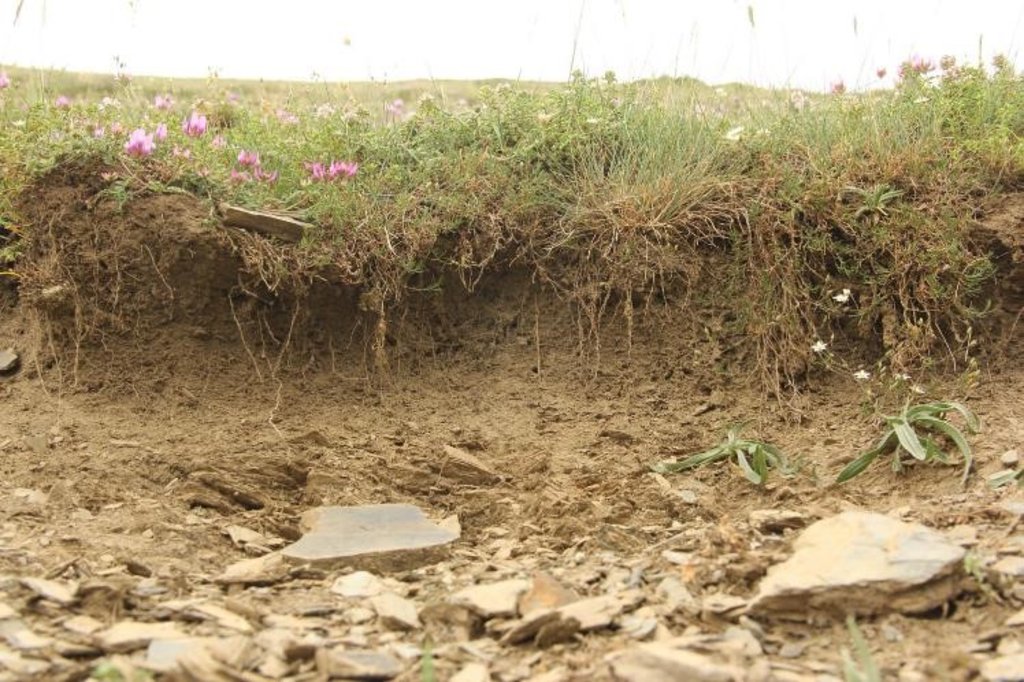
Remote Sensing as a Tool for Land Degradation Neutrality Monitoring [جورجيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Hanns Kirchmeir
- المحررون: Natia Kobakhidze, Christian Goenner
- المُراجع: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5488 - جورجيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
جامع المعلومات المشارك:
جامع المعلومات المشارك:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Integrated Biodiversity Management, South Caucasus (IBiS)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) … [جورجيا]
In the framework of the project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) were developed to implement the LDN targets at municipal level. The approach defines the process to break down global and international …
- جامع المعلومات: Daniel Zollner

Integrated Pasture Management Planning in Mountainous Regions [جورجيا]
The unsustainable use of pastures and forest areas has led to soil erosion, degradation, desertification and loss of biodiversity in the high mountain areas of the South Caucasus. The development of pasture passports is part of a broader approach to a strategic pasture management plan for Tusheti. This showcase includes …
- جامع المعلومات: Hanns Kirchmeir
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Land degradation contributes to biodiversity loss and the impoverishment of rural livelihoods in Tusheti. Above all, however, land degradation are triggered by climate change as traditional land use practise might not be adapted to new climate conditions which can cause or speed up degradation processes significantly. On the other hand, degraded land often leads to low biomass volumes and this reduces the ecosystem capability to stabilise local climate conditions. The concept of Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) and the method of using remote sensing for monitoring land degradation are tools to identify the need for local planning processes. This showcase describes the LDN monitoring concept, national targets and the technology to assess indicators, mechanism and incentives for LDN.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Purpose
The continuing global degradation of land resources threatens food security and the functioning of ecosystem services by reducing or losing their biological or economic productivity. Unsustainable land-use practices such as deforestation, overgrazing and inappropriate agricultural management systems trigger the loss and degradation of valuable land resources in Georgia. These effects are visible in all countries of the South Caucasus. About 35% of the agricultural land in Georgia is severely degraded, 60% is of low to middle production quality.
Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN)
LDN is a new international concept to combat the ongoing degradation of valuable soil resources. The LDN concept was developed by the UNCCD to encourage countries to take measures to avoid, reduce or reverse land degradation, with the vision of achieving a zero-net loss of productive land. To combat land degradation in Georgia, in 2017, the national LDN Working Group set voluntary national targets to address specific aspects of LDN, and submitted them to the UNCCD Secretariat.
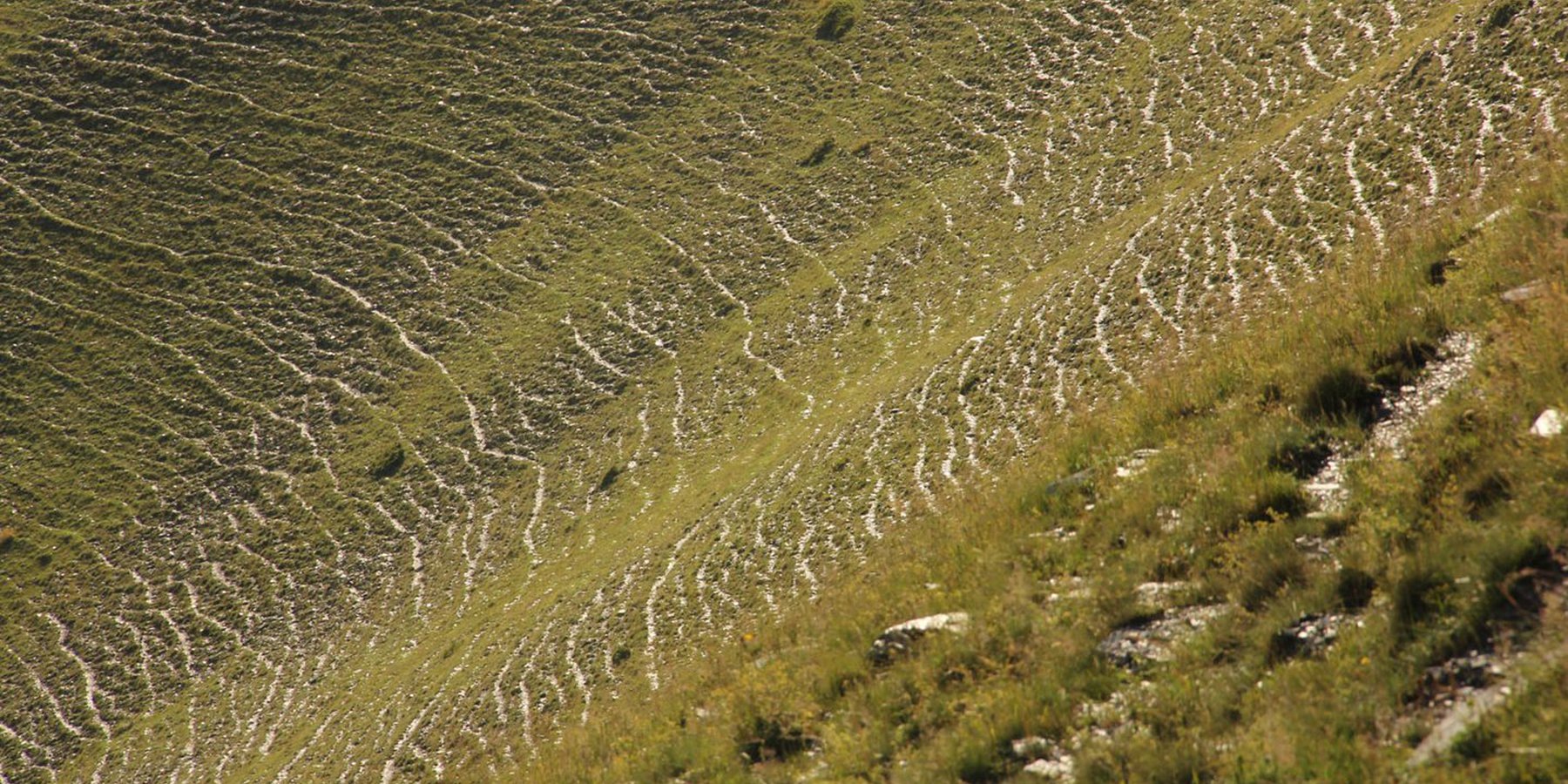
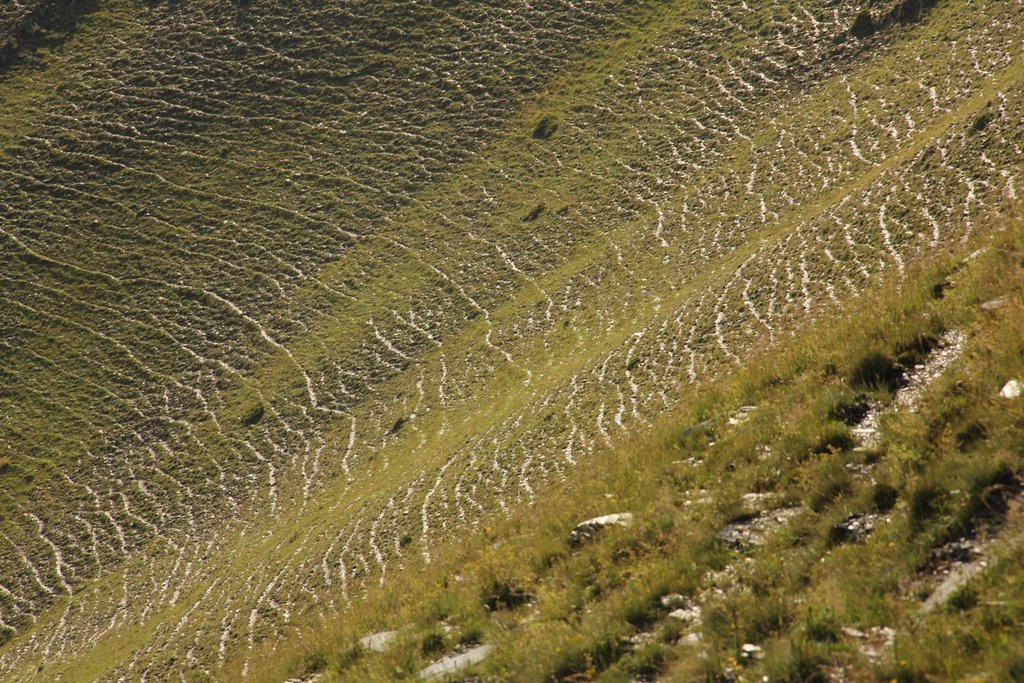
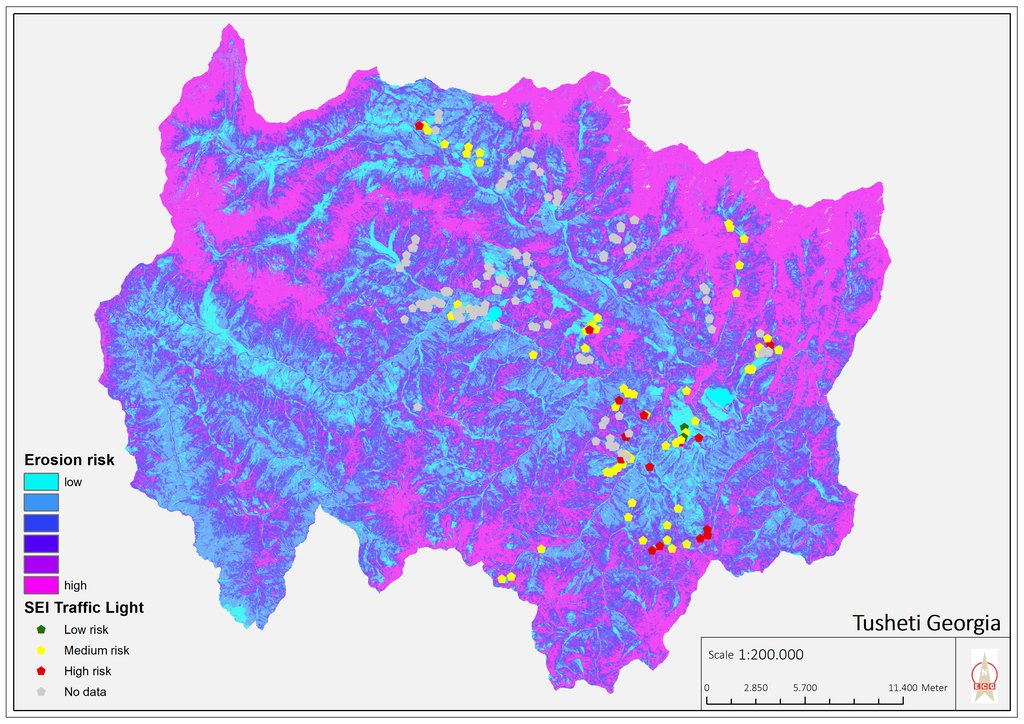
To effectively set up counter measures to combat land degradation it is important to have detailed spatial information on land cover and land cover changes as well as on trends in degradation (like size of areas effected by erosion). Therefore a remote sensing toolset was developed and tested in the pilot are of Tusheti protected landscapes in the High Caucasus in Georgia. This region shows increasing soil erosion problems by uneven distribution of grazing activities and was selected for developing erosion control measures within the Integrated Biodiversity Management in the South Caucasus Program (IBiS) funded by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ).
Sensitivity Model
The Integrated Biodiversity Management in the South Caucasus (IBiS) project in cooperation with national experts in Georgia, developed and applied a remote sensing toolset called "Erosion Sensitivity Model". This remote sensing toolset helps to assess the current state and the general erosion risk. The sensitivity model is based on the RUSLE – Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. The tool allows the calculation of erosion caused by rainfall and surface run-off. The RUSLE equation incorporates a combination of different input factors such as precipitation (R), soil type (K), slope (LS), vegetation cover (C) and protection measures (P). In this way, the estimated average soil loss in tonnes per acre per year (A) can be calculated as follows: A = R * K * LS * C * P.
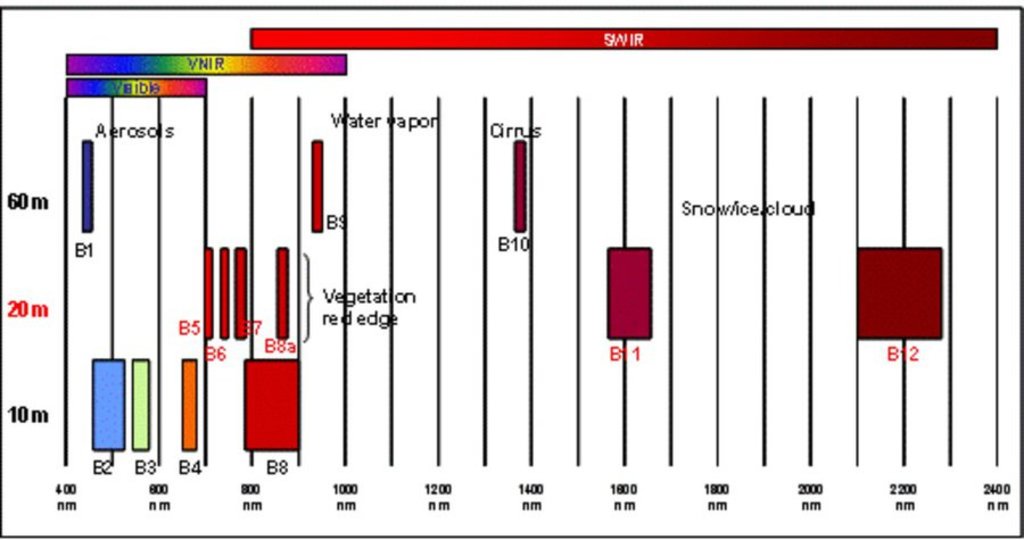
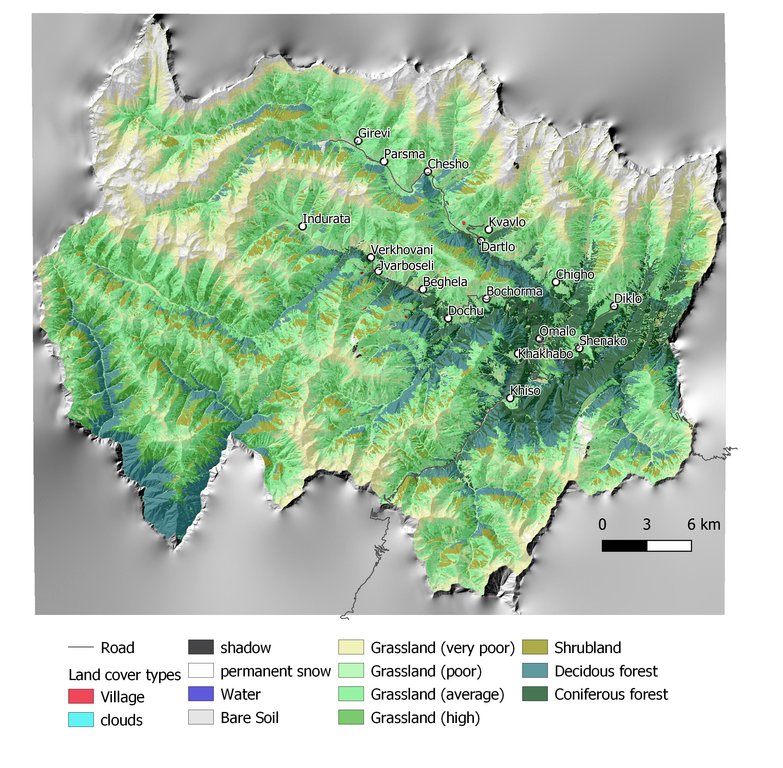
The rainfall factor (R) results from a quotient from the monthly and annual mean value of precipitation. The data come from the data platform “CHELSA – Climatologies at high resolution for the earth’s land surface areas”. For the soil type factor (K), a soil map of 1:200,000 was taken. Then, depending on the soil type, different contents of sand, silt, loam and clay were used to calculate the K factor. The slope length and steepness factor (LS) is calculated from a digital elevation model (DEM) with a raster resolution of 10x10m. The DEM is derived from the topographic map 1:25,000. The global elevation model derived from SRTM data (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) has a resolution of 30x30 m and is available worldwide free of charge. The land cover factor (C) describes the vegetation cover that protects the soil from erosion. The vegetation cover slows down the speed of the raindrops and reduces the erosive effect of the rain. It slows down surface water runoff and stabilises the soil through root systems. The main indicators, land cover and productivity, can be assessed by remote sensing. The data from satellites need to be classified and calibrated by field data (ground truthing). The technology for the assessment of these indicators with Sentinel 2 satellite images was developed and applied in 2016 to 2018 in the Tusheti region (Akhmeta municipality) in the framework of the GIZ-IBiS project. Based on spectral information from airborne or satellite images, the density of the vegetation was calculated and mapped. There are well developed vegetation indices and classification systems to derive different land cover types and vegetation densities (mainly described by the Leaf Area Index LAI or biomass indices). The LAI is the area of the leaf surface (in square meters) per square meter ground surface. Since the real surface area of the leaves is hardly measurable, the amount of biomass is a proxy for the LAI. The P-factor is rarely considered in large-scale modelling of soil erosion risk as it is difficult to estimate it with very high accuracy. Therefore, to refine the model, a more detailed DEM (digital elevation model) is required (e.g., from satellite images). Based on the input factors, a soil erosion risk map was calculated for the whole territory of the Tusheti Protected Areas (113,660 ha). Based on the different spectral bands of the Sentinel 2 satellite image, a land cover map was calculated using the Support Vector Machine (SVM) technology and spectral image information.
The results have been integrated in the development of pasture management plans ("pasture passports"). This maps and documents are indicating areas of high erosion risk that need to be excluded from grazing and the maximum number of livestock has been calculated based on the biomass maps and will be integrated into the lease contracts.
The repetition of the remote sensing after some years (e.g. 5 years) will help to evaluate, if the measures in the pasture management have been successful to stop the degradation processes.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
جورجيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tusheti region, Akhmeta municipality
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنيةا موزعة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، حدد المساحة المغطاة (بالكيلومتر المربع):
1000,0
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
The area is in the Tusheti Protected Areas (Tusheti Strict Nature Reserve, Tusheti National Park, Tusheti Protected Landscape).
التعليقات:
The whole territory was analysed by remote sensing and field records for calibration were collected on sample plots from different places in Tusheti.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2016
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- provide information to make a spatial-territorial planning
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الشعير
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - البطاطس
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- الترحال الرعوي
نوع الحيوان:
- الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
- الأغنام
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
كلا
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
أخرى (مثل ما بعد الفيضانات):
- rainfed and mixed rained-irrigation
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة

تدابير أخرى
حدد:
It is a monitoring technology to evaluate land management activities.
التعليقات:
On some pilot plots technologies to control erosion and stop land degradation have been tested. This includes fencing, rotational pasture management, mulching and installing check dams to stop gully erosion.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
التعليقات:
The main drivers of land degradation in the pilot area are overgrazing and trampling, off-road driving as well as infrastructure development (especially inappropriate road construction in steep slopes).
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
The monitoring tools presented here help to monitor the development of land degradation and to evaluate measures and development trends.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
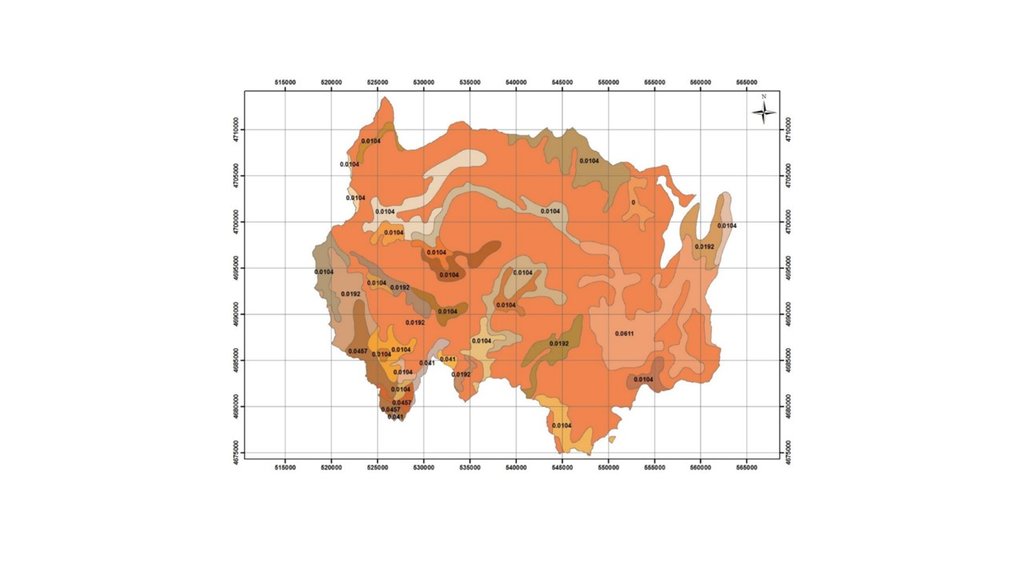
Map of erosion hot spots (pink colour) and the location of field sample plots for evaluation and ground truthing.
المؤلف:
Hanns Kirchmeir
التاريخ:
11/09/2019
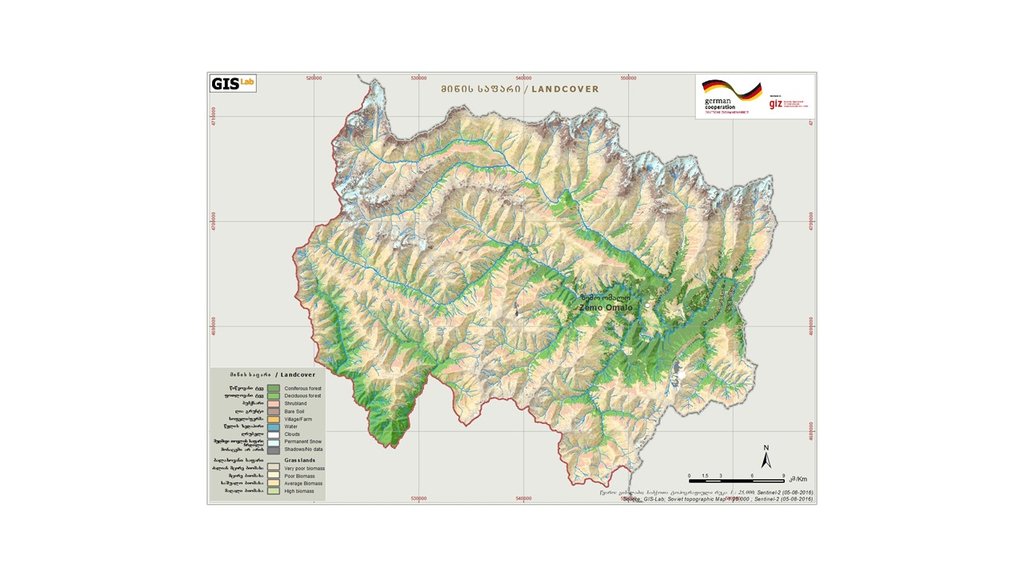
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
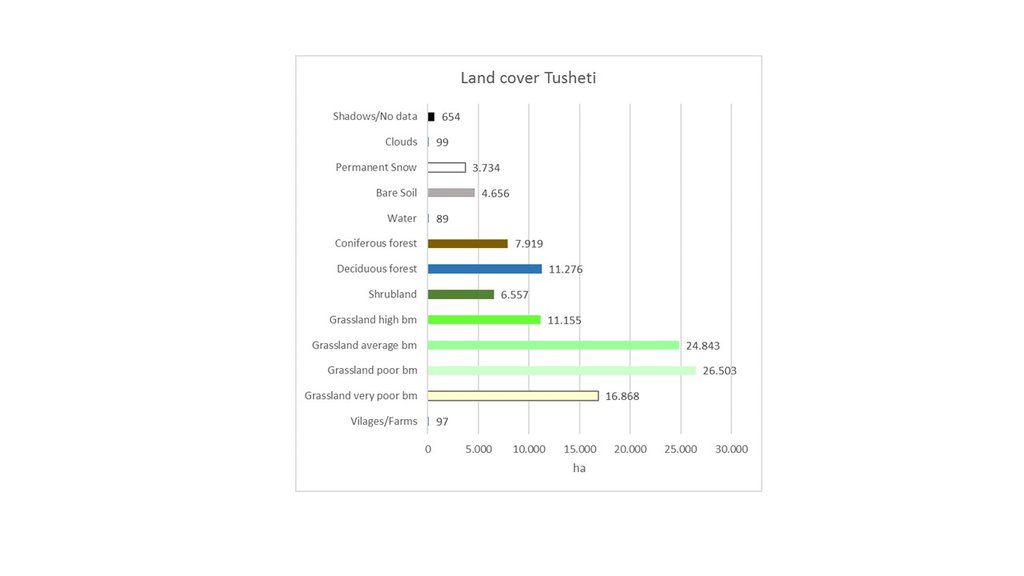
Map of land cover classification derived from satellite images. The different grassland types are classified by their biomass as an indicator of productivity and current state. Repeating the satellite image classification with the same parameters after 5 or 10 years can give a clear picture of changes in the land cover.
المؤلف:
Hanns Kirchmeir
التاريخ:
11/09/2019
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
1000 km2
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
100
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | National level. Baseline: Field assessment for remote sensing calibration (1x/20 years) | 2017 |
| 2. | Sentinel satellite image classification (multi temporal data from 2017) | 2017 |
| 3. | Statistical data from GEOSTAT Agricultural census | 2014-2016 |
| 4. | Analysis of soil carbon content from existing profiles | 2003 - 2006 |
| 5. | Conduct ongoing monitoring | 5 years intervals |
| 6. | Update sentinel satellite image classification | 1x year |
| 7. | Update statistical data from GEOSTAT Agricultural census | 4x/year |
| 8. | Resampling of soil carbon content near existing profiles | 1x/5 years |
| 9. | Municipal level. Spatial planning: Assessment of current stage of land degradation, anticipated gains and losses | 1x/10 years |
| 10. | Revision of spatial planning on Municipal level. | 1x / 5 years |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Remote Sensing analysis by Sentinel Satellite data | person days | 50,0 | 200,0 | 10000,0 | |
| العمالة | Collecting field data for satellite image callibration | person days | 40,0 | 200,0 | 8000,0 | |
| العمالة | Soil sampling (for carbon content) | person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | |
| العمالة | Including results in spatial planning | person days | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 24000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 24000,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
This covers the implementation of the baseline. Calibrating the model for erosion risk and land cover classification is an big investment but can be extended to larger areas than 1000 km² with similar resources.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repeating the application of the calibrated remote sensing model for monitoring repitition | with 5 years interval |
| 2. | Repetition of soil samples for assessing soil carbon content | with 5 years interval |
| 3. | Analysing the results and integrate them in spatial planning and policy making | with 5 years interval |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Applying the calibrated remote sensing model for monitoring repetition | person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | |
| العمالة | Repetition of soil samples for assessing soil carbon content | person days | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| العمالة | Analysing results and integrating in spatial planning | person days | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 8000,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 8000,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
For the repetition of the remote sensing no new calibration of the GIS-model is needed. Only the field samples for soil carbon need to be repeated.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Field sample collection;
Remote sensing experts.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
800,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The climate is generally suitable for agriculture with an annual precipitation of up to 800 mm, with hot and humid springs, rainfall peaks in May and June with hot and dry summers.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The remote sensing approach was applied for the total landscape of Tusheti, including a great variety of land-forms, altitudes ranging from 1600-4000 m a.s.l.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
سطحية
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- مرتفع
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
The technology is applied by the Government.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
The pasture units are fom 200 to 600 hectares and are based on the old Soviet grazing scheme.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
- مؤجر
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Within the timeframe until 2030, specific process indicators to assess the progress will be done.
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Changes in the quality of forests
التعليقات/ حدد:
tree height, stand density
Changes of the quality of pastures
التعليقات/ حدد:
biomass production
Changes in the quality of arable land
التعليقات/ حدد:
yield
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
The monitoring technology was applied for the first time to draw a baseline. Based on the results, activities have been planned and pilot measures have been implemented (exclusion from grazing, reforestation, regulation of grazing intensity). Future replications of the monitoring will show changes and evaluate success of measures. The technologies to control erosion are described separately in the WOCAT database (Community-based Erosion Control [Azerbaijan]; Pasture-weed control by thistle cutting [Georgia]; High-altitude afforestation for erosion control [Armenia]; Slope erosion control using wooden pile walls [Armenia])
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
The technology is only about the monitoring (see above).
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | الصيف | انخفاض | جيدة جدا |
التعليقات:
Technology is sensitive, it shows the climate change, the impact of the global change locally. The technology itself is not affected by climatic changes.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
The monitoring technology was applied for the first time to draw a baseline. Based on the results, activities have been planned and pilot measures have been implemented (exclusion from grazing, reforestation, regulation of grazing intensity). Future replications of the monitoring will show changes and evaluate success of measures. The technologies to control erosion are described separately in the WOCAT database (Community-based Erosion Control [Azerbaijan]; Pasture-weed control by thistle cutting [Georgia]; High-altitude afforestation for erosion control [Armenia]; Slope erosion control using wooden pile walls [Armenia]).
The costs of the remote sensing approach have not been invested by the land owners but by GIZ and the Ministry. Therefore there are no direct negative impact caused by the investment. The maintenance will be covered by public authorities as well. The positive impact for the land users are the clearly delineated pasture unit giving the exact area of grassland and the accessible amount of fodder biomass. By this, the lease-rate can be found according to the productivity and the number of livestock can be adapted to the carrying capacity of the land within the lease contract.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- حالات فردية/تجريبية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
The technology is desigend to be applied by national or regional addministrations and not by land owners themselves.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| The monitoring technology can help to find erosion and degradation hot spots and based on this spatial information counter measures can be applied to save the productivity of land. As the income from agricultural activities and livestock breeding is of high priority in this pilot region, the protection of the productivity of land is of high importance to the local land users. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| The presented remote sensing technologies are a cost efficient and objective way to monitor land degradation and land use changes on large areas on long time periods. Based on this spatial data, land use regulations can be integrated in spatial planning and other legal and practical frameworks (e.g. pasture lease contracts) to counter act the degradation processes. The success of the measures and the development of degradation and rehabilitation can be monitored by the same toolset. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The technology is complex and cannot be applied by the land user her-/himself and is sometimes hard to understand. Therefore they might mistrust in the results and are not eager to accept regulations and measures to stop degradation. | Transparent documentation of the technology and regular field visits to evaluate together with the land owners and users the remote sensing results in the field. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The institutional setup on the national level for the regular application of the remote sensing technology and the storage and management of the monitoring data is not established yet. GIS, remote sensing and soil experts are of limited availability. | Institutional capacity building and academic training courses provided at the Georgian universities can help to overcome these limitations. |
| Field data for calibration of satellite images (biomass volumes, classified land cover types, soil types, land management types) with exact information on the spatial location are rare and costly to be created. | Such data and information should be organised and gathered on national level across different sectors (agriculture, forestry, spatial planing, nature conservation ...). This would help to reduce significantly the costs and remote sensing could be applied on much larger areas. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Three field visits with national and international experts as well as representatives of administrations and local stakeholders.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Meeting with cooperation partners, key village stakeholders from three pilot municipalities.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Three mission meetings with 35 experts.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Pilot project on land degradation neutrality in Georgia Final Report. 20.10.2017.
GISLab 2016: Development of Land Cover and Erosion Risk Map based on remote sensing for Tusheti Protected Areas. Study within the frame of GIZ-IBIS.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Land Degradation Neutrality 25.10.2017
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://e-c-o.at/files/publications/downloads/D00813_ECO_policy_brief_LDN_Georgia_171025.pdf
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Tools for satellite image analysis
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://step.esa.int/main/snap-2-0-out-now/
العنوان/الوصف:
UNCCD Good Practice Guidance on SDG Indicator 15.31. (Sims et al. 2017)
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.unccd.int/sites/default/files/relevant-links/2017-10/Good%20Practice%20Guidance_SDG%20Indicator%2015.3.1_Version%201.0.pdf
7.4 تعليقات عامة
UNCCD Good Practice Guidance on SDG Indicator 15.31. (Sims et al. 2017) gives a detailed technical overview on methods and approaches to calculate LDN indicators by means of remote sensing data.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) … [جورجيا]
In the framework of the project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) were developed to implement the LDN targets at municipal level. The approach defines the process to break down global and international …
- جامع المعلومات: Daniel Zollner

Integrated Pasture Management Planning in Mountainous Regions [جورجيا]
The unsustainable use of pastures and forest areas has led to soil erosion, degradation, desertification and loss of biodiversity in the high mountain areas of the South Caucasus. The development of pasture passports is part of a broader approach to a strategic pasture management plan for Tusheti. This showcase includes …
- جامع المعلومات: Hanns Kirchmeir
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية