Mainstreaming river water to facilitate irrigation in Barind [بنغلاديش]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Udo Höggel, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Sharmongla Sech Prokolpo.
technologies_5171 - بنغلاديش
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Establishing National Land Use and Land Degradation Profile toward Mainstreaming SLM Practices in Sector Policies (ENALULDEP/SLM)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Department of Environment (DoE) - بنغلاديش1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
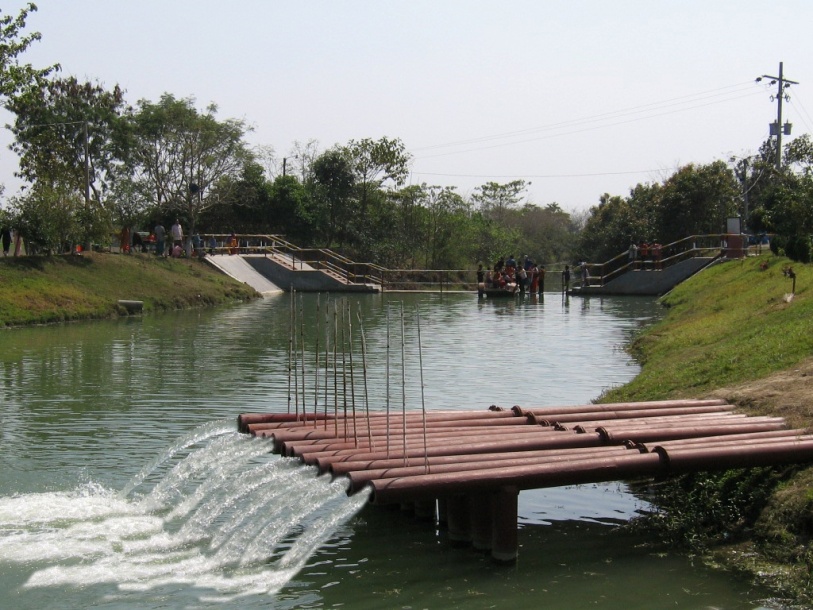
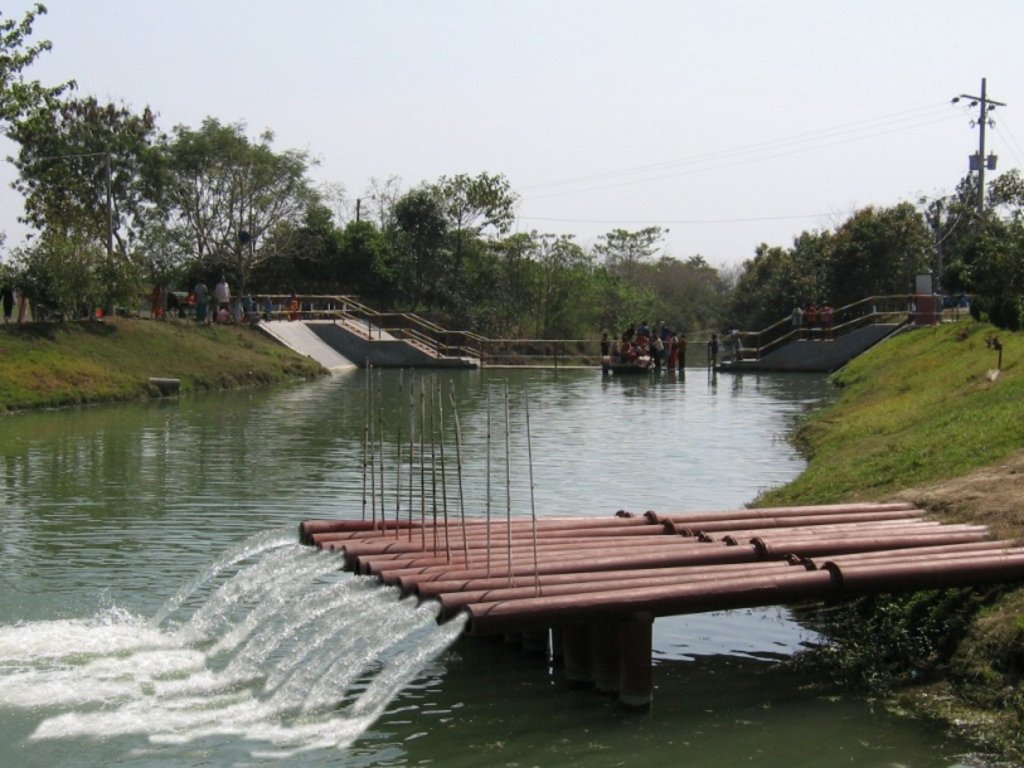
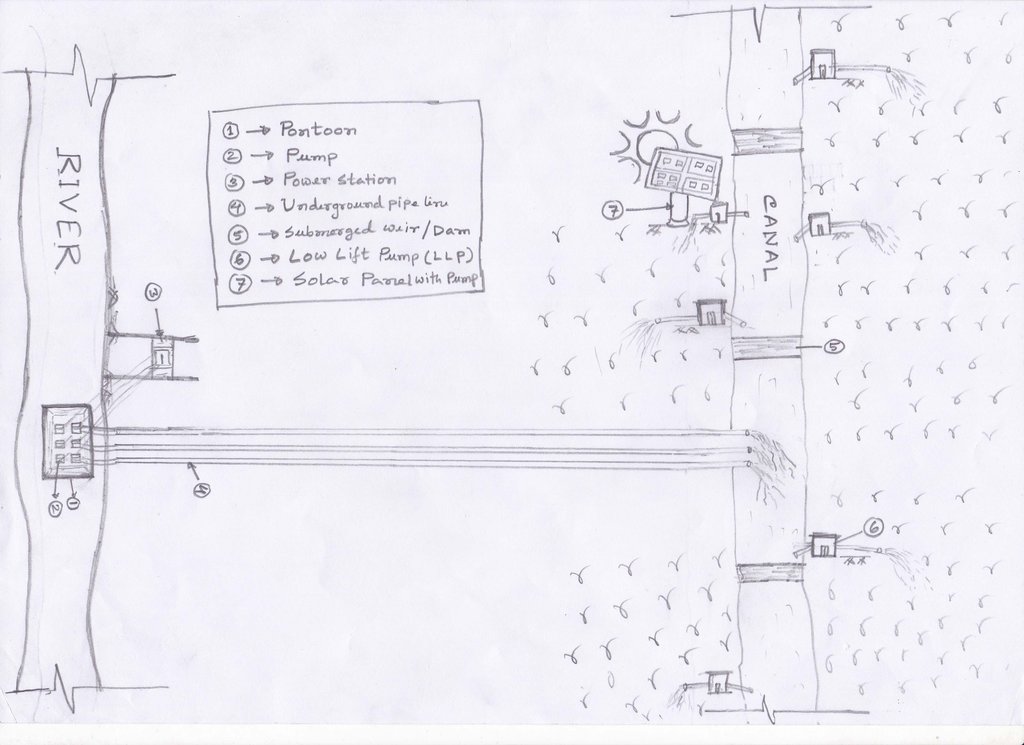
The technology promotes the lifting of river water by pump sets and conveys the water through buried pipelines to a canal. The conserved canal water is used for irrigation delivered by low lift pumps (LLP). Because water is held in the canal it revitalises the ecosystem along its length. Furthermore, using river water for irrigation avoids dangers associated with groundwater depletion.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
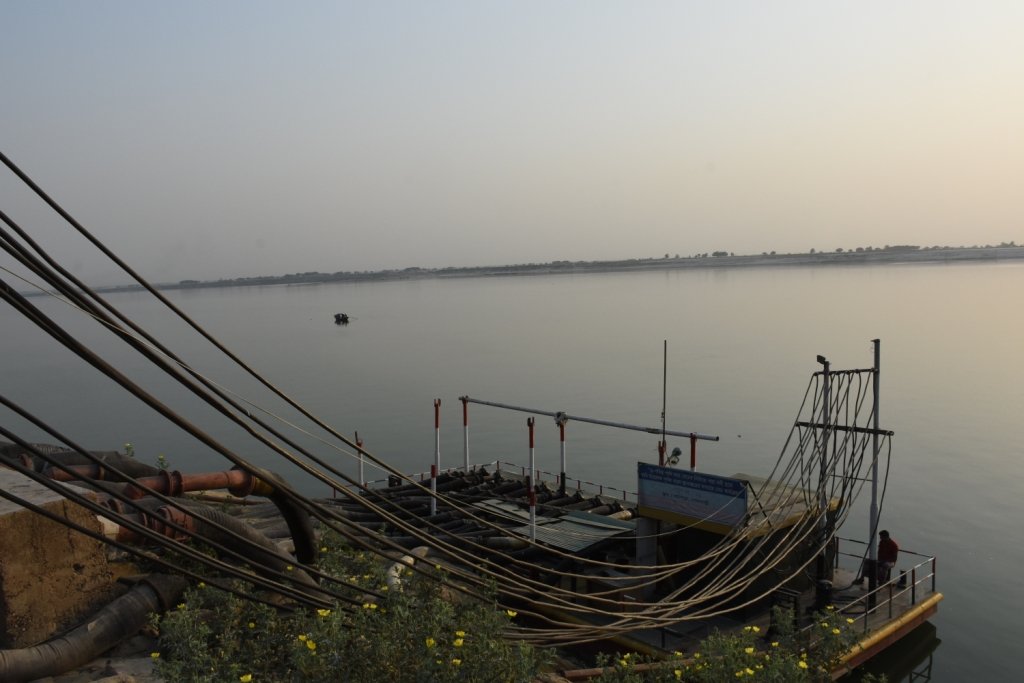
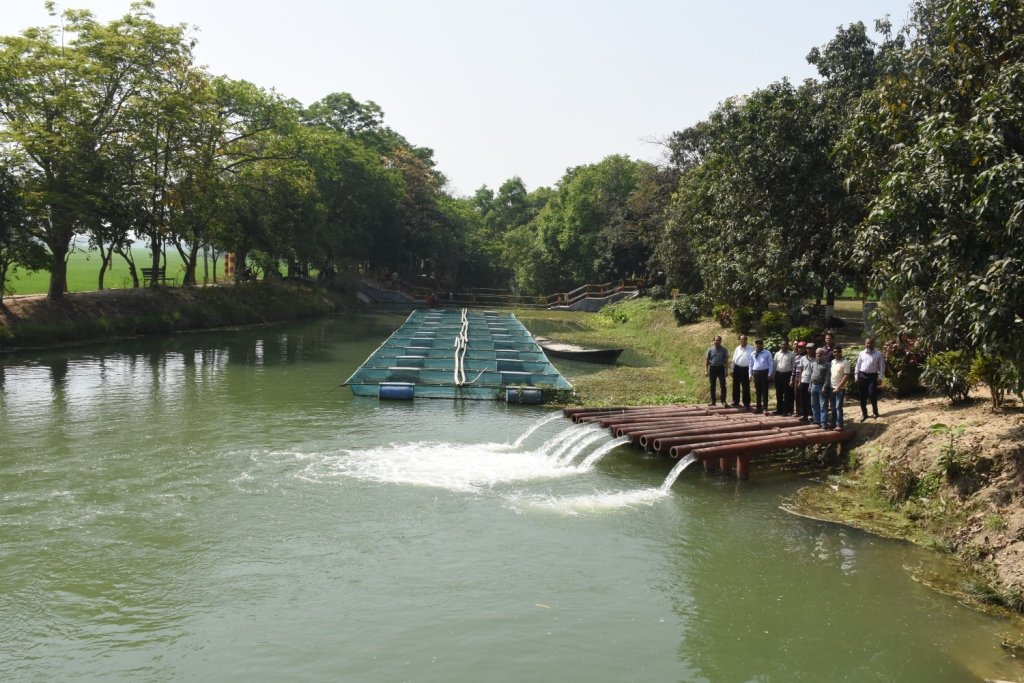
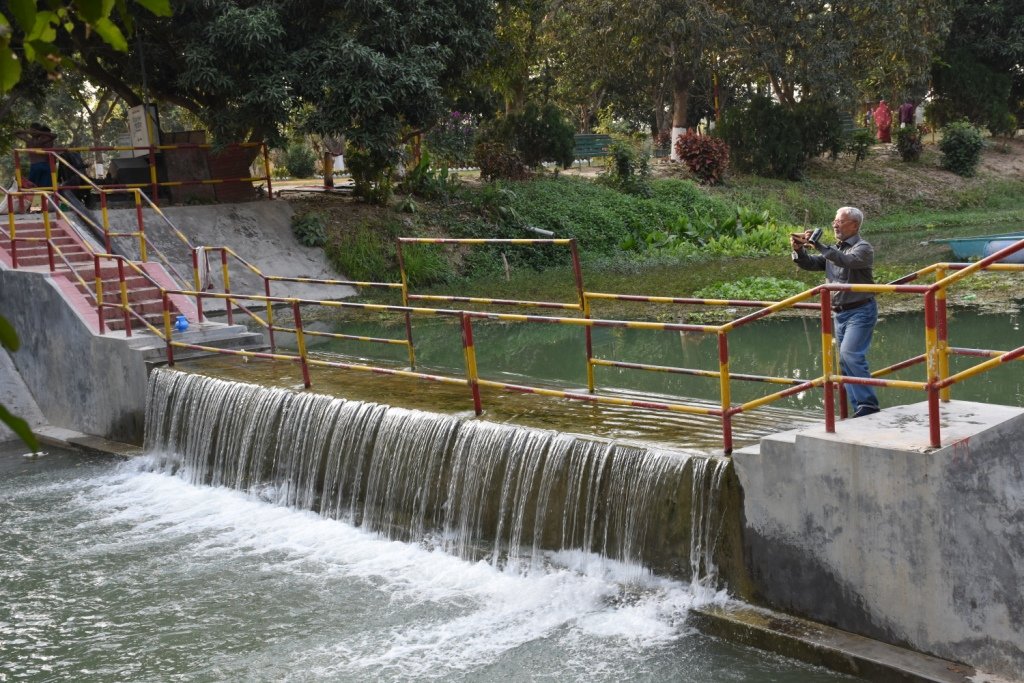
The project is sited at Sharmongla under Godagari Upazilla of Rajshahi district. The Sharmongla canal is located about 3.5 km away from the Padma river. Its total length is 29.0 km. Under this technology, water is lifted from the Padma river by pumps set on a pontoon. The lifted water is then discharged to a canal through underground pipelines. The water so discharged is lifted to the crop fields (delivery points) for irrigation. The elevation difference between the delivery points and the sourcing river is about 21 m. There are numbers of submerged weirs/dams constructed across the canal at different locations for conserving water: the water then helps regenerate the ecosystem along its banks and enriches the habitat.
Pontoon at a glance:
•Year of construction: 2004
•No. of centrifugal pumps at pontoon: 12
•Pump capacity: 50 m lifting height.
•Power of each pump: 60 HP
•Capacity of each pump: 2.5 cusec
•Total capacity of pump sets: 30 cusec
•Capacity of electric sub-station: 750 KW
•No. of discharge pipelines: 12
Sharmongla canal at a glance:
•Length of the canal: 29 km
•Average width of the canal: 15 m
•Average depth from ground level: 5 m
•No. of submerged weirs and dams within the canal: 14
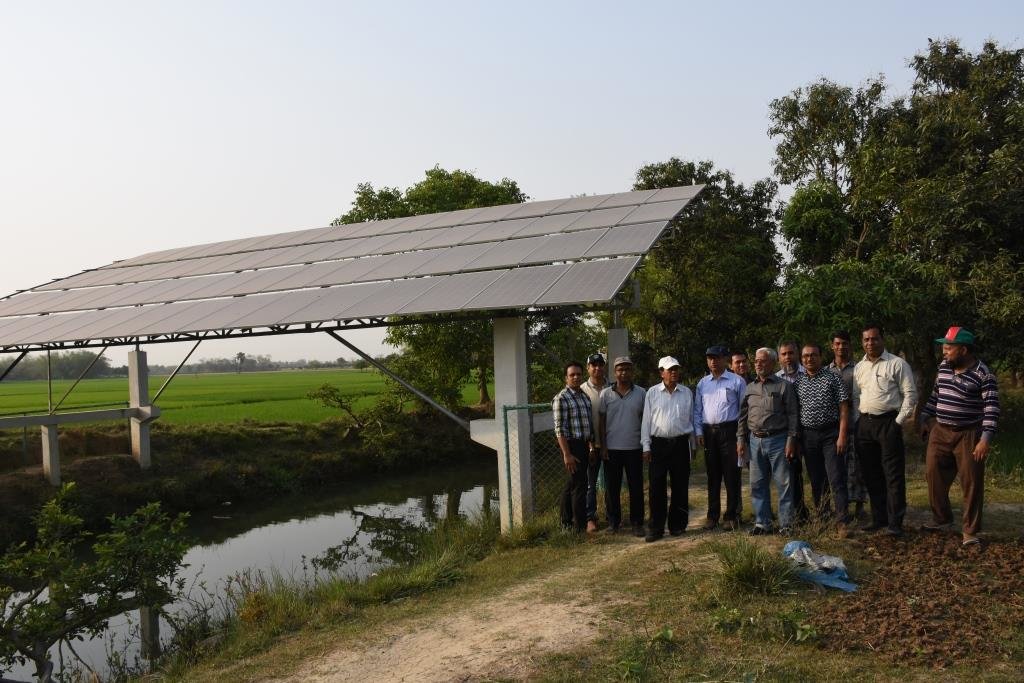
•No. of LLP (low lift pump): 27 electrified and 6 solar pumps
•Total irrigated area: 1850 ha
•Benefiting farmers: 5330
•Harvest yield of rice per year: 20,500 metric tonnes (approx.)
•Afforestation on the canal bank: 65,500 trees
Purposes/objectives of the technology:
•The main purpose of the said technology is to provide water for irrigation. This prevents abstracting of groundwater, which has adverse effects on the environment: therefore this system is environment friendly.
• Enhancing groundwater recharge thereby supports ecosystem function.
•The storing of river water in irrigation canals supports the enrichment of the habitat.
Approach for implementing the technology:
There was no irrigation facility for crop production in this drought-prone area. Government officials came to the locality, discussed with the local community, elites, as well as the farmers. Finally, the local community was convinced about the technology. Then the irrigation system could be implemented in the area. On seeing the success of the technology, the same has been replicated on approx. 9400 ha. in Barind area, benefitting approx. 32,200 farmers.
Maintenance of the technology:
In case of problems, the respective mechanic of that area informs the Assistant Engineer through the Sub-Assistant Engineer. Thus the problem is solved by their own initiative. It is also monitored by the Executive Engineer of the respective District, and finally by the Executive Director from the headquarters if needed.
Crop cultivation:
Due to the application of the technology, previously fallow land has come under cultivation/irrigation facilities, mono-cropped land has been converted into multi-cropped land. Different crops, like rice, wheat, maize, mustard, pulses, potato, tomato, spices and other vegetables are cultivated.
Farmers’ acceptance:
The technology has been well accepted by the farmers, as uncultivated land has been brought under cultivation and different crops are now being cultivated year-round.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
التاريخ:
25/03/2019
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
بنغلاديش
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The following project were providing the irrigation facilities in Barind region:
i) SEMP - Sustainable Environment Mgt. Project
ii) RWCP - Rain Water Conservation Project
iii) EIBA – Extension of Irrigation in Barind area through conservation water in canal
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
- Irrigated rice (Paddy
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- المانجو، المانغوستين، الجوافة
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 3
حدد:
Rabi-Pre-Kharif- Kharif
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Mango with rice,
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Major crop rotation is Boro (winter rice) - Transplanted Aman, Minor crop rotations are Potato-Boro- Tasplanted Aman, Rabi crops (mainly vegetables)- Boro- Transplanted Aman
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Mango and rice
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S3: الخنادق المتدرجة ،والقنوات، والممرات المائية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
- S7: معدات حصاد المياه/الإمداد/الري
- S10: تدابير توفير الطاقة

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M3: التخطيط وفقا للبيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
التعليقات:
There are two stages of harvesting water.
1 - from river water, which is not going directly to the field
2- water reserved in canals and supplied to the field
Para S10 - refers to saving conventional electricity by using solar power for distribution of water to fields
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
التعليقات:
Barind was driest part of Bangladesh. It was enhanced when groundwater abstraction increased to support cropping by irrigation. The reduction of the groundwater table enhanced the dry out of dug wells, which supported domestic consumption. Hence, aridification was prominent in the area. It is reported that after the application of this technology, there are indications of recharging of the groundwater. Due to the increase in vegetation, the local temperature tends to be cooler than before.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
This technology helps reducing land degradation through using river water rather than groundwater for irrigation, thereby
preventing land degradation through increasing the vegetation cover on land.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
1. Pontoon: Length 55 ft, Width: 25 ft, Height: 4.50 ft
2. Centrifugal pump (12 nos)—each pump 60 HP,capacity-2.5 cusec, pump head: 50m
3. Electric power station capacity: 750 KW
4. Underground water distribution line (12 nos): Length of each line is 3.50 km
5. Length of water storage canal (Sharmangla canal): 29.0 km (average width 15.0 m and depth 5.0 m)
6. Nos of submerged weir/dam to reserve water in the canal: 14 nos
7. Nos of LLP (electrified) to lift water from the canal to crop field through buried pipeline : 27 nos
8. Nos of solar pump to lift water from the canal to crop field through buried pipeline: 06 nos
9. Nos of Prepaid meter for collecting irrigation charges (Revenue): 33 nos
10. Irrigated area: 1850 ha
11. Construction materials:
-Pontoon: A kind of platform that float on water made of Mild steel sheet, Stainless steel etc.
- Power station: Transformer, electric pole, wire etc.
- Distribution line: mild steel and PVC pipe
- Dam/Submerged weir: steel bar, cement, sand, brick, stone etc.
المؤلف:
Sayed Zillul Bari
التاريخ:
25/03/2019
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
1 Pontoon, Pumps, Pipes, weir construction etc
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
Pontoon (Length 55 ft, Width: 25 ft, Height: 4.50 ft) is a platform build on iron sheets, that can float on river, where pumps were set. The pipes for water delivery were of PVC. Water canal in this case compiler referred to canals of Barind which were ephemeral. Now water reserve for year round use.Piping system includes PVC pipe to convey water to the field, where a valve was set to control water disposal. There is a pipe of 12 inch dia to maintain water head through out the system.
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
BDT
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
85,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
800 BDT
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pontoon construction and installation on the river | 60 days |
| 2. | Pumps installation on the pontoon | 30 days |
| 3. | Construction of underground water distribution line | 70 days |
| 4. | Re-excavation of derelict canal | 120 days |
| 5. | Construction of submerged weir / dam | 180 days |
| 6. | LLP installation at the canal bank (27 nos) | 150 days |
| 7. | Solar pump installation (06 nos) | 45 days |
| 8. | Pre-paid meter installation at pump sites to collect irrigation charges (33 nos) | 30 days |
| 9. | Buried pipe line construction for irrigation at crop land sites | 120 days |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| مواد البناء | Pontoon construction and installation on the river | 1 | 1,0 | 5000000,0 | 5000000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Construction of underground water distribution line | 1 | 1,0 | 27800000,0 | 27800000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Construction of submerged weir / dam | 1 | 14,0 | 1600000,0 | 22400000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Re-excavation of derelict canal | 1 | 1,0 | 29000000,0 | 29000000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Pre-paid meter installation at pump sites to collect irrigation charges | 1 | 33,0 | 243000,0 | 8019000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Solar pump installation | 1 | 6,0 | 2000000,0 | 12000000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | LLP installation at the canal bank (27 nos) | 1 | 8,0 | 2700000,0 | 21600000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Pumps installation on the pontoon | 1 | 12,0 | 1833000,0 | 21996000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Buried pipe line construction for irrigation at crop land sites | 1 | 1,0 | 23100000,0 | 23100000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 170915000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 2010764,71 | |||||
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
1439,02
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
none
التعليقات:
Labor costs etc all included in construction, pipeline installation etc.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pontoon repair and maintenance | 1/5years |
| 2. | Pump repair and maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 3. | Distribution line maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 4. | Power station repair and maintenance | As per requirement, 1/yr |
| 5. | Submerged weir / dam repair and maintenance | 1/5yrs |
| 6. | LLP repair and maintenance | 2/yr or as and when necessary |
| 7. | Buried pipe line repair and maintenance | 1/6yrs, as and when necessary |
| 8. | Prepaid meter repair | 2-3/yr |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| معدات | Prepaid meter repair | 1 | 0,2 | 100000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| مواد البناء | Buried pipe line repair and maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 0,05 | 0,05 | |
| غير ذلك | Pontoon repair and maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 500000,0 | 500000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Pump repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Distribution line maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 75000,0 | 75000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Power station repair and maintenance | 1 | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | Submerged weir / dam repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1,0 | 200000,0 | 200000,0 | |
| غير ذلك | LLP repair and maintenance (each) | 1 | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 915000,05 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 10764,71 | |||||
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
11,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
Land users share their participation in kinds and allowing installation of pipelines and other infrastructure
التعليقات:
Land users were trained and they provided land for infrastructures. For example space for outlets and underground pipe installation. Practically they did not contribute any cash.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Pontoon construction, power supply and lining of the underground piping system.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1600,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Most of the rainfall events happen during May to October
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Agroecological region 26
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
High Barind tract, mainly dissected (Closely & Broadly) terrace, soil pH is acidic, low in Nitrogen content, low CEC
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Area is above flood level
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- شباب
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
Yes. The farmers of Barind are of wide range. The large farmers are basically absentee. Medium range farmers engage themselves in their land and in addition they rent land from large farmers. So there is complex ownership.
This was from field feedback.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مؤجر
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
جودة المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
جودة العلف
إنتاج حيواني
خطر فشل الإنتاج
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
إدارة الأراضي
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الشرب
نوعية مياه الشرب
توافر المياه للماشية
نوعية المياه للماشية
توافر مياه الري
نوعية مياه الري
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
At present land users are used to grow high water demanding crops. For example Boro paddy and potato both crops require large volume of water and the irrigated area slowly increasing, that situation demand of irrigation water increasing.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
The supply of agricultural inputs increased and channelized through deploying dealers etc. Hence expenses relatively decreased
دخل المزرعة
تنوع مصادر الدخل
فروقات اقتصادية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Basically in this area could be grouped in to two. One group has almost no land and previously they have to migrate beyond barind area as labor and they were poor. At present they have job (agri-labor or otherwise) in their area and become more solvent then past 90's. On other hand the second group cultivate the land of their own or leased, which they could not in 90's. They also in handicap because of poor crop and no option to cultivate in two seasons. Hence apparently both groups as of their status are in well shape. The peoples those who have no land for cultivation now can engage them in many other entrepreneurship (e.g. farm product marketing, livestock/poultry raring, carpentering, grocery, etc etc) emerged.
عبء العمل
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
الفرص الثقافية
الفرص الترفيهية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
المؤسسات الوطنية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Along with the Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) other national institutions like Department of Agricultural Extension, Livestock, Fisheries, Bangladesh Rural Development Board (BRDB), Financial institutions- Rajshahi Agricultural Development Bank and others (NGO) are operating more effectively in the Barind in multiple dimensions. In addition students from Rajshahi University also engaged in their research on various issues. BMDA also improving its capacity and skill to develop more effective approach for Barind area.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
This comment was done comparing between conveying water by open drainage and through pipeline. Definitely there are almost no run-off from pipe line distribution. On the hand land users have to confirm their field bunds to protect run-off. Prepaid metering system also restricted land users not to allow excess water to over flow from their field. In-spite of that there may be small amount run-off, but the detachment of top soils is within tolerable limit and accumulate within field bunds.
تصريف المياه الزائدة
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التعليقات/ حدد:
It is reported that ground water slowly recharged, As a results shallow tube wells are also working , which were about to abandoned before.
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation coverage increased,
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Increased land cover-Reduced drought
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
In 90's the lands were bare and in monsoon after heavy downpour a large amount of water going to downstream as run-off with detached top soil. At present land is covered, field bunds are strengthen, restrict run-off as a result soil loss decreased.
تراكم التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Field bunds enhance soil accumulation by limiting run-off water by field bunds/dykes.
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Mechanized cultivation and usage of farm machinery however enhance soil compaction.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الفيضانات
التعليقات/ حدد:
The area is above flood level
آثار الجفاف
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Emission of carbon decreased as vegetation cover round the year increased.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
التعليقات/ حدد:
Reduced dusty wind, temperature cooler then before.
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
The Barind was almost desert like before 90's. Its natural vegetation were almost extinct. Biodiversity both Species and habitat were low. At present it is improving spectacularly.
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
In all a desert like Barind tract become green now.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Usage of surface water reduces groundwater abstraction and improves groundwater (GW) recharge
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
التعليقات/ حدد:
As the land cover has increased, that has a substantial impact on limiting polluted surface water to flow up to river.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | انخفاض | جيدة جدا | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | الصيف | انخفاض | جيدة جدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | زيادة | جيدا | |
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الصيف | زيادة | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
It could rather to explain as the beneficiaries of the technology. Truly a single land user or a group of land user will not able to install this type of system for multiple reasons. There are two components of this technology, one is the government institution who provided the scope of using surface water for irrigation and the second one are the land user who use the scope or facilities of irrigation system Here about 1800 farmers are involved to use surface water as their irrigation source.
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
Most of the farmers of the area who has land adopted surface water for irrigation instead of ground water abstraction.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، وضح الظروف المتغيرة التي تم تكييفها معها:
- توفر العمالة (على سبيل المثال بسبب الهجرة)
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
where there are no canal for water storage , local ponds are used to reserve the surface water to irrigate land surrounding the pods and obviously where river water could not be reached.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Ensured crop production through irrigation |
| Reduced ground water irrigation and decrease ground water depletion. |
| Increased work facility at project area |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Improved socio-economic condition of beneficiaries |
| Increased ground water recharge |
| Increased fish cultivation and duck farming at the canal |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Scope of individual level implementation is very limited | Community approach will facilitate the SLM implementation etc. |
| Maintenance, distribution and regulation of water etc have no control of the beneficiaries | Capacity of the beneficiaries to be developed |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Source of lifting water points may be shifted in the long run | Efficiencies of irrigation water supply need more attention with demand and supply. |
| Weak linkage with beneficiaries | Integrated approach needed to include community and implementing agencies. |
| Crops with high water demand may not sustain in the long run | Appropriate crop and cropping patterns are to be adopted with crop zoning |
| Increasing cropping intensity leads to deficiency of soil nutrients | Monitoring of soil health essential for this region. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Three times with experts of this area
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
20
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
10
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Consulted relevant project documents
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
25/03/2019
التعليقات:
A long process was maintained from building capacity of the professionals to handle WOCAT tools, initial inventory with core experts and screening with local professionals, documentation in field and compiling data in the WOCAT format, which was again validated with large local groups of scientists, extension officials, local government, NGO, lead farmers etc.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Project documents
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Available in BMDA
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Questionnaires on Tecnologies (QT)
عنوان الرابط URL:
www.wocat.net
العنوان/الوصف:
Sustainable land management (SLM)
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://knowledge.unccd.int/topics/sustainable-land-management-slm
العنوان/الوصف:
Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality at the country level
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://knowledge.unccd.int/topics/land-degradation-neutrality
7.4 تعليقات عامة
Excellent
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية