Drinking water quality improvement through conservation measures [النيبال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Madhav Dhakal
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Samrakshan bidhi dwara piune pani ko gunastar sudhar - Nepali
technologies_1496 - النيبال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dongol Bhawani
النيبال
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - النيبال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Community efforts for improving drinking water quality [النيبال]
Working with communities to demonstrate and disseminate methods for improving drinking water quality using structural and vegetative measures
- جامع المعلومات: Madhav Dhakal
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Structural and vegetative measures to improve the quality of drinking water contaminated due to poor sanitation and seepage
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
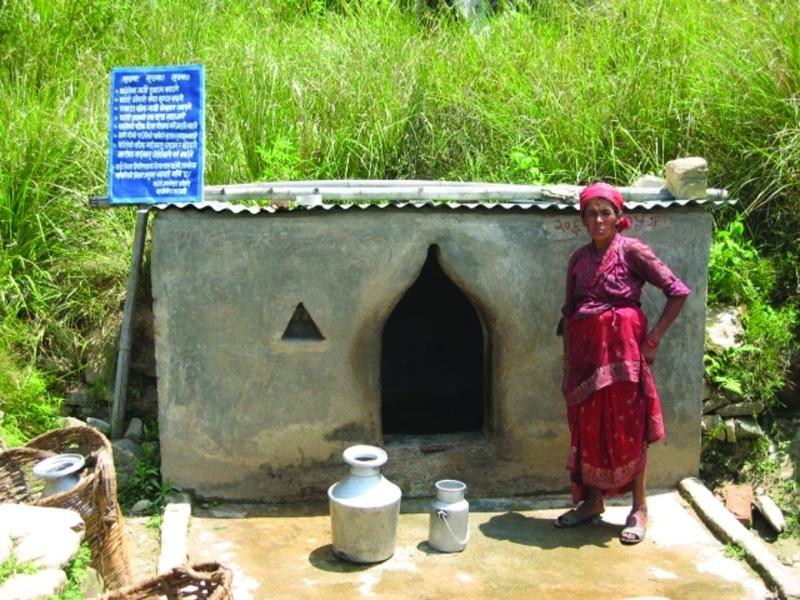
This technology combines structural and vegetative measures to improve the quality of drinking water in an open spring. The quality of water was deteriorating due to poor sanitation and seepage around the spring. The spring was located near to Dhotra village at Barbot sub-settlement, Kabhrepalanchok district. About five households depended on the spring for their drinking water supplies with a further 10 using it regularly and 10-15 using it occasionally during the dry season.
The main purpose of implementing the technology was to improve the quality of drinking water in the spring by preventing it from being contaminated by surface runoff during the rainy season. This technology has long been implemented across Nepal’s midhills. In this case a development project (PARDYP) mobilised the users and provided them with technical and material support to make the improvements.
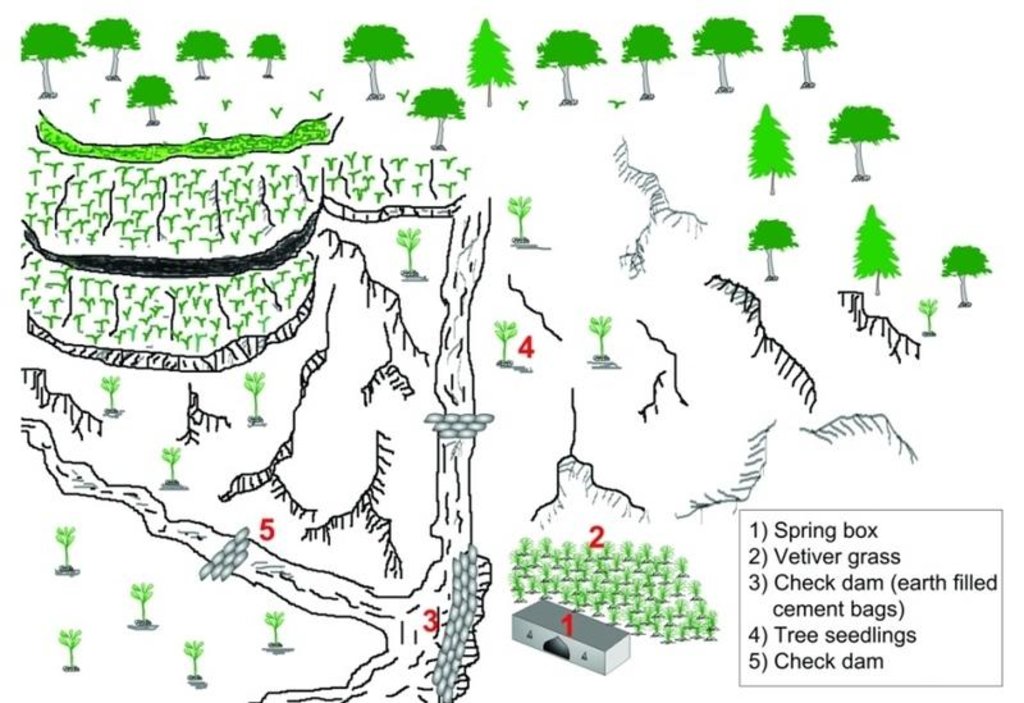
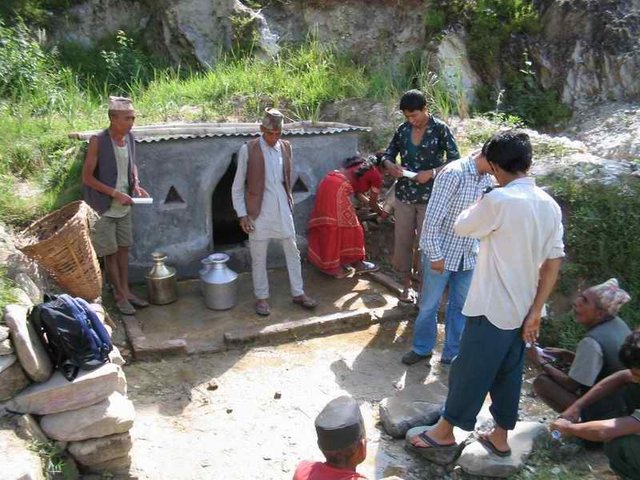
A spring user group was formed. With project help, it built a walled structure (a spring box) over the spring and check dams around the spring, and planted grasses around the spring box and trees in the catchment. These measures prevented the direct flow of surface water into the spring thus reducing contamination and turbidity. Users built a 1.8m long, 1m wide and 1.5m high spring box with a zinc sheeted roof. Check dams were built across the surrounding gullies and rills. A main 2.5m long, 0.5m wide, and 1m high check dam was constructed near the source to prevent surface runoff from entering the spring. A drainage channel was made to drain off wastewater. Vetiver grass seedlings were planted around the spring box and trees were planted in the adjoining catchment. These activities were carried out at the beginning of the rainy season.
This technology is simple and durable and the only maintenance needed is to keep the surroundings clean and to repair any damage.
The case study area receives about 1200 mm of annual precipitation of which about 80% occurs during the monsoon season (June to September). The area mostly has red soils which are highly weathered and, if not managed properly, are very susceptible to erosive processes.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيبال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kavrepalanchowk district/ Jhikhu Khola watershed
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Local community, with the contribution from individual community members or from external support have been implementing since generations. In this particular case project mobilized the spring users community and assisted them by providing technical and material support during programme implementing period.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- Improve water quality
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي

غير ذلك
حدد:
Private land-abondent by village elite, communal land-open grazing
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): High pressure on limited land resources due to overuse of crop, forest, and grazing lands; increased inputs of agrochemicals which will lead to the deterioration of drinking water quantity and quality
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water quality deterioration resulting from poor sanitation
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: private land-abondent by village elite, communal land-open grazing
Number of growing seasons per year: 3
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V2: الأعشاب والنباتات العشبية المعمرة

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wo:) تأثيرات التدهور من مواقع أخرى
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (uncontrolled access to grazing land), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (concentrated runoff during rainy season), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge - water quality treatment)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (uncontrolled access to forest land), poverty / wealth (lack of captial - conservation activities)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Structural and vegetative measures applied to improvewater quality of spring
Location: Barbot Dhotra. Kabhrepalanchowk district
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Michelia champaca
Grass species: Vetiveria lawsoni
Structural measure: spring box wall
Material: concrete
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.02
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.89
Structural measure: check dams
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Structural measure: cut-off drain
Material: Stone
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.25
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Construction material (stone): locally available
Construction material (concrete): cement, sand, brick
المؤلف:
Madhav Dhakal, A. K.Thaku
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Spring box and plants
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
1.8m long, 1m wide and 1.5m high with a zinc sheeted roof
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.60
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting vetiver grass around the spring box | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Planting tree species in the catchment | beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Building of check dams to divert stream and gully runoff water | start of the rainy season |
| 4. | Buildingof the spring box | start of the rainy season |
| 5. | Construction of concrete floor in front of spring box | start of the rainy season |
| 6. | Construction of drainage channel | start of the rainy season |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Building spring box and planting trees | Persons/day | 69,0 | 1,6 | 110,4 | 80,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Grass seedlings | unit | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Cement | unit | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Gravel / sand | unit | 1,0 | 55,0 | 55,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Bricks | unit | 1,0 | 188,0 | 188,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Empty sacks | unit | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Tinc sheet | unit | 1,0 | 16,0 | 16,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Steel wire | unit | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Transportation | unit | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 15,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 433,4 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 433,4 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
PARDYP and District Development Committee
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | replacement/ gap filling with new tree seedings | /as required |
| 2. | maintaining height of the planted grass | /as required |
| 3. | Cleaning spring box surroundings | as per need |
| 4. | Maintenance of wall/ floor against damage | as per need |
| 5. | Maintenance of check dam against damage | as per need |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Maintaining springbox | Persons/day | 2,0 | 1,6 | 3,2 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 3,2 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 3,2 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: hoe,spade, shovel, nails, hammer, pliers, trowel, steel pan bucket, and jug
The cost is only for unit technology, it can not be extrapolated to hector basis, as in 2006.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Material cost was comparatively high followed by labor cost. For this technology several actors contributed. The land users contributed 61 percent, District Development Committee contributed 26 percent and PARDYP contributed 13 percent, and the department of forest and PARDYP regional coordinator contributed by providing planting materials( vetiver).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1200,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 900 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Variable
Soil texture: Red soils with high clay content
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Water quality (untreated): More contamination during monsoon season (June- September), source: mainly natural springs
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
15% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land.
85% of the land users are poor and own 65% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
decreased women's workload for collecting water, since water is available near to the households
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
water quality improvement
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
formation of user group; less conflicts for drinking water
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
group discussion, awareness
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
conflicts due to insufficient water quantity. Especially during dry and pre- monsoon months
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Better health due to clean water.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to drainage trench and check dams
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to planted grasses and trees
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to check dams
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Clean water is available immediately after only a little investment. Government and PARDYP support meant that the short-term benefit was positive. Without this support the short-term costs would equal the benefits.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
15 households in an area of 10 ha
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
15 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Local people with inadequate access to drinking water or whose source is contaminated are
likely to adopt the technology after raising the funds themselves.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Increased availability of drinking water has reduced women’s workload during the dry season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the technology by building a closed storage tank. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Water turbidity decreased from 23 nephelometric turbidity units (NTU) in August 2004 to 7 NTU in August 2005. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage spring users to plant more multiple grasses and tree species around the catchment area |
|
Faecal contamination decreased from 500 coliform formation units (CFU)/100 ml in August 2004 to 200 CFU/100 ml in August 2005. Similarly, the levels of ammonia (NH3) and nitrate (NO3 in the spring water have decreased (NH3 from 0.5 to 0 mg/l; and NO3 from 0.7 to 0.5 mg/l). Total hardness of spring water remained the same at 30 mg/l. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance, especially cleaning the surrounding area is needed; also need a clean pot for extracting the water. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Coliform bacteria are still a problem | Treat the water using SODIS, boiling, fi lters, chlorination or other methods before drinking. |
| The water available during the pre-monsoon season is insufficient for the15 households, leading to conflicts; the water source can be contaminated from unclean water fetching pots. |
The water in the spring box should be siphoned into a storage tank fi tted with an overfl ow mechanism,cleaning outlet, lockable cover, and taps. This would protect the water source from contamination from open access and improve the quality and availability of water. The amount available could be increased by tapping other spring sources. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management: Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICIMOD
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Community efforts for improving drinking water quality [النيبال]
Working with communities to demonstrate and disseminate methods for improving drinking water quality using structural and vegetative measures
- جامع المعلومات: Madhav Dhakal
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية