Check Dam [الصين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Haiyan WEI
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Lan Sha Ba
technologies_1365 - الصين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Check Dam [الصين]
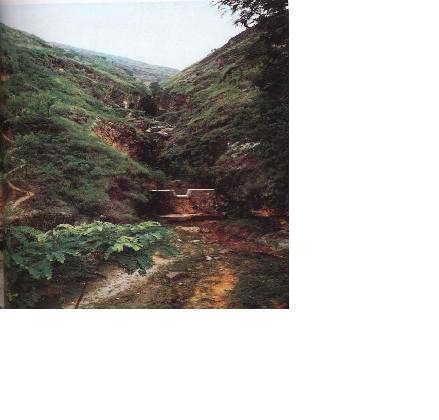
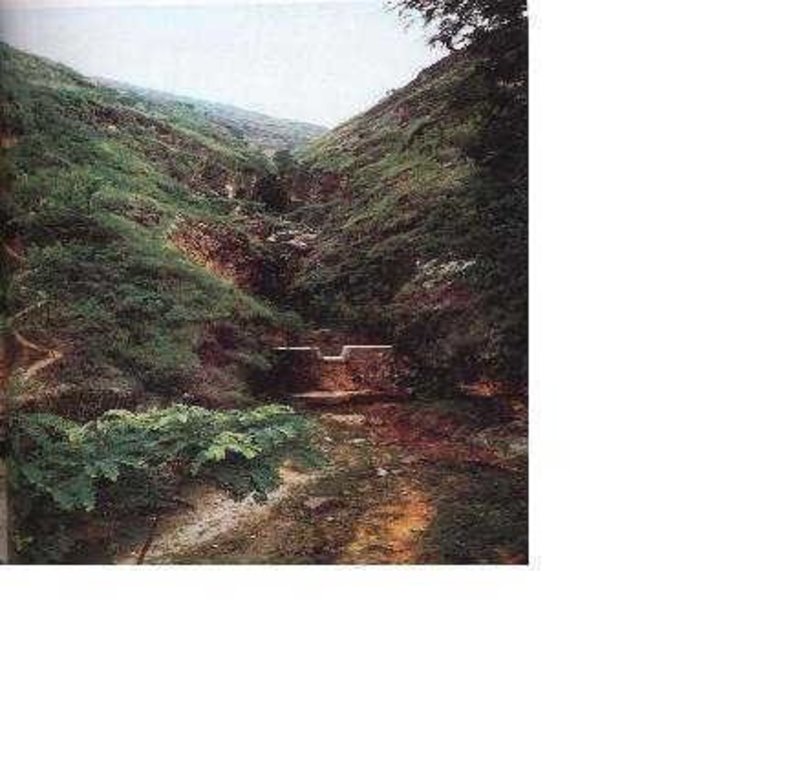
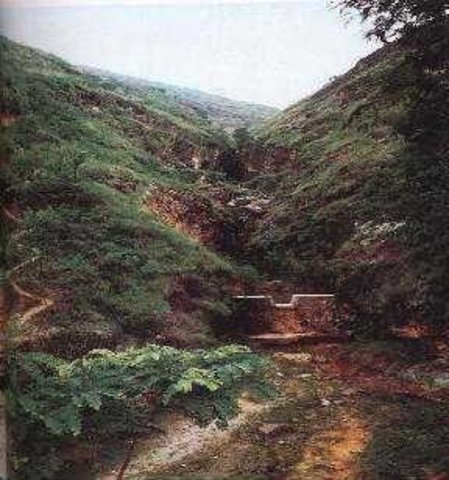
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- جامع المعلومات: Haiyan WEI
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Check dam refers to dam that constructed in the gullies or river ways and the height of the dam is often lower than 5m.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Check dams are built in the gully systems to harvest water and sediment. Usually many check dams are built in a gully or waterway to control the gully erosion. Check dams can be classified into "masonry dam", "check dam of earth", "check dam with willow" according to materials. Some strong masonry can last more than 10 years. As willow pegs in the "check dam with willow" can grow into timber after years.
Maintenance work should be done before rainy seasons every year so as to prevent the dam from destruction.
Following are the building procedures:
Masonry dam & check dam using earth:
1. Preparation---Removing grass, roots and surface soil; Digging a channel along an axis of a check dam in order to combine the dam and the bed firmly.
2. Construction---If a dam is planned to be made of earth, do scarification first, then adding earth (about 0.3m thick) and ramming it into 0.2m layer by layer. Building the dam with stones and/or rocks.
3. Base---If a bed of a gully consists of earth or sand, "base" should be built at the downstream feet of the dam. Length of the base should be twice as that of the dam and thickness should be 50-70cm.
4. Building a spillway at the top of the dam.
Check dam with willow:
1. Removing grass, roots and surface soil.
2. Cutting branches from willow; chopping the branches into pegs with the thick ends wedge.
3. Inserting the pegs into the ground.
4. Entwining wattles from willows around the pegs compactly.
5. Filling the space between two rows of pegs with stones, bricks, treetops etc. Making the stuff surface 10cm lower than the pegtop.
6. Combining the dam into a whole with iron chains.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الصين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Shanxi, Beijing
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت التقنيةا موزعة بالتساوي على منطقة ما، حدد المساحة المغطاة (بالكيلومتر المربع):
145,0
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
التعليقات:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 145 km2.
As a traditional SWC technology, check dams have been used widely in China.
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أكثر من 50 عامًا (تقليدي)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- كجزء من النظام التقليدي (> 50 عامًا)
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Experiences from the local people's many SWC practice.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب - قمح (شتوي)
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep

أراضي الرعي

المجاري المائية، المسطحات المائية، الأراضي الرطبة
- البرك والسدود
المنتجات / الخدمات الرئيسية:
Check Dam
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Serious gully erosion by water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies were widened and deepened greatly in the rainy season and crop land area is decreasing above the gully edges.
Constraints of urban land use
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة المياه السطحية (الينابيع، الأنهار، البحيرات، البحار)
- reduce loss of cropland
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- S5: السدود، الأحواض الصغيرة، البرك
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- (Wg):الانجراف الخلجاني/ الخلجان
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Description of Building Check Dam Procedures
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shanxi, Beijing
Date: 2000
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Construction material (earth): Loessial earth
Construction material (stone): if available
Construction material (wood): willow pegs
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 16%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 90%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:30
المؤلف:
LIU Baoyuan, Beijing China
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
RMB Yuan
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
8,27
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
2.00
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation | |
| 2. | Construction | Before rainy season |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 120 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | reparing after rainstorm. |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
التعليقات:
Length, width and height of check dams.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Sizes and materials of the check dams.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
580,00
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- حالات مقعرة
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average also gentle, moderate and rolling
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
مستوى المكننة:
- الجر الحيواني
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (No difference).
Off-farm income specification: The land users who made the check dams can own more "deposited land". Generally these deposited land is fertile and produces high yield.
Level of mechanization: animal traction: on steep slope
Level of mechanization: mechanized/motorized: plateau or gully flat.
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
48
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
30
التربة
فقدان التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
180
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
110
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- > 50%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
180 household are using the technology and represent 65 percent of the poeple living in the stated area
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 11-50%
التعليقات:
55% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
150 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In the past (planning economy)SWC activities are administrative action to call local land users to carry out, but nowadays in the market economic conditions, if no or little benefits obtained, land users would not like to do any more.
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing.. 2000.3.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Consideration about the check dam design and application. Liu shunzong. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1990.6.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Special Planning of Soil and Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region, Shanxi Province. 1986-2000.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
The application of the Check dam with willow in controlling gully erosion.Tu xingwen. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1986.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Check Dam [الصين]
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- جامع المعلومات: Haiyan WEI
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية