Water retention polders with adapted land use (North Sea region) [ألمانيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Martin Maier
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Fabian Ottiger
Polder mit angepasster Nutzung zur Verbesserung des Wassermanagement (Nordsee Region)
technologies_1660 - ألمانيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kleyer Michael
michael.kleyer@uni-oldenburg.de
University of Oldenburg
26111 Oldenburg, Germany
ألمانيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Karrasch Leena
University of Oldenburg
26111 Oldenburg, Germany
ألمانيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Oldenburg (University of Oldenburg) - ألمانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
06/03/2015
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Water retaining polders to reduce flood risk from heavy rainfall or runoff at high tide in coastal lowlands. Alternative production systems will be viable within thesepolders.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In the 19th and 20th century land was reclaimed from the sea to make use of the exposed fertile soils for agriculture through a process known as ‘impoldering’. The reclaimed land is now characterized by intensive grazing and cropland. This is a region where agriculture is the most important form of land use. However, the land needs to be regularly drained. Given the expected increase in precipitation in winter due to climate change, the corresponding increase in freshwater discharge needs to be managed. Furthermore, the periods when natural discharge into the sea oc-curs are likely to decrease – because of rising sea levels also caused by climate change. Consequently, in winter and spring, greater quantities of freshwater will need to be pumped into the sea rather than discharged naturally at the low or ‘ebb’ tide. Specially embanked water retention polders will be required to temporarily impound water as part of a multifunctional approach to coastal zone management.
Purpose of the Technology: These retention polders could be a cost-effective alternative to expensive invest-ments in extra pumping capacities to prevent submergence of low-lying cultivated areas. The primary aim is to restrict floods to the retention polders when the drain-age network is overburdened and cannot deal with the predicted extra demands in the future. The high evapotranspiration from the open waterbody, and the reeds growing within, will also help with reducing the amount of water. During dry sum-mers, the water in the retention polder could also be put to creative use as a source of irrigation. Another potential advantage is that subsurface saltwater intrusion in the region could be prevented by the freshwater-filled polders. During extreme storm surges and in the rare case of breaches in the sea wall, the retention polders would serve as an extra line of defence by holding seawater.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: An embankment enclosing approx. 3,000 ha will be able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ of water. This will improve the drainage of an area of approx. 49,000 ha. The invest-ment for building this water retention area is high – but for the reasons stated it serves a necessary purpose at a cost which is lower than the alternative – increased pumped drainage installations. Maintenance costs will be lower than the drainage alternative as only the integrity of the embankment needs to be monitored regularly. Agricultural land use within the polders is adapted to higher water levels and occa-sional flooding.
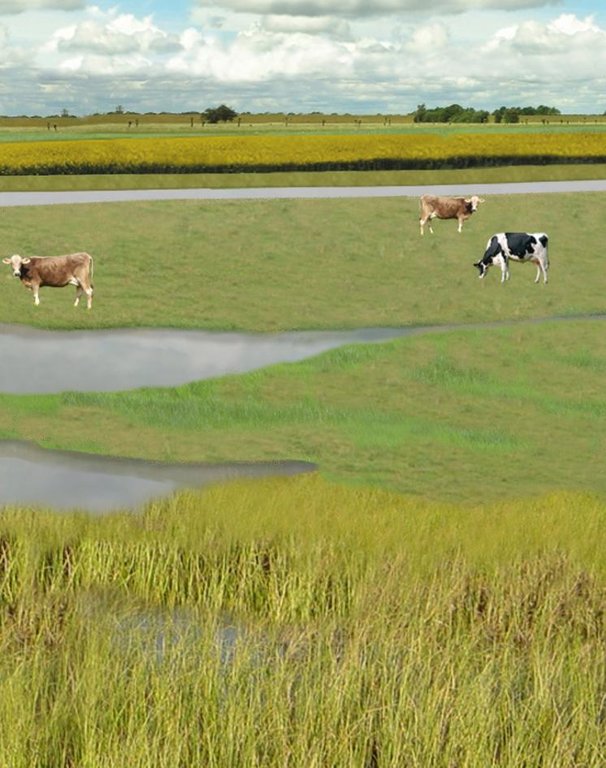
Natural / human environment: However within the proposed retention polders – the areas enclosed by the em-bankment - a change from the current intensive grazing for dairy farming and cropland to extensive grazing, open waters and wetlands covered with reeds will take place. The reeds can be harvested for their commercial value as biomass for renewable energy generation, or for other applications (e.g. thatching of roofs or industrial raw material). According to recent investigations, natural reeds growing in brackish water produce as much biomass as maize cultivated for biogas use. In con-trast to maize, no investments in tillage, fertilizer or biocides are necessary for these naturally growing reed stands. Thus the proposed land use provides an economic alternative to the current production system.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
ألمانيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Germany, Lower Saxony
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Landkreis Aurich
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major cash crop: Corn
Major food crop: Wheat, barley

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- قطع وحمل / صفر مرعى
- مراعي محسنة
الأنواع والمنتجات الحيوانية الرئيسية:
Main animal species "improved pastures": Cattle for milk and meat.
Main animal species "cut-and-carry/zero grazing": Cows for milk
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flood events and droughts may substantially disrupt the current land use system in the future and lead to higher drainage costs and higher economic risks for agricultural production. This will reduce the ecological and economic viability of the current intensive and highly productive land use under a changing climate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is no awareness of risks due to climate change.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: cows for milk
Improved pasture: cattle for milk and meat
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): needs to be adapted to regular flooding
Constraints of recreation (landscape is used for recreation and tourism): change in landscape due to retention area
Constraints of nature conservation area (protected sites): wetter conditions in retention area
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March to October
كثافة الثروة الحيوانية (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- تحويل المياه والصرف
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.7 m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change, higher rainfall in winter, lower in summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall in winter due to climate change expected), floods (Flooding due to heavy rainfall in winter)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Droughts due to less rainfall in summer (climate change)), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sea level rise)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
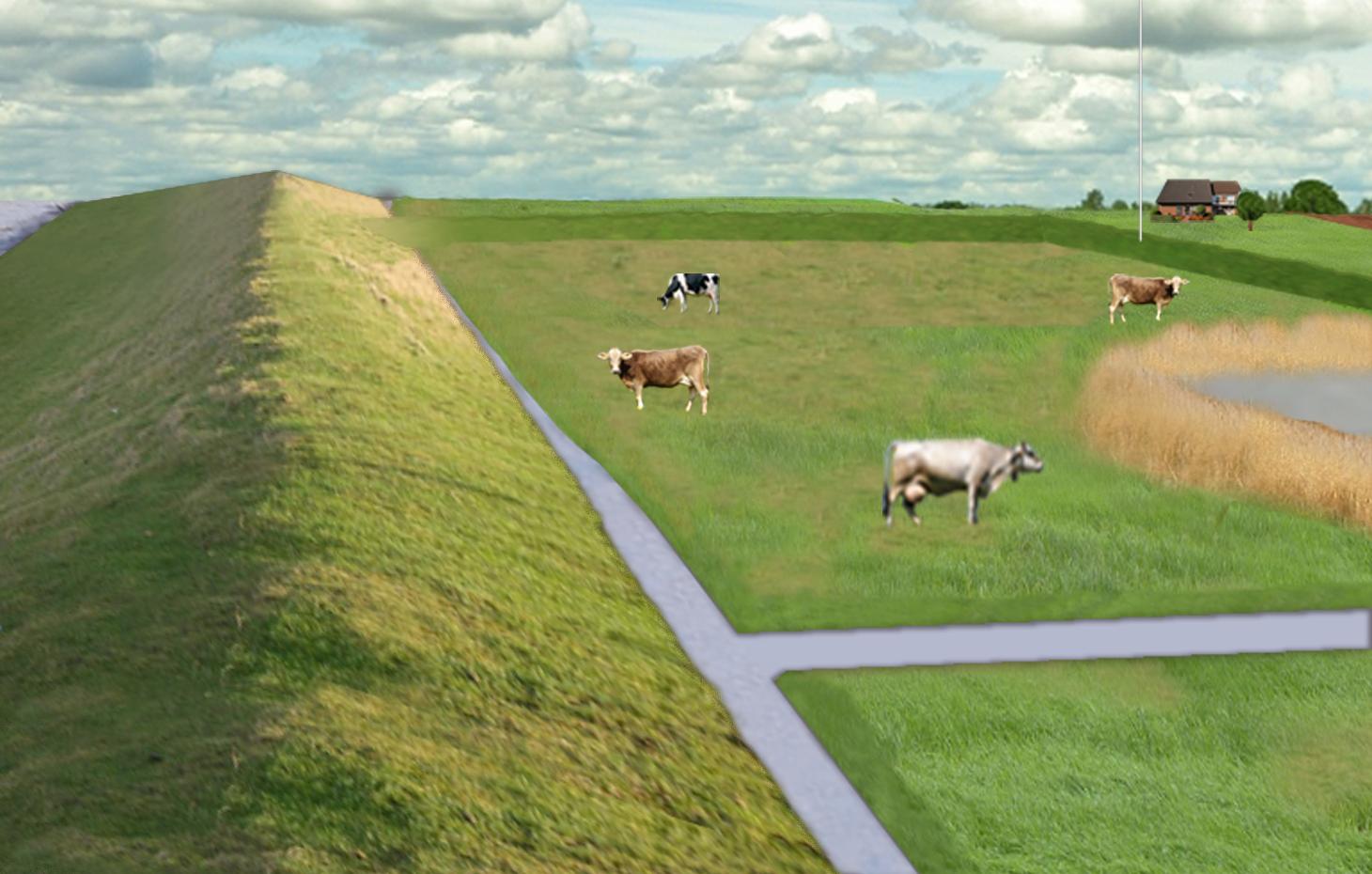
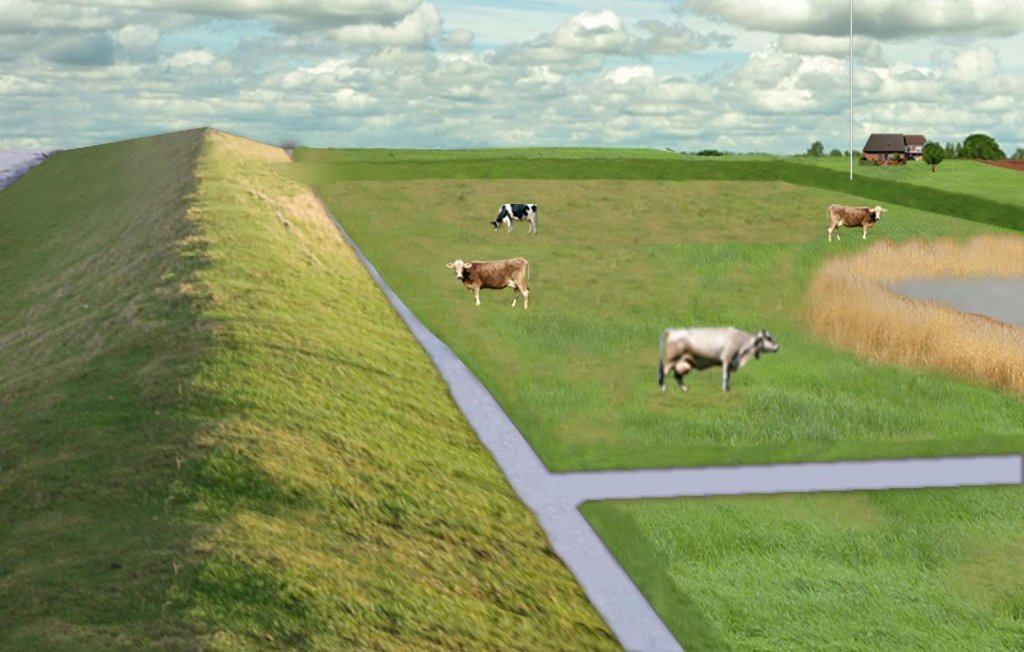
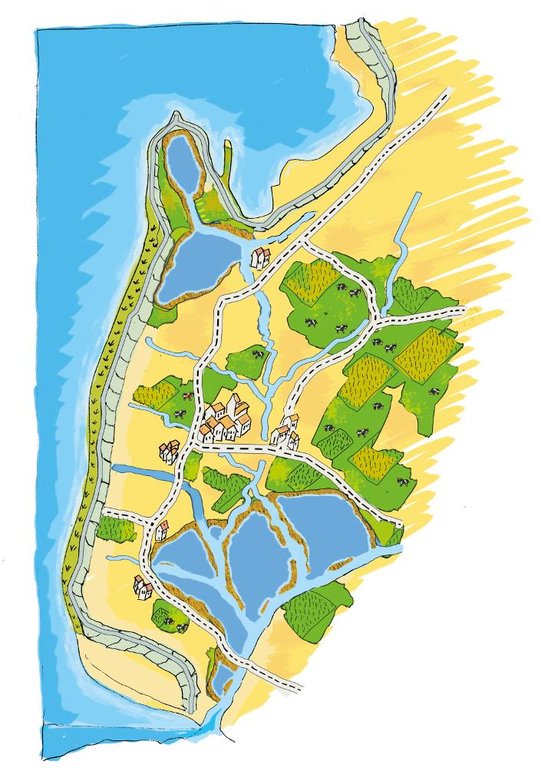
The figure shows the study region, located on the North Sea coast. The whole area is protected by a sea wall (grey). Crop fields (yellow), grasslands (green) and the drainage system (light blue) char-acterize the region. Large water bodies (blue) sur-rounded by reeds (brown) act as water retention polders. Extensive grazing and reed farming re-places current production systems within the reten-tion polders. The land around the retention area (higher parts of the landscape) profits from the retention areas as the risk of flooding is reduced and can be used for cropland and intensive graz-ing. Depending on the size of the retention polder a huge amount of excess water can be contained. Retention areas of 3,000 ha are able to store up to 25,000,000 m³ water. The height of the dams de-pends on the elevation of the landscape but in general a height of less than 2 m is sufficient.
Location: Krummhörn. County of Aurich, Lower Saxony
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (To generate income in the retention area (without existing agricultural methods))
Technical knowledge required for Water board: high (To build a new adapted drainage system with retention areas)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity)
Dam/ pan/ pond
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 30000
Construction material (earth): sand core and clay cover
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 25000000m3
Catchment area: 49000ham2
Beneficial area: 49000ham2
Other specifications: size of retention area (embanked area): 3,000.00 ha
Change of land use type: Within the retention area the conditions are wetter than before. Therefore the agricultural land use needs to be adapted to hydrological conditions.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Under the wetter conditions only a less intensitive land use is possible, e.g. no crop fields but instead extensive grazing
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Euro
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,94
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
100.00
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building of dams | بنيوية أو هيكلية | during winter months |
التعليقات:
Labour medium: 1 person 1 day, 1m dam, 700USD
Machine hours: 8h, 1m dam, 300 USD
Earth: 10000 M3 (Sand), whole retention area, 22000 USD
Earth: 23000 M3 (Klei), whole retention area, 53000 USD
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | 1,0 | 21000000,0 | 21000000,0 | ||
| معدات | Machine use | 1,0 | 9000000,0 | 9000000,0 | ||
| مواد البناء | 750000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 30000000,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of dams | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of dams | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once a year |
| 3. | Maintenance of drainage system | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once a year |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | 800,0 | ||||
| معدات | Machine use | 300,0 | ||||
| مواد البناء | Earth | 100,0 |
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: digger, open truck
The establishment costs are for a dam length of 30 km and the enclosed retention area of 3,000 ha. The establishment period will be half a year. The slope in the region determines the costs as the height of the embankments depend on this. Typical heights are from 1 m up to 2 m with a slope of 1:3. . The length of the drainage network for the whole watershed (retention area and the surroundings) is 1,134 km. Maintenance costs of the drainage network are based on long term annual mean cost of 2,270.70 Euro per km including pumping costs. The maintenance cost for the whole retention area will amount to a total of US$ 2,576,200.00.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- عالية (>3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is very high
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity high
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- موظف (شركة، حكومة)
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 1% of the land.
50% of the land users are rich and own 24% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Many farmers do additional work in industry or servicing sector
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under wet conditions in the retention area a crop production is not possible any more.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under wet conditions in the retention area an intensive fodder production is not possible any more.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Under wet conditions in the retention area the optiomal fodder quality can not ensured any more.
منطقة الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
49000 ha
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
46000 ha
التعليقات/ حدد:
For the whole catchment area a loss of approx. 3,000 ha (size of retention area).
توليد الطاقة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reeds in the retention area are very productive plants and will be used for bio energy generation.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه للماشية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to reduction of saline influx
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Only adjusted land use takes place within retention area, therefore the expenses are reduced.
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to land use adapted to the conditions the typical land use is not possible and a diversitfication will take place with reed mowing and extensive grazing in the retention area.
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Intrusion by saline groundwater
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Diversification of landscape by building the retention area will increase the attractivity for recreation and tourists.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Less intensive land use results in more diversity and conservation of regional species and habitats.
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
'Regional belonging' and 'feeling of safety' are measured.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Updwelling of saline groundwater is prevented by increased water level in the retention area.
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات/ حدد:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Instead of pumping water into the sea a higher amount is evapotranspirated naturally.
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
الملوحة
التعليقات/ حدد:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
By wetter conditions the soil organic matter will be increased.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Growth of reeds
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
By diversification of land use the number of habitats will be increased.
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Modelled is the global warming potential by gas emissions. Not yet clear if it is benefit or disadvantage. Model will show.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water from retention area.
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water stored in retention area can be used for irrigation during dry summer months.
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Measured m3 of excess water in the catchment area, leading to floods or needs to be pumped. Exact values from modelling will be added as soon as possible!
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
التعليقات/ حدد:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Retention area to tackle impact of climate change.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي للغاية
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The benefits will be visible in the longer time frame. There will be benefits of the investments when considering sea level rise in the upcoming 100 years.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The SLM Technology is not implemented by local land users but this SLM technology needs to be implemented by spatial planning of the county / federal state.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The SLM Technology is not yet implemented by land users but first it needs to be considered in spatial planning of the county and the federal state. Land users and local experts showed during participatory workshops that there may be a chance for implementation.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
The retention area will support the drainage of the arable fields and pastures outside the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other technical solutions for protection against flooding (including strengthening of the ditch system and in-creasing pumping capacity). |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Prevention of flooding during strong rainfalls and possibility to irrigate during dry periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? The larger the retention areas are the more water can be stored. |
|
Prevention of salt water intrusion in the region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fresh water in the retention polders prevents saline ground water from intrusion. Build polders in areas where saline ground water intrudes. |
|
Endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Extensive land use can help to optimize the habitats for endangered species and increase attractiveness for tourism. |
|
Through investments in building retention areas the very expensive strengthening of the existing drainage system is not necessary anymore How can they be sustained / enhanced? By increasing the attractivity for touristic use in the retention area benefits for land owner can be generated and the probability to build up retention areas instead of strengthening the existing drainage system is increased. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Retention polders in an important tourism region will change the landscape and this may reduce the value of the region for tourism. | Include tourism concerns in the retention area (access, infor-mation, attractiveness). |
| Loss of land for agricultural production (highly productive arable land) | Establish retention area in low elevated parts, where there is not a high interest for agricultural production. |
| Endangered species might lose habitats when building up the retention area | Do not build a retention area where endangered species live. |
| Loss of livelihoods | Retention areas should be planned for parts of the landscape without settlements. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| High water levels (especially with changing water levels) may generate high emission of greenhouse gas | Ground water levels should kept stable near to the soil surface. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية