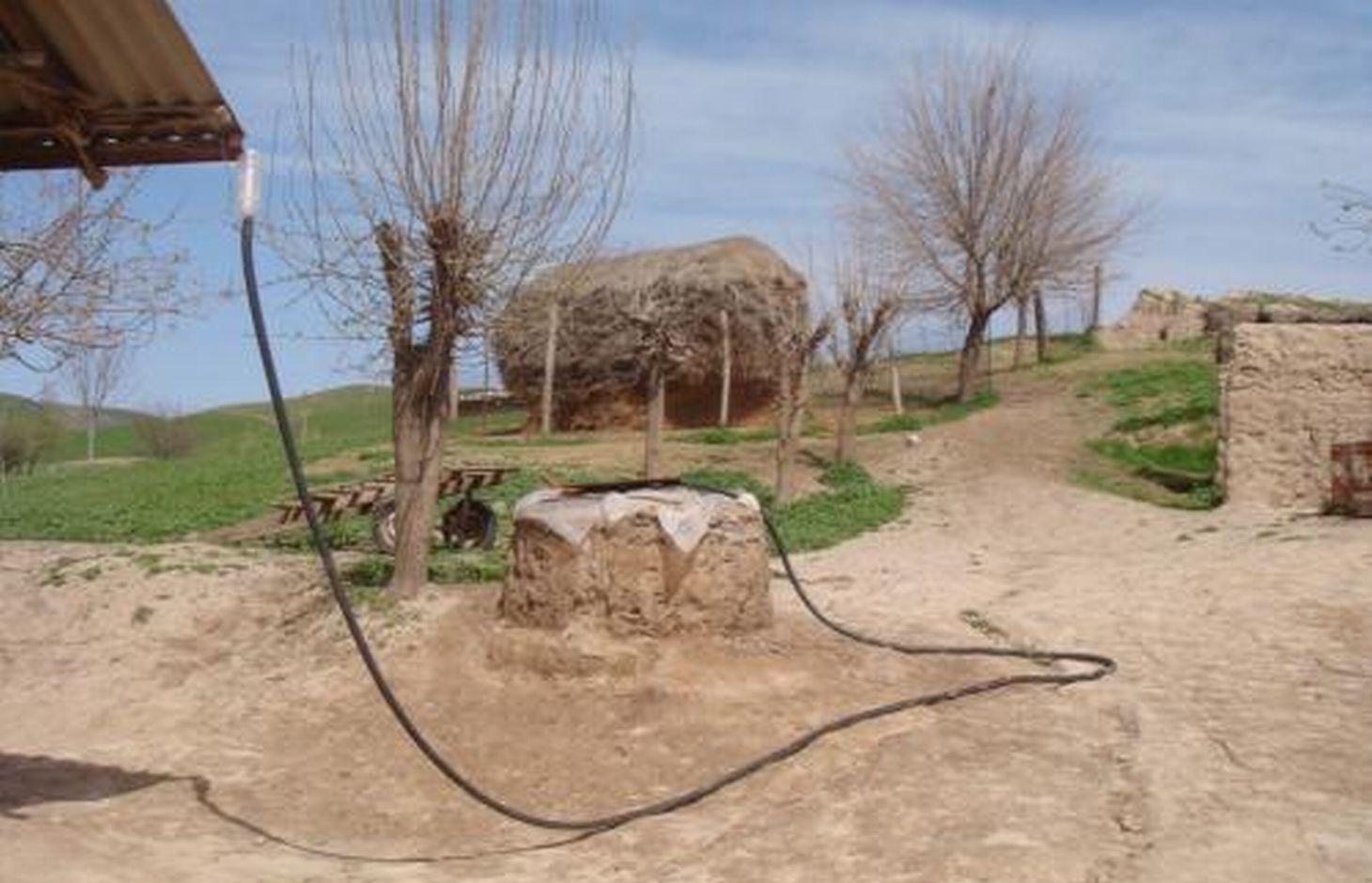
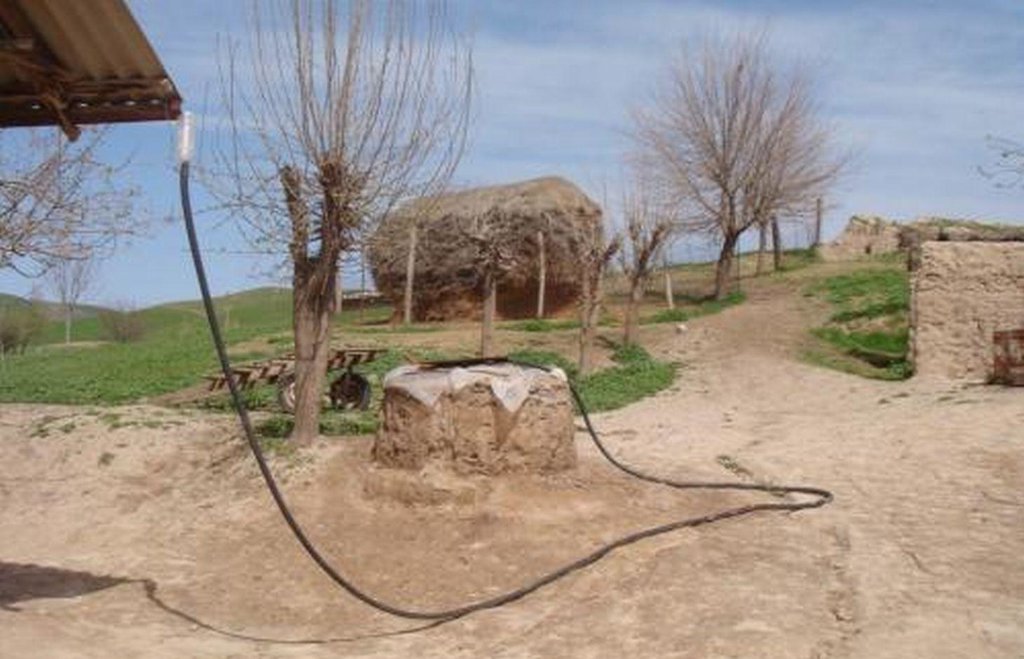
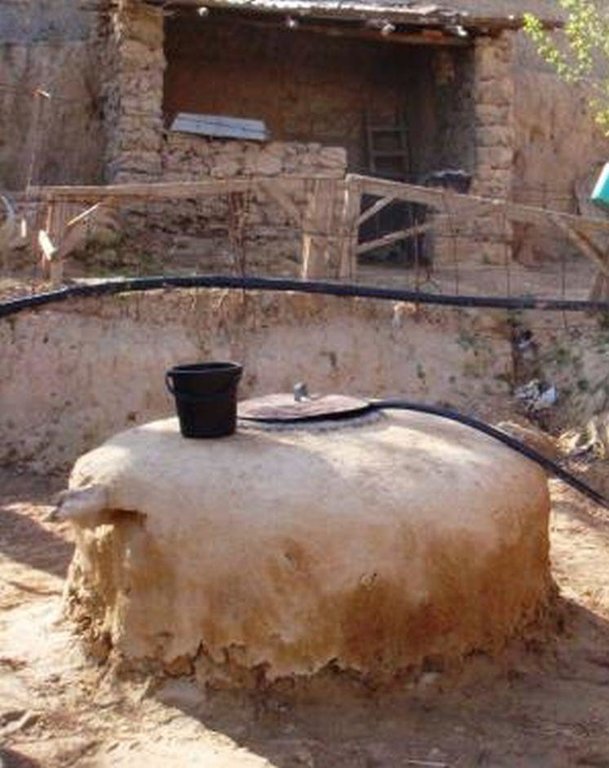
Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank. [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Daler Domullojonov
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
Чамъоварии оби борон аз руи боми хона
technologies_1446 - طاجيكستان
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 4 إبريل، 2018 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 15 أغسطس، 2019 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 19 يوليو، 2017 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 6 مايو، 2017 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 14 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe (Welthungerhilfe) - طاجيكستاناسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience Tajikistan (PPCR Tajikistan) - طاجيكستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
06/04/2011
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
The use of an earth tank lined with a polyethylene sheet to retain rainwater collected from the roof of the house.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
An earth retention tank is a simple low cost structure that can be used to retain rain water from the rooftop. A hole is prepared and lined with a polyethylene sheet to prevent leakage. The top of the hole is covered with a metal lid for access. The roof of the house is fitted with a plastic guttering that captures the rainwater and funnels the water via a plastic pipe into the earth tank. The water in the earth tank then can be utilised for the irrigation of crops (especially during the hot dry summer months), sanitation, and potentially drinking water.
Purpose of the Technology: The population in Southern Tajikistan consists largely of subsistance farmers and are thus highly reliant upon their kitchen garden plots. As the population in the area continues to expand, the pressure on the land increases. The latter is already in a poor state, because it is becoming degraded through deforestation, overgrazing and general over exploitation. There is much precipitation during the rainy season from autumn until spring in Southern Tajikistan, but the scarcity of water from late spring to the end of autumn poses a problem with water shortages.
During the rainy season, a lot of water is lost as surface runoff, this water can be saved in a retention tank to be utilised during the dry season. It can be used to water crops to help increase yields as well as crop diversity and quality. The additional water can also be used for sanitation, drinking water and watering of livestock.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of such a retention tank several steps are needed. In preparation, a rough estimation of the potential volume of harvested rainwater needs to be calculated. Thereafter, a location for the tank needs to be selected so that expenses are minimised and it is easy to access. The establishment of ponds near big trees is not recommended, because the polyethylene layer might be punctured by the roots.
Natural / human environment: The actual steps of constructing the tank involve:
(1) digging the pond, (2) plastering the inside walls with a fine soil and water mixture to smooth them, (3) lining the pond’s walls with double polyethylene layer, (4) connecting the inside polyethylene sheets with the pond coverage through a piece of cord, so that it can be taken out of the pond any time to be cleaned of sediments, (5) covering the pond with any available material such as a soil, water and straw mixture, reinforced by several poles, leaving an opening of 0.25 x 0.25m to extract water, (6) finally connecting the roof to the pond with a plastic pipe. To avoid dirty water flowing from the roof into the pond, the pipe should only be connected to the pond some time after the rainfall has started.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Khatlon province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Temurmalik, Baljuvon
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The technology was developed through a Welthunger Hilfe Project and promotion in the local communities started in 2008.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

المستوطنات والبنية التحتية
- المستوطنات والمباني
ملاحظات:
Kitchen garden
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Inefficient natural resource management, which is mainly visual because people throw potential organic fertilisers away instead of spreading them on the fields. Incorrect ploughing techniques which leads to the acceleration of erosion, deforestation and waste of fuel materials in inefficient stoves and ovens. Overgrazing leading to pasture degradation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): lack of water
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 100-10 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification, Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Inproper land management), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting trees and shrubs), overgrazing, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (poor water supply)
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (the population is increasing over time.), poverty / wealth (lack of funds)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المؤلف:
Daler Domullojonov, 14, Giprozem str., Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Harvesting water from the household roof to an earth built retention pond with plastic sheet lining. The retention pond is covered with a removable metal plate for access.
Location: Davad village, Vatan jamoat, Temurmalik district,. Khatlon province, Tajikistan
Date: June 2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (No special knowledge is needed for implementation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Any farmer can implement, once they understand the basic concept.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Construction material (earth): digging in earth, plastering and cover
Construction material (wood): pole for cover
Construction material (other): polyethelene sheets, plastic pipe
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 3.96m3
Catchment area: 72 m2m2
Beneficial area: 0.2h.am2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.5
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
TJSomoni
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
4,5
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
6.60
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manual digging of pond;smoothing and plastering;covering pond | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once in the beginning |
| 2. | polyethylene sheet and pipe procurement, preparation and placement; | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once in the beginning |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Manual digging of pond | Persons/day | 2,0 | 30,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Placing sheet | Persons/day | 0,1 | 30,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Wooden poles for pond | poles | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Earth | tons | 0,1 | 45,0 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Polyethylene sheet | square meters | 10,0 | 2,3 | 23,0 | 50,0 |
| مواد البناء | Cord | meter | 20,0 | 0,025 | 0,5 | 50,0 |
| مواد البناء | Plastic pipe | meter | 5,0 | 2,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Bucket | pieces | 1,0 | 4,5 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 125,5 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of pond (washing out sediments) | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once every year |
| 2. | Changing polyethylene sheet;covering | بنيوية أو هيكلية | once every 2 years |
| 3. | Changing polyethylene sheet;covering | إدارية | once per 2 years |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Cleaning of pond (washing out sediments) | Persons/day | 0,1 | 45,0 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Changing polyethylene sheet (every 2 years) | Persons/day | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Polyethylene sheet | square meters | 10,0 | 2,3 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Cord | square meters | 1,13 | 8,85 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Earth | tons | 0,05 | 45,0 | 2,25 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 49,75 | |||||
التعليقات:
The above costs were calculated for the building of one retention tank. One household could have several ponds in one kitchen garden.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The type of earth in Tajikistan is very good for making the retention ponds, the labour is provided by the land user, and the plastic pipes can be manufactured out of empty plastic bottles. The polythene sheet and cord have to be purchased from the shop.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Average annual precipitation is 575 mm (according to data from the last 15 years), most of which falls between late autumn and spring time.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
Continental conditions
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: Mainly communities in this range
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium and if it is not overused the fertility can be increased.
Topsoil organic matter: Usually locals collect cow dung and use it as fuel.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium because the loess material contains clay material
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table can also be below 50 m.
Availability of surface water is so poor du to deforestation the natural water balance is disturbed.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: In this example the farmer's son has migrated to Russia.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- فردي
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
إنتاج حيواني
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
120 litres
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
12000 litres
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water storing capacity of household increased
توافر المياه للماشية
توافر مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100
التعليقات/ حدد:
vegetables and greens are available for own consumption
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
no need to carry water
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
Livelihoods and human well-being
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
more water available
حصاد / جمع المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
more water available
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
only in kitchen garden
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | نوع التغير المناخي/ المتطرف | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
التعليقات:
To minimise the damage to the polyethylene waterproofing layers and, reduce evaporation rates, pond is covered. As the pond is dug into earth the temperature remains fairly stable. If precipitation decreases less water can be harvested.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Before the implementation of this technology, one family would spend an avarage of $44.5 on one truck of water per month. A pond costs around $25 to build, and should provide families with around 4 months worth of water after the rainy season.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- أكثر من 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
600 households (in an area of 10-100km^2)
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 50-10%
التعليقات:
58% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
350 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: In the initial stages of the project, they were provided with 50% of the costs of the polyethylene sheets and cord only.
42% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: After observing the benefits of the technology and the high cost benefit ratio, many people in the community and surrounding villages have replicated this technology themselves.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Easy and quick to establish, and maintain. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
It is a low cost technology and can be made from many locally available materials. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To disseminate these ideas in areas with water scarcity through local Extension Service providers / NGOs or local inhabitants. |
|
It reduces the time and effort to collect water and also the cost to buy water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promotion of different water saving methods and technologies by interested and line departments. |
| More water available for gardening and household purposes |
|
Increases access to water for drinking and sanitation purposes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of larger and/or more tanks. |
|
Provides water for irrigation during the hot dry months, therefore improving crop diversity and yields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training and education on kitchen garden farming techniques to optimise the use of the extra water supply. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The polyethylene only lasts for 2-4 years. | To increase the number of layers or use a thicker polyethylene sheet |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The plastic layers have a limited lifespan. | To find thicker and more hardy materials, or apply multiple layers. |
| Th waterproof layer can easily be degraded by mice and large insects. | |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Brochure - Converting drought prone areas into productive gardens! Low cost options to improve rainwater harvesting in Southern Tajikistan rain fed areas …. and beyond! 2009
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office,
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Training film - Simple ways to improve management of kitchen gardens in Southern Tajikistan rain fed areas …. and beyond. 2009
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية