Check dam ponds [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Eyasu Yazew
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
May me'ekori ketri
technologies_1547 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kifle Weldearegay
+251 90 233 5495
Mekelle University
P.O.Box 231, Mek'ele, Ethiopia
أثيوبيا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Mekelle University (Mekelle University) - أثيوبيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
11/11/2012
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
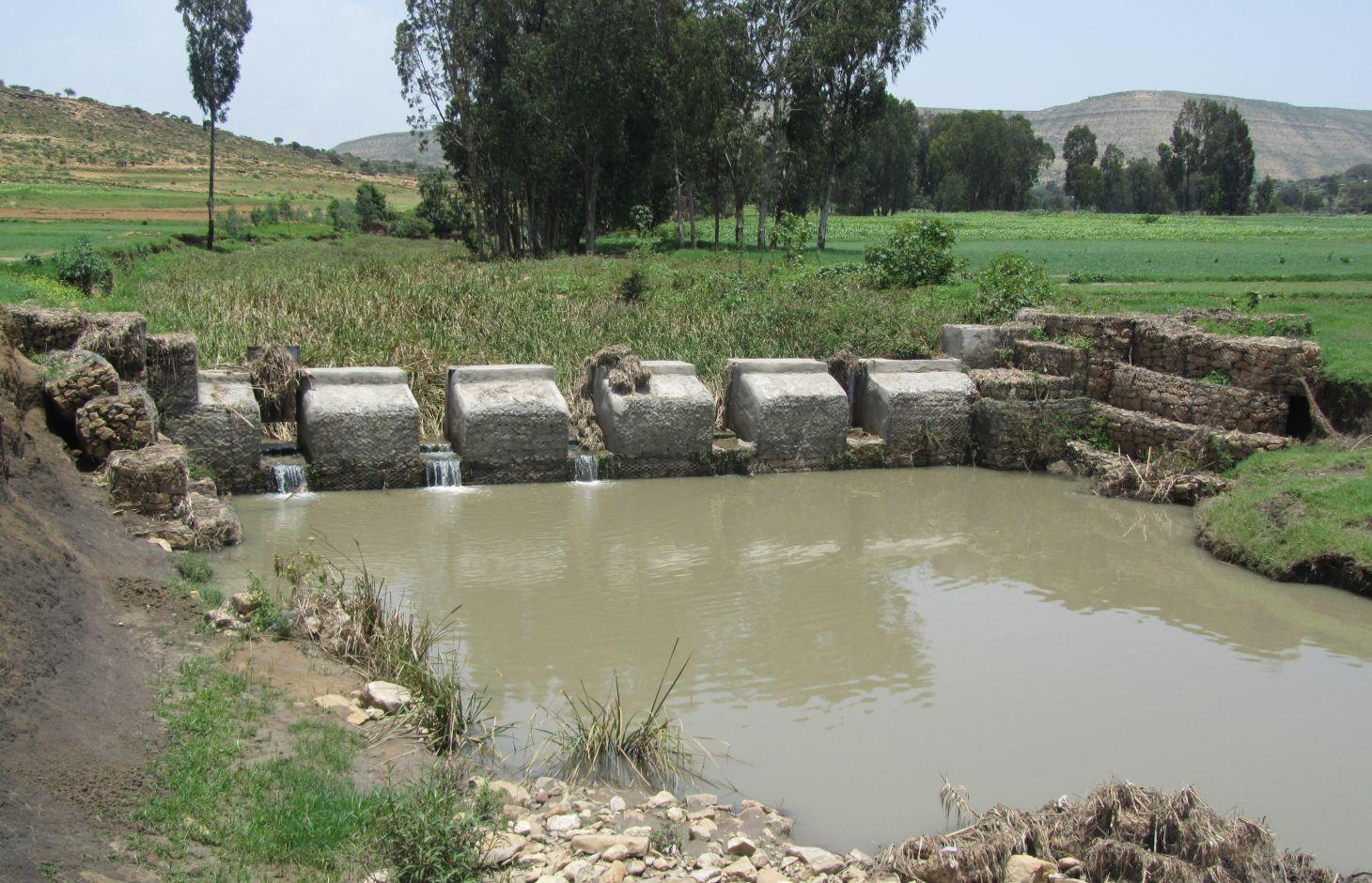
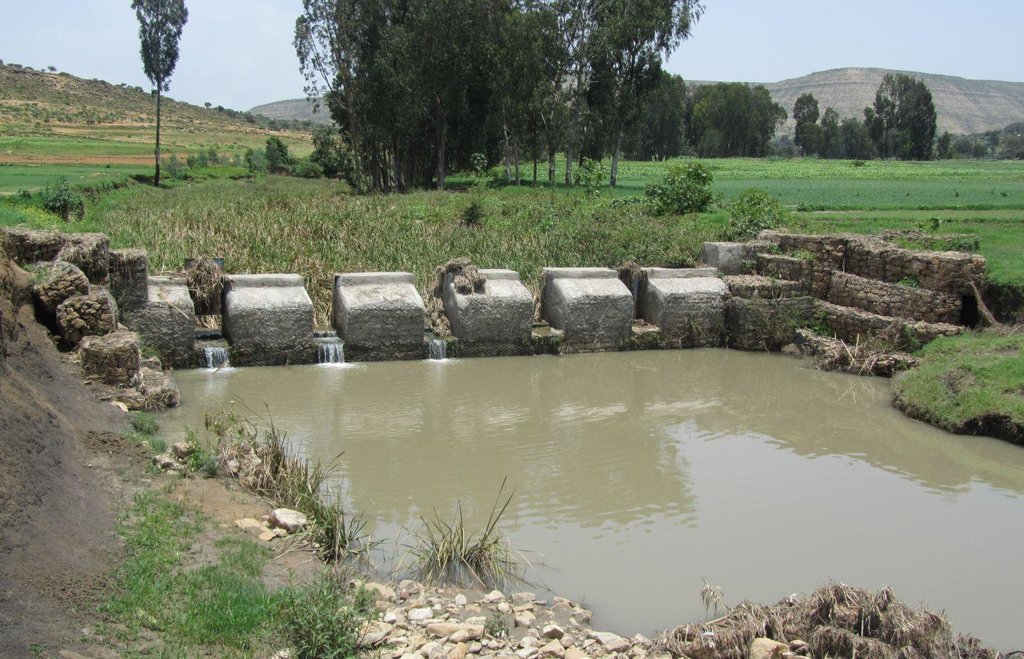
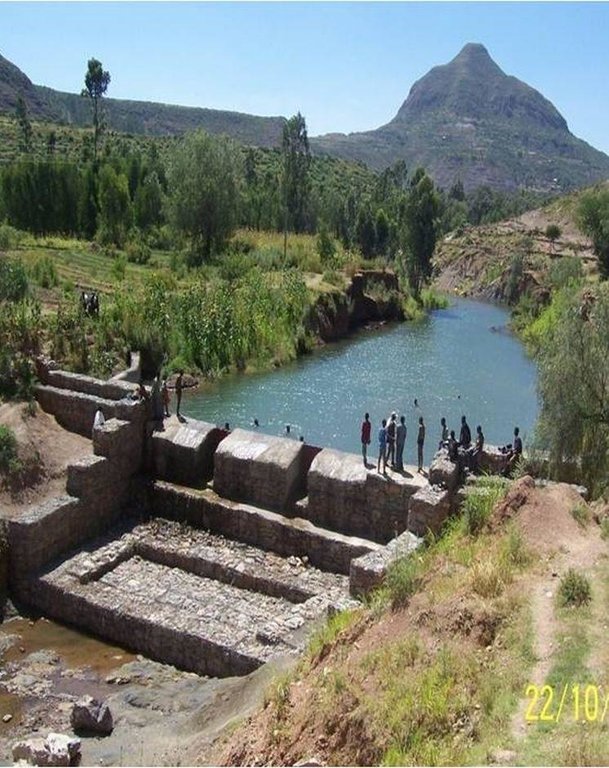
It is a raised wall constructed across a stream/gully using stone, concrete and/or gabion for dual purpose, namely, to pond/store the stream flow behind it for irrigation purpose while at the same time reducing the runoff velocity and enhancing gully rehabilitation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
A check dam pond is a raised wall constructed across a gully from stone, concrete and/or gabion to store water behind it for irrigation purpose using either gravity or lifting mechanism. The structure generally consists of construction of foundation, apron, retaining wall and the checkdam. The width of the checkdam ranges between 1 - 2 m while the height varies between 1 - 2 m depending up on the gully depth. The length of the checkdam depends on the gully width. The spacing between adjacent checkdams is determined based on two factors, namely, the gradient of the river bed and the availability of potential land that can be irrigated. It is also provided with a number of sluice gates which will be removed during the main rainy season to minimize siltation.
Purpose of the Technology: In addition to storing water for irrigation, check dam ponds decrease slope length, slope angle, runoff velocity and minimize soil erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment of a check dam pond starts with collection and transportation of stone and sand. The construction is started by setting out the dimensions from the design on the selected site and excavating the foundation for the different parts, namely, key trench, apron and retaining wall. The check dam is then constructed using gabions filled with stones and tightly tied together with wire. Finally the superstructure is plastered using mortar to prevent the passage of water through the body. Gates of about 1 m wide are finally constructed at about 1 m interval and fitted with sluice gates. Maintenance usually involves fixing damaged gates and reinforcing gabions.
Natural / human environment: Check dam pond is implemented in gentle (2 - 5%) and moderate (5 - 8%) slopes and in medium and light soil types of at least 1 m depth. It increases water availability for irrigation and livestock consumption purposes. It also reduces runoff velocity thereby decreasing soil erosion and enhancing gully rehabilitation.
It requires skilled labour and high construction cost. As a result, it is constructed through external support. However, the number of communities seeking for external support and willing to contribute their share is at the rise. The technology minimizes greatly the risk of crop failure and improves the livelihood of the land users.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tigray
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kilite Awlaelo
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major cash crop: Vegetables such as tomato and onion
Major food crop: heat, barley, teff, maize
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation and overgrazing, high erosion risk, gully formation and land loss, decline in productivity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Population pressure, deforestation, flood, soil erosion, reduced productivity.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: June - NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 105Second longest growing period from month to month: January - April
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
- (Wm): مجموعة كبيرة من الحركات الأرضية/انزلاقات أرضية
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep topography that increases amount and velocity of flood), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, floods, land tenure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
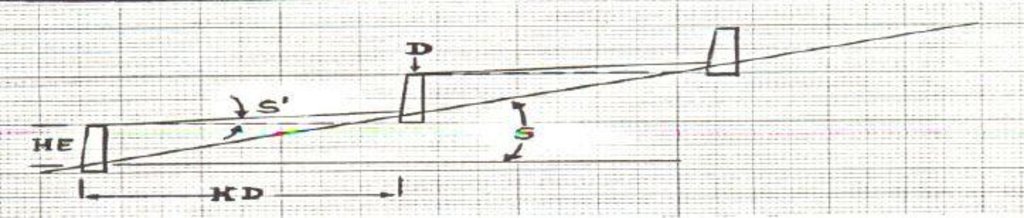
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Check dam ponds are raised walls constructed across a stream/gully using stone, concrete and/or gabion for dual purpose, namely, to pond/store the stream flow behind it for irrigation purpose while at the same time reducing the runoff velocity and enhancing gully rehabilitation.
Location: Tigray. Kilte Awlaelo
Date: 10/10/2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Technical knowledge required for Engineer/designer: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 - 2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 - 2
Construction material (stone): Stones are usually shaped in order to piece together very well.
Construction material (concrete): The chekdam is usually plastered by concrete on the upstream side to prevent the passage of water th
Construction material (other): Gabion, Sheet metal and Angle iron.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Birr
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
18,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.50
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearance and excavation of foundation | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 2. | Stone collection and transportation | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 3. | Sand collection and transportation | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 4. | Gabion masonry work | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
| 5. | Plastering | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4678,0 | 4678,0 | 25,0 |
| مواد البناء | Cement | ha | 1,0 | 953,0 | 953,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Gabion | ha | 1,0 | 6268,0 | 6268,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Sheet metal | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Angle iron | ha | 1,0 | 56,0 | 56,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 11999,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fixing damaged gates and reinforcing gabions | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Dry season |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Digging hoe, shovel, hammer, crow bar
Since the check dam ponds generally vary in depth, width and most importantly in length depending up on the gully profile, calculation of cost per meter length will not be a reliable presentation. As a result, one typical check dam pond was selected and the total volume of the structure and the corresponding total cost of construction calculated. Then, the cost per cubic meter of the check dam was determined by dividing the total construction cost to the total volume of the structure.
The calculation includes the cost for the purchase of industrial materials (cement, gabion, sheet metal and angle iron) and cost of labour used for the construction including site clearance and excavation of foundation, stone and sand collection and transportation, gabion masonry work and plastering.
The price of the industrial materials and the labour wage used in the cost calculation apply to 2012. The daily labour wage for plastering is 180 Birr while it is 50 Birr for all other works.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour, availability of construction material, depth and width of gully.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Average rainfall of 450-550 mm, Main rainy season from Mid-June to August.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is low (medium soils, ranked 1) and very low (light soils, ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium (ranked 1) and good (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water is good (September - January). Also medium (February-June)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 55% of the land (35 Birr/day/person).
30% of the land users are poor and own 35% of the land.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average land holding is 0.6 ha per household.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
Mobile communication:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
خطر فشل الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه للماشية
نوعية المياه للماشية
توافر مياه الري
نوعية مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
دخل المزرعة
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Also: Requires skilled labour
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased investment in health care as a result of increased income.
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
حصاد / جمع المياه
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
فقدان التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
500 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is no trend for spontaneous adoption due to high costs. However, communities are increasingly seeking external support to implement this technology.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Increased water availability for irrigation and livestock consumption How can they be sustained / enhanced? Watershed management |
|
Reduced soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of retaining walls |
|
Increased employment opportunity and income from irrigation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cultivation of high value crops |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Increased water availability for irrigation as well as livestock consumption How can they be sustained / enhanced? Integrated watershed management |
|
Reduce slope length, angle and erosion risk and enhance gully rehabilitation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High cost of construction | Selecting a site that has good availability of construction material and that can irrigate as large area as possible. |
| Require skilled labour | Training of land users |
| Labour intensive | Mass mobilization |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Staff members of the Kilte Awlaelo Wereda Office of Agriculture and Rural Development and Office of Water Resources Development
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية