Pepsee micro-irrigation system [الهند]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Shilp Verma
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Pepsee
technologies_1477 - الهند
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Sadagani Amitabha
International Development Enterprises
الهند
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
IWMI International Water Management Institute (IWMI) - الهنداسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
International Development Enterprises - India (iDE-India) - الولايات المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Market support and branding for input quality (Krishak … [الهند]
Market development and support through use of a brand name - Krishak Bandhu ('the farmer's friend') - to help ensure quality amongst manufacturers and suppliers of drip irrigation equipment.
- جامع المعلومات: Shilp Verma
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
A grassroots innovation that offers most of the advantages of conventional micro-irrigation at a much lower establishment cost.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
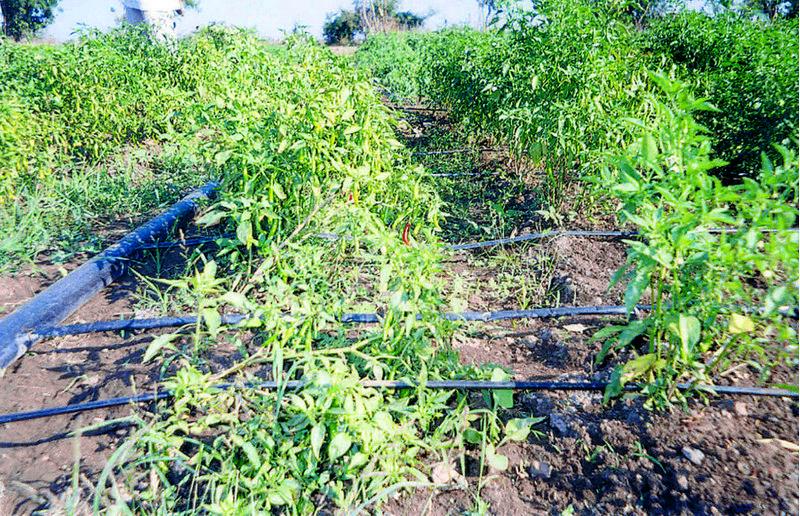
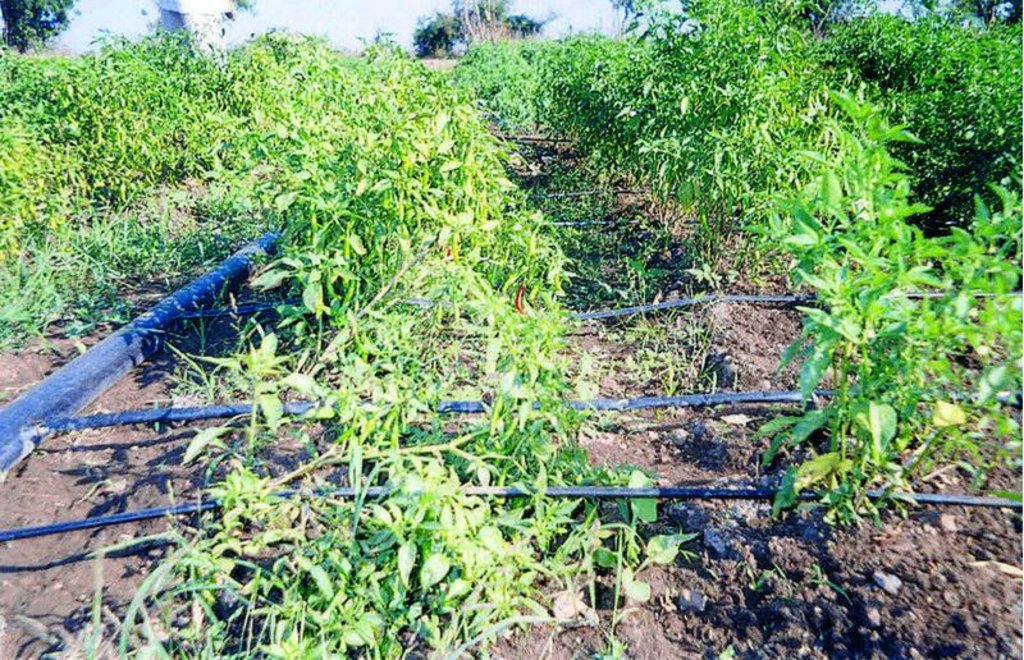
الوصف:
The continued expansion of irrigation in India is causing increasing water shortages. This may be compounded by the potential effects of climate change. Drip irrigation - delivering small amounts of water directly to the plants through pipes - is a technology that could help farmers deal with water constraints. It is considerably more efficient in terms of water use than the usual open furrows or flood irrigation.
In West Nimar, Madhya Pradesh, droughts, diminishing groundwater, limited and erratic power supply coupled with poverty, compelled farmers to look for a technology that would enable them to irrigate their crops (mainly cotton) within these constraints. They tried out several cost-saving options such as using old bicycle tubes instead of the conventional drip irrigation pipes. But nothing caught on - until about five years ago - when a local farmer experimented with thin poly-tubing normally used for frozen fruit-flavoured ‘lollypops’ called pepsee. It spread to neighbouring cotton farmers, and its popularity has meant that today pepsee has become widespread in the region. Pepsee micro-irrigation systems slowly and regularly apply water directly to the root zone of plants through a network of economically designed plastic pipes and low-discharge emitters.
Technically speaking pepsee systems use low density polythene (65-130 microns) tubes which are locally assembled. Being a low pressure system the water source can be an overhead tank or a manually operated water pump to lift water from a shallow water table.
Such a system costs less than US$ 40 per hectare for establishment. But the tubes have a short life span of one (or two) year(s); an equivalent standard buried strip drip irrigation system amounts to between five and ten times the initial cost. The latter would, however, last for five to ten years. The critical factor is the low entry cost. Pepsee systems thus act as ‘stepping stones’ for poor farmers who are facing water stress but are short of capital and cannot afford to risk relatively large investment in a technology which is new to them, and whose returns are uncertain. The technology is today available in two variants: the original white pepsee and a recently introduced black pepsee which is of slightly better quality.
Recently, a more durable and standardised version of pepsee, given the brand name ‘Easy Drip’, has been developed and promoted by a local NGO, IDEI (see corresponding approach). Easy Drip is one product within a set of affordable micro-irrigation technologies (AMIT) promoted by IDEI.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الهند
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Madhya Pradesh
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
West Nimar
Map
×2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- محاصيل الألياف - قطن
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Mar
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Acute groundwater stress associated with lowering of the groundwater table limits water for irrigation, coupled with poverty and reluctance to risk investing in relatively expensive- but efficient - drip irrigation systems.
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- ري كامل
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إدارة الري (بما في ذلك إمدادات المياه والصرف الصحي)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير البنيوية

التدابير الإدارية
التعليقات:
Main measures: structural measures, management measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تدهور المياه
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, droughts, land tenure (land subdivision), Land alienation
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
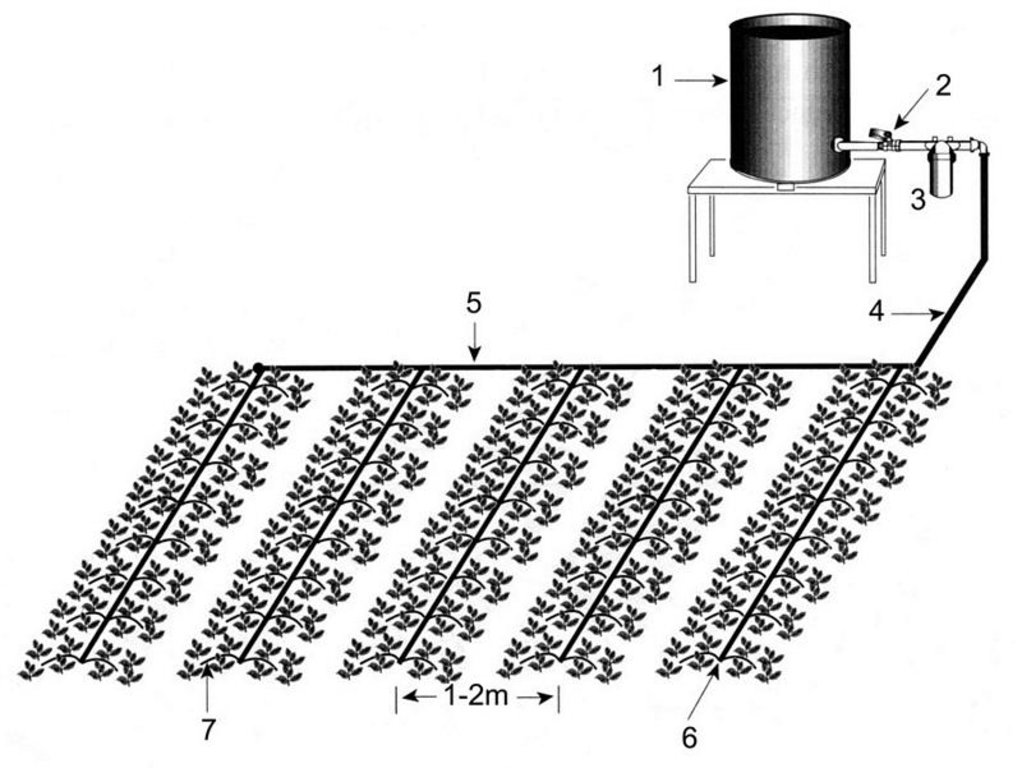
Components of pepsee/‘Easy Drip’ irrigation systems are described below.
1) Water source: For pepsee, commonly a water pump (in most cases electric) is used to lift water from a well and directly feed the irrigation system.
Alternatively, an overhead tank (minimum of 1 m above ground level) can be used for smaller systems up to 400 m2 area.
2) Control valve: valve made of plastic or metal to regulate pressure and flow of water into the system
3) Filter: Strainer filter to ensure that clean water enters into the system (optional in pepsee systems).
4) Mainline: 50 mm PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) or PE (Polyethylene) pipe to convey water from source to the sub-main.
5) Sub-main: PVC/PE pipe to supply water to the lateral pipes which are connected to the sub-main at regular intervals.
6) Lateral: PE pipes along the rows of the crops on which emitters are connected directly. Pipe size is 12–16 mm.
7) Emitters/micro-tubes: Device through which water is emitted at the root zone of the plant with required discharge. In pepsee farmers simply make pin holes in the plastic tube for water to pass. Easy Drip has inbuilt drippers/outlets along the lateral line which give a continuous wetting strip.
It is mainly used for row crops.
Pepsee uses cheap, recycled plastic tubes instead of the rubber pipes used in conventional drip irrigation kits. Space between emitters is variable, for cotton cultivation it is commonly 1.2 m (between plants, within and between rows). There is (usually) one emitter for each plant. Different sizes of valves, mainlines, etc, are available, depending on flow rate of water in the system. Additional components are joints (connectors) and pegs (used to hold the lateral and micro-pipes in place).
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water supply, improved water-use efficiency (reduced loss, well directed, selective - and targeted irrigation
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, higher - germination and establishment rate
Structural measure: irrigation infrastructure
Construction material (other): poly-tubes - low density polythene (65-130 microns)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from furrow to drip irrigation
المؤلف:
Sijali IV 2001, Drip irrigation, RELMA, Nairobi
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of water pump, control valve, filter (optional) and PVC piping(main/sub-main and lateral pipes). | dry season |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Lateral piping (Pepsee tube) | ha | 1,0 | 17,0 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Main/sub-main PVC piping | ha | 1,0 | 34,0 | 34,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Other parts (valves, joints et | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 95,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 95,0 | |||||
التعليقات:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Re-installation of lateral pepsee tubes | dry season/ (every 1–2 years). |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Lateral piping (Pepsee tube) | ha | 1,0 | 17,0 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 21,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 21,0 | |||||
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- متوسطة (1-3%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (black cotton soil; mostly vertisols, partly inceptisols and entisols)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- تجاري/سوق
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
منطقة الإنتاج
التعليقات/ حدد:
More land brought under irrigation. This is seen as a negative aspect
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
irrigated area
التعليقات/ حدد:
Greater irrigated area with same amount of water
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
استخدام الأراضي / حقوق المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
More farmers able to irrigate their land
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
Poverty reduction
Social acceptance
التعليقات/ حدد:
Drip irrigation confers the image of a progressive farmer
الآثار الايكولوجية
الآثار الايكولوجية الأخرى
Water use efficiency
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: No detailed information available regarding spread - though this is estimated to be several thousand farmers within West Nimar. All adoption has been spontaneous, without incentives, and the group which has adopted best comprises those who were previously using furrow irrigation. A large number of pepsee adopters are the resource poor farmers but rich farmers have also adopted pepsee.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Low initial investment and recurrent costs: risk in adopting new system limited How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep costs of new variations of pepsee low. |
|
There are significant benefits in terms of reduced water use per unit of land, and in terms of yield per unit land area as well. |
| Few extra skills required to implement and operate the system. |
|
An eventual shift to conventional drip system is feasible: pepsee acts as a ’stepping stone’ How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote improved drip systems where pepsee has taken off. |
|
Higher yields, better quality, higher germination rate, lower incidence of pest attack; facilitates pre-monsoon sowing. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
|
Pepsee is based on drip pipes which have a limited life: delicate and cannot withstand high pressure |
Develop/use stronger piping materials such as ‘Easy Drip’. |
|
The increased water use efficiency has allowed an expansion in the area irrigated – which has used up the water ‘saved’. |
Develop/use stronger piping materials such as ‘Easy Drip’. |
|
Pepsee systems require replacement of lateral pipes each year and thus incur recurrent input and labour costs |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Verma S, Tsephal S. and Jose T: Pepsee Systems: grassroots innovation under groundwater stress. Water Policy, 6,pp. 303–318.. 2004.
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
http://www.iwaponline.com/wp/00604/wp006040303.htm
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Market support and branding for input quality (Krishak … [الهند]
Market development and support through use of a brand name - Krishak Bandhu ('the farmer's friend') - to help ensure quality amongst manufacturers and suppliers of drip irrigation equipment.
- جامع المعلومات: Shilp Verma
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية