Furrow-enhanced runoff harvesting for olives [الجمهورية العربية السورية]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Francis Turkelboom
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1005 - الجمهورية العربية السورية
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Tubeileh Ashraf
ICARDA
الجمهورية العربية السورية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
La Rovere Roberto
الجمهورية العربية السورية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Burggeman Adriana
الجمهورية العربية السورية
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - لبنان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/11/2004
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Participatory technology development [الجمهورية العربية السورية]
Participatory technology development, through close researcher-farmer interaction, for sustainable land management of olive orchards in dry marginal areas.
- جامع المعلومات: Francis Turkelboom
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
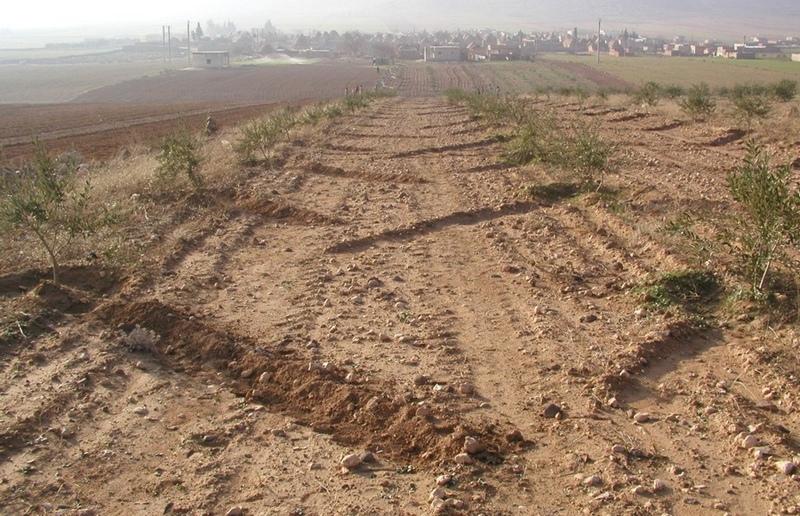
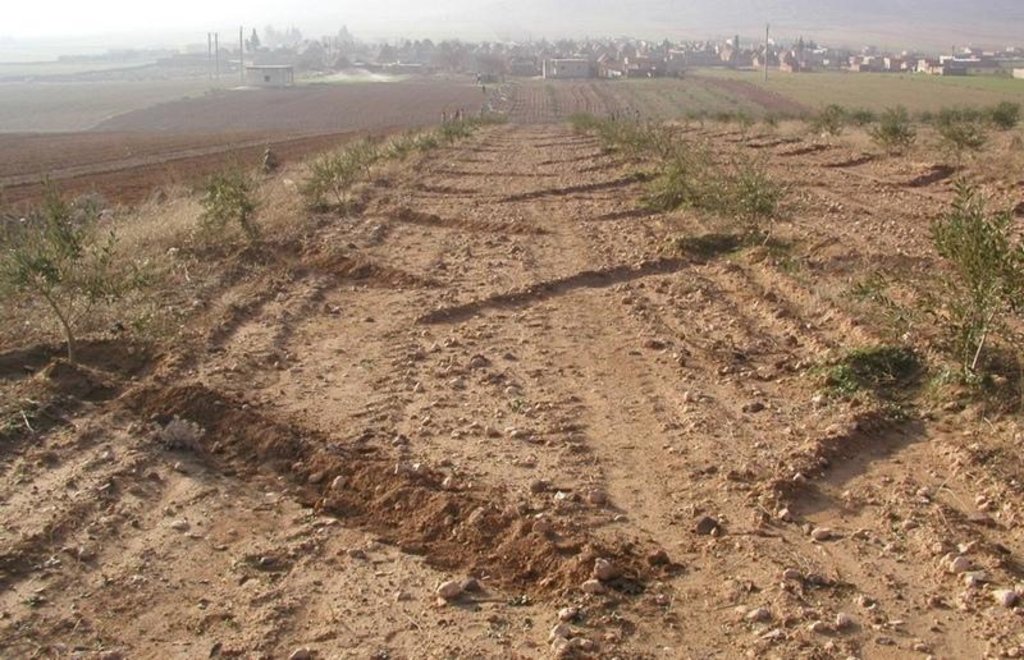
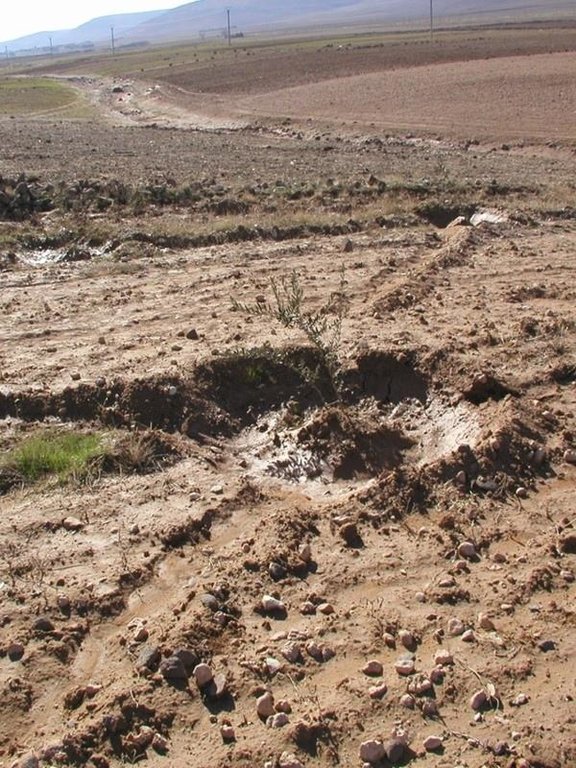
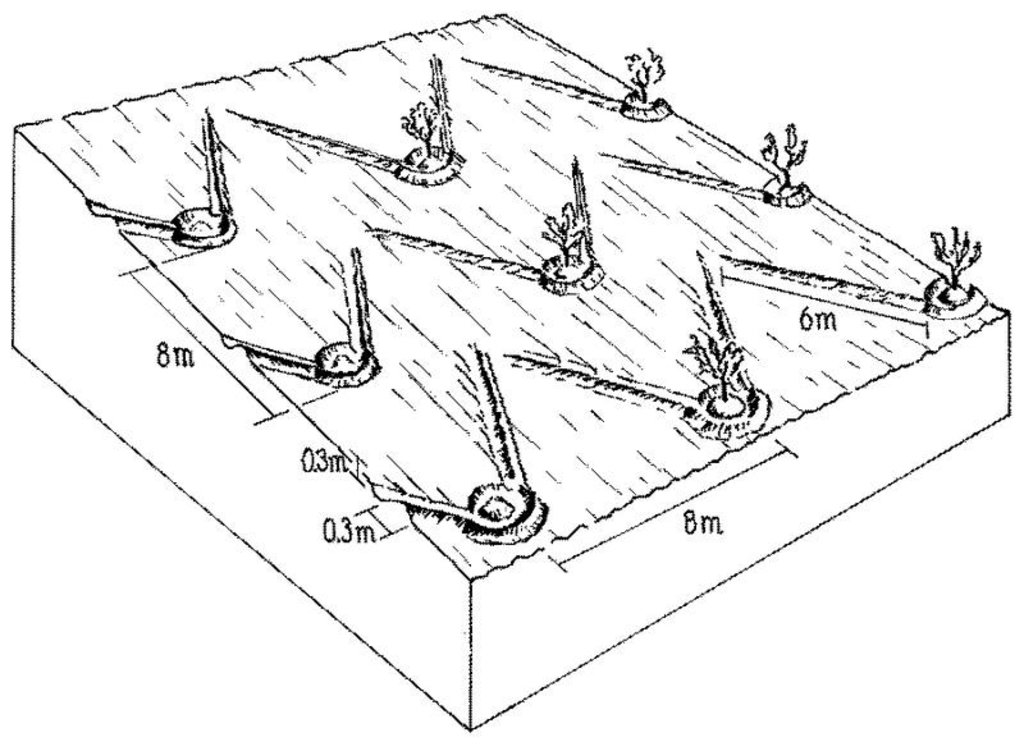
Runoff harvesting through annually constructed V-shaped microcatchments, enhanced by downslope ploughing.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The Khanasser Valley in north-west Syria is a marginal agricultural area, with annual rainfall of about 220 mm/year. Soils are shallow and poor in productivity. The footslopes of degraded hills are traditionally used for extensive grazing or barley cultivation. However to achieve self-sufficiency in olive oil production, several farmers have developed orchards in this area - which is generally considered too dry for olives.
Trees are spaced at 8 m apart, within and between rows. Traditionally, farmers prefer to till their orchards by tractor in order to keep them weed-free (weeds may attract sheep, lead to fires and compete for water with the olive trees). As this tillage operation is usually practised up and down the slope, the resulting furrows stimulate runoff and erosion. However, when this is combined with Vshaped and/or fish-bone shaped microcatchments around individual trees, the furrows created can be used to harvest runoff water for improved production.
The V-shape earthen bunds (reinforced with some stones) are constructed manually, by hoe, around each tree. The furrows then divert runoff systematically to the microcatchments where it concentrates in basins around the trees. Each tree is effectively served by a catchment area of 60 m2. The catchment: cultivated area ratio is thus approximately 60:1 (assuming the area exploited by the tree.
This technology saves irrigation water during the dry season, enhances soil moisture storage, and stimulates olive tree growth. Furthermore, fine particles of eroded soil are captured in the microcatchments. While these may be nutrientrich, they also tend to seal the surface. The bunds need to be rebuilt every year. If the structures are damaged after a heavy storm, they need to be repaired. Labour input for establishment and maintenance is low, the technology is easy and cheap to maintain, and there is enough local skill to sustain and expand the system. A supporting technology is to mulch the area around each tree with locally available stones (limestone and/or basalt) to reduce soil temperature during the summer, decrease surface evaporation and improve infiltration. The catchment areas between the trees are sometimes planted with low water-demanding winter annuals (lentils, vetch, barley, etc) especially when the trees are young. This helps to reduce surface erosion. Implementation of furrow-enhanced runoff water harvesting in olive orchards started in 2002, and adoption by farmers is growing gradually.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الجمهورية العربية السورية
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Aleppo, NW Syria
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Khanasser Valley
Map
×2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
Major cash crop: Olives

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
- الرعي الحرجي
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Main products: Olives, barley, ext. grazing
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There are a series of problems in this area, including: low and erratic rainfall, drought, low land productivity, poor water use efficiency, land degradation, limited ground water for irrigation, few agricultural options, and low income from agriculture.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: before SWC
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150, Longest growing period from month to month: Dec - Apr
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
- تحويل المياه والصرف
3.5 انتشار التقنية
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.05 km2.
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية

التدابير البنيوية
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
V-shaped micro-catchments which harvest water for the olive trees: the furrows up-and-down slope help channel the runoff to the olives.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed
Agronomic measure: up and down tillage
Remarks: (for runoff collection)
Structural measure: V-shaped bunds
Structural measure: mulching with stones (supportive, see also 2.8)
Construction material (stone): limestone, basalt (locally available)
4.4 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Up-and-down tillage by tractor driven plough | بنيوية أو هيكلية | in winter |
| 2. | Construction of runoff harvesting bunds and micro-basins, manually by hoe | بنيوية أو هيكلية | November/December; beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | V-shaped bunds are seasonal structures and thus established every year. Construction of runoff harvesting bunds and micro-basins |
4.5 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Construction (10 person days) | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 63,0 | |||||
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance of bunds in winter/rainy season | بنيوية أو هيكلية | after heavy rainfall 1-3 times a year |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Repair (5 person days) | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 25,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: tractor, hoe, tractor-driven plough
The calculation covers the runoff harvesting technology alone - annual activities of ploughing and water harvesting structure establishment and maintenance. Planting of olive trees and their maintenance are not included here.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: Also rolling (ranked 2) and gentle (ranked 3)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Also shallow (ranked 2) and deep (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and very low (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Off-farm income specification: from farm labour and non-agricultural activities in nearby cities
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 5-15 ha (ranked 3)
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
- individual
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إدارة الأراضي
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Through water saving
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Tree growth
Dependency on tractor
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
Landscape and environmental quality
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التربة
رطوبة التربة
فقدان التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increase in soil fertility
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
التنوع الحيواني
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased weed growth around trees
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support. There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Generally moderate adoption: Mainly applied by ‘agriculturalists’, that is households whose livelihoods mainly depend on agriculture. Farmers with more interest in off-farm labour or sheep rearing - less interested. Is expanding slowly but gradually.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Increases soil moisture storage in low rainfall areas and allows expansion of olive plantation into drier areas |
| Easy, low-cost and requires no extra external inputs. |
| Reduces soil erosion. |
| Reduces summer irrigation needs |
| Improves olive productivity |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Extra labour needed | Construct during off-season. |
| Increases weed growth in the tree basin | More stone mulching. |
| Trees will still need some irrigation in summer | Make irrigation practices more efficient. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Tubeileh A and Turkelboom F, Participatory research on water and soil management with olive growers in the KhanasserValley. KVIRS project, ICARDA, Aleppo, Syria. 2004.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Tubeileh A, Bruggeman A and Turkelboom F, Growing olive and other tree species in marginaldry environments. ICARDA, Aleppo, Syria. 2004.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Participatory technology development [الجمهورية العربية السورية]
Participatory technology development, through close researcher-farmer interaction, for sustainable land management of olive orchards in dry marginal areas.
- جامع المعلومات: Francis Turkelboom
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية