Check Dam [Chine]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Haiyan WEI
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateurs : David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Lan Sha Ba
technologies_1365 - Chine
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Check Dam [Chine]
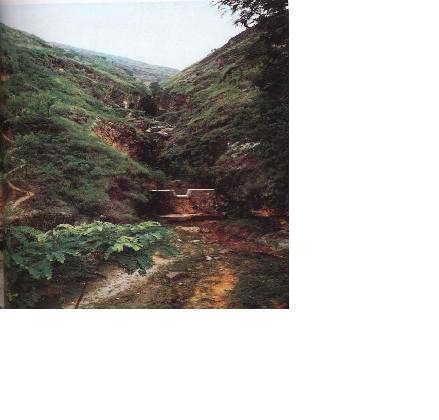
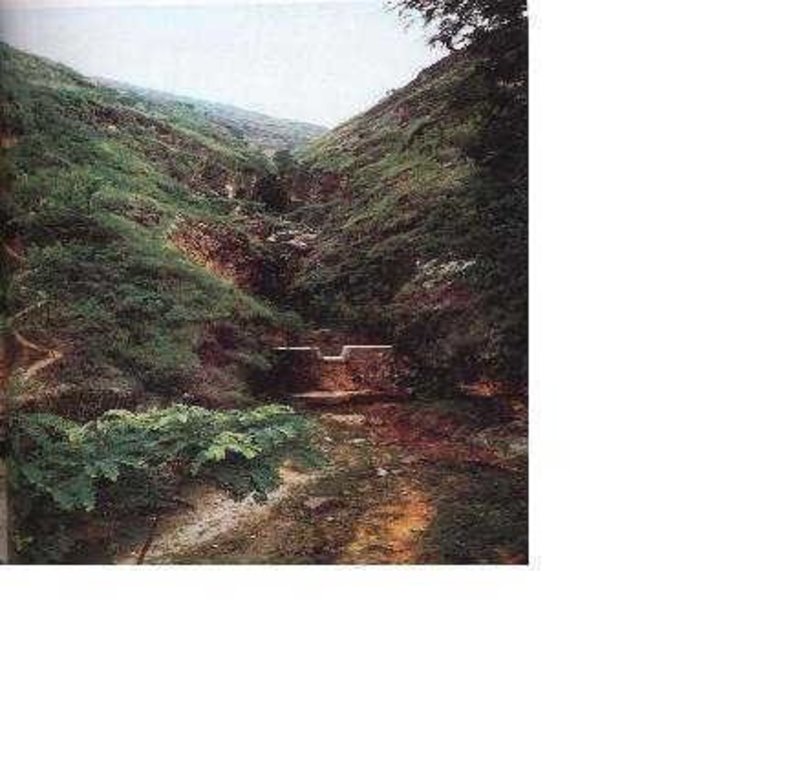
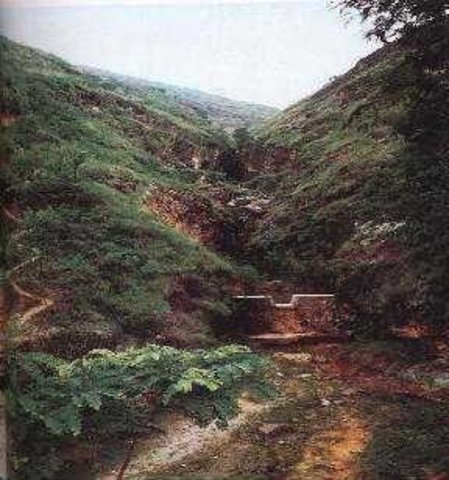
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- Compilateur : Haiyan WEI
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Check dam refers to dam that constructed in the gullies or river ways and the height of the dam is often lower than 5m.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Check dams are built in the gully systems to harvest water and sediment. Usually many check dams are built in a gully or waterway to control the gully erosion. Check dams can be classified into "masonry dam", "check dam of earth", "check dam with willow" according to materials. Some strong masonry can last more than 10 years. As willow pegs in the "check dam with willow" can grow into timber after years.
Maintenance work should be done before rainy seasons every year so as to prevent the dam from destruction.
Following are the building procedures:
Masonry dam & check dam using earth:
1. Preparation---Removing grass, roots and surface soil; Digging a channel along an axis of a check dam in order to combine the dam and the bed firmly.
2. Construction---If a dam is planned to be made of earth, do scarification first, then adding earth (about 0.3m thick) and ramming it into 0.2m layer by layer. Building the dam with stones and/or rocks.
3. Base---If a bed of a gully consists of earth or sand, "base" should be built at the downstream feet of the dam. Length of the base should be twice as that of the dam and thickness should be 50-70cm.
4. Building a spillway at the top of the dam.
Check dam with willow:
1. Removing grass, roots and surface soil.
2. Cutting branches from willow; chopping the branches into pegs with the thick ends wedge.
3. Inserting the pegs into the ground.
4. Entwining wattles from willows around the pegs compactly.
5. Filling the space between two rows of pegs with stones, bricks, treetops etc. Making the stuff surface 10cm lower than the pegtop.
6. Combining the dam into a whole with iron chains.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Chine
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Shanxi, Beijing
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
145,0
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 100-1 000 km2
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 145 km2.
As a traditional SWC technology, check dams have been used widely in China.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
Experiences from the local people's many SWC practice.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Oui
Précisez l'utilisation mixte des terres (cultures/ pâturages/ arbres):
- Agropastoralisme (y compris les systèmes culture-élevage intégrés)

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - maïs
- céréales - blé d'hiver
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep

Pâturages

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- Etangs, barrages, retenues d'eau
Principaux produits/ services:
Check Dam
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Serious gully erosion by water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies were widened and deepened greatly in the rainy season and crop land area is decreasing above the gully edges.
Constraints of urban land use
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- mixte: pluvial-irrigué
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
- reduce loss of cropland
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

structures physiques
- S5: Barrages/retenues, micro-bassins, étangs
Commentaires:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wg: ravinement/ érosion en ravines
Commentaires:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Description of Building Check Dam Procedures
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shanxi, Beijing
Date: 2000
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Construction material (earth): Loessial earth
Construction material (stone): if available
Construction material (wood): willow pegs
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 16%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 90%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:30
Auteur:
LIU Baoyuan, Beijing China
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
RMB Yuan
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
8,27
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
2.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation | |
| 2. | Construction | Before rainy season |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 120 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | reparing after rainstorm. |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
Commentaires:
Length, width and height of check dams.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Sizes and materials of the check dams.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
580,00
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Slopes on average also gentle, moderate and rolling
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- moyen (1-3%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Revenus hors exploitation:
- 10-50% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Niveau de mécanisation:
- traction animale
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (No difference).
Off-farm income specification: The land users who made the check dams can own more "deposited land". Generally these deposited land is fertile and produces high yield.
Level of mechanization: animal traction: on steep slope
Level of mechanization: mechanized/motorized: plateau or gully flat.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
48
Quantité après la GDT:
30
Sols
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
180
Quantité après la GDT:
110
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
180 household are using the technology and represent 65 percent of the poeple living in the stated area
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
Commentaires:
55% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
150 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In the past (planning economy)SWC activities are administrative action to call local land users to carry out, but nowadays in the market economic conditions, if no or little benefits obtained, land users would not like to do any more.
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing.. 2000.3.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Consideration about the check dam design and application. Liu shunzong. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1990.6.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Special Planning of Soil and Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region, Shanxi Province. 1986-2000.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
The application of the Check dam with willow in controlling gully erosion.Tu xingwen. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1986.
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Check Dam [Chine]
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- Compilateur : Haiyan WEI
Modules
Aucun module trouvé