Soil Cement Water Collection Pond for Supplemental Irrigation Purpose in Dry Season [النيبال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Kabita Nhemhafuki
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Isabelle Providoli
Mato, Baluwa ra Cement bata Nirmit Sinchai Pokhari - Nepali
technologies_5684 - النيبال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Shah Ram Deo
The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED)
النيبال
مستخدم الأرض:
Gautam Laxmi
النيبال
مستخدم الأرض:
K.C Prashuram
النيبال
مستخدم الأرض:
Neupane Kumar
النيبال
مستخدم الأرض:
Adhikari Apsara
النيبال
مستخدم الأرض:
Shrestha Jay Ram
النيبال
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Resilient Mountain Solutions Initiative, ICIMOD (RMS initiative)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - النيبال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
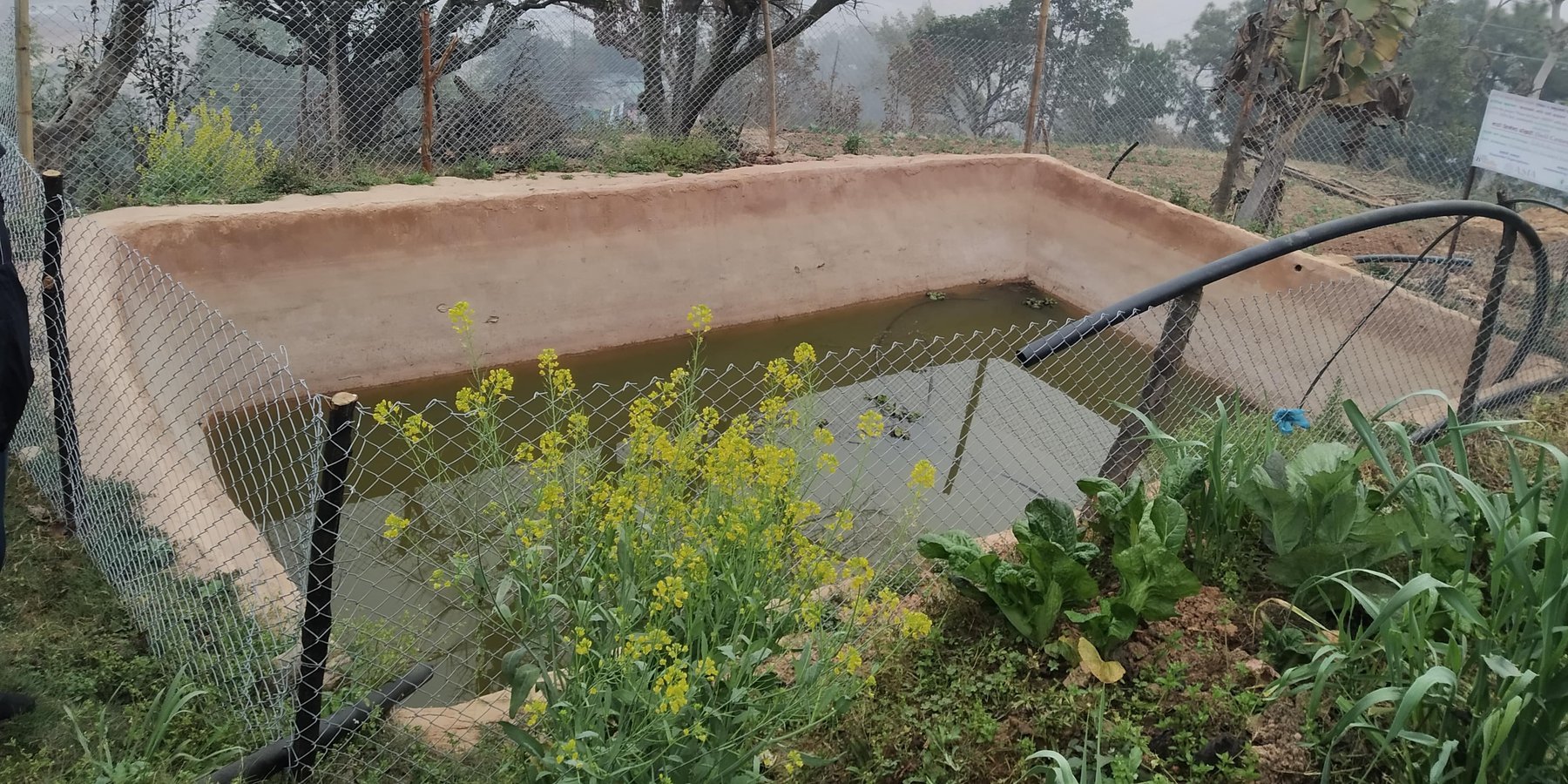
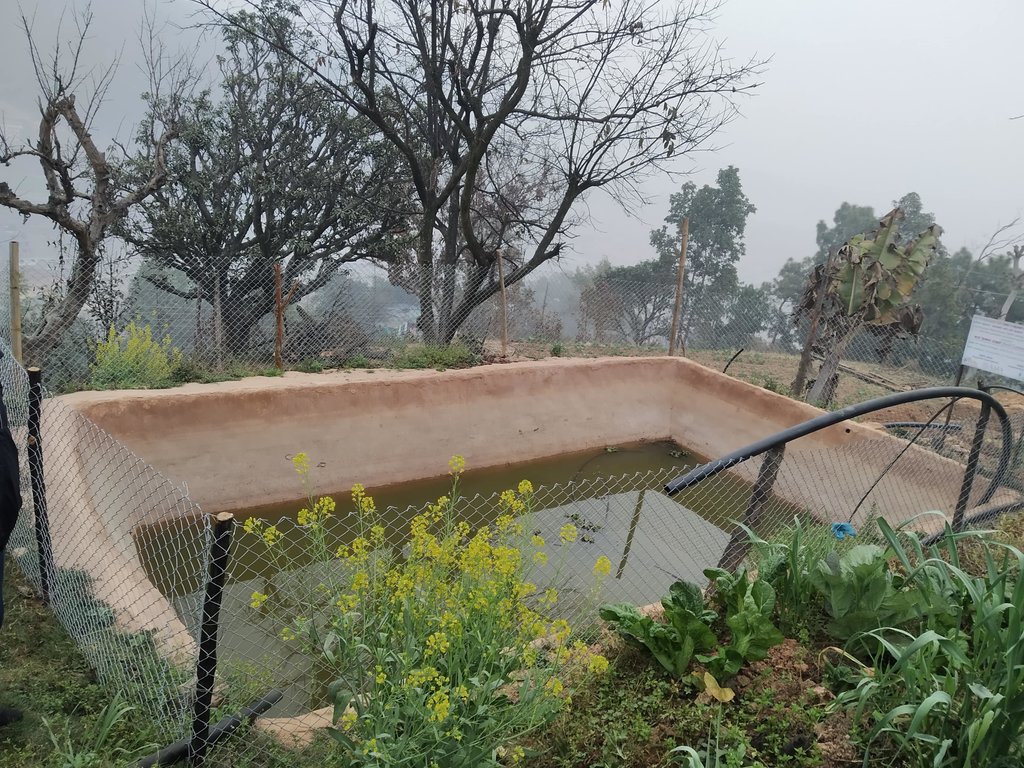
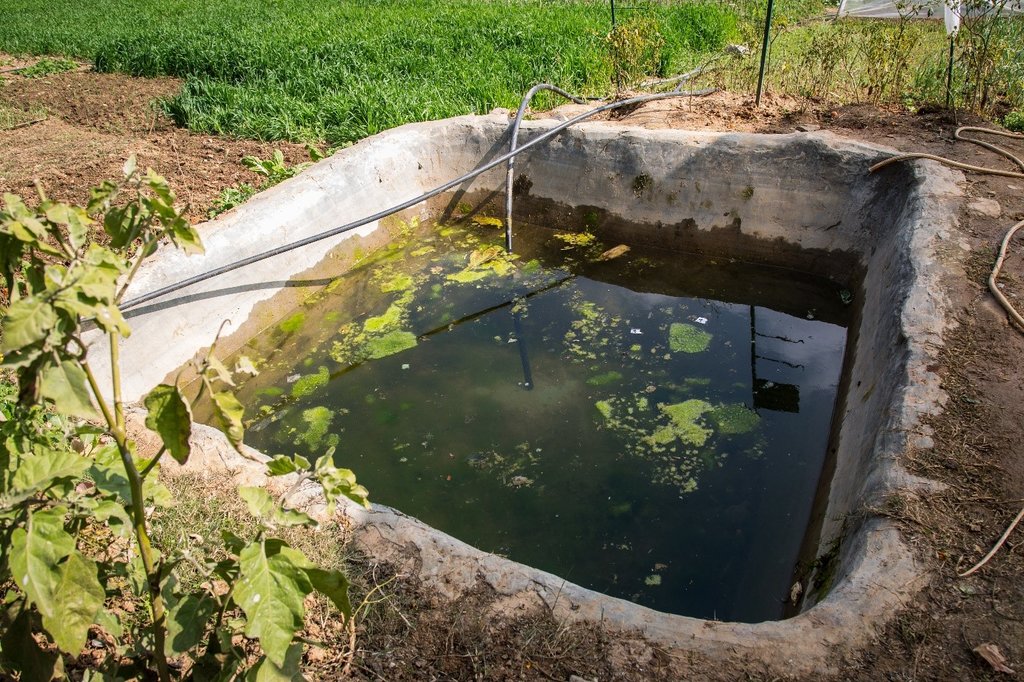
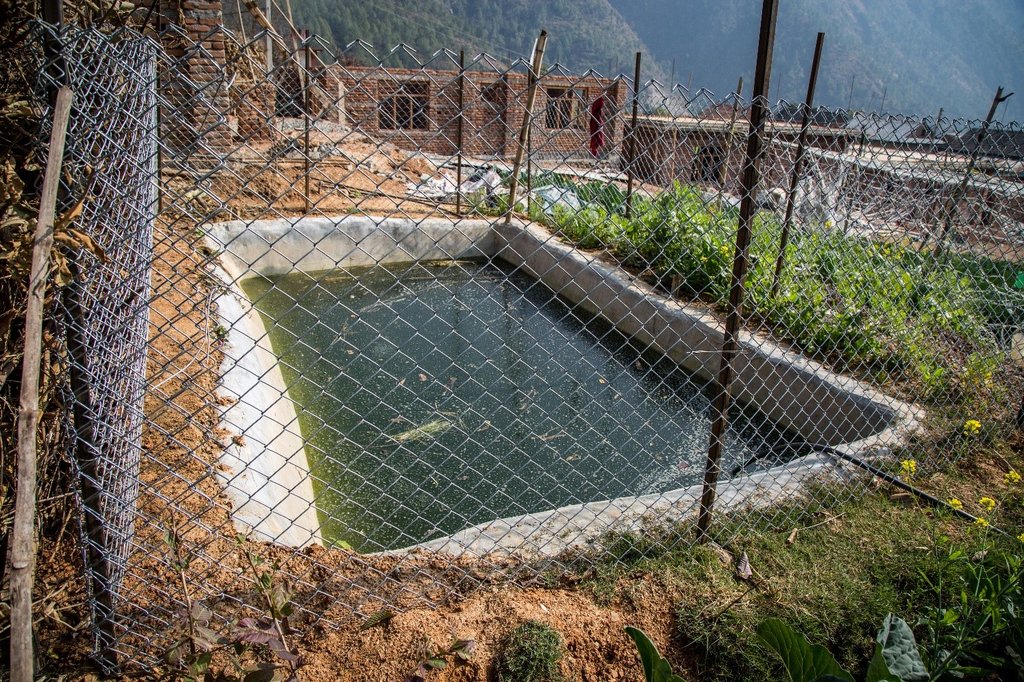
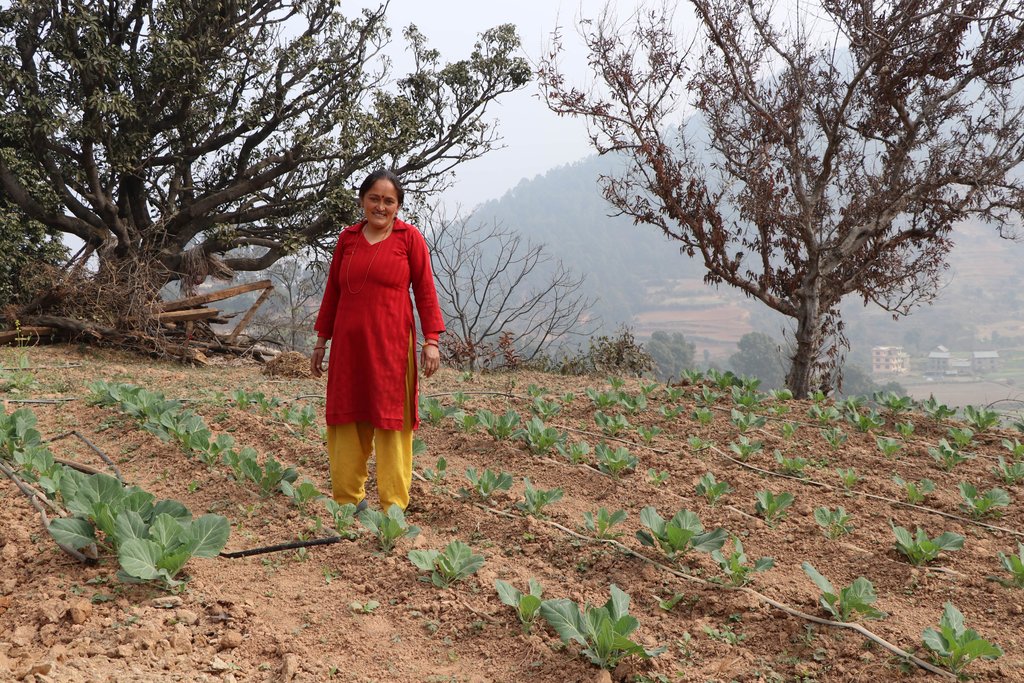
A soil cement water collection pond to store rainwater, runoff and household kitchen waste water free from soap and detergent for supplemental irrigation purpose during dry seasons.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
In Nepal's mid-hills mountain farmers face problems during dry seasons to irrigate their fields, as they entirely depend on rain- water. Soil cement water collection pond are ideal to tackle this challenge, as they can capture excess rainfall during monsoon, which is later available during prolonged seasonal water shortage.
The Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) project of ICIMOD together with its local partner, CEAPRED tested and demonstrated soil cement ponds with a capacity of 24000 liters. The conservation ponds were used for irrigating high value off-season horticultural crops (vegetables, fruit, and spices). These crops were irrigated with drip irrigation and micro sprinklers. The ponds were fed from rainwater, upland springs and taps, and household wastewater from kitchen free from soap and detergent. They were established during the dry season during 3 months. They were prepared by selecting a suitable site with a sufficient catchment; mapping out the area and depth of the pond; digging out the soil; removing protruding stones and roots; and compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond. Then gravel and pebbles were used for the base and the floor and side walls were leveled off. Initial mixture of soil, sand and cement (3:3:1) was applied to roughly plaster all the side walls and gravel was mixed in the mixture while plastering the floor. The following day, the roughly plastered pond was watered and was covered with wet jute sack to keep it moist. This was continued for 3-4 days. Then again a second mixture of soil, sand and cement (2:2:1) was applied to smoothly plaster the floor and side walls. The pond was watered for the next 3-4 days and was covered with wet jute sacks. Around 4-5 days after the second plaster, the pond was filled with water. For safety, pond was enclosed with a gabion wire/ bamboo fence (or using any locally available material). The total establishment cost for a soil cement pond with 24000 liters capacity was USD 311.
The main maintenance activity was to maintain the gabion wire/bamboo fence to prevent livestock and people from entering the pond, and to remove the sediment that accumulates in the pond. The sediment has to be removed once a year carefully by hand and if cracks occur, it should be sealed with a mixture of soil, sand and cement (3:3:1). The total annual maintenance cost for 24000 liters soil cement tank was USD 68.
This technology has somehow helped small-land holding farmers to irrigate their rain-fed land during dry months which has increased the crop production and their income as well.
Land user's particularly liked that their production increased and that they were able to grow up to three crops per year. Trough this the farmers were able to diversify their crops, and they were less vulnerable to the dry season. In addition, soil cement water ponds are more efficient than plastic-lined conservation ponds which are easily damaged by rats. Although cost effective, the fixed price for this technology is quite high, particularly for smallholder farmers. To lessen this financial burden, local governments can provide subsidies to women and marginalized groups interested in this technology. Self-help groups with a revolving grants system would help expand the use of these ponds and ensure sustained use across Nepal.
2.3 صور التقنية
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
Size of soil cement pond depends upon the area of land to be irrigated.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيبال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Province no: 3
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Namobuddha Municipality, Kavrepalanchowk District, Nepal
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
ICIMOD demonstrated this technology through the program of Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) with the help of its implementing local partner, The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED) in its pilot project sites in Kavrepalanchok district.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- Improve water availability during dry seasons
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب - الأرز (في الأراضي المرتفعة)
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - البطاطس
- المحاصيل البذرية - السمسم، الخشخاش، الخردل، وغيرها
- الخضروات - الخضروات الورقية (السلطات، الملفوف، السبانخ، وغيرها)
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 3
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Tomato and raddish
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- حصاد المياه
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر
- S7: معدات حصاد المياه/الإمداد/الري
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
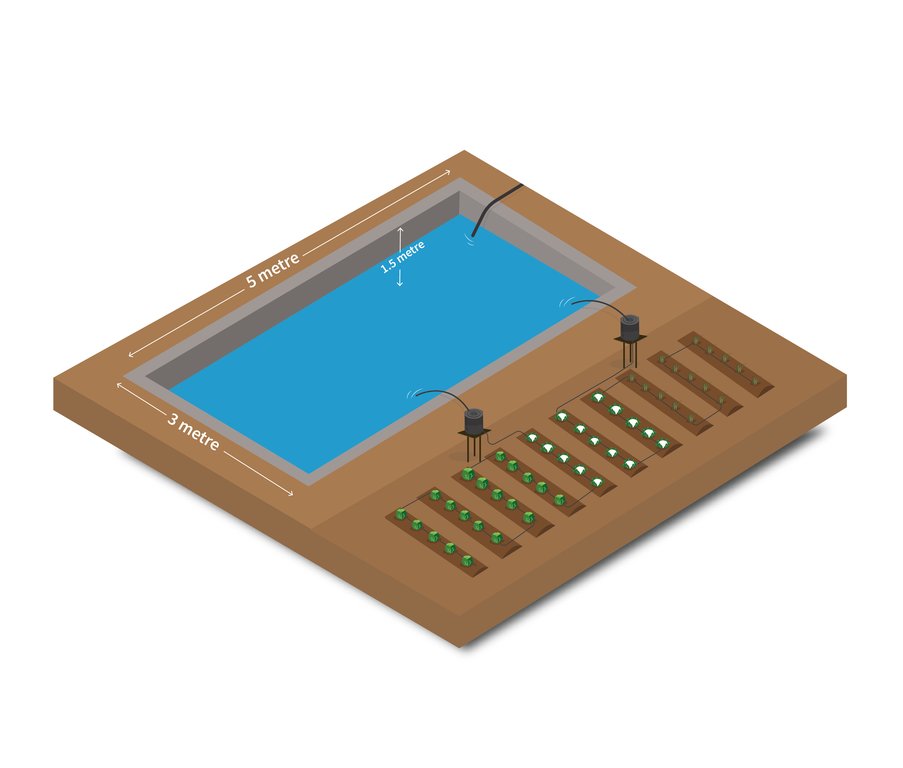
Soil Cement Water Collection Pond for Irrigation Purpose in Dry Seasons
Location: Charange fedi, 03, Namobuddha Municipality, Kavrepalanchowk
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Structural measure: pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5
Capacity of the tank= 24000 litres.
Construction material (earth): Clay
Construction material (other): Cement, sand and water-proofing liquid
المؤلف:
Kabita Nhemhafuki, Ram Dev Shah
التاريخ:
01/12/2020
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
0.0024 ha
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
1 ha = 10000 square metres
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
5.68
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a preferably stable ground with a sufficient catchment area | dry months |
| 2. | Measure the area to be irrigated and estimate the size of the pond | dry months |
| 3. | Measure and mark out the pond | 1st day |
| 4. | Dig out the soil to the pre-determined depth and remove protruding stones and roots | 1st day |
| 5. | Compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond | 2nd day |
| 6. | Apply initial mixture of soil, sand, cement (3:3:1) to roughly plaster all the the side walls and mix gravel in the mixture while plastering the floor. | 2nd day |
| 7. | The following day, the roughly plastered pond should be watered and covered with wet jute sack to keep it moist. This should be continued for 3-4 days. | 3rd day |
| 8. | Apply a second mixture of soil, sand, and cement (2:2:1) to smoothly plaster the floor and side walls. | 5th day |
| 9. | Water the pond for the next 3-4 days and cover with wet jute sack. | 8th day |
| 10. | Around 4-5 days of second plaster, fill the pond with water. | 13th day |
| 11. | For safety, the pond can be enclosed with gabion wire/ bamboo fence (or using other locally available materials) | 14th day |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Dig out pond | persons/unit | 7,0 | 5,68 | 39,76 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Stone soiling | persons/unit | 1,0 | 8,74 | 8,74 | |
| العمالة | Cementing | persons/unit | 10,0 | 8,74 | 87,4 | |
| العمالة | Wiring | persons/unit | 2,0 | 8,74 | 17,48 | |
| معدات | Spade | piece | 3,0 | 2,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Measuring tape | piece | 2,0 | 1,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Shovel | piece | 3,0 | 7,0 | 21,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Hammer | piece | 3,0 | 4,0 | 12,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Cement mixing iron pan | piece | 2,0 | 3,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Trowel | piece | 3,0 | 2,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Sand | bags | 24,0 | 0,87 | 20,88 | |
| مواد البناء | Cement | bags | 6,0 | 7,43 | 44,58 | |
| مواد البناء | Water proofing liquid | bottle | 1,0 | 2,62 | 2,62 | |
| مواد البناء | Gabion wire sheets | sq.ft | 120,0 | 0,31 | 37,2 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 311,66 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 311,66 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED) covered the remaining cost
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintain and repair wire fence to prevent livestock and humans from entering the pond | once in a year |
| 2. | Removing accumulated sediment once a year carefully by hand | dry months/once in a year |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Clean and maintaining the pond | persons/unit | 3,0 | 5,68 | 17,04 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Maintain and repair wire fence | persons/unit | 2,0 | 7,0 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Gabion wire | sq.ft | 120,0 | 0,31 | 37,2 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 68,24 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 68,24 | |||||
التعليقات:
The cost given above is for unit technology having 24000 liters capacity as in 2020.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Cost of cement and sand
Members of a household contributed as labour in all sites.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1584,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Water source is mainly spring.
More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: spring
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- مرتفع
تنوع الموائل:
- مرتفع
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Nepal harbors 3.2 % and 1.1 % world's known flora and fauna respectively despite occupying only 0.1 % of global area. Particularly, beta diversity is high in Nepal (BCN and DNPWC, 2011).
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 154 - 453 persons per km2 ( Census, 2011)
Annual population growth : 2% - 3%
Among 100% land users, 80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land (ranked by land users). 20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification:
Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages.
Due to loss of farmland and increasing urbanization and loss of farmlands many people are switching from agriculture to non-farm occupations such as working in brick kilns.
The opening of the BP Highway has led to the establishment of many hotels and restaurants and the development of local market places such as Bhakundebesi.
Most local businesspersons are small entrepreneurs with limited investment capacity.
Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: Vegetables- commercial
Level of mechanization: Manual labor consists of planting, irrigation , harvesting, while field preparation is carried out by animals, also machines but just in valley bottom.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- مجتمعي (منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
Waste management:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليقات:
Health facilities: There are nine health facilities centre in Namobuddha municipality, Kavre. The main health facilities are Methinkot Hospital, which is a 15-bed district level government hospital, and Dapcha Health Center, which is run by Kathmandu.
Education: There are eight academic institutes for higher studies ( higher secondary schools and colleges). The main academic institutes are:
Dapcha Krishna
Multiple Campus (community), Dapcha;
Janahit Secondary School (public), Khanalthok
Janak Multiple Campus (community), Methinkot
Janak Secondary School (public), Methinkot
Kanpur Campus(community), Kanpur and
Kanpur Secondary School
(public), Kanpur.
Employment ( off-farm): Due to loss of farmlands and increasing urbanization, many people are switching from agriculture to non-farm occupations such as working in brick kilns. The opening of the BP Highway has led to the establishment of many hotels and restaurants and the development of local market places such as Bhakundebesi. Most local businesspersons are small entrepreneurs with limited investment capacity.
Market: Bhakundebesi is the emerging marketplace due to its strategic location in the middle of the municipality astrid the BP Highway. Most local business activities in the municipality take place in Bhakundebesi bazaar. It is a major place for local people to purchase consumer goods.
Energy
Cooking fuel:
In 2011, 88% of households mainly used firewood for cooking, followed by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) (4.92%). In Puranogaun Dapcha, almost all households (99.8%) relied on firewood for cooking. LPG was relatively popular in Dapcha Chatrebhanjh (10.3%) and Khanalthok (11.5%). Less than 6% of households used biogas for cooking, with its use relatively high in Mathurapati Fulbari (19.3%) and Methinkot (15.9%) (CBS, 2011).
Lighting :
93% of households used electricity for lighting while 5% depended on kerosene. Dependency on kerosene was relatively high in Khanalthok (8.1%) and Methinkot (7.4%). There was little solar lighting except for in Khanalthok where 3% of households relied on it (CBS, 2011).
Roads and Transportation:
Namobuddha Municipality is easily accessible by motorable road from neighboring areas via the BP Highway, which splits the municipality into almost two equal halves . The highway, which runs from Banepa to Bardibas in the Terai, is the shortest route from the Kathmandu Valley to the eastern hills and Terai. The limited width of the road and its sharp bends mean that public transportation along the BP Highway is mostly by small buses and jeeps.
Drinking water and Sanitation:
In 2011, about 60% of households had access to taps or piped water with accessibility varying across the municipality. While about 80% of PuranogauDapcha households had taps or piped water, only 37.5% of households in Simalchour Syampati enjoyed such services. Other sources of drinking water were covered wells (12.3%), uncovered wells (20.2%) and water spouts (6.3%). Methinkot (40.8%) and Simalchour Syampati (31.4%) residents were most reliant on uncovered wells. Covered wells served sizeable household populations in Dapcha Chatrebhanjh (35.3%) and Simalchour Syampati (23%) (CBS, 2011).
Toilet facilities: In 2011, about 63% of households had accessto toilet facilities, with about 40% overall having flushtoilets. The least toilet coverage was in Kanpur Kalapaniand Simalchour Syampati VDCs where 63% and 58% ofhouseholds respectively did not have their own toilets. Almost all households in Puranogaun Dapcha had their own toilets, mostly flush toilets (CBS, 2011).
Waste Management: – Namobuddha is in the early phase of urbanization with no systematic waste management.The Municipality Office is searching for a landfill site.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Before they used to plant only one crop per year but now due to adoption of this technology, crop production has increased as they plant three crops per year.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Crop quality has become good due to availability of more water for irrigation and integration of this technology with bio-pesticide jholmol and mulching.
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to availability of water for irrigation, farmers have turned many fallow land into agricultural land.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Water needed for irrigation has increased as all the waste water from households, rainwater and taps waters are stored in this tank for irrigation in dry seasons.
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Irrigation water availability has increased crop production in turn farmer income has increased by selling those crops in market.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers are becoming more self sufficient due to high production of crops.
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to informal network of farmers with pond has strengthened community institutions.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmers share their knowledge and experiences with each other and discuss on how they can overcome the challenges they have been facing recently.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to availability of more irrigation water.
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Most of the fallow land are turned into crop land.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to trapped runoff
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | غير معروف |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | باعتدال |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة الأخرى المرتبطة بالمناخ (الكوارث)
| أخرى (حدد) | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ |
|---|---|
| reducing growing period | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 11-50%
التعليقات:
Till now 24 land user families of Namobuddha Municipality have adopted this technology.
Among 24 land user families, 18 have adopted this technology with external material support through Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) project and 6 land users families have adopted this technology without any external support.
Comments on spontaneous adoption (Through survey results) : There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the technology because this technology is quiet expensive, compared to plastic- lined conservation pond.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Water stored in this tank is sufficient to irrigate 2-3 ropani (1 ropani = 508 sq.m.) land in one season. |
| This technology can be enhanced by sharing the advantages of this technology with large number of people. |
| It is more sustainable and efficient than plastic-lined conservation pond. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Good income can be achieved even from a small piece of land by sales of vegetables in the dry season . |
| These ponds are fed with rainwater and household kitchen wastewater free from soap and detergent and from springs and taps. The pond water was mainly used for micro irrigation including drip irrigation and micro-sprinkler. |
| It helps to promote the use of other water conserving techniques like mulching when using the harvested water. |
| It has reduced the dependence on large scale water supply schemes. |
| How can they be sustained / enhanced? Harvest all possible sources of water. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Soil cement tank is expensive for poor farmers. | Subsidized cost for poor farmers. |
| It is unsafe for small children. | Protection structures should be constructed. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Cement and sand rate is very expensive for poor farmers. | Make it available in the local market at a subsidized cost for poor farmers. |
| The ponds attract insects, mainly mosquitoes, that cause disease; and the ponds are unsafe for small children. | Regularly clean the pond and fence them. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
6
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
5
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
1
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
2
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
20/02/2020
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
ICIMOD (2018) Building Mountain Resilience: Solutions from the Hindu Kush Himalaya. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
ICIMOD
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
SCWMC (2004) Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Measures and Low Cost Techniques. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Component - Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
DSCWM, Kathmandu
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Namobuddha Municipality, Nepal Situation Analysis for Green Municipal Development, 2018
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://gggi.org/site/assets/uploads/2018/07/GGGI_GMD-Assessment_Namobuddha.pdf
العنوان/الوصف:
Farmers in Kavre reaping benefits from soil cement tanks, 2021
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.icimod.org/article/farmers-in-kavre-reaping-the-benefits-of-soil-cement-tanks/
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية