Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping) [طاجيكستان]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Erik Bühlmann
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff
technologies_1002 - طاجيكستان
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 2 نوفمبر، 2021 (public)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 20 أغسطس، 2019 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 19 يوليو، 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 17 يوليو، 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based Agroforestry (intercropping): 10 مارس، 2017 (inactive)
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - قرغيزستان1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
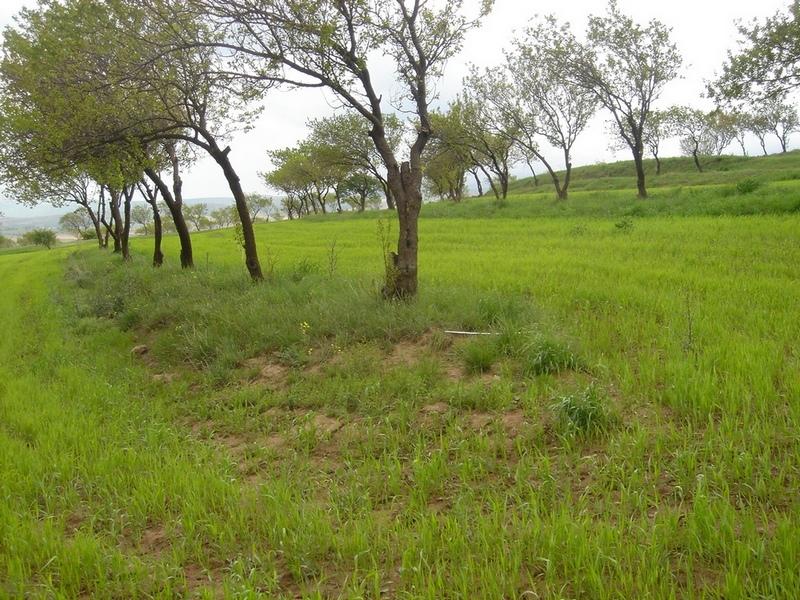
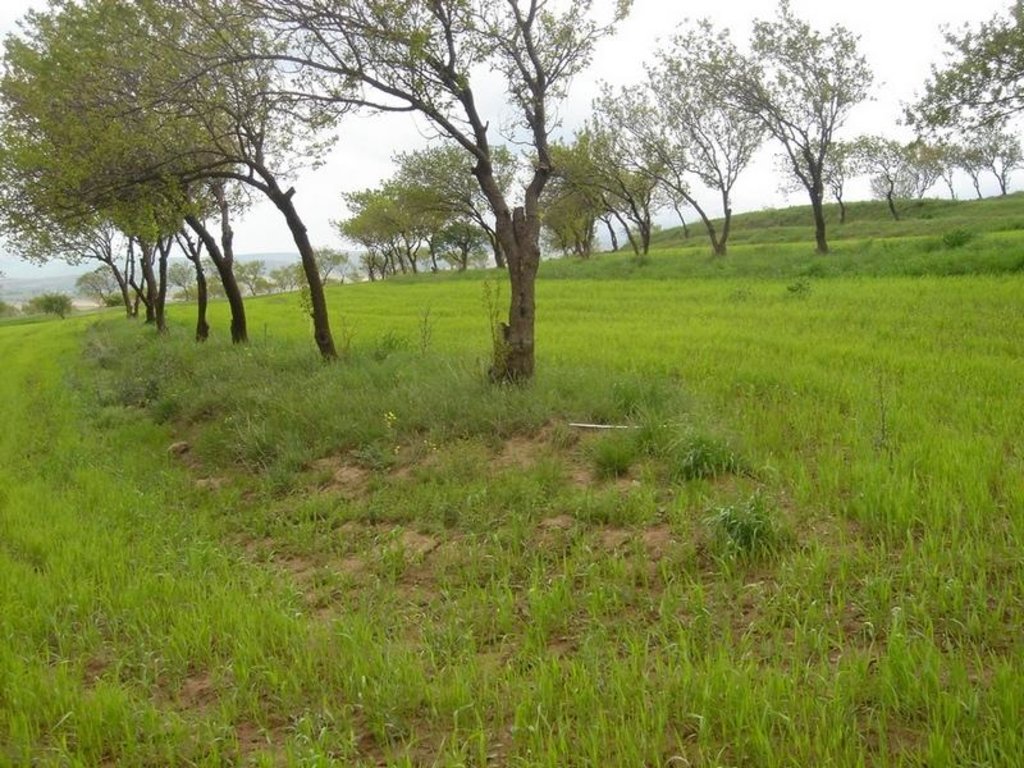
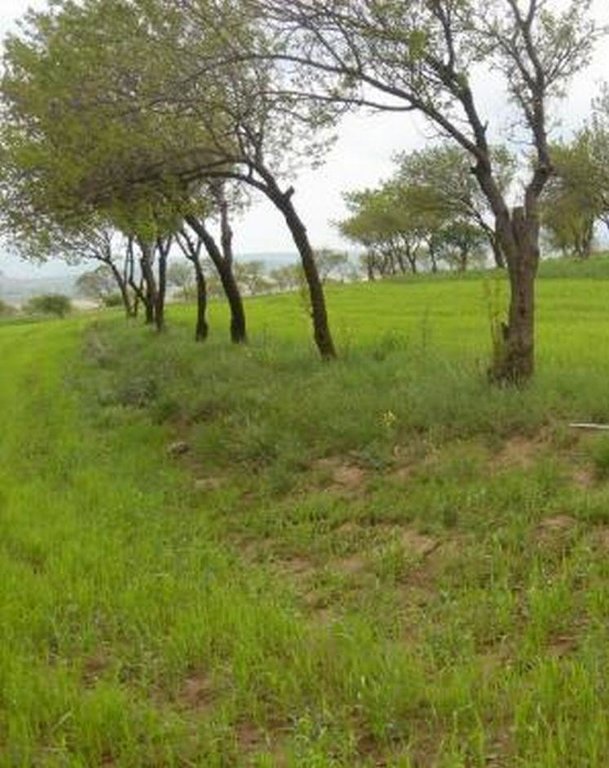
Intercropping of wheat in an existing orchard that was established during the Soviet period.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The technology involves intercropping wheat in an existing apricot orchard, that was established during soviet times to increase farm production, by integrating different resources in an environment protected from soil erosion. The intercropped area is ploughed by tractor. In general, farmers do not practice crop rotation since they usually allocate cereal production to the most fertile field plots of their farm.
Along the trees aligned on contour, a three metre wide grass strip is left uncultivated to control runoff, and to protect the ground from splash erosion. Spacing between rows is 13 metres, which allows unhindered farm operations.
Most orchards in Faizabad Rayon were established during Soviet times. Tree rows were planted close together in order to obtain maximum yields from the orchard monoculture systems. Some of the tree rows were removed, allowing more space for intercropping.
Purpose of the Technology: The technology is applied in existing orchards which generally range between 10-25% in gradient. In existing orchards, intercropping alone is relatively cost intensive. Harvesting two crops at a time increases overall farm production and improves food security since harvests of intercropped food crops are found to be more reliable than those on exposed annual cropland. However, many orchards are still owned by state farms which usually do not practice intercropping. Since management of fruit trees require considerable labour and material inputs (e.g. chemicals for pest/disease control as well as fertilisers) which often cannot be met by farmers, yields of fruit trees have declined after the privatisation of these areas. Furthermore, farmers often lack knowledge of appropriate orchard management techniques and miss opportunities to gradually replace old trees by new seedlings.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
طاجيكستان
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tajikistan
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Faizabad Rayon
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 10-1 كم2
Map
×3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- البازلاء
- محاصيل الألياف - كتان وقنب وغيرها
- الحبوب - قمح (ربيعي)
- محاصيل الأعلاف - أخرى
- محاصيل الأعلاف - البرسيم (الفصة)
- esparzet
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- فواكه أخرى
- الفواكه ذات النواة (الخوخ، المشمش، الكرز، البرقوق، الخ)
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): severe water erosion (rills and gullies) and subsequent fertility decline on cropland and overgrazed pastures
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): fertility decline, soil erosion and washing downslope of seeds before they can sprout
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Intercropped winter wheat and sometimes chickpeas are sown in autumn; flax, alfa alfa, esparzet, and also chickpeas are sown in early spring
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)

الأراضي الزراعية
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Intercropping of wheat between apricot trees aligned on contour
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A7: أخرى

التدابير النباتية
- V5: أخرى

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
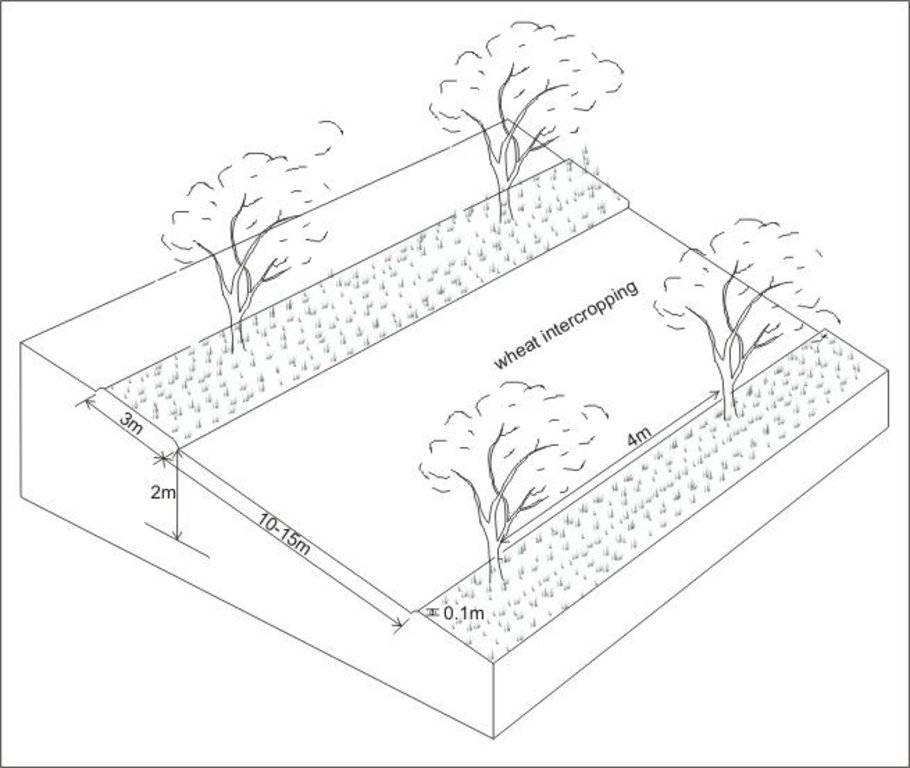
Intercropping of wheat between apricot trees aligned on contour
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad Rayon, RRS
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: winter wheat
Quantity/ density: 150kg/ha
Remarks: intercropping between tree rows
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: superphosphate, silitra
Quantity/ density: 200kg
Remarks: only for intercropped wheat
Contour tillage
Remarks: between tree rows
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 13
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vegetative measure: aligned: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apricot trees
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 18.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
المؤلف:
Erik Bühlmann, Berne, Switzerland
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
3.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | establishment of apricot orchard by state enterprise | established in 1989 |
| 2. | acquiring land use rights for existing orchard lands from local authorities | |
| 3. | thinning and clearing of tree rows |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | thinning and clearing of tree rows | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | tools | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 31,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 31,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | disc ploughing (area for intercropping) | before sowing / annual |
| 2. | sowing (winter wheat) | |
| 3. | applying of fertiliser | early spring / each cropping season |
| 4. | harvesting | summer / each cropping season |
| 5. | pruning of fruit trees | autumn/winter /annual |
| 6. | cutting of grass strip | summer /annual |
| 7. | applying manure for fruit trees | winter/early spring /annual |
| 8. | removal of twiggs affected by insects/deseases | spring /weekly |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | sowing and weeding | ha | 1,0 | 18,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | pruning of fruit trees | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | cutting of twiggs affe | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 218,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 218,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Machinery/ tools: tools: saw, sickle, pruning shears, fork, bucket
per hectare (with the described spacing of trees and tree rows)
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
The number of trees influences costs considerably, since orchard management is labour and input intensive
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
- شبه قاحلة
growing period between 180-210 days
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: low-high
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium - good
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
- ثري
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
5% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
75% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land (local authorities sometimes need to be bribed in order to acquire land use rights for orchard land).
Off-farm income specification: In general, all farmers (including those applying SWC technologies) are highly dependent on off-farm income, which in most cases is earned in Russia either by themselves or by their relatives.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): Only surpluses are sold or exchanged for other goods
Level of mechanization: Ploughing is carried out using a tractor whenever possible, but animal traction also existent.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
التعليقات:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology also 0.5-1 ha
Households with 1-2 ha are depending on available working force, labour is limiting factor
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to intercropping, management of trees gets more difficult
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
intercropped wheat requires additional inputs to an already input intensive orchard system
دخل المزرعة
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
fruit production
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to lack of fertilisers and pesticides
fruit yields
التعليقات/ حدد:
due to inappropriate pruning
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
NA
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In general, there is a growing demand for orchard land for intercropping. However, a considerable amount of orchards are still managed by state farms which usually do not maintain intercropping systems.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
two harvests at a time How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase in farm production |
| good wheat harvests in intercropping systems |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| low costs for establishment (intercropping only) |
| wheat production with very little soil erosion |
| intercropping can improve food security of low income families |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| yield of fruit trees insufficient because required inputs are not affordable | gradually replace old trees by new seedlings |
| Insufficient yields of intercropped plants because of shadow of old/large fruit trees | |
| orchard systems vulnerable to pests, late frost and strong winds |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| productive orchard systems require considerable amounts of recurrent inputs (e.g. chemicals for pest/disease control, fertiliser) which locals often cannot afford | avoiding intercropping of sparsely growing crops in vulnerable intercropping systems; improving ground cover by mulching |
| in comparison to orchards with an intact grass cover, intercropping of sparcely growing plant species increases the risk of soil erosion | |
| intercropped wheat hinders maintenance activities of fruit trees |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية