Infilling of gullies with vegetative structures [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Daler Domullojonov
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Пуркунии селрохахо
technologies_1450 - طاجيكستان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Barotov Bahrom
Welthungerhilfe
طاجيكستان
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Ashurov Bakhtiyor
Welthungerhilfe
طاجيكستان
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe e. V. (Welthungerhilfe) - طاجيكستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/05/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Reclamation and infilling of eroded gullies using barriers of willow branches and live mulberry cuttings to trap loess soil from surface water runoff.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
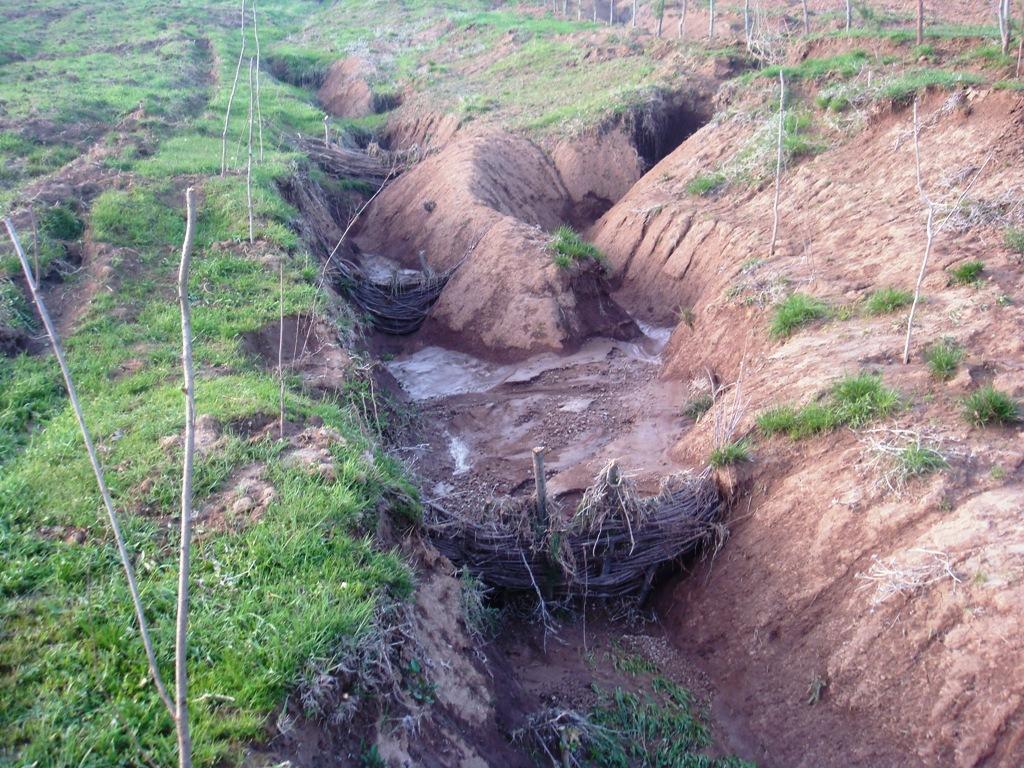
Due to many different factors and mechanisms, soil erosion is at an advanced stage in many of the hilly and mountainous parts of Tajikistan. After disrupting the soil cover in steep areas, starting the process of soil detachment and transportation water runoff gets concentrated into specific areas. As a result, rills develop on the steep areas, and eventually enlarge into gullies.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, low cost barriers are constructed from flexible living branches of a sprouting variety of tree, such as willow. These branches are placed along the gulley at intervals of 3-10 metres, so that they slow down the flow of surface water and trap the sediment, thus eventually filling in the gulley over a period of several years.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The barriers are designed to slowly help infill eroded gullies by trapping the sediment from muddy surface water runoff. This helps prevent further erosion, increases the amount of land available for pasture, and reduces the risk of mud flows or floods further down the slope.
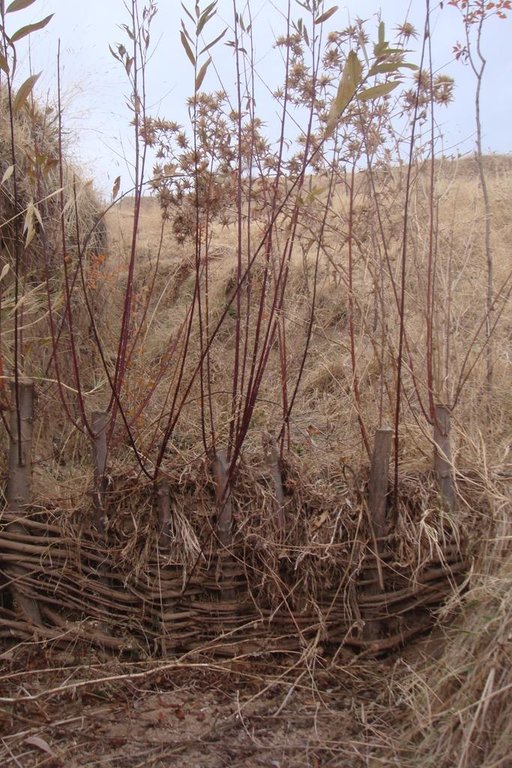
In gullies no wider than 1-2m, live cuttings from local tree varieties with a diameter of 3-5cm and 1 metre in length can be used to establish horizontal woven barriers across the gulley. The barriers are placed at 3-5m intervals along the gulley, starting at the base.
These barriers are constructed from cuttings that are woven in narrow sections with 5-6cm intervals between them. Enforcement and strengthening of these plugs can be achieved through the use of long branches of locally available mulberry. The height of the plug should not exceed 0.5m. The construction activities start in the spring and within several weeks some of the cuttings begin to sprout and grow. To avoid erosion at the sides of the structure, the cut offs are embedded into the sides of the gulley.
Natural / human environment: Gulley plugging is used in pasture land that suffers from overgrazing, deforestation and trampling, which has resulted in the degradation of the soil. Subsequently, the soil has become more vulnerable to the impact of heavy rain in the spring and autumn months, and is prone to erosion from surface water runoff.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tajikistan / Khatlon
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Khovaling / Dorobi
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology was developed and promoted using the framework of EC TACIS funded Welthungerhilfe project in Khatlon
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
cows, goats, sheep
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing on pasture lands, that leads to reduced vegetation cover and deforestation, contributes greatly to the causes of top soil erosion and gulley formation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies are formed after intensive rainfall events. There is nothing in place to stop this erosion.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cows, goats. sheep
Grazingland comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of grazing system comments: There is local grazing on this land, but some areas are subjected to nomadic grazing during the migration of livestock between the winter and summer pastures.
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: March - June
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.017 m2.
Approximately an 800 m long eroded gully was reclaimed.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Trees were cut from a steep slope on the side of the hillside.), overgrazing (Freely grazed area, carrying capacity less than animal numbers grazing.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (More intensive rainfall.), land tenure (Lack of control of livestock grazing activities.), poverty / wealth, war and conflicts (Gullies appeared after civil war.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
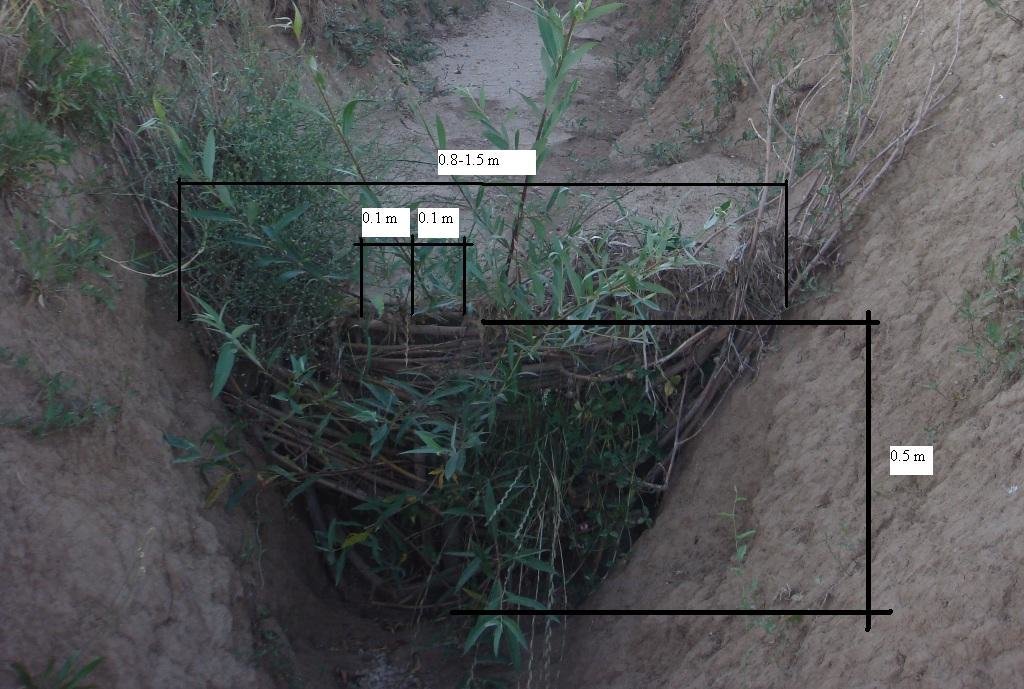
For the plugging of the gully, a low cost and simple barrier was made from locally available fast sprouting species of trees; in this case live willow cuttings were used. In the gully a narrow section was selected, and cuttings (3-5 cm diameter, 1 m length) were placed in a line with 10 cm intervals in between. One third of the cuttings were planted in the gulley, and the rest were used to create a 'wave' wall of flexible branches, which was planted with local mulberry trees (1-1.5 cm diameter). The weaved branches have to be pushed down from the top to make the barrier suitably dense. The ends of the mulberry branches have to be stuck securely to the soil inside the gulley.
Location: Dorobi village. Khovaling / Khatlon / Tajikistan
Date: 2nd July, 2010
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: mulberry
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Construction material (wood): Willow and mulberry branches
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Tajik Somoni
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,5
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5.50 $
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | planting mulberry in willow wave structure | نباتية | spring |
| 2. | establishment of barriers in gully bed | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once in the beginning |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Planting mulberry | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Establishment of barriers in gully | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 90,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reinforce structure with additional seedlings when needed | نباتية | annually |
| 2. | establishment of additional barriers after filling existing barriers with sediments | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once per year in beginning of rainy season |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Reinforce structure | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Establishment of additional barriers | Persons/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Mulberry seedlings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Willow cuttings | Pieces | 20,0 | 1,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 90,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
The unit cost is for a gulley plug, 1.5 metre wide and around 1m in height.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The materials used to construct the gulley plug are locally available, and are therefore free of charge to the land user. The labour (or time in labour) is the most substantial cost, and this is directly proportional to the number of gulley plugs required to infill the entire eroded gulley. If there is a big sediment load in the surface water runoff it will back fill behind the gulley plugs rapidly and additional barriers will need to be established.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Precipitation is concentrated during the autumn and spring, averaging 1100-1200mm
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 1257 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Average slope 12.6%, max slope 17.2%
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture = loess soil
Soil fertility is low due to over use and lack of fallow time.
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water: In the area around the gulley the land is compacted.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 2%
20% of the land users are average wealthy.
80% of the land users are poor.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
The trees can be harvested once the gulley is full of sediment.
منطقة الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1.5
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1.6
التعليقات/ حدد:
Gully filling can help create new areas of arable land.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
Livelihood and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Sediments are trapped
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انزلاقات أرضية / تدفقات الحطام
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
القدرة على التخفيف / الترشيح
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
التعليقات:
As a living barrier it needs to grow, and therefore it is sensitive to drought conditions.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
10 households in an area of 1.7 ha
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is little trend towards (growing) spontaneous adoption of the technology.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
No training and additional skills are required. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Broad promotion to other communities with similar climatic conditions and similar issues. |
| It is low cost option. |
| Easy to establish, with a low workload. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Gulley plugs are relatively easy to construct and have a low initial outlay. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be further supported by the strong involvement of local authorities, through the organisation of cross visits, and disseminating ideas between farmers. |
| It is flexible as various varieties of local sprouting trees can be used to build the gulley plug. |
| It can prevent further erosion and expansion of the gulley. It can also increase the amount of land available for pasture activities. |
| Environmentally friendly |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The gulley plug is weak in the beginning as the mulberry trees become more established. It is more susceptible to the impact of heavy rainfall events and concentrated run off down the gulley. | High levels of maintenance in the first initial few seasons. |
| The gulley plug becomes less effective as the gullies become wider and deeper. | Fencing around the gulley. |
| The gulley plug has to be protected from livestock who will eat the vegetation. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Welthungerhilfe projects in Khatlon region, Temurmalik district
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية