Ficus Natalensis Agroforestry System [اوغندا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Okusimba emituba n'ebimera
technologies_1153 - اوغندا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Lubega Emmanuel
Rakai district
اوغندا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - إيطاليا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Community development appraoch [اوغندا]
The approach involves the community and other development partners identifying opportunities, challenges and appropriate solutions through collective action.
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
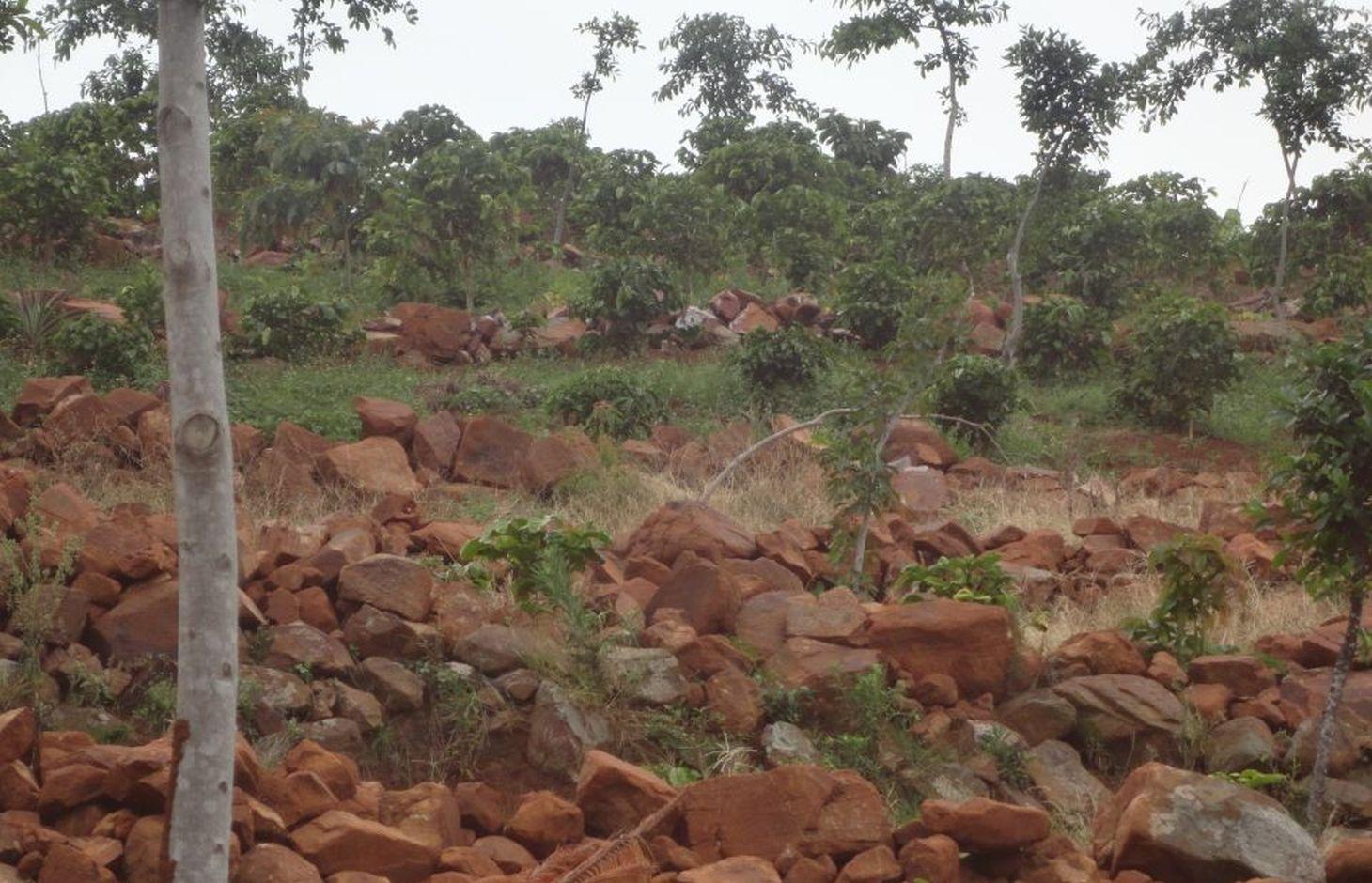
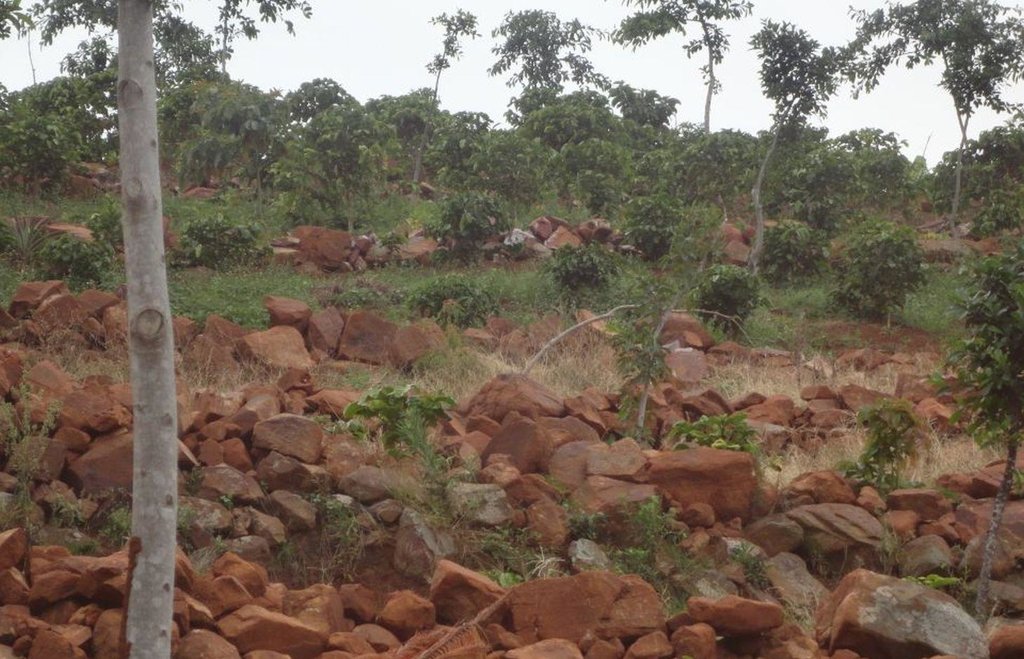
Ficus natalensis based agroforestry system protects crops on windy hill slopes facing Lake Victoria and reduce runoff towards the meandering Kagera River Valley.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
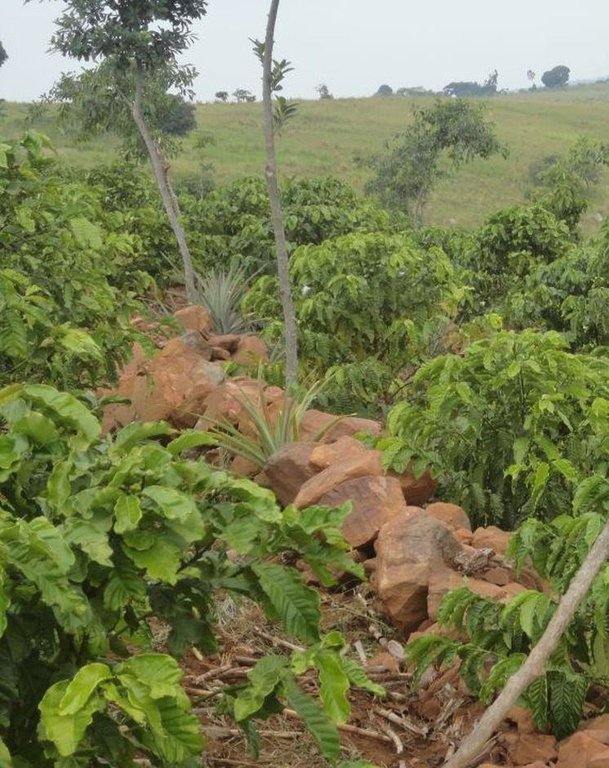
Ficus natalensis is traditionally scattered in crop fields as a land management practice in central and south-western Uganda. The improved technology designed through community participation involves planting lines of Ficus natalensis along the contour at an interval that enables the tree to provide shade to young crops without depriving them of sunshine. When planted together with coffee trees or in banana plantations, the tall Ficus tree forms the top storey that protects the crop from the hot sun.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of Ficus based agroforestry is to protect the soil from erosion. Within 3 to 5 years the Ficus tree forms a deep root system that stabilizes the soil. In addition, it drops leaves which quickly decay to provide both soil cover and manure thereby increasing the fertility of the soil. The trees provide firewood, fodder for livestock and bark cloth which can be used domestically or sold to supplement household income. They also act as wind breaks.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Ficus Natalensis is propagated using cuttings from young branches which are planted vertically 6 m apart along a contour. Propagation material is readily available and cheap, making the technology inexpensive to establish. Any annual or perennial crop can be inter-cropped with Ficus spp. provided the tree canopy is managed well. The tree is quite robust and can attain heights of over 20m, with a very extensive canopy if left to grow. Pruning raises its canopy to the desired height above the ground. In its early stages, fencing is required to protect the tree from damage by livestock. Within 12 to 18 months, however, the tree is established enough to withstand browsing. Only simple tools like hoes and garden forks for digging holes/pits are essential for establishment of the technology. The implementation of the technology on steep slopes (> 50%) is not possible without other supportive SLM interventions, in Rakai these include construction of stone lines and mulch application.
Natural / human environment: The pruned branches of Ficus natalensis are used as fuel wood when dry. Therefore scarcity of fuel wood may lead to over-harvesting of branches and destroying the canopy. Nonetheless, the tree regenerates quickly with the coming of the rains. Ficus tree can live for a hundred years.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
اوغندا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Uganda
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Rakai District (Kijonjo Parish)
التعليقات:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.96681 31.69066; -0.96706 31.69111; -0.96717 31.69033; -0.96757 31.69038; -0.96774 31.69073
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.06 km2.
The technology is becoming dominant in Kijonjo parish and other parts of Rakai district especially due to climatic changes that have led to shorter rainy seasons. However, farmers also recognize its potential for soil conservation.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Agroforestry is a traditional practice but was reintroduced in a better structured, systematic form by organizations like VI-Agroforestry and Kagera TAMP.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- البن، في مزارع مفتوحة
- التين
- Ficus Spp.
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to December

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
منتجات وخدمات:
- حطب الوقود
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Severe deforestation as trees were cut down for firewood, charcoal, timber and for agricultural use;
Overgrazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Prolonged dry weather, destructive rainstorms and declining soil fertility
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Agro-forestry is used in combination with banana and coffee growing.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A7: أخرى

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: mulching (supp.
Specification of other structural measures: stone lines (supp.
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Lack of conservation measures), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Over cultivation), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting trees for timber and opening up more agricultural land), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Cutting trees for fuel wood and charcoal), poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep and very steep slopes)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
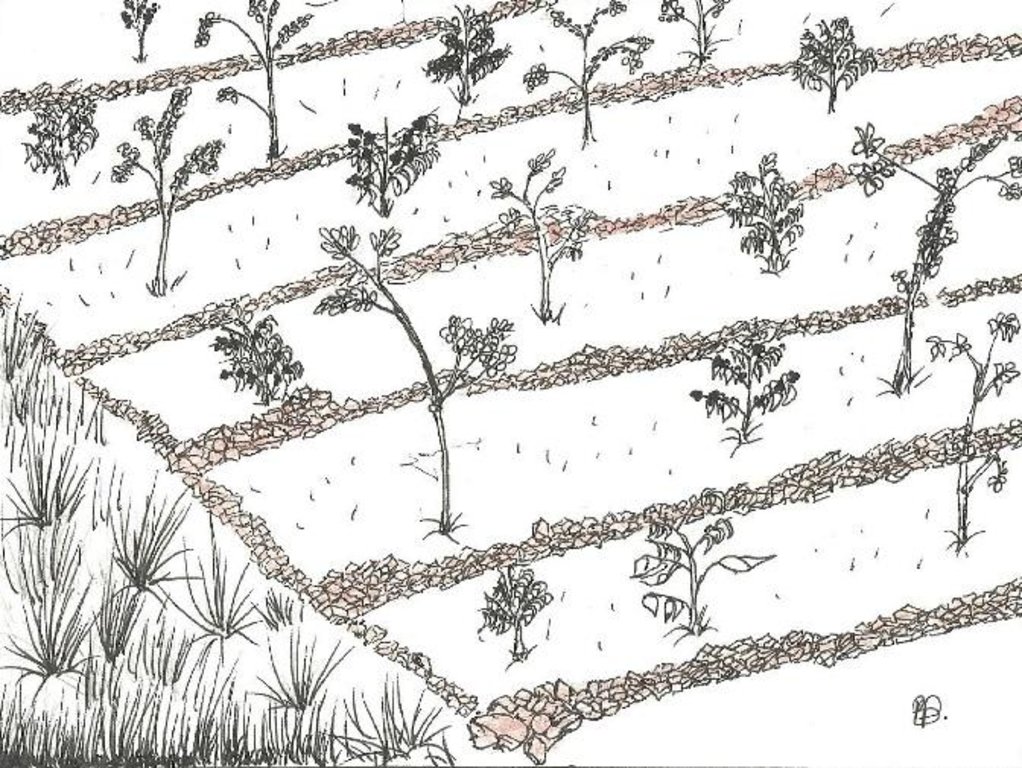
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
A diagram showing Ficus spp. trees planted to provide shade to coffee trees.
Location: Kijonjo B. village. Rakai
Date: 2013-12-05
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Knowledge of which trees will do well with the crops to be cultivated)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Land user dedication and a little guidance is enough for the implementation of the technology.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 250
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 20m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 20m
Trees/ shrubs species: Ficus natalensis (also serves as perennial fodder), planted in the field using stem cuttings
Perennial crops species: Robusta coffee planted using seedlings bought from specialized nurseries
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 35%
المؤلف:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabale
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Ushs
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
2500,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sourcing planting materials | Beginning of rains |
| 2. | Making pits | Beginning of rains |
| 3. | Planting cuttings | Wet season |
| 4. | Spot weeding | Wet season |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Sourcing planting materials | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Making pits | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Planting cuttings | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | |
| العمالة | Spot weeding | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | |
| معدات | 2 panga | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | 2 hoes | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Cuttings (500 stern cuttings) | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 122,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,05 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Spot weeding | twice a year |
| 2. | Pruning | Wet season |
| 3. | Removing and processing the bark into bark cloth | Once in 2 years |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Spot weeding | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Pruning | ha | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | |
| العمالة | Removing and processing the bark into bark cloth | ha | 1,0 | 14,0 | 14,0 | |
| معدات | 1 panga | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | 1 hoe | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 38,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,02 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: The technology only requires simple tools like hoes and pangas.
The costs were calculated for wind breaks and optimum canopy after establishment. Calculations were done in December 2013, considering activities of the previous (September-November) wet season.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The most important factor affecting cost is labor to transport the bulky stem cuttings to the site. However, Ficus Natalensis is easy to establish and is durable (over 100 years) depending on management. It is extremely hardy and when it grows to 50cm to 100cm stem diameter it can be used for timber or to make dugout canoes. Establishment costs are easily recovered.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The area receives two rainy seasons (March-May & September-December)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. The area lies at the equator.
The area has a dry and a wet season, but other factors influencing its weather include proximity to Lake Victoria and the Kagera River.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات محدبة أو نتؤات
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 1001-1500 m a.s.l (1269-1310m a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Steep (ranked 1, while technology is good for all kind of slope, the description given here is for a steep slope) and hilly (ranked 2)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1) and very shallow (ranked 2). The technology has also adopted to moderate to deep soils to support root development of trees.
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, 70% of the soil in the area is sandy) and medium (ranked 2, 20% of the soil is loamy)
Soil fertility: Medium
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (the organic matter is medium but has improved with agroforestry)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (soils are manly sandy)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (soils are predominantly sandy)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: 5-50 m (The technology does best in soils with ground table of 5-50m to enable root developement)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (ranked 1, there is no surface water in dry season) and medium (ranked 2, some, in the wet season)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, from unprotected source in swamps)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
While the surrounding valleys below are swampy and very rich in biodiversity, only a fraction remains at the slopes due to destruction of habitats.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: n/a
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
21% of the land users are rich and own 57% of the land (Business men.).
63% of the land users are average wealthy and own 34% of the land (Teachers).
16% of the land users are poor and own 9% of the land (orphans and widows.).
Off-farm income specification: There is a difference in income levels between those who have implemented the technology and those who have not.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (only manual labour is used-casual labourers)
Market orientation: Subsistence (ranked 1, most produce is for home consumption only surplus is sold) and mixed (ranked 2)
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Ranked 1: 0.5-1 ha. For most average income families.
Ranked 2: <0.5-1ha. For the poor.
Ranekd 3: 1-2 ha. For the rich households.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
Most land users have access to untittled land and have open access to water.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
100
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
400
التعليقات/ حدد:
coffee and bananas
إنتاج الخشب
التعليقات/ حدد:
For wood fuel (firewood & charcoal). there was almost nothing before.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
conservation of moisture, improved soil fertility
تنوع المنتج
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Agricultural land on which Ficus is planted
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
respondents reported increses in income but not documented.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Realization of the benefits has led many farmers to need more help therefore raising the cost of labour
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
incresed agricultural produce.
الفرص الثقافية
التعليقات/ حدد:
backcloth is used for cultural functions .eg. burying the dead.
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The technology has improved availability of both food and fuel wood. Some products from trees used in agroforestry such as backcloth (Embugo - Luganda) are sold, diversifying household income.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
dried tree leaves add humus and organic matter in the soil.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
various tree species are used for agroforestry.
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انزلاقات أرضية / تدفقات الحطام
التعليقات/ حدد:
Prevention of predisposition towards landslides
سرعة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
windbreaks reduced wind velocity.
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Risk of lightening strikes
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | غير معروف |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
The costs for both establishment and maintenance are a small fraction of the benefits accruing from the technology.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
8
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
8 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There is spontaneous adoption of the technology as it builds on traditional farming practices in the area.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: High demand for shade-grown coffee and bananas in addition to the highly valued bark cloth used in art and crafts has increased farmer appreciation.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
Ficus is used to provide backcloth that is sold for the making of Art and crafts and for cultural functions. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Management to accelerate healing of the bark within a shorter period should be investigated |
|
Trees shield crops from dangerous storms /rains and intense sunshine. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage the spread of the canopy |
|
Ficus is good and attractive to birds and insects How can they be sustained / enhanced? Provision of material support in form of seedlings, farm tools for accelerated multiplication |
|
Ficus natalensis leaves are cut and fed to livestock like goats. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Encourage indeginous trees and growing fodder crops such as calliandra and nappier grass |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Demand for wood fuel is high How can they be sustained / enhanced? Local bye laws should be enacted to control deforestation and encourage tree growing |
|
It improves soil fertility-Ficus natalensis sheds leaves once every year, adding to soil humus. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More guidance should be given to the farmers for sustained spontaneous adoption of the technology |
|
It checks the speed of wind thereby protecting crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Other agricultural, ecological and social benefits could be explored in this scenic area facing the Kagera River where it enters Lake Victoria |
|
Stakes made from the Ficus branches can be used to grow climbing plants eg. passion fruits, yams as well as climbing beans How can they be sustained / enhanced? More tree planting should be encouraged |
|
Prevents soil erosion by checking raindrop splash, speed and amount of surface runoff and stabilizes the soil. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Because the ficus tree takes time to establish, other technologies such as trenches and grass strips could be used to reinforce it |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The trees can hinder crops from light if canopy is dense | Prune periodically to enable other crops access to light |
| Some trees can fall especially during heavy and stormy rains, damaging plants and animals. | cutting excessive branches to reduce the load borne by trees. |
| Trees can attract lightening ,which destroys plants and animals. | Avoid putting animals under tall trees. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Some tree species especially with short roots , compete with crops for nutrients. | Planting tree species with deep roots to avoid competition for nutrients. |
| It is a home for weaver birds and caterpillars. | Use scarecrows and biological control. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Community development appraoch [اوغندا]
The approach involves the community and other development partners identifying opportunities, challenges and appropriate solutions through collective action.
- جامع المعلومات: Wilson Bamwerinde
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية