Area closure on degraded lands [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Deborah Niggli
Yetrakot Meret mekelel (Amharic)
technologies_1598 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Bekure Melese
WLRC
أثيوبيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Water and Land Resource Centre Project (WLRC)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [أثيوبيا]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- جامع المعلومات: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Area closure on degraded lands is a land management practice used to rehabilitate and conserve the natural resource bases, and enhance its natural regeneration and restoring capacity and productive functions by excluding animal and human interferences through community consultation and collective actions.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
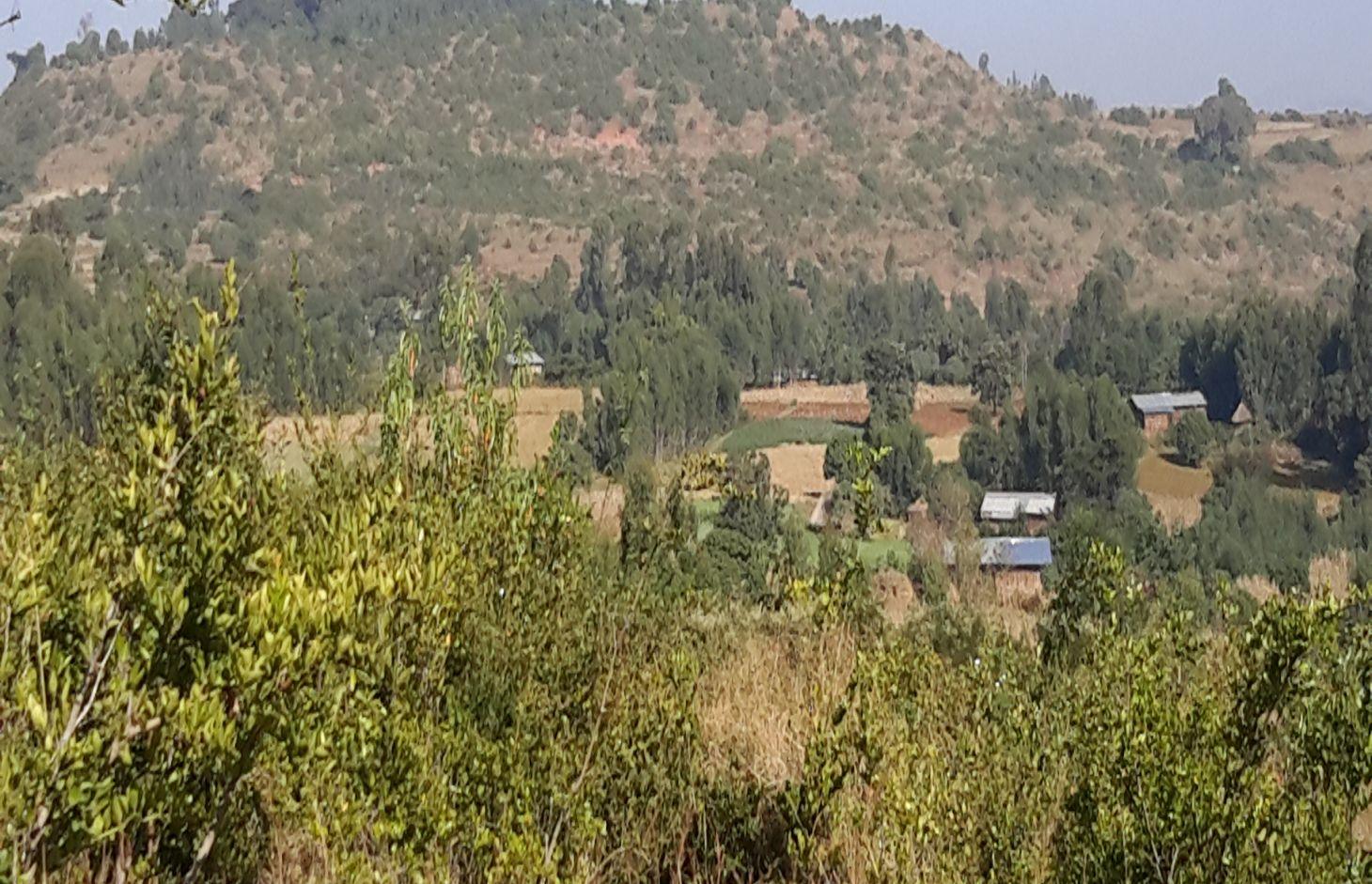
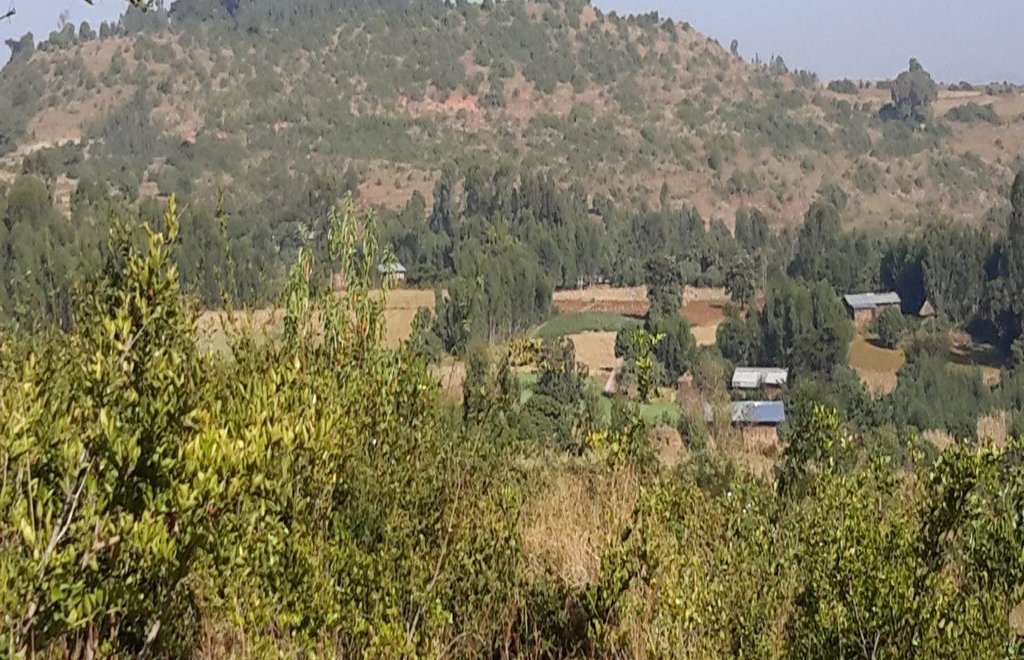
Area closure is a land management practice that helps to rehabilitate degraded lands, restore the biophysical conditions like soil, vegetation and hydrology by avoiding the interference of animals and human. Because of over grazing and erosion impact, areas delineated for closure are usually degraded shrub or pasture lands that served for grazing. First of all, implementing area closure requires continuous dialogue and discussion with community to reach consensus to close. The community wants to make sure they have benefited from the technology as the land was serving for grazing. They should take the responsibility and create sense of ownership to implement conservation measures, protect and maintain closure areas, and regulate utilization of benefits gained out of it. Questions raised from the community must be discussed thoroughly ahead of the implementation. What part of the degraded land? For what purpose the area is closed? Who are the users? Who are responsible to protect and manage the developed resourcess? How is the benefit sharing among identified users? Commonly, the shared benefits from area closures are hay for livestock through cut-and-carry system, timbers from plantations, and honey production.
Depending on the soil, rainfall and slope conditions different structural and vegetative measures are integrated to enhance the fast regeneration of plant species, restore the soil and increase water availability. It includes enrichment used to rehabilitate and increase the vegetation cover, vegetative and structural measures to retain the soil and water on its place. Structures such as hillside terrace often integrated with grass or shrub hedgerows is used to control soil erosion. In-situ water harvesting structures such as trenches or half moon or eye brow are used to harvest and infiltrate rain or runoff water to increase regeneration and survival of planted trees. Trees and/or shrub species that have high rehabilitation and multipurpose values are used as enrichment plantations. Closed areas need collective action to protect, maintain and manage the common resources. Collective user rights have to be entitled to bring equity on resource sharing and minimize social conflicts.
The purposes of area closure are: 1) rehabilitate degraded lands, 2) protect and restore the natural resource base, and 3) change into productive land and enhance economic and environmental functions of rehabilitated lands.
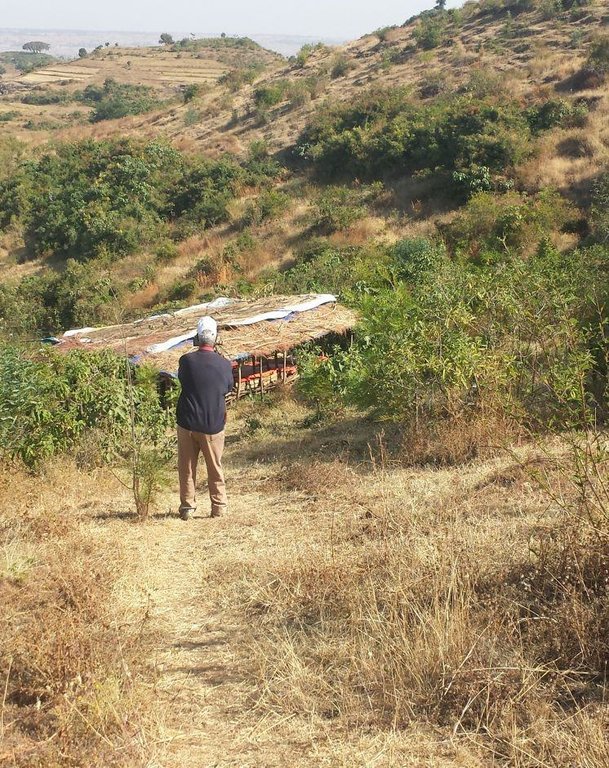
Implementation of area closure begins with the selection and demarcation of area through genuine participation of land users. After identifying the area to be closed, at establishment stage construction of ditches and terraces is made using stones combined with grasses or shrubs of multipurpose value such as Vetiver grass, Dinsho grass, Bana grass, susbania, etc. Depending on site conditions, enrichment tree species which have rehabilitation and soil restoration purposes are planted in the form of wood lot or scattered tree plantation. Among the common species, A. albida, A. saligna, A. decurrense, Gravilia robusta, etc. are used to rehabilitate and serve as fuel wood and timber. In moisture stress areas structures like trench, level bunds, and half moon should be constructed to increase survival rate of planted tree/shrub species whereas in areas having sufficient moisture these structures, depending on the landforms and soil drainage conditions, help to increase infiltration and recharging of ground water in downstream areas. Therefore, site selection and demarcation, construction of soil conservation and moisture conservation structures, and seedling management and plantation of multipurpose trees, shrubs and grasses are the activities accomplished at establishment stage of area closure. The required inputs are stones, seeds/seedlings, grass cuttings/splits, hand tools, and collective labor. For recurrent maintenance activities, seedlings and cuttings for re-plantation purpose or replace dead seedlings, stones to repair damage stone terraces and moisture conservation structures. Harvesting and transporting of area closure products such as grass and timber become a recurrent activity. Person days per hectare per year required for plantation (preparation of holes and planting) is 11.5, for harvesting and transporting harvested grass is 30, and for terrace construction is 26.5.
Area closure management is commonly practiced on degraded hills where soil is highly depleted, its water holding capacity is low, and vegetation is denuded. Usually degraded lands are used to serve for communal grazing system. The degree of land degradation becomes severe where there are high livestock and human population pressure. Management of closure area and the benefit sharing has to be regulated using agreed bylaws.
The living condition depends on subsistence crop-livestock mixed farming. On average households have 5-6 family size. Crop production is meant for home consumption with small surplus for local market. The services related to water supply, energy supply, and infrastructure are low. Besides it is an asset, animals often used to cope shocks during drought periods.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Amhara National Regional State
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Mecha / Yilmana Densa / Bahir Dar Zuria
2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Area closure as an integrated SLM technology is practiced in recent years. However, the land users have their own traditional practice by closing grass lands or shrub lands during the rainy season.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
أراضي الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الزراعي
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation due to different forms of soil erosion and nutrient depletion, excess removal of crop residues, excessive overgrazing, shortage of pasture lands and its low productivity, excessive and inappropriate construction of traditional ditches, and increased demand of trees for the purpose of fuel wood and timber.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion and soil nutrient depletion, shortage of cultivated land, shortage of grazing land and wood for fuel wood
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 220, Longest growing period from month to month: May to December; Second longest growing period in days: 180, Second longest growing period from month to month: June to November
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إغلاق المنطقة (إيقاف الاستخدام، دعم الاصلاح)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- الحواجز والضفاف
- S3: الخنادق المتدرجة ،والقنوات، والممرات المائية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed, in blocks
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing, population pressure, governance / institutional
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
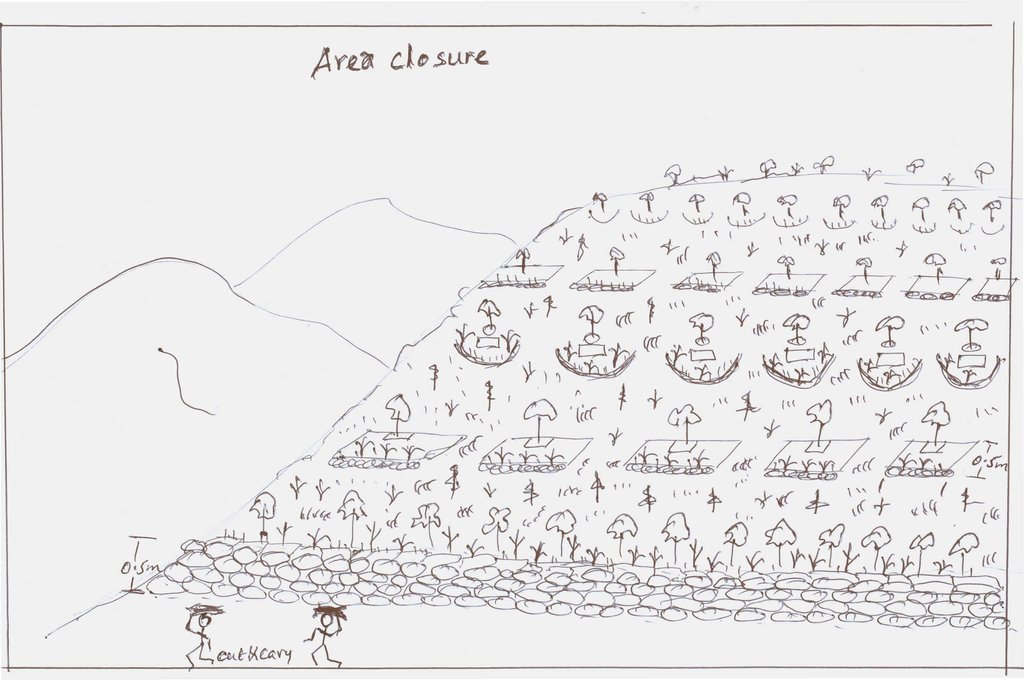
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Integrated practices of area closure including hillside bunds, trenches, micro-basins, and trees/shrubs
Location: Debre Yacob Learning Watershed. Mecha/West Gojam/Amhara
Date: 2014-5-23
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Field staffs need to acquire technical knowledge on how to integrate different practices and strategies depending on the conditions and degree of degradation.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Land users require low knowledge. Once they implement practices in the closure area, they are able to coordinate and respect the bylaws and equitable distribution of benefits.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 4000-6000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-1.0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 160
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Trees/ shrubs species: Gravilia, Susbania, Acacia decurrence
Grass species: Napier
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20-30%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.5%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3-0.7
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2-2.8
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100-250
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5-2.0
Bund/ bank: level
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15-35%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Initially, the land is highly degraded and waste land. After an increase in vegetation cover and biomass, its use is thus changed from waste/shrub land/open grazing to cut-and-carry grazing system
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The land use management is changed from open access /communal grazing or shrub land to regulated or organized form of land use management
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
ETB
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
20,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.50
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of seedlings | نباتية | March-May |
| 2. | Transporting seedlings | نباتية | July |
| 3. | Transporting grass splits | نباتية | July |
| 4. | Sowing seeds on bunds | نباتية | July |
| 5. | Planting of trees and shrubs | نباتية | July |
| 6. | Planting of grass splits or cuttings | نباتية | July |
| 7. | Construction of bunds or terraces | بنيوية أو هيكلية | February-April |
| 8. | Construction of cutoff drains and ditches | بنيوية أو هيكلية | Fegruary-April |
| 9. | Construction of waterways | بنيوية أو هيكلية | February-April |
| 10. | Surveying or layout of structures | بنيوية أو هيكلية | January-March |
| 11. | Consultation of the community | إدارية | |
| 12. | Establish bylaws to control free grazing | إدارية | |
| 13. | Establish user groups and arrange equitable benefit sharing | إدارية |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 1766,0 | 1766,0 | 80,0 |
| معدات | tools | ha | 1,0 | 300,6 | 300,6 | 50,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 405,6 | 405,6 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | stone | ha | 1,0 | 1300,0 | 1300,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 3792,2 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of seedlings | نباتية | March-May |
| 2. | Seedling transportation | نباتية | July |
| 3. | Grass split transportation | نباتية | July |
| 4. | Planting seedlings | نباتية | July |
| 5. | Planting grass splits | نباتية | July |
| 6. | Maintenance of bunds / cutoff drains | بنيوية أو هيكلية | |
| 7. | Enforcing bylaws | إدارية | Throught the year |
| 8. | Benefit sharing among user groups | إدارية | Throughout the year |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | labour | ha | 1,0 | 624,0 | 624,0 | 29,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 874,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, pickaxe, crowbar,
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The costs of area closure affected by the labour availability, regeneration capacity of trees on the degraded lands
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women has their own role in the establishment of the rea closure by collecting stones, support construction and planting activities. In addition they will harvest and transport fodder for livestock
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مجتمعي (منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Mainly serve for grass harvest
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Cut and carry improve the production
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
By improving the land use management, production area for pasture increased
الدخل والتكاليف
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
People try to diverse apiculture production in closed areas
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Labor requirement to harvest and transport fodder and pasture increase
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Establishment of user groups and watershed users association
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase the level of awareness that area closure can shortly reverse land degradation
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduce conflict arise due to pasture shortage
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Some rural unemployed youths get employed in apiculture production and fruit production
contribution to human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The livestock production is moderately improved due to increase in biomass/ pasture harvest
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
تنوع الموائل
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
End of Nov
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mar-April
التعليقات/ حدد:
Because of high vegetation cover, the recharrging capacity improved resulting in prolonging the stream flow/baseflow
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Short term economic benefits can be attained by harvesting forage biomass for livestock while in the long term downstream agricultural productivity can be improved as they witnessed the change in stream flows to be used for irrigation. This is very much pronounced in Aba Gerima watershed where farmers in the downstream get to access more water.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
The technology is implemented in group or at community level.
The spontaneous adoption of this technology is possible without integrating plantations of improved trees/shrubs and grasses
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Adoption to area closure is increasing as it provides better pasture for livestock and benefit those who do not have power or for poor community groups
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Increase in vegetation cover and biomass production for livestock feed |
| Increase the duration and flow of streams |
| Decrease erosion |
| Decrease transmission of animal disease often a problem during open grazing system |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Increase the fodder and grass biomass production for livestock feed |
| Increase the regeneration of lost plant diversities |
| Create alternative livelihood options (off farm activities like honey production, timber, tree or fodder seed production) |
| Enhance the micro-climatic conditions and on-site vegetation cover, organic matter, and soil water holding capacity. In addition it improves off-site surface and subsurface water flows |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Land users' perceived that implementation of the technology decreases open access to communal pasture lands to maximize their benefit | Awareness creation activities has to be provided |
| Shortage of labor to harvest and transport forages to feed animals | Cost effective technologies to prepare feed, handle and transport forage has to be introduced and adopted. It can be overcomed by organizing service provider groups. |
| The amount of pasture/fodder produced and shared among users is much less than the feed requirement of all animals hold by a household | Introduce fodder species producing high biomass and high quality fodder; decrease livestock number per household. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Labor constraint for cut-and -carry for stall feeding | It can be sustained through organizing service providers groups |
| Stall feeding restricted the cross breeding of animals in the village easily accessible during open grazing | Artificial insemination and bull services and synchronization breeding system has to be promoted |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Sustaining the win-win benefits of improved grazing land management in EthiopiaPost written by Wolde Mekuria, WLE. March 30, 2015
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
WLE post
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
http://www.bioone.org/doi/pdf/10.1659/0276-4741(2005)025%5B0044%3ATROCIC%5D2.0.CO%3B2
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Vegetation Improvement in Communal Closed Areas in Tigray, Ethiopia.Sarah Tewolde-Berhan 1,4, Ralph Mitlöhner 2, Bart Muys3 , and Mitiku Haile 4
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Natural Regeneration Practice in Degraded High Lands of Ethiopia Through Area Enclosure Wondie Mebrat, Department of Biology, Adigrat University, Adigrat, Tigray, Ethiopia, 2015
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Area Closure: Rehabilitation of Degraded Lands and Grasslands and its Multiple Benefits. WLRC Brief No. 2. June 2015
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
www.wlrc-eth.org
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [أثيوبيا]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- جامع المعلومات: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية