Afforestation /Tree planting [اوغندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Okubyara emiti ahiyabire etari (Runyankore)
technologies_1577 - اوغندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mpiirwe Emmy
Dept. of Agriculture, Mbarara District Local Government
Mbarara District
اوغندا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mazimakwo Kukundakwe
Kabale District
اوغندا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry, and Fisheries of Uganda (MAAIF) - اوغندا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Afforestation/Tree planting [اوغندا]
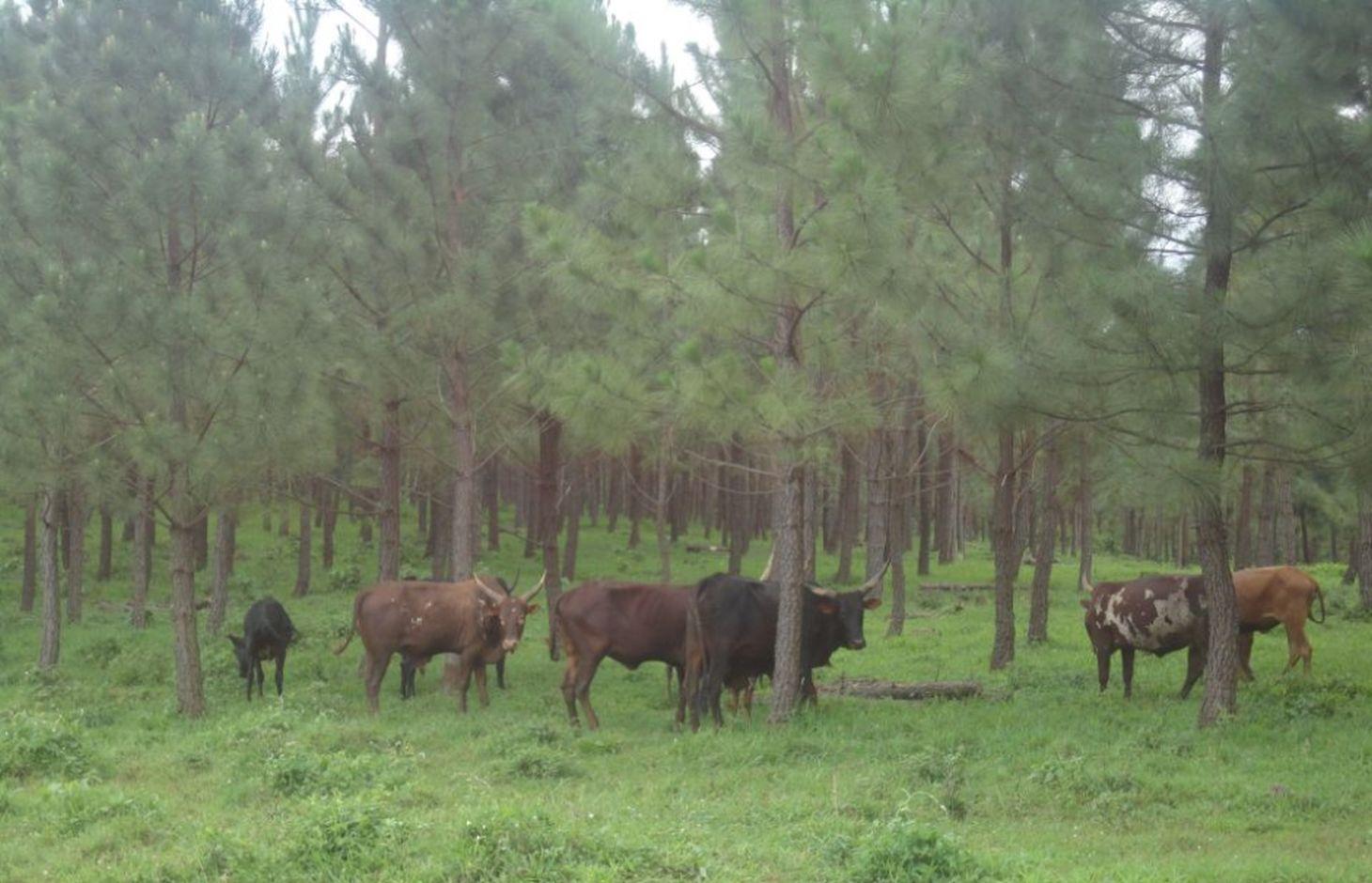
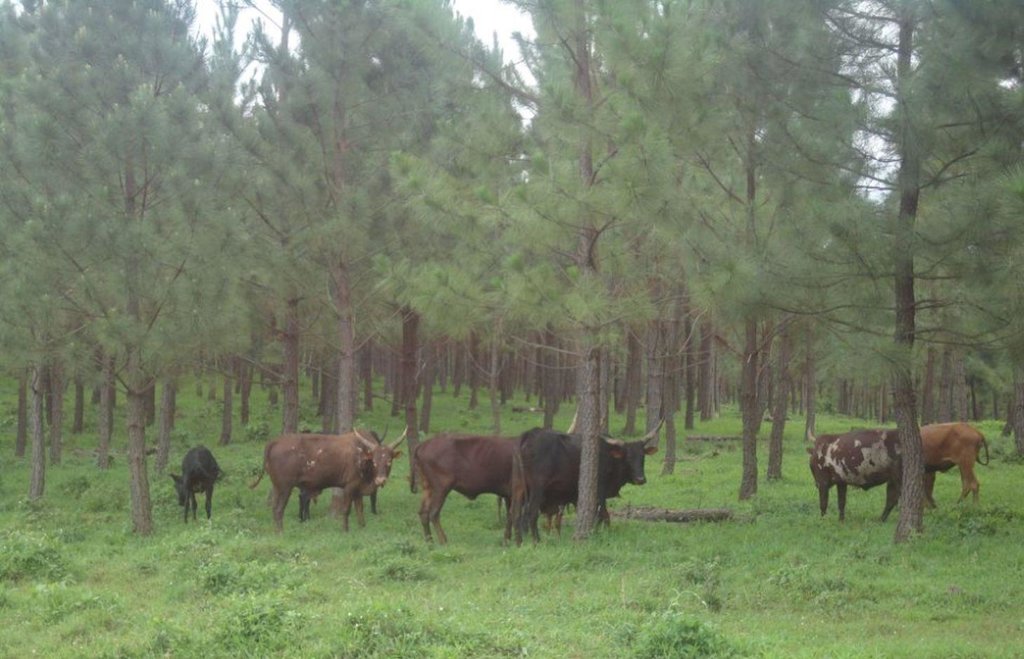
Tree planting carried out by individual land users on hilly slopes to improve soil cover ,reduce wind strength , provide wood fuel & household income.
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Pine tree forests have been strategically planted on previously bare ridges and slopes to mitigate mass soil movement.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The technology has mitigated soil erosion and damage on road infrastructure by fast flowing runoff, and rejuvenated biodiversity in the area. Much forest cover in Mwizi has been decimated as the need for fuel wood, charcoal and land for agriculture has increased. Coupled with changing weather patterns, human and livestock pressure, many ridges and hilly slopes have been left bare. With annual rainfall of over 1200 mm, runoff often causes extensive damage to cropland and road infrastructure.
In Rubagano, the Forest Department of the Government of Uganda set aside over 20 km2 of degraded ridges and hilly slopes for tree planting. The department planted the first part as a demonstration. The other part is being planted by individuals. Projects such as ULAMP (5 to 10 years ago) and Kagera TAMP (since 2011) have worked with the communities in the area, encouraging the technology by supplying Pinus spp seedlings, training farmers to start their own tree nurseries and forming Farmer Field Schools as vehicles for generation of community consensus on sustainable land management interventions.
Purpose of the Technology: The objectives of afforestation are to provide protection of the land against soil erosion, to return productivity to degraded hilly slopes, to reduce crop (banana) devastation caused by strong winds during rainy season, to grow the capacity of available fuel wood in the area, to diversify future households incomes and protect public infrastructure, especially the road network during the rainy season.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Most of the older trees, 3 years and over, were planted from seedlings bought from established tree growers. Currently, the Farmer Field Schools are planting seedlings from their own nurseries. In the nursery, plastic sleeves called poly-pots are packed with top-soil mixed with animal manure to provide a growing medium. A calculated amount of sand is added to enhance drainage. Sowing, watering and root pruning are carried out manually.
Out on the hilly slopes, the land user establishes the woodlot and maintains the trees using his own resources. Field trainers facilitated by Kagera TAMP provide technical guidance to farmers regularly.
Natural / human environment: Woodlots are established on degraded hilly slopes or any other land use type that is not under crop production. The trees need to be protected against destruction by wild fires and livestock.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
اوغندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Uganda
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mbarara
التعليقات:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.85203 30.62232; -0.85792 30.62021; -0.85850 30.62204
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
2 years for concerted project initiative but more than 10 years for land user initiative.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الحماية من المخاطر الطبيعية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الزراعي
- الرعي الحرجي
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion on hilly slopes denuded by livestock overgrazing.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Continuous loss of soil and livestock pasture due to lack of, or inadequate vegetation cover
Plantation forestry: It takes long to harvest.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The adoption is slow because trees take long period to mature and it is expensive in establishment stage.
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.5 m2.
Tree planting is continuous over a 20 km2 area.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting of short savannah trees for fuel & agricuture land .), overgrazing (Communal and with large herds (over 150 per household)), droughts (Extended droughts over several years in the past decade)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Thatch, mulch, etc.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المؤلف:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabale
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara District. Uganda
Date: 5-DEC-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (A good grounding in planted forest management including best practices and what could go wrong.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Needs technical knowledge on seedling, planting, thinning weeding and spacing; maintenance including protection from fires and disease)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Trees/ shrubs species: Trees (pine spp.) planted from seedlings
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15-25%
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
UGX
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
2600,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.85
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging holes | نباتية | Beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Buying tree seedlings | نباتية | Beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Transporting seedlings to the site | نباتية | Beginning of rainy season |
| 4. | Planting tree seedlings | نباتية | Beginning of rainy season |
| 5. | Fencing | نباتية | Any time before the beginning of relevant rainy season |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 18,63 | 18,63 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 6,8 | 6,8 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 28,43 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
US $ per unit and US$ per hectare is not quantified because labour was contracted yearly at a cost of Shs 3,000,000.
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | نباتية | Once every rainy season |
| 2. | Pruning | نباتية |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 9,0 | 9,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 0,7 | 0,7 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 12,7 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: pangas, hand hoes
Planting 900 pine tree seedlings per hectare (on average), at 3m by 3m spacing.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Availability and cost of labour are the most determinate factors affecting establishment and maintenance of the technology.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
September to December and March to May rains. Altit
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average annual temperature 18°C to 24°C, very close to the equator.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: The plantation area ranges between 1650 and 1850 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (it is easy to reach the underground rock)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (rocky and coarse)
Soil fertility: Very low (ranked 1, soil fertility was poor) and low (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (the land was bare with rocky soil)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (water infiltrates slowly/easily)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (the soil drains easily)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: >50m (It is very hard to reach ground water table)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (while the rainfall is good, permanent wells are scarce. Runoff dams behind natural rock formations or concrete walls on a rock base, but quickly drys up after the rainy season)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, while it looks a muddy brown, it has been used for drinking and other domestic purposes without observable harm to the users)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Slowly rejuvenating since the establishment of the technology.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: In Rubagano, the women are mostly involved in ensuring food security of the household and are not normally involved in aforestation. However, the Farmer Field School methodology has brought many women on board and, helped by the understanding that fuel wood collection is a women's role, women are developing interest in the technology.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 40% of the land.
40% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The technology is new and apart from providing grazing land in the short to medium term, it will yield dividends in 20 to 25 years. Meanwhile, those who are keen on the technology continue to depend on their usual income generating activities, on-farm or off-farm.
Market orientation: Mixed (Land user wanted to reduce soil erosion , increase fuel wood , diversify future income of households)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Most households have less than 1 ha. Few land users have 5-15 ha.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
التعليقات:
The land users own land individually inherited or bought by the holders. Water harvesting and storage in underground tanks is slowly introducing individual water rights and household water security.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantification of benefits is difficult at the moment because there is no harvest from the planted trees now.
تنوع المنتج
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The costs of maintainance.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The land was bare before, land slides were destroying infrastructure like roads. Problem well mitigated.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not yet to reap the economic benefits of tree planting because trees have not matured.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
التعليقات/ حدد:
With dense forest come the risk of fire. this is common in a neighboring district (Kiruhura) but is not yet a problem in Rubagano.
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
Once established, the pine trees can tolerate all kinds of weather extremes. However, before the initial 12 or so months of establishment, the seedlings are very sensitive to drought and dry spells and will likely dry up because irrigation is not an option in Rubagano, water sources being quite scarce. Mulching helps in preserving soil moisture but the mulch should be at least 30cm away from the plant to avoid destruction by pests.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The land users expect to benefit from the technology when fully established.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
125
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
125 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: While the external material contribution was by way of tree seedlings and contributed probably just 5%, all seedlings were supplied by the project.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Land users have committed their own resources (over 95% of total establishment costs) but all received the seedlings, at least initially, form the project. The incentive was a wake-up call and the farmers have adopted the technology with enthusiasm.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The trend is slow due to high cost of initial investment and limited land for tree planting.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Protection of soil cover. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fencing off the woodlots from livestock and other land users. |
|
Provision of fuel woodl. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular pruning and thinning. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
The technology has improved soil cover and reduced soil erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More effort should be put into mobilization of land users in order to scale up best practices onto other areas with bare hills and slopes. |
|
The technology provides an easier alternative source of fuel wood from the remaining pockets of natural woodland. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular thinning should provide even more fuel wood and convince land users, especially women, of the advantages accruing from adopting the technology. |
|
Diversification of future household income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular monitoring of the growth of trees to check for pests & diseases. |
|
improvement of micro climate conditions. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting trees that have little negative effects on other crops in other land use types. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Loss of biodiversity due to trees suppressing under growth of other species. | Copicing to raise the canopy and experimenting with multistory cropping could improve sunlight penetration and improve the emergence of undergrowth. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Afforestation/Tree planting [اوغندا]
Tree planting carried out by individual land users on hilly slopes to improve soil cover ,reduce wind strength , provide wood fuel & household income.
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية