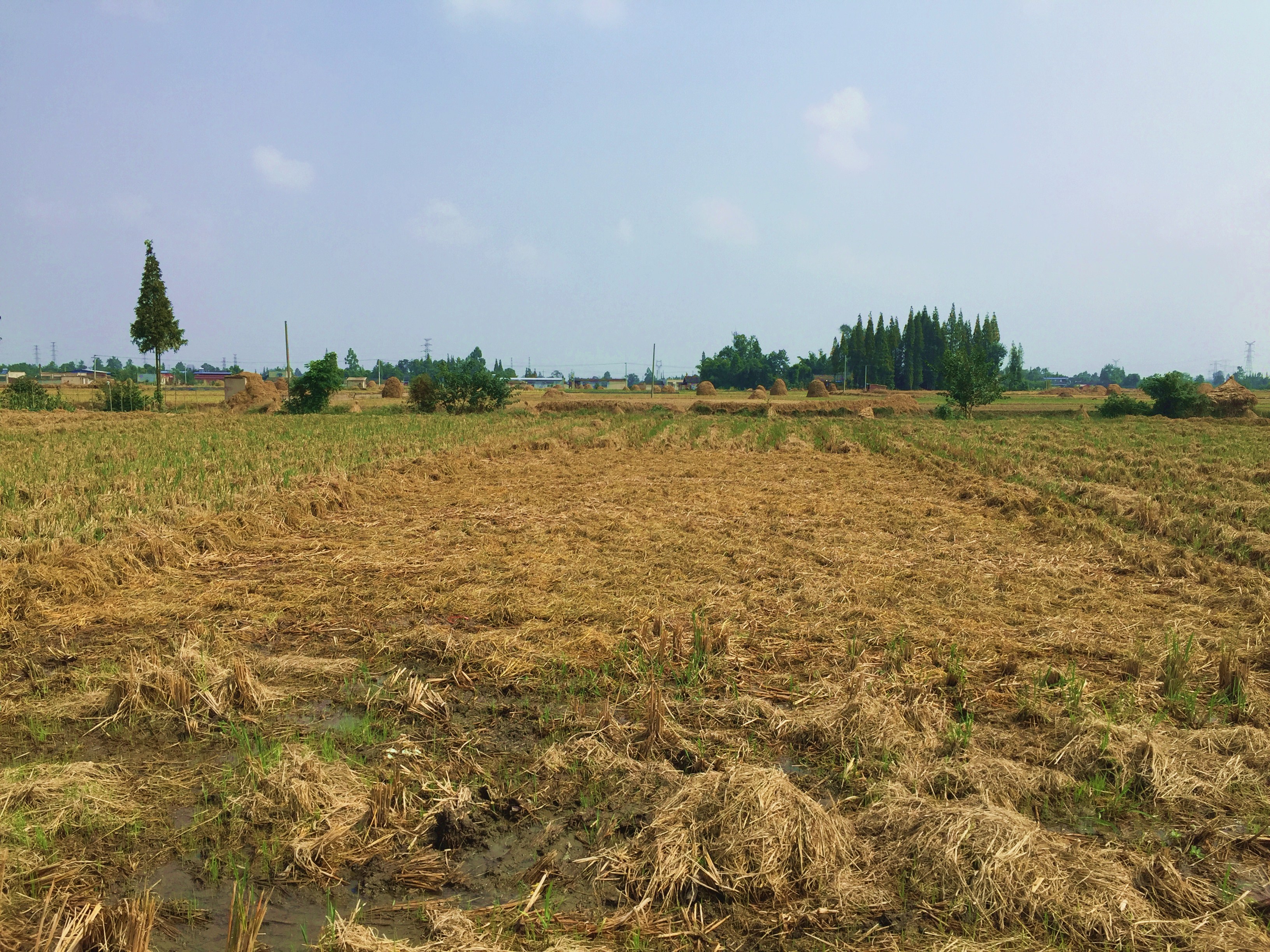
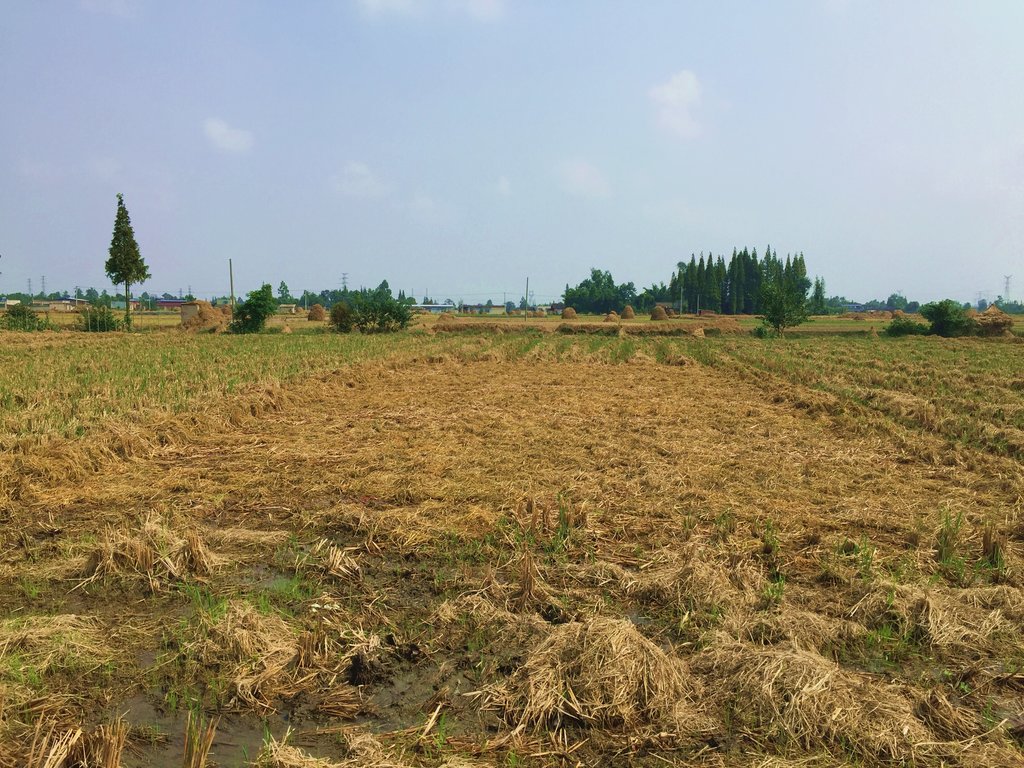
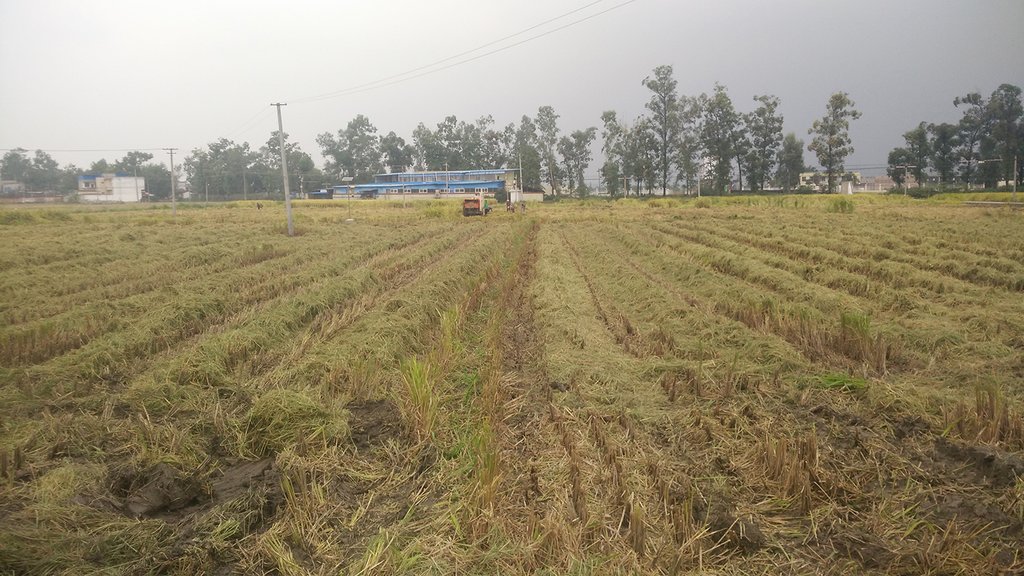
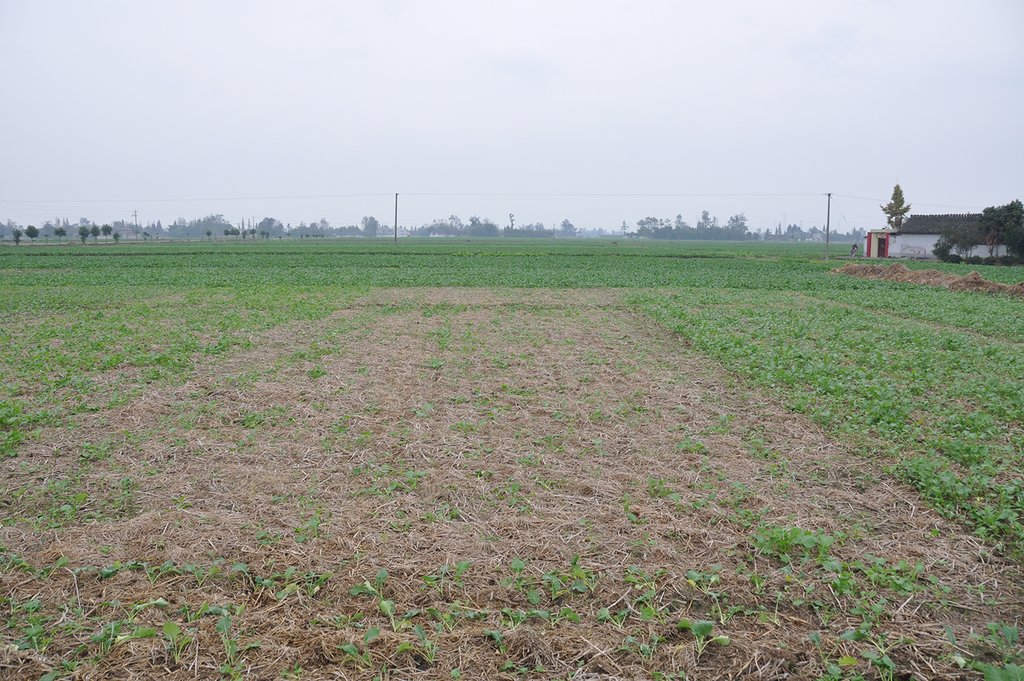
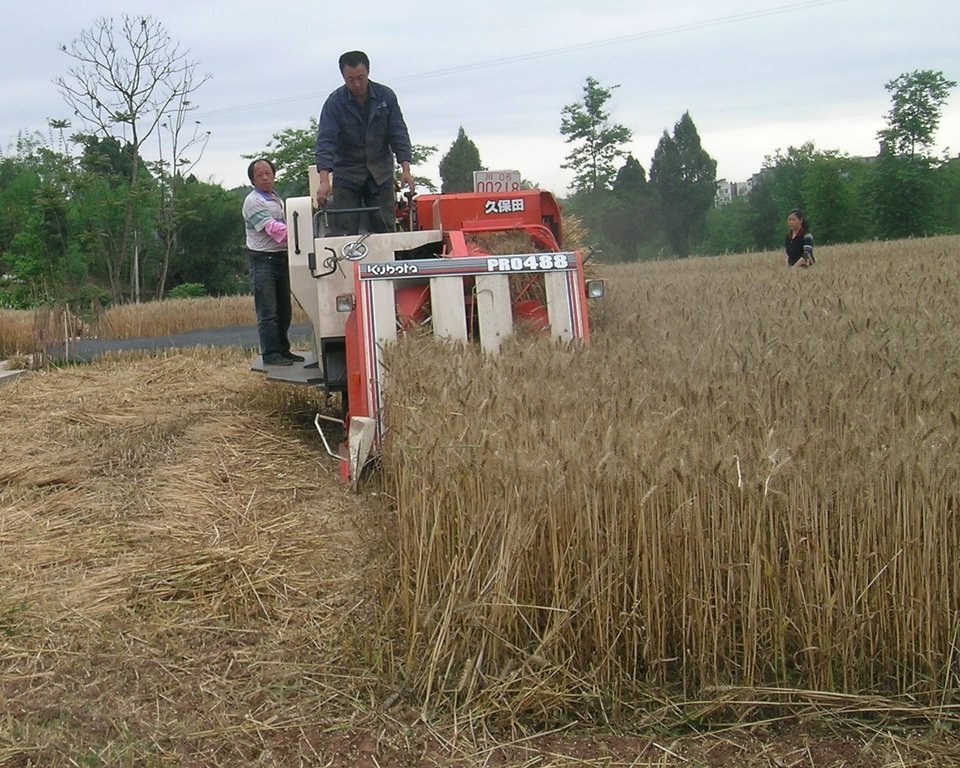
Straw residues left on field after harvest and no tillage [الصين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Song Guo
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Gudrun Schwilch, Ursula Gaemperli
No tillage planting
technologies_3239 - الصين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Hongzhu Fan
hongzhufan@126.com
Soil and Fertilizer Institute of the Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences
No. 4 Shizishan Road Jinjiang District Chengdu City, Sichuan Province
الصين
مستخدم الأرض:
Wu Shengde
+86 13990221127
Baili village, Xigao Town, Guanghan City, Sichuan Province
الصين
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
‒ Soil and Fertilizer Institute of the Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (SFI) - الصين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
20/09/2016
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Method of this agricultual technology the rice straw will be left on the field after mechanized harvesting. Succession crop, such as rape, wheat or potato, were seeded directly under no tillage condition. Both measures aim at better soil regeneration and soil conditions for agriculture and subsequently increased yield and less soil degradation.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The SLM practice (straw mulching and no tillage) is applied in the Chengdu Plain Paddy Soil. The Chengdu plain has mild climate and abundant rainfall. It belongs to the warm humid subtropical Pacific monsoon climate zone.The main types of soil in the Chengdu plain are paddy soil and purple soil.The total land resources of the Chengdu plain are 1331800 hectares, and the per capita land resources are about 0.1044 hectares per person. In 2010, the total amount of cultivated land in the Chengdu plain was 478069 hectares, accounting for 35.90% of the area of the plain, accounting for 42.36% of the total area of agricultural land in the region, and the per capita arable land area was only about 0.0375 hectares. The Chengdu Plain is an important grain production base in Sichuan. Rice field-upland field rotation (rice - wheat, rice - rapeseed) is an important agricultural system.
On the case study area, the N, P and K fertilizers were applied as urea, calcium superphosphate and potassium chloride at the rates of 120-150 kg N ha-1, 75-120 kg P2O5 ha-1,and 75-120 kg K2O ha-1, during every crop. During crop season, the rate of 60% of N, 100% of P, and 50% of K fertilizers were applied as base fertilizer, while remaining 40% of N and 50% of K were used as top dressing fertilizer. The main measures of this SLM is rice straw or wheat straw mulching while havesting (leaving the straw after havest scattered on the field). Crops were harvested by a combine harvester (Kuotian combine harvester, model PR0488), then straw and stubble of crops were left at size of less than 20 cm in the field. The seeding of succession crop such as wheat and oil seed rape is done by a direct seeding machine. The land users are working eighter with a contractor or they use their own machines and labour force. The purposes of this technology were to increase production and improve soil fertility. Although plough layer can become shallow by long-term no tillage cultivation, more and more land users like this technology because it promises increased grain yield, reduction of fertilizers (and subsequently cost), and it improves soil physical, chemical and biological properties of soil. Thus, it is expected that the measures of this SLM-Technology ends up in improved soil moisture, higher diversity of soil life and finally soil fertility .
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الصين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Basin plain, Chengdu, Sichuan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Guanhan City, Wenjiang District, Chongzhou City
التعليقات:
This long-term straw mulch experiment was started in the 2005. This site is situated in subtropical monsoon region with anverage annual temperature of about 16.3℃, 281 days frost free. Annual precipitation is about 890mm.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The current case study bases only on a test area within the scope of the iSQAPER Project. A long-term straw mulch and fertilization experiment was initiated in 2005 at Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Soil and Fertilizer Research Institute’s Guanghan agricultural experiment station in Sichuan province, southwest China. Thus, effects of long-term fertilization and straw much on crop yields, soil physical and chemical properties under rice-rapeseed rotation were assessed in a paddy soil
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
المحاصيل الرئيسية (المحاصيل النقدية والغذائية):
rape, rice, wheat
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
3.4 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- أنظمة التناوب (تعاقب المحاصيل، البور، الزراعة المتنقلة)
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
3.5 انتشار التقنية
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنية منتشرة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، فحدد المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
The SLM practice (straw mulching while harvesting and no tillage) is applied in the Chengdu Plain paddy soil. The main measures of this SLM method is straw mulching while harvesting and no tillage. Crops are harvested by machine (actually in this case study by Kuotian combine harvester/model was PR0488), and then straw and stubble were left at size of less than 20 cm on the soil surface. The N, P and K fertilizers to the succession crop were applied in form of urea, calcium superphosphate and potassium chloride at the rates of 120-150 kg N ha-1, 75-120 kg P2O5 ha-1, and 75-120 kg K2O ha-1. Rates of 60% of N, 100% of P and 50% of K fertilizers were applied as base fertilizers, while the remaining 40% of N and 50% of K were used as top dressing fertilizers. After previous crop harvest of rice the succession crop as for example wheat, oil rape, maize will be seeded directly under no tillage condition.
4.3 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1 hectare
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Renminbi (RMB)
أشر إلى سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (إذا كان ذا صلة): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
6,6
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
120 RMB per day
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | mechanized harvesting | زراعية | August or September |
| 2. | spreading the straw residues after havest on the field | زراعية | after harvest of crops |
| 3. | fertilization | زراعية | October |
| 4. | no tillage and direct seeding | زراعية | October |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | All reccurent labour (above) is done within the familiy* | person-day | 0,5 | 120,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | harvester (machine from contractor without labour force)* | ha | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Direct seeding machine (from contractor without labour force)* | ha | 1,0 | 1800,0 | 1800,0 | |
| المواد النباتية | seed (weat, rape) | kg | 120,0 | 2,0 | 240,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | urea | kg | 280,0 | 3,0 | 840,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | calcuim superphosphate | kg | 810,0 | 1,0 | 810,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | potassium chloride | kg | 200,0 | 3,5 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 7450,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
*The labour (for harvesting, fertilizering and seeding ) is unpaid when those were done by farm familiy.
But in China, there is no contractor to do all work (for harvesting, fertilizing and seeding). If all works done by a contractor, farms will give up planting crops. Usually, a contractor provide machine to farm, but no labor. Farm members engaged in agricultural production will do most of the work by themselves in order to save cost.
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Most of important factor affecting the costs of this technology is the type of machine used for harvest. (E.g. cost is high by the mini combine harvester because of the low efficiency).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil type is alluvial soil, PH is 5.5, SOC 31.3g/kg, N 2.02g/kg,P 1.04g/kg, K 7.69g/kg, available nitrogen 189.7mg/kg, available phosphorus 12.6mg/kg, ammonium acetate extractable potassium95.5mg/kg.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
< 5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- مرتفع
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
In China, land ownership belongs to the state, but land use rights belong to farm. In other words, farm can decide to plant rice, wheat, or fruit tree in the land, but the farm cannot sell this land.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
14.9 t ha-1*
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
15.5 t ha-1*
التعليقات/ حدد:
* yield for rape
Wheat yield were 6.3 t ha-1 before SLM and 6.7 t ha-1 after SLM, respectively. Rice yield were 8.6 t ha-1 before SLM and 8.8 t ha-1 after SLM, respectively.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
No tillage is an important way to reduce cost by machine plough field. Less fertilizing work and amount of fertilizers by leaving straw on field (straw contains a large amount of C, N, P, and K)
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Straw mulching can decreased demand for irrigation water, because water can be keep in the straw, and straw mulching on the soil also can reduced evaporation of water.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
No tillage is an important way to reduce cost by machine plough field. Less fertilizing work and amount of fertilizers by straw return compared with no straw mulching (straw contains a large number of C, N, P and K. Therefore agricultural inputs can be reduced.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Do to better yield and reduction of costs.
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased knowledge on the benefits of straw mulching by the land users.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to straw mulching, because the water can be kept in the straw and soil evaporation can be reduced to improved oil cover.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to the mulching by straw, the soil remain covered practically the whole year round.
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Without ploughing the soil crusting can occur at long term use of the technology (findings from a long-term straw mulch and fertilization experiment was initiated in 2005 at Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Soil and Fertilizer Research Institute’s Guanghan agricultural experiment station in Sichuan province)
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Without ploughing the soil gets more compact at long term use of the technology (findings from a long-term straw mulch and fertilization experiment was initiated in 2005 at Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Soil and Fertilizer Research Institute’s Guanghan agricultural experiment station in Sichuan province)
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to mulching by rice straw (crop residues)
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to mulching by rice straw (crop residues)
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to mulching by rice straw (crop residues), soil life has increased.
الأنواع المفيدة
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Traditional burning of rice straw on the fields has been reduced, as straw is needed for mulching. Subsequently the C can be bound within the soil and will not be emitted into the air in form of CO2.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Traditional burning of rice straw on the fields has been reduced, as straw is needed for mulching. Subsequently the C can be bound within the soil and will not be emitted into the air in form of CO2.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 50-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 100-90%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| This technology can improve the yield |
| It can save labour by leaving straw on the field |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Straw mulching can increase the soil carbon input, and improve the soil quantity. |
| This technology can reduce land degradation. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Soil structure was deteriorated by no tillage cultivation. | tillage |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Soil hardening occured, and also a thin impervious layer was built at the soil surface | It could be good to plough up the soil after an interval of 5 years |
| Obstruction of rainwater infiltration | |
| Soil plough layer becomes shallow |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
94 people
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Composition of Wheat Rhizosphere Antagonistic Bacteria and Wheat Sharp Eyespot as Affected by Rice Straw Mulching. CHEN Huai-Gu, CAO Qi-Guang, XIONG Gui-Lin, LI Wei, ZHANG Ai-Xiang, YU Han-Shou and WANG Jin-Sheng.2010.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Effects of pre-sowing irrigation and straw mulching on the grain yieldand water use efficiency of summer maize in the North China Plain. Zhenxing Yan, Chao Gao, Yujie Ren, Rui Zong, Yuzhao Ma, Quanqi Li. 2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Effects of snow cover plus straw mulching on microorganisms in paddy soil during winter.Hao Zhanga,b, Jie Tanga, Shuang Liang.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Effects of Non-flooded Cultivation with Straw Mulching on Rice Agronomic Traits and Water Use Efficiency. QIN Jiang-tao , HU Feng , LI Hui-xin , WANG Yi-ping , HUANG Fa-quan , HUANG Hua-xiang.2006
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Growth Characteristics and Yield of Late-Season Rice under No-tillageand Non-flooded Cultivation with Straw Mulching. WANG Dong, LI Hui-xin, QIN Jiang-tao, LI Da-ming, HU Feng.2010
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Impact of tillage practices on soil bacterial diversity and composition under the tobacco-rice rotation in China. Yanping Lei, Yongliang Xiao, Lifeng Li,Chaoqiang Jiang, Chaolong Zu, Tian Li, and Hui Cao.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Nutrient Decomposition Rate and Sugarcane Yield as Influenced by Mung Bean Intercropping and Crop Residue Recycling Tie-Guang He,Li-Rong Su,Yang-Rui Li,Tian-Ming Su2 Fang Qin,Qin Li.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Process rates of nitrogen cycle in uppermost topsoil after harvesting in no-tilled and ploughed agricultural clay soil. Merjo Laine . Tobias Ru¨ tting . Laura Alakukku . Ansa Paloja¨rvi . Rauni Stro¨mmer.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Research on the effect of straw mulching on the soil moisture by field experiment in the piedmont plain of the Taihang Mountains. LI Man, ZHANG Wei, HE Yu-jiang, WANG Gui-ling.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Rice–wheat cropping system: tillage, mulch, and nitrogen effects on soil carbon sequestration and crop productivity Keshav R. Adhikari,Khem R. Dahal,Zueng-Sang Chen,Yih-Chi Tan,Jihn-Sung Lai.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Soil Carbon Sequestration and Crop Yields in Rice–Wheat and Sugarcane–Ratoon–Wheat Cropping Systems Through Crop Residue Management and Inoculation of Trichoderma viride in Subtropical India.S. K. Shukla,Swaha Shee,S. K. Maity,S. Solomon,S. K. Awasthi,Asha Gaur,A. D. Pathak,V. P. Jaiswal.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ScienceDirect. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
成都平原麦稻双免耕秸秆还田技术模式.汤永禄 , 黄钢, 郑家国, 李朝苏,邓先和,付书明.2008
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.cnki.net/. No
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Influence of straw mulching with no-till on soil nutrients and carbon pool management index.CHEN Shang-hong, ZHU Zhong-lin, LIU Ding-hui, SHU Li , WANG Chang-quan.2008
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.cnki.net/. No
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Effects of pre-sowing irrigation and straw mulching on the grain yieldand water use efficiency of summer maize in the North China Plain.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.02.017
العنوان/الوصف:
Effects of snow cover plus straw mulching on microorganisms in paddy soil during winter
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.05.023
العنوان/الوصف:
Growth Characteristics and Yield of Late-Season Rice under No-tillageand Non-flooded Cultivation with Straw Mulching
عنوان الرابط URL:
DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(08)60117-1
العنوان/الوصف:
Impact of tillage practices on soil bacterial diversity and composition under the tobacco-rice rotation in China
عنوان الرابط URL:
DOI 10.1007/s12275-017-6242-9
العنوان/الوصف:
Nutrient Decomposition Rate and Sugarcane Yield as Influenced by Mung Bean Intercropping and Crop Residue Recycling
عنوان الرابط URL:
DOI 10.1007/s12355-017-0548-0
العنوان/الوصف:
Process rates of nitrogen cycle in uppermost topsoil after harvesting in no-tilled and ploughed agricultural clay soil
عنوان الرابط URL:
DOI 10.1007/s10705-017-9825-2
العنوان/الوصف:
Rice–wheat cropping system: tillage, mulch, and nitrogen effects on soil carbon sequestration and crop productivity
عنوان الرابط URL:
DOI 10.1007/s10333-015-0511-1
العنوان/الوصف:
Soil Carbon Sequestration and Crop Yields in Rice–Wheat and Sugarcane–Ratoon–Wheat Cropping Systems Through Crop Residue Management and Inoculation of Trichoderma viride in Subtropical
عنوان الرابط URL:
DOI 10.1007/s12355-016-0470-x
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية