Night Corralling [النيجر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Julie Zähringer
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_952 - النيجر
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Night corralling of cattle, sheep and goats on cropland during the dry season (November-April) replenishes soil fertility of agricultural land depleted by continuous cropping.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
This technology is mainly applied in semi-arid and sub-humid areas on sandy/loamy plains with low soil organic matter content, low soil pH, and with slopes below 5%. Adequate spacing of animals helps to homogenously distribute the manure on the field (see photo): in cattle this is ensured through tying the animals to poles, in sheep and goats a movable fence serving as night enclosure helps to save labour. Corals and animals are moved to a new spot within the field every 4-5 nights to homogeneously manure fields. Ideal is a rate of 2.5 tons of faecal dry matter per hectare. The application of this amount results in superior grain yields (millet, sorghum) as compared to an unmanured field. High yield response is achieved in the cropping season directly following the corralling (year 1) and in the subsequent two to three years, in which no new deposit of faeces and urine, i.e. no further corralling, is needed. While a 250 kg cow deposits about 1 kg of manure dry matter per night, 7 sheep or 7 goats are needed to produce this same amount. Thus, to cover 1 hectare of land with 2.5 tons of manure, a herd of 15 cattle would need to be corralled during 167 nights; alternatively 178 nights would be needed if 70 small ruminants were corralled. Since individual herds are often smaller than 15 cattle (or 70 small ruminants) and fields are larger than 1 hectare, it is recommended to organize corralling of fields within a community (village) of farmers and especially to revitalize the traditional corralling contracts (‘contrats de parcage’) with transhumant herders.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيجر
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Fakara region (near Niamey)
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Chikal territory (near Filingué)
Map
×3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

مختلطة (محاصيل/ رعي/ أشجار)، بما في ذلك الحراجة الزراعية
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Loss of soil fertility (organic matter, nutrients, pH decline) due to continuous cropping
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
إذا تغير استخدام الأراضي بسبب التقنية، قم بالإشارة إلى استخدام الأرض قبل تنفيذ التقنية:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 مزيد من المعلومات حول استخدام الأراضي
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M1: التغيير في نوع استخدام الأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المؤلف:
Eva Schlecht, Animal Husbandry in the Tropics and Subtropics, University of Kassel and Georg-August Universität Gö
4.2 المواصفات الفنية/شروحات الرسم الفني
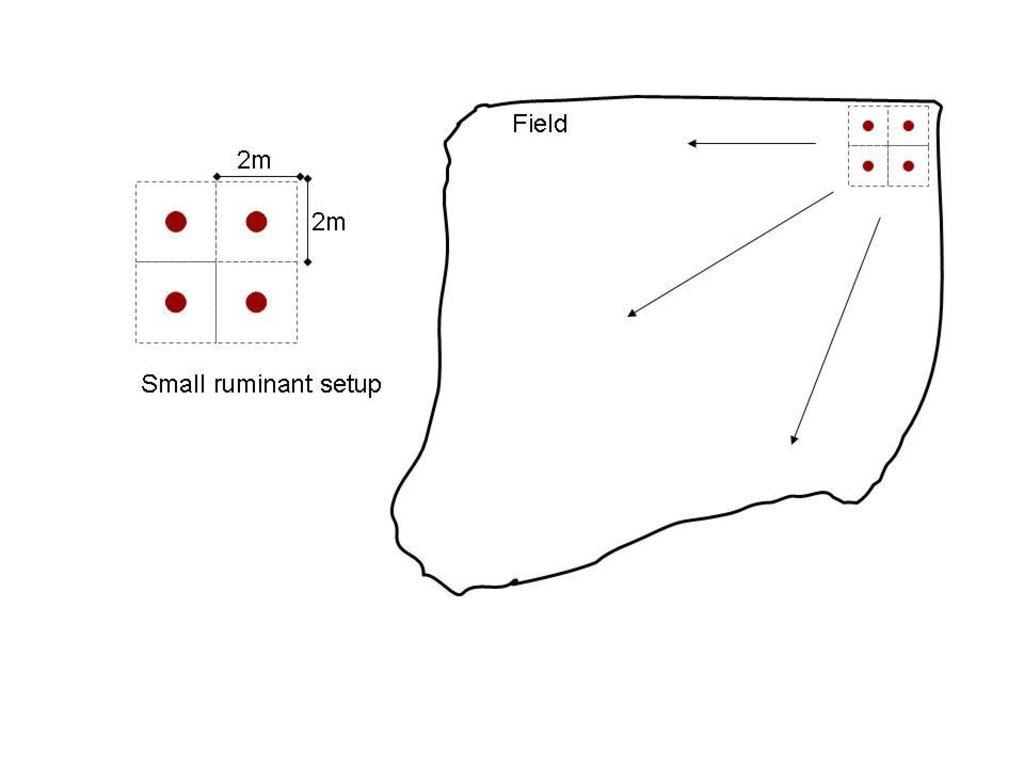
Corralling area of 4 sheep to poles (brown circles) during 5 nights (left) and principle of shifting corralling areas across a field of undefined size (right)
Location: Chikal territory. Fakara region
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (spacing and timing of animal placement need to be respected))
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: faecal dry matter
Quantity/ density: 2.5
Remarks: t/ha
4.6 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | نوع التدبير | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Placing poles in the field at 2m x 2m spacing for small ruminants and at 4m x 4m spacing for cattle, starting at the field border | زراعية | in year 1 of 3-year cycle |
| 2. | Attach individual animals (adult small ruminants, adults or calves if you work with cows) to the pole during night | زراعية | in year 1 of 3-year cycle |
| 3. | Shift the poles to an adjacent unmanured part of the field every 4 days in cattle, and every 5 days in small ruminants. | زراعية | in year 1 of 3-year cycle |
| 4. | To cover the whole field (1 ha) with manure: with 15 cattle you will need a total of 167 nights of corralling; with 70 small ruminants you will need 178 nights | زراعية | in year 1 of 3-year cycle |
| 5. | Cultivate the field for 3 subsequent cropping seasons (year of application, plus year 2 and 3) without further corralling in year 2 and year 3 | زراعية | in year 2 and 3 (of a 3-years cycle) |
4.7 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
costs were calculated for 1 ha with 15 cattle
4.8 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour costs incur in a 3-years cycle: putting and changing the poles on a specific field is done in year 1, while in years 2 and 3 the respective field is cultivated, and no corralling takes place. Actual labour inputs for corralling in year 1 is 4–5 days (= 10–15 minutes during approx. 170 days), equivalent to US$ 10–13; maintenance costs given in the tables above refer the average expenses of the whole 3-years cycle
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض المملوكة أو المستأجرة من قبل مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
individual land us rights for field, communal for pastures
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المؤسسات المجتمعية
الآثار الايكولوجية
التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
التعليقات:
Technology not much affected by climatic extremes or changes.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
Labour input in year 1 (dry season) pays through high yields in harvest seasons of years 1–3.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Relatively high, but incomplete in the sense that homogeneity of dung application is lacking
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Strong increase of soil organic matter and therefore soil fertility which leads to an increase in crop yield and revenues |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Implementation constraint: organization of rotational corralling is necessary to effectively manure fields of a village community; this needs skillful organization | |
| Need to invest some money in poles | |
| High labour investment in year 1 | |
| Difficulty to revitalize trustful partnership with transhumant pastoral groups, as more and more crop residues are harvested and stored at the homestead (no dry season feed for mobile herds) | |
| Extensive consultation and coordination is needed if rotational (community) corralling or involvement of transhumant herders is necessary due to low animal numbers (<12 cattle, <50 small ruminants) at the level of individual households |
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية