Maize strip tillage [سويسرا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Unknown User
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Streifenfrässaat
technologies_1008 - سويسرا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Buddeke Giulietta
Geographisches Institut der Universität Bern -GIUB
سويسرا
مستخدم الأرض:
Friederich Jürg
Landwirtschaftliches Lohnunternehmen Seelandzenturm Suberg
سويسرا
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Jürg Friederich Lohnunternehmung - سويسرااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
University of Bern, Institute of Geography (GIUB) - سويسرا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Maize strip tillage is used for corn cultivation and the technology ensures that only those stripes are cultivated where seed is applied.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
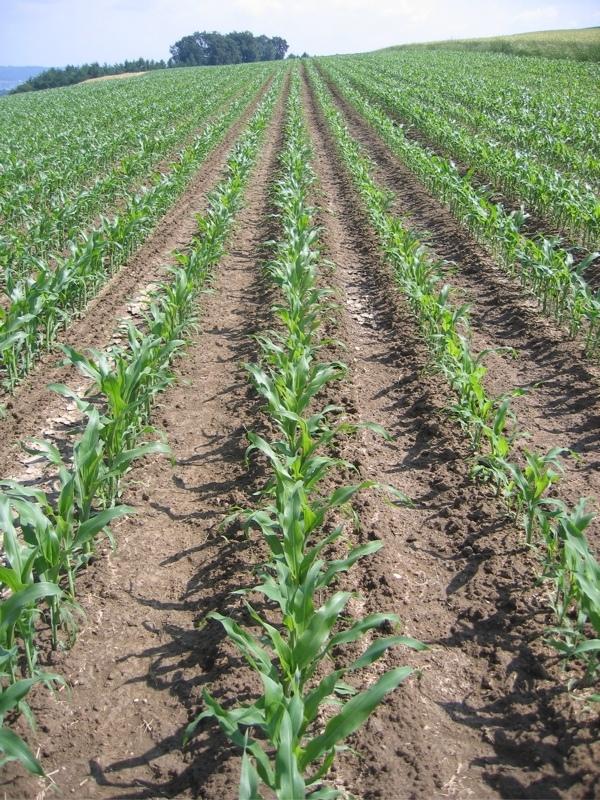
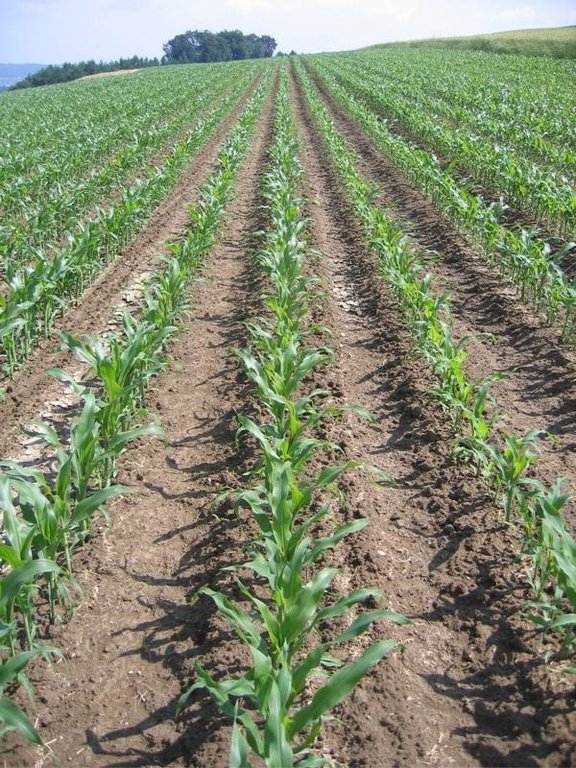
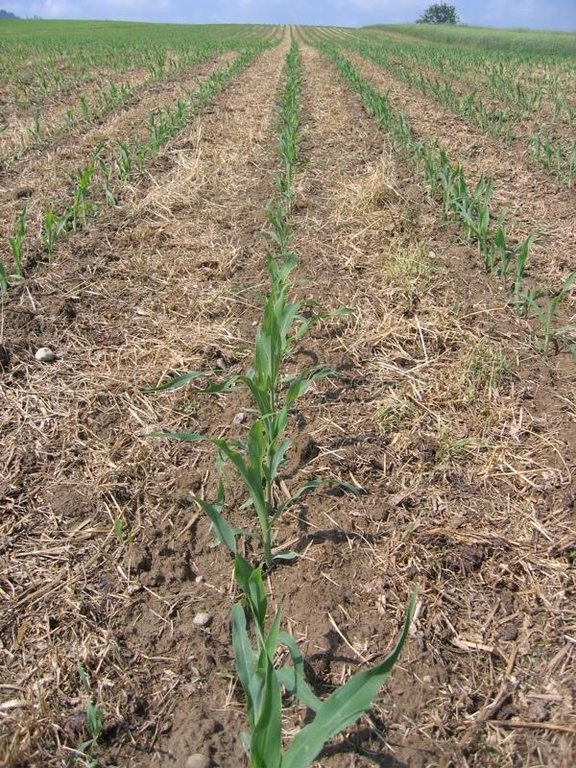
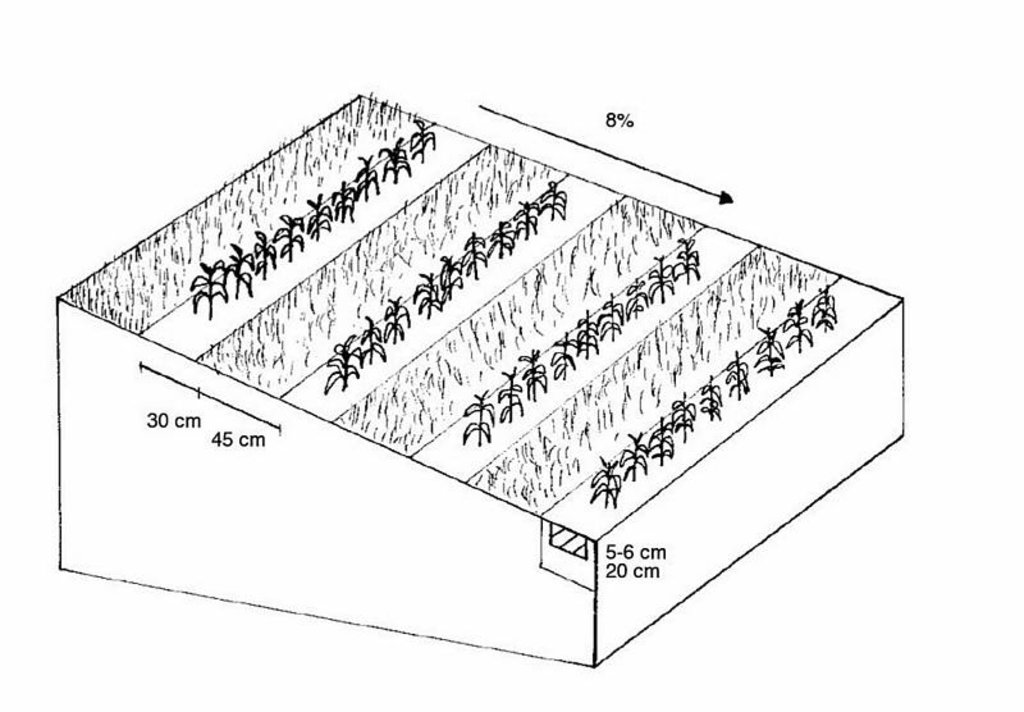
Maize strip tillageis a soil conservation method used in crop production. First of all the grass in the area needs to be prepared by splattering round-up some 3-10 days in advance. Then the actual maize strip tillage machine carves a stripe and the seed are inserted within this 30 cm strip. At the same time fertilizer is added on these cultivated stripes. Between those cultivated stripes the mulch-grass stripes (45cm) are unmechanised and protect the soil by increasing its stability. Due to these mulch-stripes the matrix of the soil is more complex and therefore the stability is better especially during the harvest in September. The interviewed farmer said it was cause of the improved soil structure that his tractors are not subside and compaction is also less likely to occur. Another advantage is the decreased risk of soil erosion when having more and heavy precipitation, as it is expected for next decades due to climate changes in Switzerland. Thanks to the SLM technology, water infiltration increases and organic matter as well which adds up to a promising growth period.
There are also clear economic advantages, by adopting the technology. In springtime only one working step is needed for seeding compared to the five steps needed with the traditional technique using a plough. Therefore the costs are finally lower with this technology and farmers can use the opportunity when having free labour to work part-time outside the farm. At first sight, the costs might seem higher when adopting this technology cause the farmer needs to hire a subtractor, in the end the costs are lower due to the lower labour input and the lower equipment costs. After having seen the advantages, the interviewed farmer said that the technology is usually maintained.
A high level of knowledge about the natural condition is needed when adopting this technology. On the one hand, the farmer must time the date for seeding adequately to the natural conditions, it needs some 4 days with no precipitation. Then on the other hand, the farmer has to apply Glyphosphat after the seeding in order to guarantee an optimal growth period for the corn. The timing to start seeding with this technology may be later cause corn is sensitive towards rival plants, low temperatures and humidity. These are some of the limits that the technology implies. If springtime is humid, the farmer should be allowed to use the traditional technique, regardless of the subsidies as indicated by the interviewed farmer. The canton of Bern is providing subsidies if the farmer commits to use a five year cycle which inherits not to use the plough during this period but using a mulch system. The interviewed farmer suggests that the canton of Bern could commit itself not only in giving subsidies to the areas but also to support if contractors like him would get subsidies for the investment for machines that are needed. For a single farmer the establishment costs for the equipment are too high so that the average is hiring a contractor who could work for a lower salary when having support to buy machines, so subsidies from the Cantons would be an asset.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
سويسرا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Bern
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Suberg
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 0.1-1 كم2
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- أثناء التجارب/الأبحاث
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Peter Hofer made different experiments wiht SLM Technologies and after successful implementation of maize strip tillage, idea was adopted
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion in hilly areas
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Due to changed weather conditions, basically an increase of percipitation, soil erosion increased
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد الأدنى من اختلال التربة
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, mulching, manure / compost / residues, rotations / fallows, minimum tillage
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (using a plough in hilly area increases soil erosion)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Swiss Franc
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
1,08
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
194.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy a machine for technology |
التعليقات:
Number of parties sharing: 2
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | applying round-up | ha | 1,0 | 97,0 | 97,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | maize strip tillage | ha | 1,0 | 388,0 | 388,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 56300,0 | 56300,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 56785,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 52578,7 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Applying round up on the field | 1 |
| 2. | Applying maize strip tillage | 1 |
| 3. | Add herbicide on field | 1 |
| 4. | Harvest of the corn | 1 |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Establishment costs are estimated for the contractor on the one hand and labour costs indicated above are the ones that the contractor is demanding for if he is hired. Additionally, those farmers who adapt this technology can get subsidies from the Canton if he/she commits to apply soil conservating measurements during 5 years, in Bern it is 450 CHF per ha.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour costs and costs for diesel are much higher for the traditional technology (plough). The investment for the technology are high in the first term and the labour costs indicated above are given by the contractor if he is hired. So for a regular farmer only these 388 USD are relevant.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Tendency towards increased rainfall
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 101-1000 m a.s.l. (depending on the area)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water: good, medium ( depending on the area )
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water ( generally good quality of water )
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
depending on the area
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Generally speaking, men tend to work on the fields therefore are mainly responsible for technologies, women tend to work in the houshold and are responsible for administrative tasks. In Switzerland there is a traditional labour division between men and women, there might be exceptions but if addressing new technology one has to deal with male farmers. Assuming that decisions to adapt new technologies or for investments are made by both.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Off-farm income specification: For those farmers working off-farm it is likely to delegate work to contractor. On the other hand when hiring a contractor there is less labour needed for the farmer and the possibility to work off-farm slightly higher.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، لا يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
Half of the land is leased and the other was bought by the farmer. He said there is a tendency towards land selling.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Conditions need to be good, if season too wet, harvest can decrease
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Use of pesticides
التعليقات/ حدد:
Consequences of using pesticide are not known yet, traces in drinking water might be likely to occure
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التربة
فقدان التربة
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
More crows are on the fields after seeding
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Infiltration
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | ليس جيدا |
التعليقات:
With the grass stripes between the corn rows, the water can infiltrate faster and the soil is more stable and protected. The technology can be more tolerant towards intensive rainfalls but only to a certain extent. The technology is more sensitive when having humid conditions in spring and problems can occure then when trying to apply the stripe mill cropping..
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: When having good experiences with technology, some 80-90% of the farmers are maintaining this technology
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
|
less workload How can they be sustained / enhanced? Farmers should estimate their own labour time as well and then compare the costs of traditional technology and the SLM technology |
|
less costs How can they be sustained / enhanced? In the long-term costs for a farmer decrease by a third. Less diesel costs are needed. |
|
less erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Subsidies of the cantons could ensure that farmers adapt technology, therefore enhance their knowledge about soil erosion and the costs. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
reduction of soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Enhancing knowledge about soil erosion |
|
improvement of soil structure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Enhancing knowledge by experiments shown to farmers |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Timing is needed | Enhance knowledge about technology when conditions are too wet, farmers should be allowed to use plough instead of SLM technology |
| Subsidies only for areas | Canton could subsidies/support if contractor or farmer invests in a machine used for strip mill cropping. 5 years of subsidies might be too short |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| use of pesticide | It is not estimated yet whether the use of pesticide has traces in the drinking water |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية