Fodder provision to goats and sheep to reduce grazing pressure on natural vegetation [قبرص]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Michalakis Christoforou
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Παροχή σιτηρεσίου στα αιγοπρόβατα ως εναλλακτική τροφή με σκοπό τη μείωση της υπερβόσκησης στα φυσικά οικοσυστήμα(greek)
technologies_1247 - قبرص
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Cyprus University of Technology (Cyprus University of Technology) - قبرص1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Use of different types of fodder in order to reduce grazing impact on natural vegetation
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
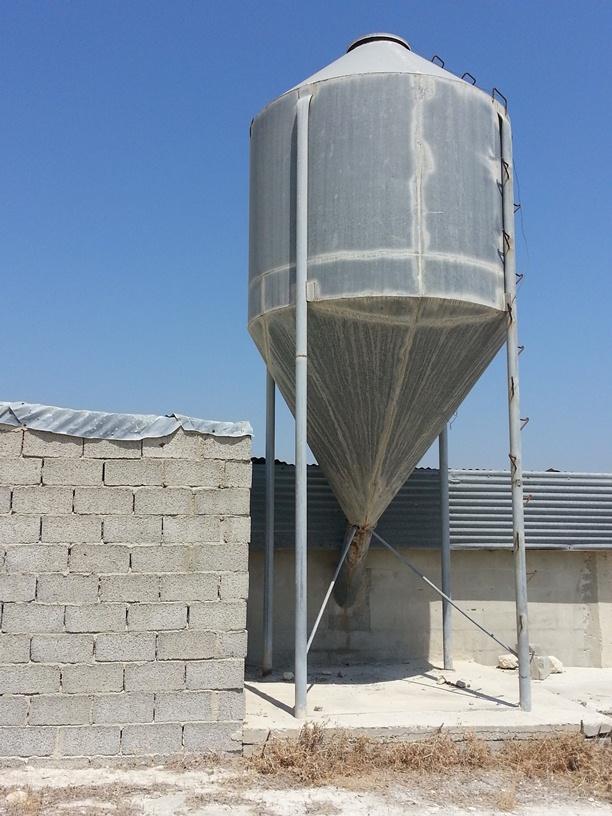
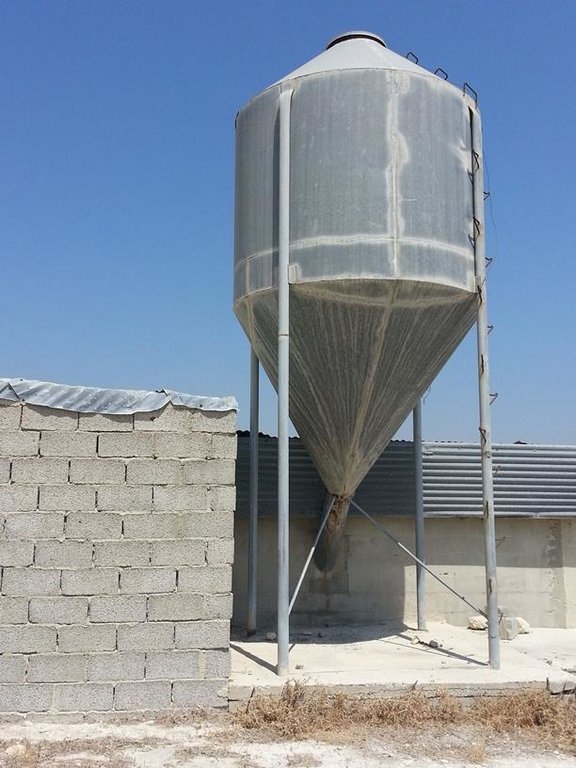
Goats graze on almost all plants even on thorny shrubs. The pastoralist in the past (some still do now a days) use to spread seeds on the grazing area in order to provide fodder for the animals. Another method is to provide fodder within the farm using dry seeds of wheat, barley, soya etc which can be stored in big silos.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is to provide to the animals with the food they need in order to minimize or even stop them from grazing on the wild flora such as shrubs, trees and annual plants. Within the study area, most of the vegetation is vanished and only traces of plant species can be found. Even the thorny shrubs like Callicotome villosa and Rhamnus oleiodes are suffering from overgrazing.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Fodder can be provided in-farm and out-farm. In-farm fodder is provided using a silo in which dry fodder can be store, mixed and deliver to the animals mechanically. Out-farm fodder is provided seasonally since the seeds should be seeded and plants must grow up before eaten by the animals
Natural / human environment: By providing fodder to the animals in-farm, grazing is avoided since the animals remain within the farm. This way, animal diseases transmission from one farm to another can be minimized. Also, animals may travel a long distance to find food whose energy miight be less than the energy they use.
Seeding on the hills will attract the goats and stop them from grazing on other wild plant species. Minimizing grazing will allow to the vegetation to recover and grow up providing good aesthetic view and also shelter for the wild animals. Furthermore, vegetation increase will contribute to the decrease of soil erosion and the increase of organic matter.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
قبرص
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Limassol
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Pissouri
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 100-10 كم2
التعليقات:
The total area in which goat and sheep farmer are allowed to grow animals is around 400 Km2. The area affected by overgrazing is around 100Km2
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
EU funding gave the opportunity to some new farmers to buy new equipment for fodder provision. In this way the new farmers were able to feed their animals and increase their productivity
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: March to JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 100Second longest growing period from month to month: September to December

أراضي الرعي
الرعي الواسع النطاق:
- رعي شبه مرتحل
- مربى ماشية محدد
نوع الحيوان:
- الماعز
- الأغنام
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): overgrazing due to a large amount of animals, drought, erosion
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): drought, poor calcareous soils, incomes are not enough to buy food
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: goats/ rabbits, birds
Ranching: goats
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)

أراضي الرعي
- Extensive grazing
3.4 إمدادات المياه
التعليقات:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الرعي وإدارة المراعي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة

التدابير البنيوية
- S11: غير ذلك
التعليقات:
Main measures: agronomic measures, structural measures
Specification of other structural measures: Use of Silos in order to provide fodder to the animals
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, legume inter-planting
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (large number of animals), change in temperature (hot summers & cold winters force the animals to eat more in order to obtain water and energy from plants), change of seasonal rainfall (summers without rain and winters with some rain), droughts (heavy droughts every 3-4 years), poverty / wealth (farmers can not afford to feed the animals)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (about 90 years ago), urbanisation and infrastructure development (Urbanisation mostly at the coastal zone has forced the animals to move to the North. A large number of animals is concentrated in the northern site, increasing the overgrazing problem), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (A highway road split the area in two), war and conflicts (In 1974 many refugees moved from the North to the South due to the invasion of Turkish troops. Most of them who established in the area became farmers, and therefore increased the number of animals)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (animal feeding specialist with good knowledge on goat and sheep fodder)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (be able to follow the specialist advice and protocol for feeding animals)
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of animal feeding on natural vegetation
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: cereal seeds (wheat, barley, etc)
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: seeds should be seeded by hand during the rainy season
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: spread the seeds before the last rainfall in spring
Structural measure: Silo
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Construction material (other): stainless steel
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 9,42m3
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
euro
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
0,77
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
38.85
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy or make a Silo | anytime |
| 2. | Buy cereal seeds (200kg) | |
| 3. | Buy legume seeds (200kg) |
التعليقات:
Inputs: Stainless steel
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 116,0 | 116,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Stainless steel silo | ha | 1,0 | 2589,0 | 2589,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Fodder transfer tubes | ha | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Agricultural | ha | 1,0 | 427,0 | 427,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 4132,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 5366,23 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
Life-span of cereal seeds: 6 months
Life-span of legumes seeds: 3-4 months
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | spreading seeds | during rainfall (oct - Mar) |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 233,0 | 233,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 427,0 | 427,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 660,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 857,14 | |||||
التعليقات:
Cost were calculated according to the farmers opinion which was confirmed by the agricultural department. Seeds and labor are calculated as units per ha and the silo per unit (farm)
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Cost for applying fodder is affected by 3 factors: a) the price of the Silo which is applied only once, b) the cost of the seeds and c) the labor needed for spreading the seeds. The slope in the area where the technology is applied is steep and makes the seeding difficult.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Annual rainfall for the year 2013 was 207 mm. From june to october rainfall was 0. In the last three years annual rainfall was between 207 and 540 mm
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
- قاحلة
Thermal climate class: tropics. Winter 0-25 °C, and Summer 20-45 °C
Thermal climate class: subtropics. During the winter, mean temperature can be 15-18 °C
According to the FAO, Cyprus is considered to be an arid to semi-arid area
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Altitudinal zone: 100-500 m a.s.l (The area where the technology is applied is 1km far from the sea)
Landforms: Hill slopes (The area of interest consists of steep hill slopes)
Slopes on average are rolling (most common) and hilly (sometimes after soil erosion)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- خشن / خفيف (رملي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average is very shallow (the area is considered to be rocky) to shallow (only where soil is concentrated)
Soil texture is coarse (Analysis has shown that soil texture is 50% sand, 25% silt and 25% Clay)
Soil fertility is low
Topsoil organic matter is medium where some vegetation is, low where no vegetation is and high where vegetation is
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor (inter patch), medium (patch-interpatch) or good (plant patch)
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water is poor/none (there is no surface water available in the area)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Thorny shrubs, olive and carob trees, annual grass
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: no young women are involved with goat farming
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land (they make profit).
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land (they barely survive).
Off-farm income specification: Some of the pastoralists who apply the SLM technology, have apartments which they rent to tourists during the summer season
Market orientation of production system: Equipment and structure subsidy (50% of the equipment and structures are funded)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial): Pastoralists receive subsidy from EU funds annually
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق واسع
التعليقات:
The animal numbers are 10 times the amount permitted to graze in the area
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
- فردي
التعليقات:
More than 70% of the land belongs to the government (forestry department) and the land is open to everybody. The pastoralists do not pay rent for using the land. The land which belongs to individuals is used by the owners or is been rented to the pastoralists
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
Spreading cereals and legumes
إنتاج حيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
By providing fodder all year round
خطر فشل الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
By providing fodder all year round
تنوع المنتج
التعليقات/ حدد:
Better quality of dairy products
إدارة الأراضي
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
During the first year, the cost of the Silo
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to production increase
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
In-farm fodder provision. Labor hours are reduced due to the presence of fodder in the silo. Simplified farm operations through using the silo.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Animals from different farms are no more in contact
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Seeding on the hill reduces erosion
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
التعليقات/ حدد:
Between pastoralists
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Shepherds who provide fodder and/or are seeding cereals and legumes on grazing land, produce more milk and meat. Therefore, they have higher incomes and a better life. They are able to send their children to school and provide a health care insurance to their families.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to vegetation cover
التبخر
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to vegetation cover
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to vegetation cover
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Due to soil cover by cereals and legumes
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
May be in the near future, antagonism between cereals and legumes with other wild type species will appear
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Especially birds
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الأضرار التي لحقت بحقول الجيران
التعليقات/ حدد:
On site since the animals will graze in the seeded area
الضرر على البنية التحتية العامة/ الخاصة
التعليقات/ حدد:
On site since the animals will graze in the seeded area
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | ليس جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | غير معروف |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | ليس جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | غير معروف |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي للغاية
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
Shepherds who apply the technology and are in a better socio-economical status are satisfied with their incomes but they believe that things could get better. Shepherds who don't apply the technology are poor, not satisfied with the incomes they receive and at the same time they are negative in applying the technology although they see other shepherds being in a better socio-economic status than them.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: New farmers-shepherds can have up to 60% funding from EU and government funds for construction and equipment
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The cost of buying fodder is extremely high. Also the equipments (silo) is considered to be expensive.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Using the Silo for providing fodder, they spend less hours in the farm. |
| By providing fodder, the quality and quantity of milk and meat is better |
| By keeping the animals in the farm, they save work hours and also the threat of animal poisoning is minimized |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
By providing fodder in and out of the farm the animals receive a better quality of fodder and the right quantities of fodder they need. How can they be sustained / enhanced? experts can give advices to the shepherds about the type of fodder, and the quantity during different seasons |
|
Through grazing in a specific area marked and seeded by the shepherd, the animals avoid direct contact with other animals. This minimizes the spread of diseases between animals of different farms. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Shepherds should come to an agreement about the area their animals graze and create borders |
|
Seeding cereals and legumes within the grazing areas decreases overgrazing on shrubs and annual plants How can they be sustained / enhanced? in the case where the shepherd is leading the animals, he should not allow the animals to graze on shrubs |
|
The presence of a Silo in a farm makes fodder provision easier and therefore less work is required How can they be sustained / enhanced? Government funding can cover the cost of the silo |
| seeding in the grazing area leads to improved soil cover which minimizes soil erosion |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| It is difficult to spread seeds on the rocky hills | |
| Buying fodder is expensive |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Not all shepherd are able to buy the Silo and large amounts of fodder to store in the silo | Government funding can cover the cost of the silo |
| The Randi forest area is suffering from prolonged droughts. Seeding cereals in the grazing land will not be achieved without rain. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية