Land terracing in olive groves [اليونان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Deborah Niggli
Αναβαθμοί Greek
technologies_1512 - اليونان
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mentzidakis Ioannis
imetzis@nagref-cha.gr
National Agricultural Research Foundation - NAGREF, Institute of OliveTrees and Subtropical plants
Agrokipio, 73100 Chania, Crete
اليونان
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
07/02/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Sustainable development of olive groves III [اليونان]
لا يوجد وصف متاح.
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Terraces are constructions built mainly in hilly areas to reduce water erosion losses from cultivated erodible soils and for water conservation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
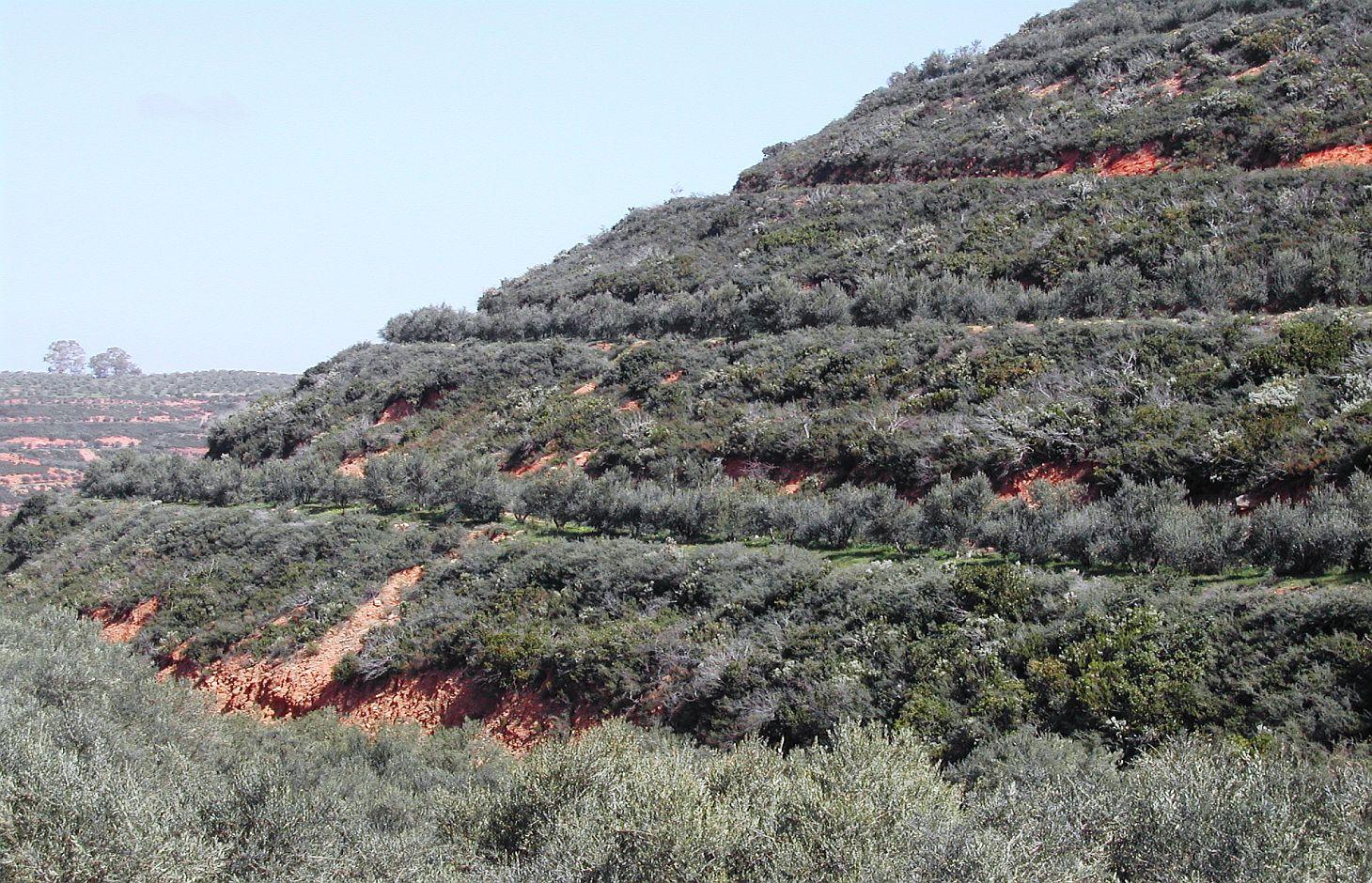
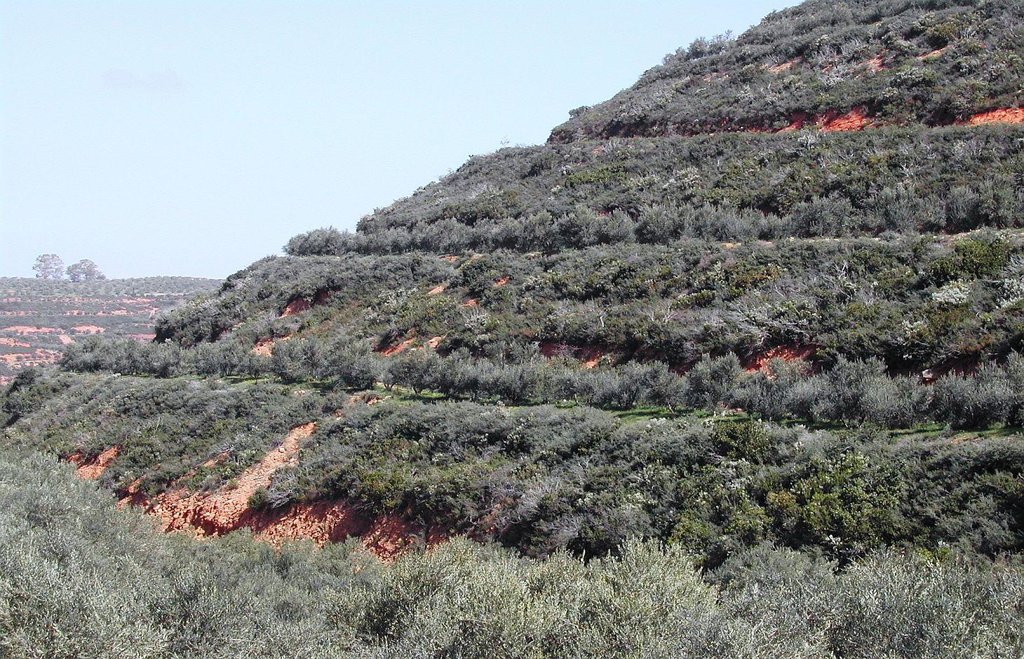
Bench terrace is the main type of terraces existing in the area of Chania. Land terracing is mainly found in the middle and upper zone of the study area and especially in steep slopes and in soils formed mainly in shale or conglomerates parent material. The land in which terraces have been constructed is estimated to 7.7% of the total area of Chania. Some bench terraces have been constructed recently in very steep slopes for cultivating the land.
Local agronomists recommend the construction of terraces as a measure for soil erosion protection in hilly areas.
The first step for construction of bench terrace is to clear the field of trash, dead furrows are filled in, and small ridges are levelled. The interval between terraces depends on soil characteristics and amount of rainfall. Usually, it is not recommended space interval narrower than 30 meters. Terrace system design usually begins with a technician evaluating the water regime of the field from observations, soil surveys, and other information. The next decision is whether waterways should follow natural draws or be constructed on new sites. The channel along the terrace for removing excess of runoff water is at least 30 to 45 cm deep and the maximum allowed gradient 0.4% for most soils to avoid serious erosion. Terrace layout begins from the highest point of the field. The vertical fall and slope gradient from the high point to the approximate site of the top terrace, usually 30 to 50 m downslope (depending on gradient), is determined with an engineering level. It is usually preferable to begin staking a terrace at the waterway and work up to the top end. Usually some stakes need to be reset to avoid short, sharp curves and to make field work parallel to the terrace easier. The first layout of a terrace system seldom achieves the most satisfactory design. Some unexpected topographical feature may show up and necessitate changing one or more terrace lines. The final terrace positions should be identified by plough furrows or other implement marks before construction begins. Conventional terraces can be built with bulldozers, motor patrol graders, carryall scrapers, elevating grader terracers, mould-board ploughs, disk tillers with 60 cm or larger disks, and with hand tools and baskets, headpans, or other carrying devices. Terraces rarely should be longer than 600 m. Terraces should not be longer than 375 m on already gullied land. Longer terraces need to be sub¬divided with an outlet provided for each segment. Terraces must be wide enough to accommodate the equipment that will be used in the field, generally not less than 4.5 m. The flatter these slopes are, the easier is to farm but the more expensive they are to build. Trees are usually planted in the upper part of the terrace. In modern terraced fields crop cultivation is fully mechanized. In such terraced fields all farm operations should carried out as nearly as parallel to the terrace as possible to minimize water and soil movement between terraces and to reduce damage to the terrace ridges. The most evident effect of tillage operations, after several years is the increase in the base width of the terrace. The best method of maintaining the shape of the terrace cross section and counteracting erosion from the inter-terraced area is by ploughing with a reversible mouldboard. In steep slopes is recommended to keep the natural vegetation in the part of the steep slope for soil erosion protection.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
اليونان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Selinos province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Chania-Cete
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion and loss of water
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Difficulties in cultivatiing the land and harvesting the olive fruits
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: March to July, Second longest growing period in days: 150, Second longest growing period from month to month: March to August
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 55 m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S1: المصاطب المتدرجة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Clearing of natural vegetation for planting olives. Natural vegetation is kept in the steep slope for soil erosion protection), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (access to the field by machineries)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (destroying soil characteristics)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
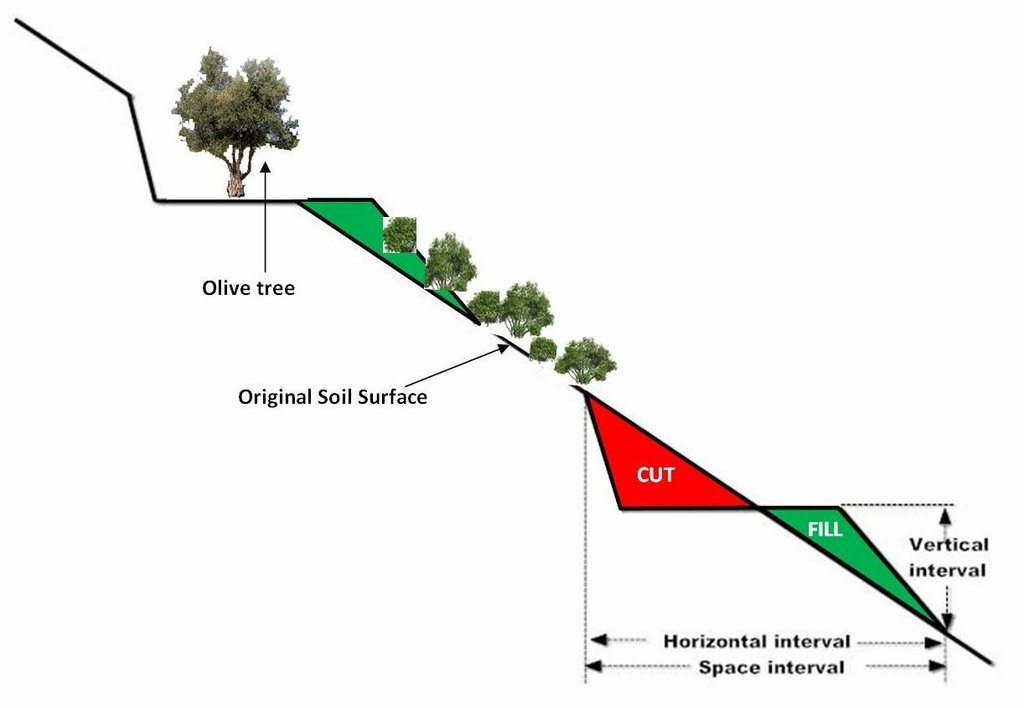
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
size of the terrace including bench and sloping part is 35 meters. The original slope with the natural vegetation is 64%. The bench width is 6 meters, the size of the sloping part with natural vegetation is 22 meters, and the length of the bench 145 meters. Olive trees have been planted 2 meters from upper part of the bench.
The vertical interval (VI in meters) between two adjacent terraces can be estimated by the formula given by the U.S. Soil Conservation Service: VI = xS + y. Where x is rainfall factor, S is slope gradient (%), and y is soil and cropping factor. The U.S. Soil conservation Service recommends values for x and y 0.12-0.24, and 0.3-1.2, respectively. The horizontal interval (HI in meters) can be calculated from the equation: HI = (VI/S)*100.
Location: Strovles. Crete
Date: 5/2007
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It needs planning of location of various strips and water outlets)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (technical supoport)
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Terrace: bench level
Spacing between structures (m): 35
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 145
Construction material (earth): Displacement of soil for constructing the bench
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 65%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 65%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Euro
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
1,39
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
80.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Shaping the land using a bulldoze and constructing terraces, cost 1950 euro/ha | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 1950,0 | 1950,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1950,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | clearing waterways, and checking terraces for collapse, cost 60 euro/ha | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once per year |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 60,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Bullldoze
year 2011
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Slope angle, soil depth, parent material
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
670 mm, 6 months dry period
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics, temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- الجر الحيواني
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women use to work in the house
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1200 kg/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1500 kg/ha
تنوع المنتج
إدارة الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
120 euro/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80 euro/ha
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3600 euro/ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
4500 euro/ha
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
increase farmers income and reduction the off site effects
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
15% more water stored into the soil
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
75% reduction in runoff
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
10% increase in soil moisture
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
75% reduction in soil loss
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 90-50%
التعليقات:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
150 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
85% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
240 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| increase of farmers income from the land exploitation in less favourable areas |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Land terracing is one of the soil conservation and cultivation techniques for combating land desertification . It is a practice applied to reduce rainfall runoff on sloping land, from accumulating and causing serious problems of soil erosion. Terraces, usually allow better management of soil and water, improve access to land and facilitate farm operations. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Planning of land terracing | Local institutes and experts to help them |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Disturbing natural environment and landscapes | Better planning |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Sustainable development of olive groves III [اليونان]
لا يوجد وصف متاح.
- جامع المعلومات: Costas Kosmas
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية