construction material (stone): stone is main material , usually stones are collected in the field, sometimes solid rock is broken,
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: livestock management - farmers pooling small area of grazing land
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Ethiopia Birr
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
7,0
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting | نباتية | beginning of and during rainy season |
| 2. | manuring | نباتية | beginning of and during rainy season |
| 3. | collecting stones | بنيوية أو هيكلية | May-June |
| 4. | piling stones | بنيوية أو هيكلية | May-June |
| 5. | observing slope | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 6. | digging | بنيوية أو هيكلية | May-June, small 'dry' season between small and big |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | weeding | نباتية | /annual, several times |
| 2. | cutting branches (gesho) | نباتية | /every 2nd to 3rd year |
| 3. | piling stones | بنيوية أو هيكلية | February-June/annual |
| 4. | reparing broken terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | February-June/annual |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
length of structure, per day one person constructs about 3 m new stone bund
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
financial costs are very small compared to manual labour. Costs for labour as indicated in 2.7.1. are given as opportunity costs!
much of the labour is done using traditional group work debo (= working party) or wenfel (= reciprocal work) or newly introduced group work (mass mobilisation).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Two growing seasons for teff
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep, also deep (soil depths estimated only. soil depth also varies depending on location in relation to stone bund.)
Soil fertility is medium
Soil infiltration/drainage is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich (yield lasts for 12 months).
80% of the land users are average wealthy (yield lasts for 8 months).
15% of the land users are poor (yield lasts for less than 8 monts and people are involved in petty trade).
Off-farm income specification: Some families rely heavily on off-farm income (petty trade, handicraft). For these families, off-farm income can be as high as 50%, usually it is in the order of 10-20%.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
Comments on adoption trend: young farmers are a bit more reluctant to continue building new bunds, however they maintain existing bunds.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية