Pepsee micro-irrigation system [Энэтхэг ]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Shilp Verma
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Pepsee
technologies_1477 - Энэтхэг
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Sadagani Amitabha
International Development Enterprises
Энэтхэг
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
International Water Management Institute (International Water Management Institute) - ЭнэтхэгТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
International Development Enterprises - India (iDE-India) - Америк1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (WOCAT ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Market support and branding for input quality (Krishak … [Энэтхэг ]
Market development and support through use of a brand name - Krishak Bandhu ('the farmer's friend') - to help ensure quality amongst manufacturers and suppliers of drip irrigation equipment.
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Shilp Verma
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
A grassroots innovation that offers most of the advantages of conventional micro-irrigation at a much lower establishment cost.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
The continued expansion of irrigation in India is causing increasing water shortages. This may be compounded by the potential effects of climate change. Drip irrigation - delivering small amounts of water directly to the plants through pipes - is a technology that could help farmers deal with water constraints. It is considerably more efficient in terms of water use than the usual open furrows or flood irrigation.
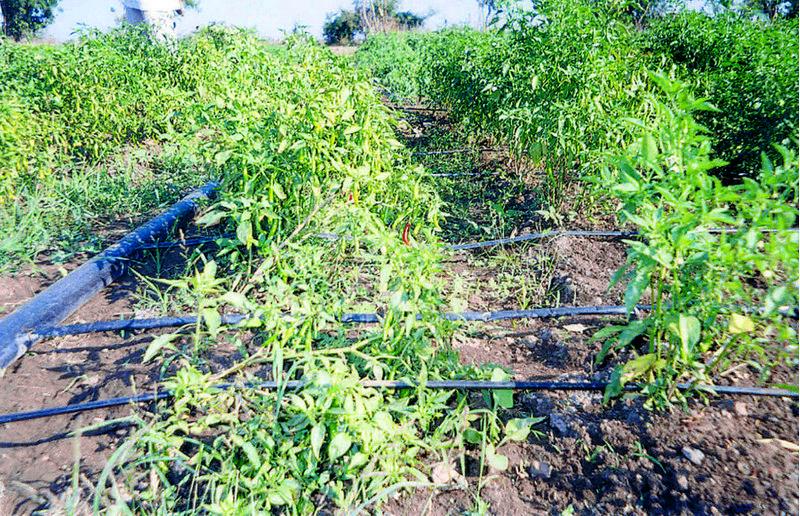
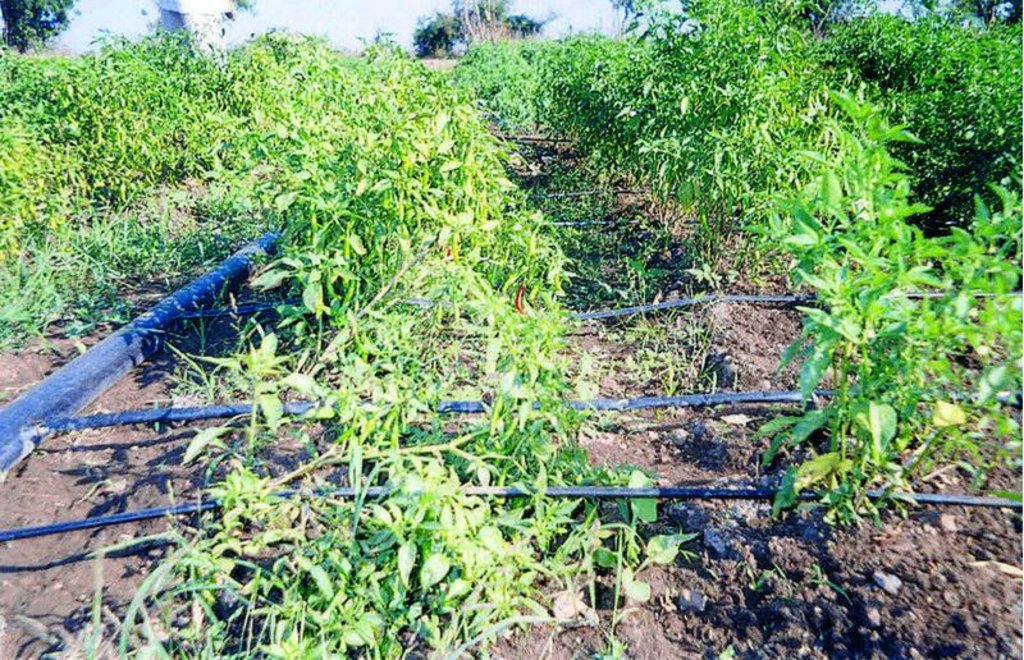
In West Nimar, Madhya Pradesh, droughts, diminishing groundwater, limited and erratic power supply coupled with poverty, compelled farmers to look for a technology that would enable them to irrigate their crops (mainly cotton) within these constraints. They tried out several cost-saving options such as using old bicycle tubes instead of the conventional drip irrigation pipes. But nothing caught on - until about five years ago - when a local farmer experimented with thin poly-tubing normally used for frozen fruit-flavoured ‘lollypops’ called pepsee. It spread to neighbouring cotton farmers, and its popularity has meant that today pepsee has become widespread in the region. Pepsee micro-irrigation systems slowly and regularly apply water directly to the root zone of plants through a network of economically designed plastic pipes and low-discharge emitters.
Technically speaking pepsee systems use low density polythene (65-130 microns) tubes which are locally assembled. Being a low pressure system the water source can be an overhead tank or a manually operated water pump to lift water from a shallow water table.
Such a system costs less than US$ 40 per hectare for establishment. But the tubes have a short life span of one (or two) year(s); an equivalent standard buried strip drip irrigation system amounts to between five and ten times the initial cost. The latter would, however, last for five to ten years. The critical factor is the low entry cost. Pepsee systems thus act as ‘stepping stones’ for poor farmers who are facing water stress but are short of capital and cannot afford to risk relatively large investment in a technology which is new to them, and whose returns are uncertain. The technology is today available in two variants: the original white pepsee and a recently introduced black pepsee which is of slightly better quality.
Recently, a more durable and standardised version of pepsee, given the brand name ‘Easy Drip’, has been developed and promoted by a local NGO, IDEI (see corresponding approach). Easy Drip is one product within a set of affordable micro-irrigation technologies (AMIT) promoted by IDEI.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Энэтхэг
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Madhya Pradesh
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
West Nimar
Map
×2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- Үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)

Тариалангийн газар
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- даавууны таримал - хөвөн
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Mar
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Acute groundwater stress associated with lowering of the groundwater table limits water for irrigation, coupled with poverty and reluctance to risk investing in relatively expensive- but efficient - drip irrigation systems.
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Бүрэн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Усжуулалтын менежмент (усан хангамж, ус зайлуулалт зэрэг.)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
Тайлбар:
Main measures: structural measures, management measures
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Усны доройтол
- Гүний усны чанар муудах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, droughts, land tenure (land subdivision), Land alienation
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
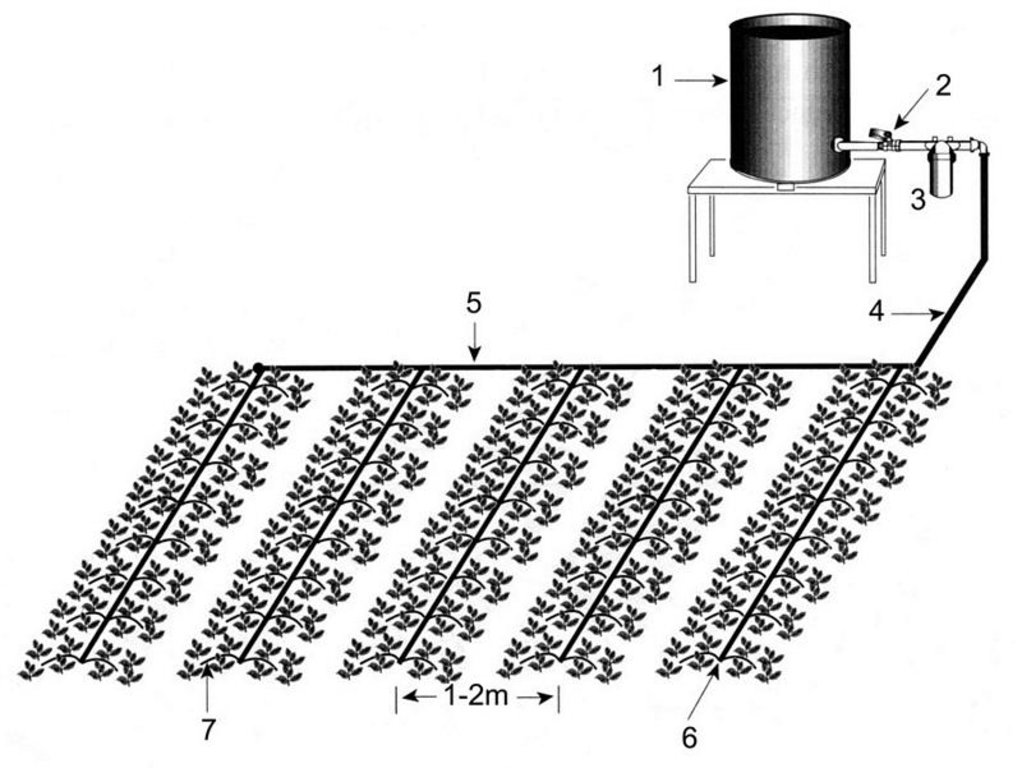
Components of pepsee/‘Easy Drip’ irrigation systems are described below.
1) Water source: For pepsee, commonly a water pump (in most cases electric) is used to lift water from a well and directly feed the irrigation system.
Alternatively, an overhead tank (minimum of 1 m above ground level) can be used for smaller systems up to 400 m2 area.
2) Control valve: valve made of plastic or metal to regulate pressure and flow of water into the system
3) Filter: Strainer filter to ensure that clean water enters into the system (optional in pepsee systems).
4) Mainline: 50 mm PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) or PE (Polyethylene) pipe to convey water from source to the sub-main.
5) Sub-main: PVC/PE pipe to supply water to the lateral pipes which are connected to the sub-main at regular intervals.
6) Lateral: PE pipes along the rows of the crops on which emitters are connected directly. Pipe size is 12–16 mm.
7) Emitters/micro-tubes: Device through which water is emitted at the root zone of the plant with required discharge. In pepsee farmers simply make pin holes in the plastic tube for water to pass. Easy Drip has inbuilt drippers/outlets along the lateral line which give a continuous wetting strip.
It is mainly used for row crops.
Pepsee uses cheap, recycled plastic tubes instead of the rubber pipes used in conventional drip irrigation kits. Space between emitters is variable, for cotton cultivation it is commonly 1.2 m (between plants, within and between rows). There is (usually) one emitter for each plant. Different sizes of valves, mainlines, etc, are available, depending on flow rate of water in the system. Additional components are joints (connectors) and pegs (used to hold the lateral and micro-pipes in place).
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water supply, improved water-use efficiency (reduced loss, well directed, selective - and targeted irrigation
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, higher - germination and establishment rate
Structural measure: irrigation infrastructure
Construction material (other): poly-tubes - low density polythene (65-130 microns)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: from furrow to drip irrigation
Зохиогч:
Sijali IV 2001, Drip irrigation, RELMA, Nairobi
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of water pump, control valve, filter (optional) and PVC piping(main/sub-main and lateral pipes). | dry season |
4.4 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Lateral piping (Pepsee tube) | ha | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Main/sub-main PVC piping | ha | 1.0 | 34.0 | 34.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Other parts (valves, joints et | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 95.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 95.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Re-installation of lateral pepsee tubes | dry season/ (every 1–2 years). |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Lateral piping (Pepsee tube) | ha | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 21.0 | |||||
| Технологи сайжруулах нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 21.0 | |||||
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас хуурай
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil texture: Fine/heavy (black cotton soil; mostly vertisols, partly inceptisols and entisols)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын %10 доош хувь
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Хувь хүн, цол эргэм бүхий
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
Газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
More land brought under irrigation. This is seen as a negative aspect
Орлого, зарлага
хөдөлмөр хүчний хэмжээ
Бусад нийгэм-эдийн засгийн нөлөөллүүд
irrigated area
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Greater irrigated area with same amount of water
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
газар ашиглалт / усны эрх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
More farmers able to irrigate their land
Нийгэм, эдийн засгийн хувьд эмзэг бүлгийнхний нөхцөл байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Poverty reduction
Social acceptance
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Drip irrigation confers the image of a progressive farmer
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Бусад экологийн үр нөлөө
Water use efficiency
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
Технологийг өөрийн талбайд нэвтрүүлсэн бусад иргэдээс хэд нь үүнийг өөрийн хүчээр, өөрөөр хэлбэл ямар нэг материал, техникийн дэмжлэг, төлбөр авалгүй хийсэн бэ?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: No detailed information available regarding spread - though this is estimated to be several thousand farmers within West Nimar. All adoption has been spontaneous, without incentives, and the group which has adopted best comprises those who were previously using furrow irrigation. A large number of pepsee adopters are the resource poor farmers but rich farmers have also adopted pepsee.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Low initial investment and recurrent costs: risk in adopting new system limited How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep costs of new variations of pepsee low. |
|
There are significant benefits in terms of reduced water use per unit of land, and in terms of yield per unit land area as well. |
| Few extra skills required to implement and operate the system. |
|
An eventual shift to conventional drip system is feasible: pepsee acts as a ’stepping stone’ How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote improved drip systems where pepsee has taken off. |
|
Higher yields, better quality, higher germination rate, lower incidence of pest attack; facilitates pre-monsoon sowing. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
|
Pepsee is based on drip pipes which have a limited life: delicate and cannot withstand high pressure |
Develop/use stronger piping materials such as ‘Easy Drip’. |
|
The increased water use efficiency has allowed an expansion in the area irrigated – which has used up the water ‘saved’. |
Develop/use stronger piping materials such as ‘Easy Drip’. |
|
Pepsee systems require replacement of lateral pipes each year and thus incur recurrent input and labour costs |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Verma S, Tsephal S. and Jose T: Pepsee Systems: grassroots innovation under groundwater stress. Water Policy, 6,pp. 303–318.. 2004.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
http://www.iwaponline.com/wp/00604/wp006040303.htm
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Market support and branding for input quality (Krishak … [Энэтхэг ]
Market development and support through use of a brand name - Krishak Bandhu ('the farmer's friend') - to help ensure quality amongst manufacturers and suppliers of drip irrigation equipment.
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Shilp Verma
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна