Indigenous Management of Tapia Woodlands [مدغشقر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1359 - مدغشقر
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Kull Christian
christian.kull@arts.monash.edu.au
School of Geography and Environmental Science, Monash University
Wellington Rd, Clayton VIC 3800, Australia
أستراليا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
School of Geography and Environmental Science, Monash University - أستراليا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
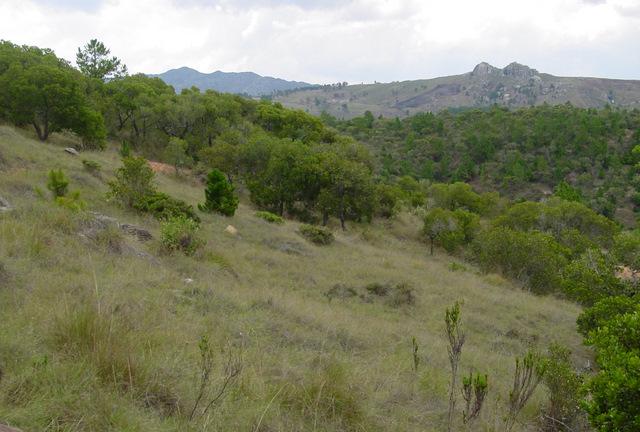
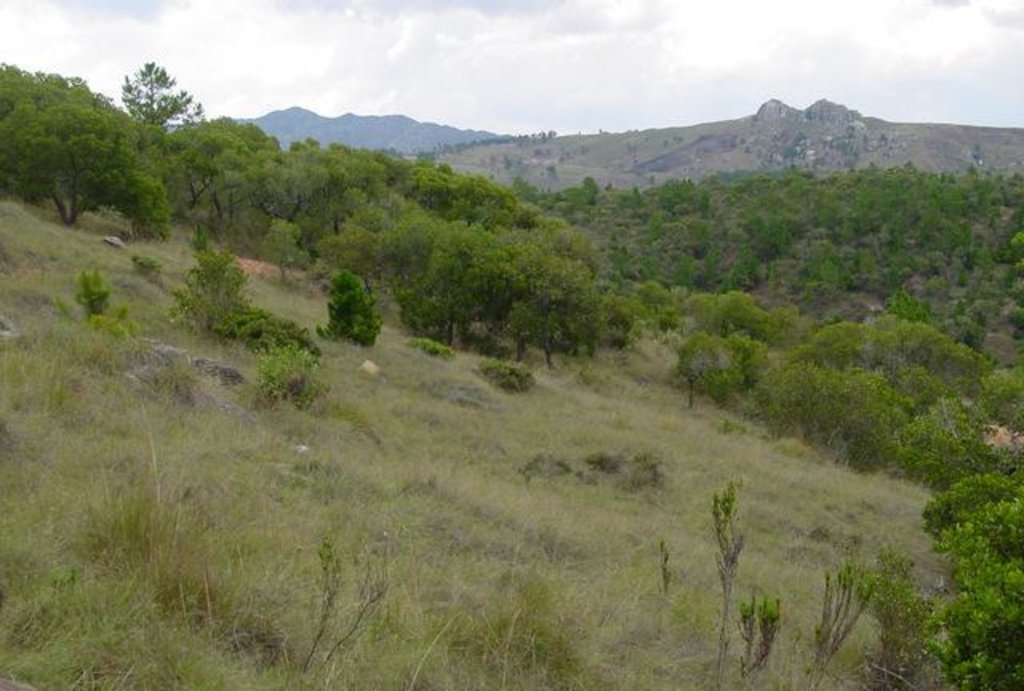
For centuries, the population of the highlands of central and south-western Madagascar has sustainably managed and conserved the local tapia woodlands.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
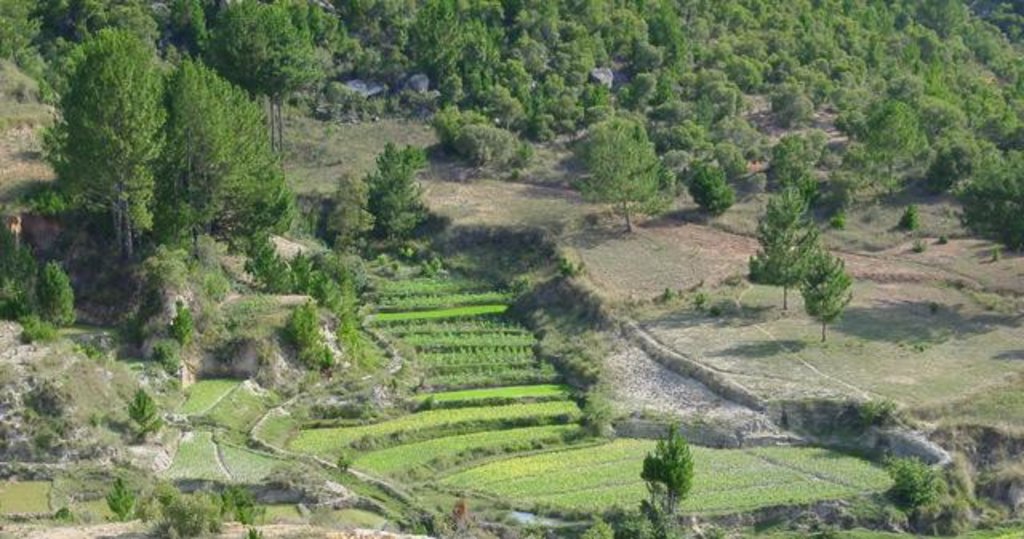
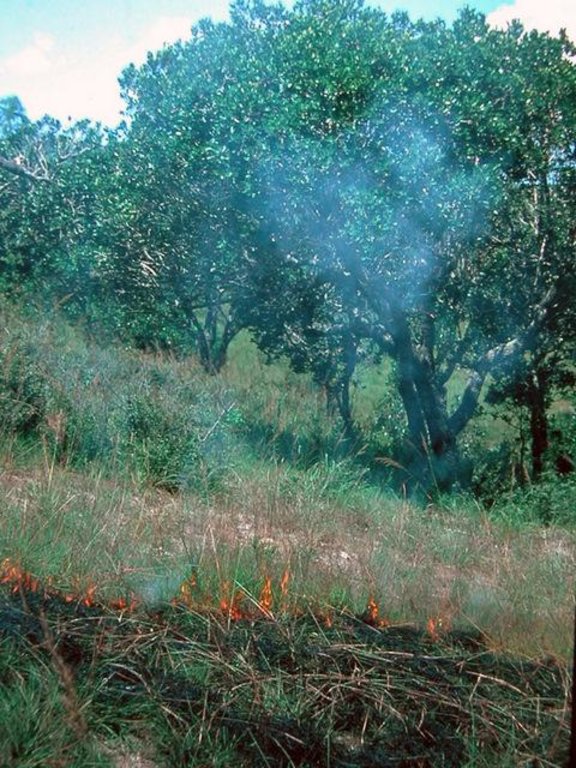
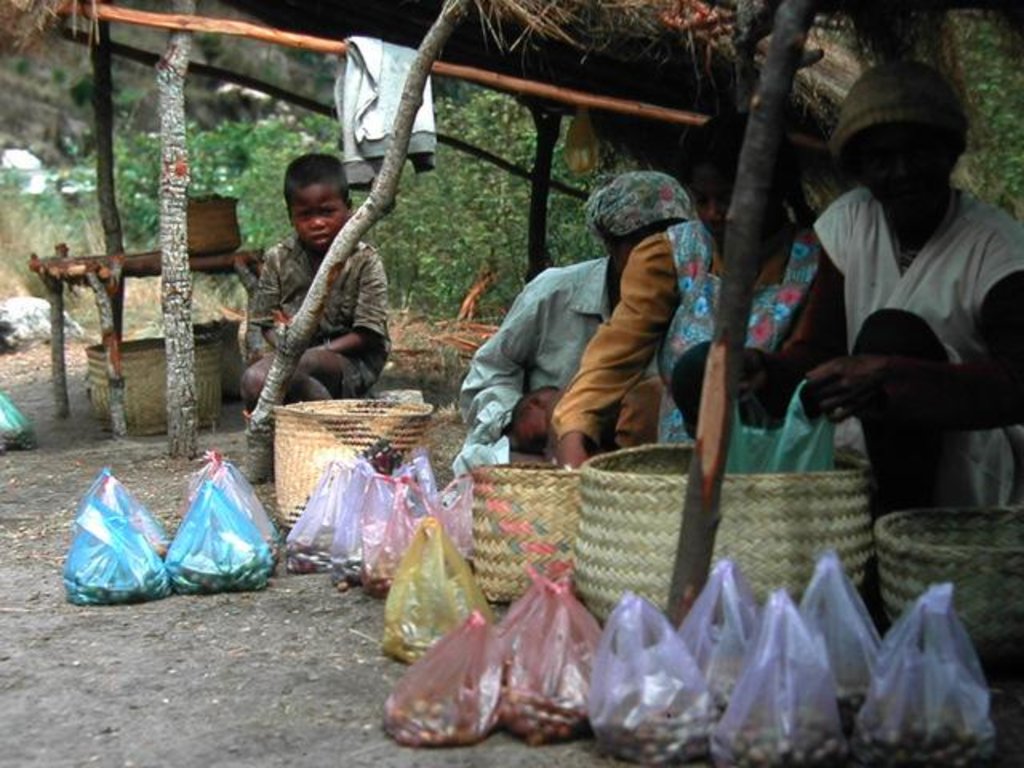
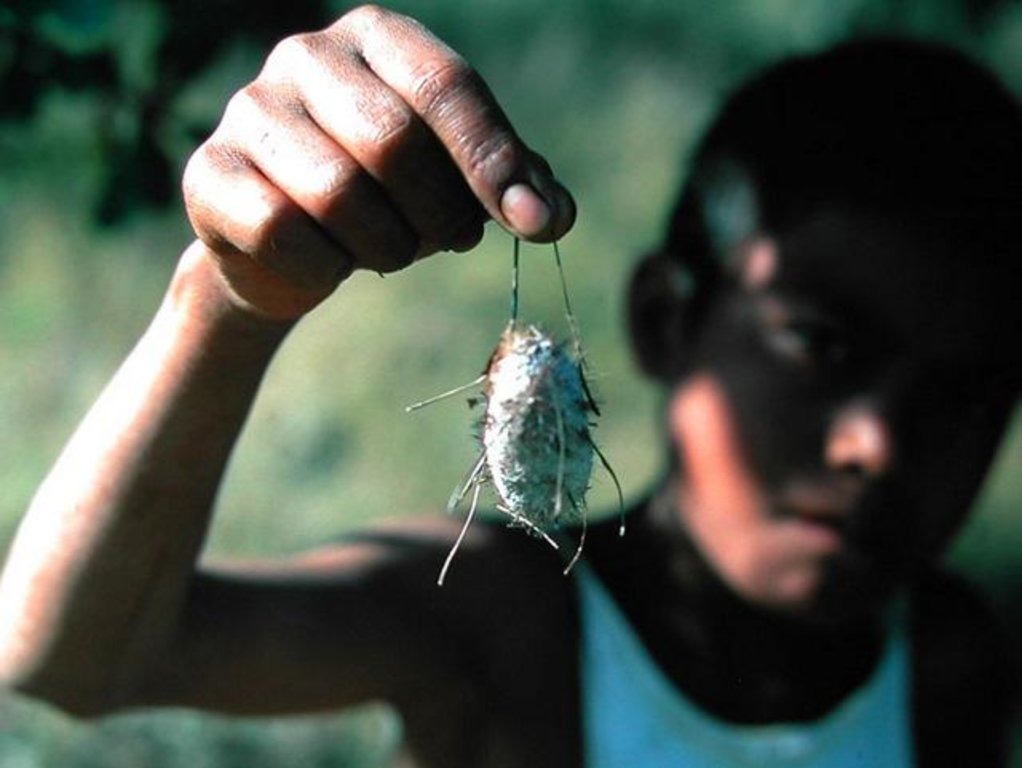
These woodlands play an important economic role as a source of non-timber forest products (NTFP) such as wild silk, fruit, mushrooms, edible insects, and herbal medicines. Tapia trees (Uapaca bojeri) comprise up to 90% of all trees in these woodlands, bear an edible fruit, and their leaves nourish an endemic silkworm (landibe). Landibe silk is used to produce ritual burial shrouds throughout the highlands. Trading silk products and tapia fruits is a crucial source of cash income for the local communities. The tapia woodlands are maintained by the local villagers through burning and selective cutting. Burning favours the dominance of pyrophytic (fire-tolerant) tapia trees and protects silkworms from parasites. Selective cutting of non-tapia species and pruning of dead branches also favours tapia dominance and perhaps growth. Other common species include the endemic Sarcolaena eriophora and the invasive Pinus patula/khasya. The Tapia woodland is clearly an anthropogenically shaped forest. However, the creation and maintenance of the woodlands should be seen as positive transformation rather than a form of degradation.
Local and state-imposed regulations protect the woodlands from overexploitation. The Forest Service has placed restrictions on forest cutting and burning while allowing for traditional use rights. The collection of forest products is regulated through a type of common-property regime. For example, fuelwood collection is limited to dead trees or fallen branches. It is forbidden to break off large branches to access cocoons. Thanks to these protective regulations, forest boundaries are mostly stable, and woodland density has increased in several cases.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
مدغشقر
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Col des Tapia
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Antsirabe and Ambositra
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
- Sustainable forest management
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الفواكه والمكسرات
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الحرجي
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduction of vegetation cover; Quantity biomass decline
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Other type of forest: sustainable forest management
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الغابات الطبيعية وشبه الطبيعية
- تربية النحل، واستزراع الأسماك، والدواجن، وتربية الأرانب، وتربية دودة القز، الخ.
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2600 m2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
التعليقات:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: (traditional practice)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (children often harvest fruit; silk cocoon harvest is easy)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The tapia woodlands are maintained by the local villagers through burning and selective cutting
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | N |
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective cutting of non-tapia species, especially invasive pines | إدارية | |
| 2. | Pruning of dead branches | إدارية | |
| 3. | Controlled burning mainly through understory fires after the rainy season | إدارية | Jan-May |
| 4. | Collection of non-wood forest products such as fruits, medicinal plants, mushrooms, berries, insects, and hunting of mammals etc | إدارية | Sept.-Dec |
| 5. | Collection of landibe silkworm twice a year. The cocoons are cooked, spun and woven into silk fabric | إدارية | Nov-Dec and May-June |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 20,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Traditional method; no establishment phase and costs.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The estimation of costs is difficult - fruit are gathered over a two month period by school children going out for an hour in the early morning each day; the silkworms are collected by individuals (usually experienced collectors) on free days. In some areas, projects exist that run silkworm nurseries, establish firebreaks in the woodlands, grow and plant tapia seedlings, and finance the purchase of silk looms. These projects obviously require much larger budgets.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
7 months of dry season
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: hilly (16-30%), steep (31-60%), very steep (>60%)
Altitudinal zones: 500-2000 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture is coarse/light (sandy) (silica-rich soils compared to the main lateritic soils of highland Madagascar)
Soil fertility is low ( mostly nutrient-poor or rocky soils )
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Population density: 20-40 persons/ km2 in the central highlands and 10-20 in the western highlands
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
Woodlands are officially state-owned, but in practice managed by neighbouring communities (either unofficially, or increasingly through community-based management contracts
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
Stable supply of fuelwood
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Through selling silk-fabrics and other NTFP
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Production of NTFP as important dietary supplements
Provision of medicinal plants
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Thorugh the forest products
الفرص الثقافية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Sacred forest
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Endemic biodiversity
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
التعليقات:
Silk and fruit harvests vary from season to season but drivers are poorly understood (could include precipitation and temperature)
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The larger rainy season silk harvest provides crucial cash income during the meagre months before the rice harvest. In 1998 the price of 200 cocoons was between US$ 0.10-0.15. For a basket of Tapia fruits villagers earned between 0.02-0.06 US$/ kg. During
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
Comments on adoption trend: see Annex 3
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Thanks to these protective regulations, forest boundaries are mostly stable, and woodland density has increased in several cases |
| La vente des produits en soie et des fruits de Tapia est une source de revenus capitale pour les communautés locales |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Partly individual indiscriminate cutting and/or strong use of fires leads to overuse of the forest resources | needs clear regulations, guidelines and observation of the rules by the local authorities as well as awareness raising about the multiple benefits of the forests. As long as the communities continue to be interested in the forests and its products, they will protect it from destructive cutting. |
| Invasion of exotic tree species such as pine and eucalyptus from private and village woodlots | the forest service has rightly been encouraging communities to cut these trees from the tapia forests without the need for complicated permits. |
| Insecure land use rights | in 1996 a new legislation opened the way to officially decentralize management of state-owned renewable natural resources to adjacent communities, which would aid woodland protection by increasing stakeholder involvement. |
| In some areas, silkworm populations have been very low for decades | recent projects seek to establish silk nurseries and reintroduce the worm |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kull CA (2002): The ‘Degraded’ Tapia Woodlands of Highland Madagascar: Rural Economy, Fire Ecology, and Forest Conservation. Journal of Cultural Geography Spring/ Summer 2002.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية