Vermicomposting: an effective liquid fertilizer and biopesticide [كينيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: William Akwanyi
- المحررون: George Onyango, Innocent Faith, Noel Templer
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6685 - كينيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Mururi Wamunga Job
Welthungerhilfe farmer
كينيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
Farmers who have used vermicompost and vermijuice have recorded good harvests and there are no adverse impacts on their farms.
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Vermicomposting is an on-farm waste management strategy where worms are used for biodecomposition of wastes to produce a natural liquid fertilizer and pesticide.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Vermitechnology is biodecomposition of wastes using worms such as red wigglers. It includes vermicomposting (production of compost) and vermiculture (production of worms to ensure sustainability of the enterprise).
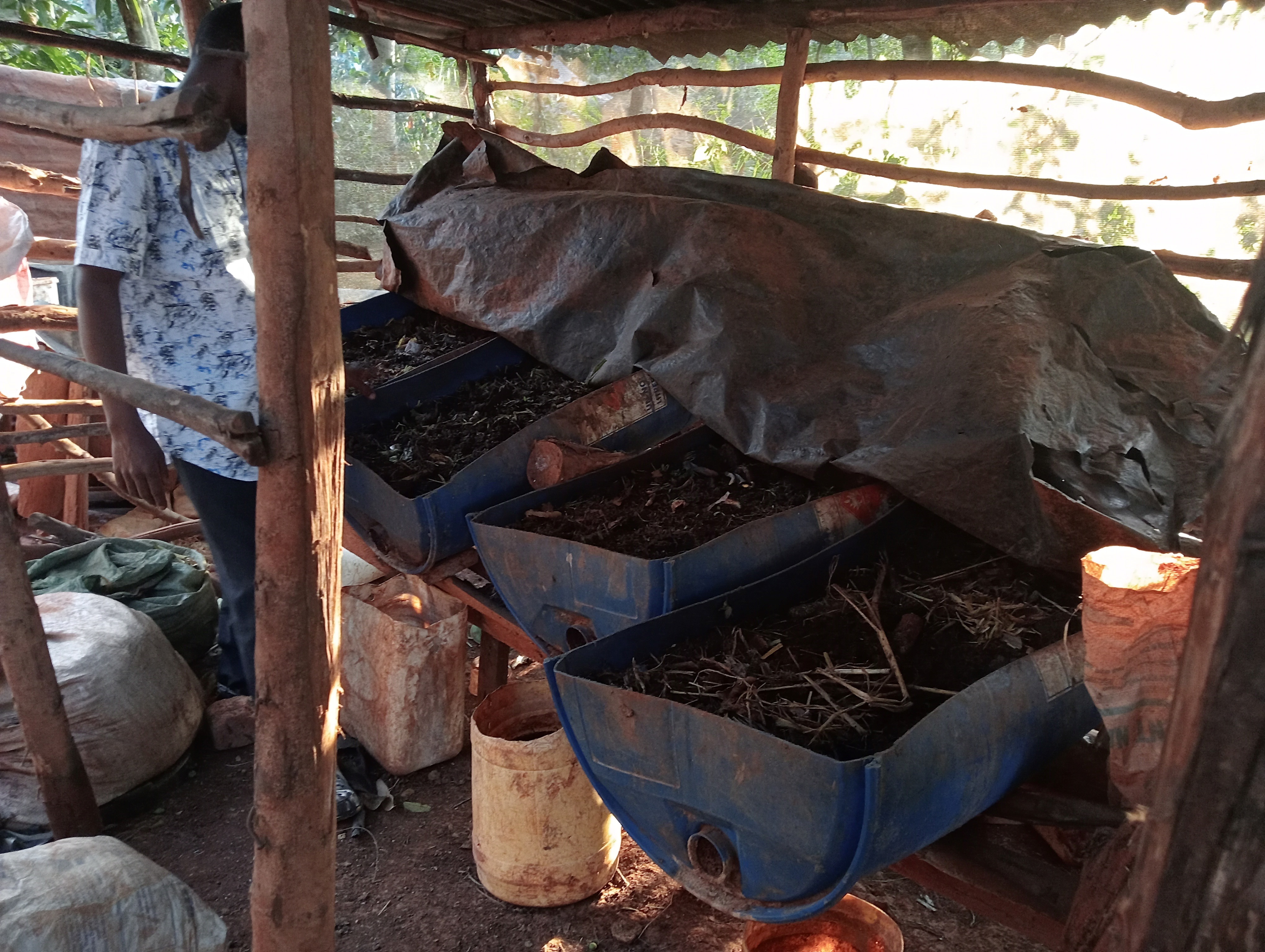
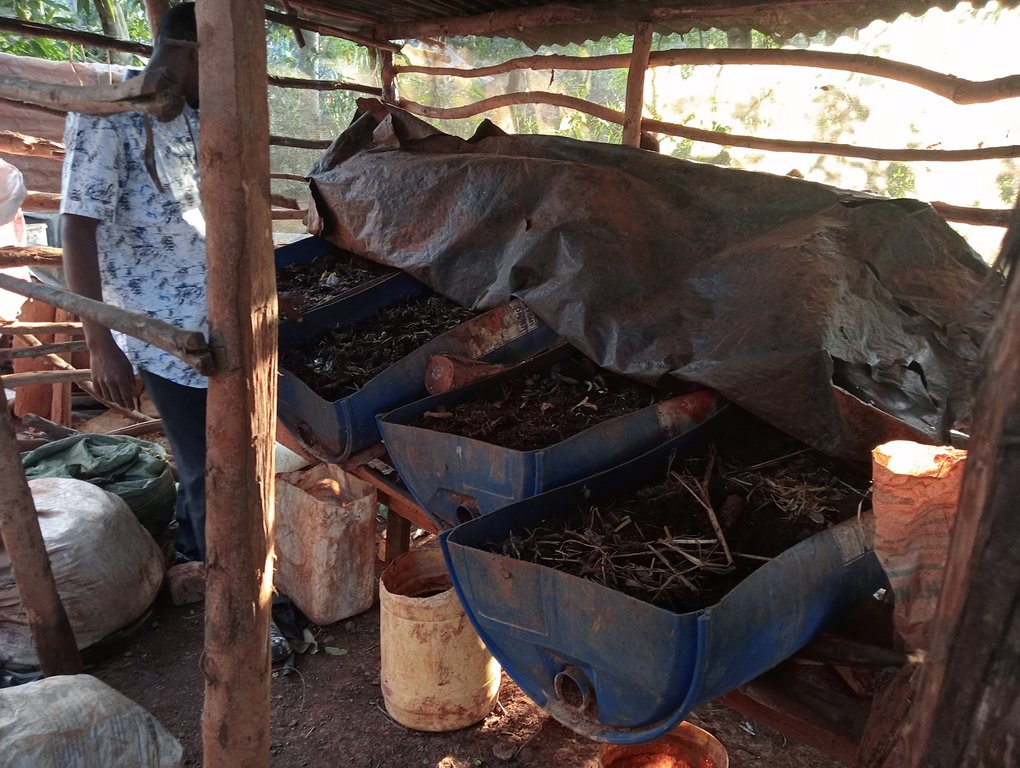
A vermicomposting structure is installed under shade and covered with a black polythene sheet to protect worms from the heat of the sun, and to prevent volatilization of nitrogen. The structure itself can be made by cutting a 60 cm radius and 120 cm height drum into two halves lengthwise. The half to be used must be thoroughly cleaned of oil or chemical residue. A hole is drilled at one end of the half drum for the installation of a tap. A base is made using wooden rails fastened on wooden posts using nails. The container is angled at 30° with the outlet pipe or tap on the lower side to allow free flow of leachate/ vermijuice. Materials are introduced in the half drum, including a gunny sheet covering the entire inside surface and ends hanging outside on the edges of the drum, a 7 cm layer of small stones followed by a 0.5 cm layer of sand on the stones, 10 cm layer of bedding materials on the sand, and 10 cm layer of worm food (kitchen and/ or animal wastes) on the bedding material. 20 litres of water are evenly sprinkled on the worm food. The worms and casts are introduced and evenly spread on the food. A bucket is placed at the outlet to collect drops of vermijuice.
Bedding materials include maize cobs, chopped maize straw, agroforestry tree bark, husks, old cartons and paper, and sugarcane bagasse. Temperature and humidity are checked by a thermometer and a hydrometer respectively. However, temperature can be checked by hand also. It is advisable that food (waste) is decomposed before being added onto the bedding material to maintain the temperature within the desired range of 15 - 20°C. Worms coil at the top of the material whenever temperatures go higher. Humidity is often higher in culture bins than in composting beds. Hence, more leachate in culture bins than in composting beds. However, humidity content in both culture bins and composting beds should not exceed 60% since the worms can take in a lot of water and die.
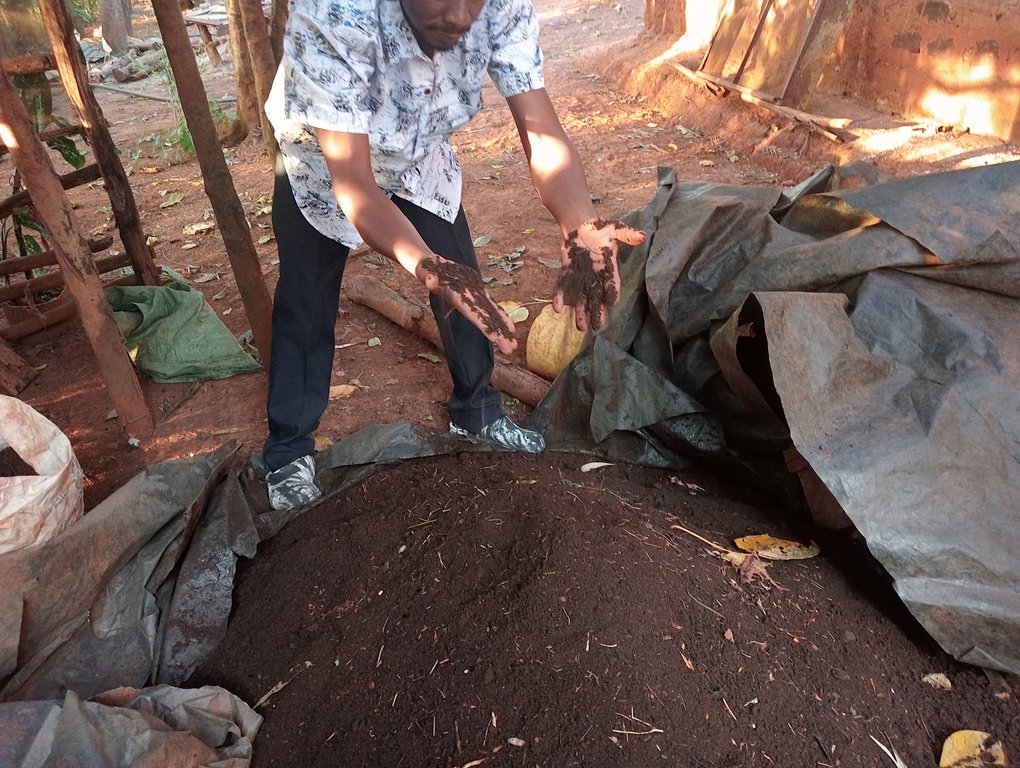
Feeding of the worms is done every 2 weeks where a mixture of 1 kg of chopped fresh tithonia, 3 kg of fresh cow dung, and 3 kg of cooked maize meal (“ugali”) is added and evenly spread on the decomposing material. Collected juice is returned to the system every 2 weeks for a period of 2 months. After the 2 months, the juice will be ready for use as folia fertilizer and pesticide. The casts become ready manure after about 2.5 - 3 weeks. It is harvested by dividing the container into 2 equal halves widthwise and not introducing food to the upper half to make the worms concentrate on materials on the lower half. The worm-free compost on the upper part is completely removed to be used as manure. The remaining material containing the worms is spread uniformly in the half drum. Worm food is then added evenly spread on top.
The system described above produces about 30 kg of ready-to-use compost and about 10 litres of vermijuice in 3 months. Provided that all inputs are available, a farmer can produce vermicompost and vermijuice 4 times from the same system in a year i.e., 40 litres of vermijuice and 120 kgs of ready-to-use compost in a year. Normally, a one-acre (0.4ha) farm requires about 20 tonnes of compost for planting maize. Vermijuice is mixed with water in the ratio of 1 part of vermijuice to 10 parts of water when required as a folia fertilizer and in the ratio of 1 part of vermijuice to 5 parts of water when required as a pesticide. 20 – 30 litres of vermijuice can be applied to a 0.4 ha farm. However, the amount required for fertilizer varies from farm to farm depending on the conditions of the soil and the crop(s) to be grown. It is important that soil testing is done to determine the conditions of the soil to ensure that the compost is added at the correct rate.
Vermicomposting requires less space and less maintenance labour compared to normal composting. It takes a shorter time to get compost from vermicomposting than from normal composting. On the other hand, large farms would require the installation of several vermicomposting units in order to meet the farm demand. The choice of either technology or both depends on a number of factors, including the size of the farm, the amount of compost required, the time required to produce the compost, etc.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
كينيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Kakamega County in western Kenya
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Matora A Village, Ebukuti Sub-location, Manyala Location, Marama South Ward, Butere Sub-county
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The are no protected areas within the area i.e., sub-county
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2017
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
ProSoil project under WHH as the implementing partner
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي الحرجي

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- المحاصيل الجذرية/الدرنية - البطاطا الحلوة، واليام، والقلقاس/الكوكويام، وغيرها
- الخضروات - الخضروات الورقية (السلطات، الملفوف، السبانخ، وغيرها)
- خضروات - اخرى
نظام زراعة سنوي:
الذرة/الذرة الرفيعة/الدخن في زراعة بينية مع البقوليات
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
- محاصيل الأعلاف - الأعشاب
- زهرة الباسيفلورا-فاكهة زهرة الآلام- ماراكويا
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- الافوكادو
- فواكه أخرى
- المانجو، المانغوستين، الجوافة
- البابايا
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Crops planted during long and short rain seasons.
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Maize and beans
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Some sections of the farm are left fallow during the short rains to allow for soil regeneration.

أراضي الرعي
الرعي المكثف/ إنتاج الأعلاف:
- مراعي محسنة
نوع الحيوان:
- الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
- الماعز
- الدواجن
هل يتم تطبيق الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Cattle dung and poultry droppings are used as inputs in vermicomposting. Compost is applied on soil where livestock fodder is planted.
المنتجات والخدمات:
- الأمن الاقتصادي، ,وجاهة الاستثمار
- البيض
- اللحوم
- الحليب
الصنف:
الماشية - لإنتاج الألبان واللحوم (على سبيل المثال الزيبو)
العدد:
2
الصنف:
الماعز
العدد:
3
الصنف:
الدواجن
العدد:
4
التعليقات:
There are assorted trees on the farm, and these provide litter that is an input in composting.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
التعليقات:
Crops are planted all year round due to availability of irrigation water from Eshiatukha and Luanda streams which supplement rain water.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
- الإدارة المتكاملة للآفات والأمراض (بما في ذلك الزراعة العضوية)
- إدارة النفايات / إدارة مياه الصرف الصحي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A6: إدارة المخلفات
A6:حدد إدارة المخلفات:
A 6.3: تم جمعها
التعليقات:
Some plant residues, especially leaves are collected and used as input in vermicomposting.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Ca):التحمض
- (Cp): تلوث التربة
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة
التعليقات:
Compost and vermijuice stabilize soil pH and have potential to suppress some soil-born plant pathogens that would have caused plant diseases.
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Prevents pathogens
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
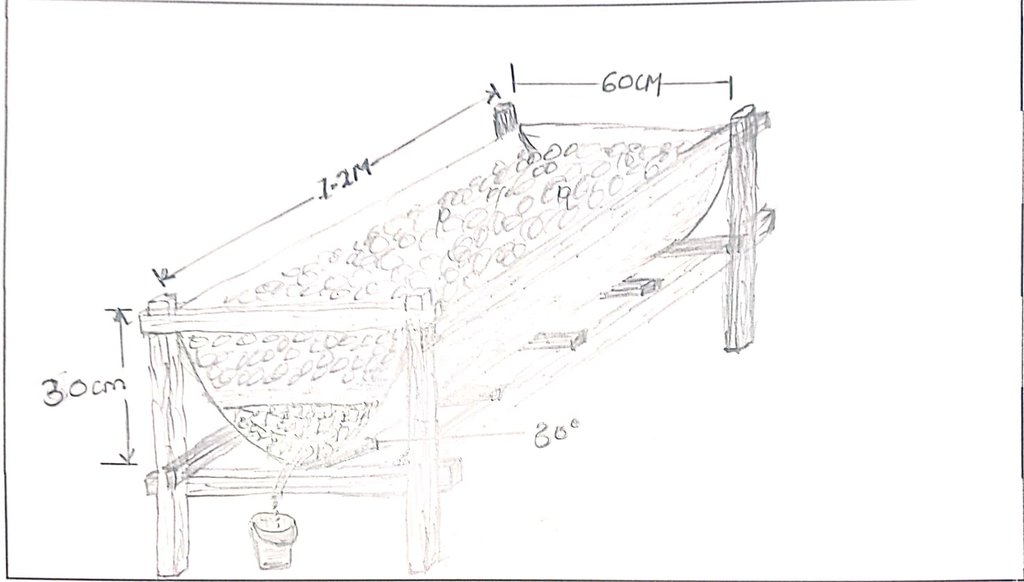
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
The drawing above is of a half drum; 60 cm radius and 120 cm height.
The half drum is supported on rails fastened on wooden posts using nails.
The half drum is positioned in a slanting manner at 30° to the horizontal level to enable free flow of the juice.
The outlet of the vermijuice is on the lower side.
Materials introduced in the half drum include the following: a gunny sheet covering the entire inside surface and ends hanging outside on the edges of the drum; 7 cm layer of small stones followed by a 0.5 cm layer of sand on the stones, 10 cm layer of bedding materials on the sand, and 10 cm layer of worm food on the bedding material. The worm food material are determined by the required soil nutrients e.g., banana trunk for potassium (K)-rich manure and/ or vermijuice, crushed eggs for calcium (Ca)-rich, and tithonia for nitrogen (N)-rich.
The worms and cast are introduced and evenly spread on the food.
A bucket is placed at the outlet to receive dropping vermijuice.
المؤلف:
William Akwanyi
التاريخ:
30/01/2023
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
A half drum vermicomposting unit as described in 2.2
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
0.17 cubic metres
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
KES
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
122,95
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
300
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of vermicomposting unit, inclusive shed | Before procuring worms |
| 2. | Adding materials | Before procuring worms |
| 3. | Introduction of worms | After completion of construction |
التعليقات:
The system described above produces about 30 kg of ready-to-use compost and about 10 litres of vermijuice in 3 months. The farmer should have the structure ready with all materials except food for the worms before procuring the worms.
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Construction of the vermicomposting structure | |||||
| العمالة | Construction of shade over the vermicomposting structure | |||||
| معدات | Hammer | |||||
| معدات | Hand saw | |||||
| معدات | Tape measure | |||||
| المواد النباتية | Bedding material | |||||
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Worms in cast | |||||
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Kitchen or animal wastes | |||||
| مواد البناء | Half drum | |||||
| مواد البناء | Gunny sheet | |||||
| مواد البناء | Nails | |||||
| مواد البناء | Iron sheets | |||||
| غير ذلك | Gravel | |||||
| غير ذلك | Sand | |||||
| غير ذلك | Water |
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قم بتقديم تقدير للتكاليف الإجمالية لإنشاء التقنية:
7000,0
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
The ProSoil project provided the worms
التعليقات:
The farmer was unable to break down the costs of the listed items. The costs refer to the equipment described in 2.2. The cost is in Ksh/ KES equivalent to 56.93 USD.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring humidity and temperature | Daily |
| 2. | Feeding | Biweekly |
| 3. | Watering | Biweekly |
| 4. | Predator control | Daily |
| 5. | Harvesting compost | Every 2.5 - 3 months |
| 6. | Collection of vermijuice | Daily |
التعليقات:
Temperature and humidity are checked by a thermometer and a hydrometer respectively.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
إذا لم تتمكن من تفصيل التكاليف في الجدول أعلاه، قدم تقديرًا للتكاليف الإجمالية لصيانة التقنية:
2000,0
التعليقات:
The farmer was unable to break down the costs of the listed items. The cost is in Ksh/ KES equivalent to 16.27 USD.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Rate of man-days vary from one place to another. It is not easy to attach monetary value to some of the input e.g., wastes and water.
Exchange rate for January 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
1300,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Kakamega Meteorological Station
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
The climate in the area favours most agricultural activities.
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
The farm is located at an area that is lower in altitude compared to other areas in the larger area. The altitude of the farm is 1,319 meters above sea level.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil pH of most farms in the area ranges from moderately acid (4) to moderately alkaline (7).
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه الشرب سيئة (تتطلب معالجة)
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية والسطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depts are not more than 50 metres.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
The area has high agrobiodiversity since most farms are under crops and trees.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
- كبار السن
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
The farmer uses the land together with his other family members.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
Farmers with more than 2 ha in the area are considered to have large pieces of land since there is high level of land fragmentation in the area.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مؤجر
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
حدد:
Each landowner has full control of the way he/ she wants to use his/ her land.
التعليقات:
The farmer has an official title deed for his piece of land. He also leases other people's pieces of land for farming. Water in the streams such as Eshiatukha and Luanda and springs is freely accessed without restrictions. There is a borehole in the neighbourhood, and the managers of this borehole have set rules for accessing the water thereat.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليقات:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
8
التعليقات/ حدد:
Number of 90Kg bags of maize harvested per acre of land. Based on estimate by the farmer.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy to quantify by the farmer. Based on estimate by the farmer.
إنتاج الأعلاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5
التعليقات/ حدد:
Number of harvesting cycles in one season. Based on estimate by the farmer.
جودة العلف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Based on estimate by the farmer.
إنتاج حيواني
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
6
التعليقات/ حدد:
Amount of milk in litres from one cow. Based on estimate by the farmer.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
70
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the probability of crops failing to do well in any season.
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify. Land management has been eased because use of manure from vermicomposting improves the soil structure making it easier to plough.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10,000
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the amount of money in KES spend on fertilizers. The farmer no longer purchases fertilizers.
دخل المزرعة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2,000
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50,000
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the amount of money earned from sell of farm produce. Currently, he sells manure, worms, and vermijuice and also offers services in construction of vermicomposting structures.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
5
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the number of farm products that the farmer sells to earn income. Based on estimate by the farmer.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
4
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the number of months when there in no food in the house and the household has to purchase all food required in the house.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Based on estimate by the farmer.
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
10
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the percentage of moisture content in the soil during the dry season.
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
80
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimation of soil cover on his farm.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
4
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil organic matter has increased due to use of manure.
الحموضة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Based on estimate by the farmer.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
20
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the farmer's estimated vegetation cover at his farm.
التنوع النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
8
التعليقات/ حدد:
Quantity refers to the number of crops that the farmer establishes on his farm.
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
There are earthworms at the farm.
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy for the farmer to quantify.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Not easy to quantify. Compost improves carbon sequestration in the soil.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
No recorded data is available for reference. All are estimates based on the farmer's explanation or as given by him.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| أمراض وبائية | جيدة جدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
التعليقات:
Use of vermicompost and vermijuice reduces the farmer's dependence on inorganic fertilizers and pesticides.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
The project was implemented in the entire ward. Very few farmers have vermicomposting structures.
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
Most farmers are not implementing yet they were taken through the vermicomposting training by the ProSoil project.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
نعم
أخرى (حدد):
Design
حدد تكيف التقنية(التصميم، المواد/الأنواع، الخ.):
The farmer does not fit taps on the composting structures as outlets for the vermijuice since someone can accidentally close the tap and forget to open, especially during humidity checking leading to high humidity which can cause the death of the worms.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| It is an agribusiness venture. |
| It is a source of manure and pesticide. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Compost and vermijuice can be sold to earn income. |
| Structures can be made from locally available material. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Not effective for large scale farming. | Establishment of many bigger structures. |
| The technology is not common among many farmers. | Need for increased awareness creation among farmers, especially on proper knowledge on composting. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Possible death of worms due to unfavourable temperature and humidity. | Ensure regular checking of temperature and humidity. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
One visit at one farm
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
One farmer interviewed at his farm. Follow-up on phone.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
ProSoil team and project implementers from Welthungerhilfe consulted.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
Kakamega County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022 and online sources reviewed.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
30/01/2023
التعليقات:
One field visit and several follow-up consultations.
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Kakamega County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Free download at https://kakamega.go.ke/public-participation-county-development-plans/
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Vermicompost Suppression of Pythium Aphanidermatum Seedling Disease: Practical Applications and an Exploration of The Mechanisms of Disease Suppression
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://ecommons.cornell.edu/bitstream/handle/1813/31195/alh54.pdf;sequence=1
7.4 تعليقات عامة
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, UNCCD, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية