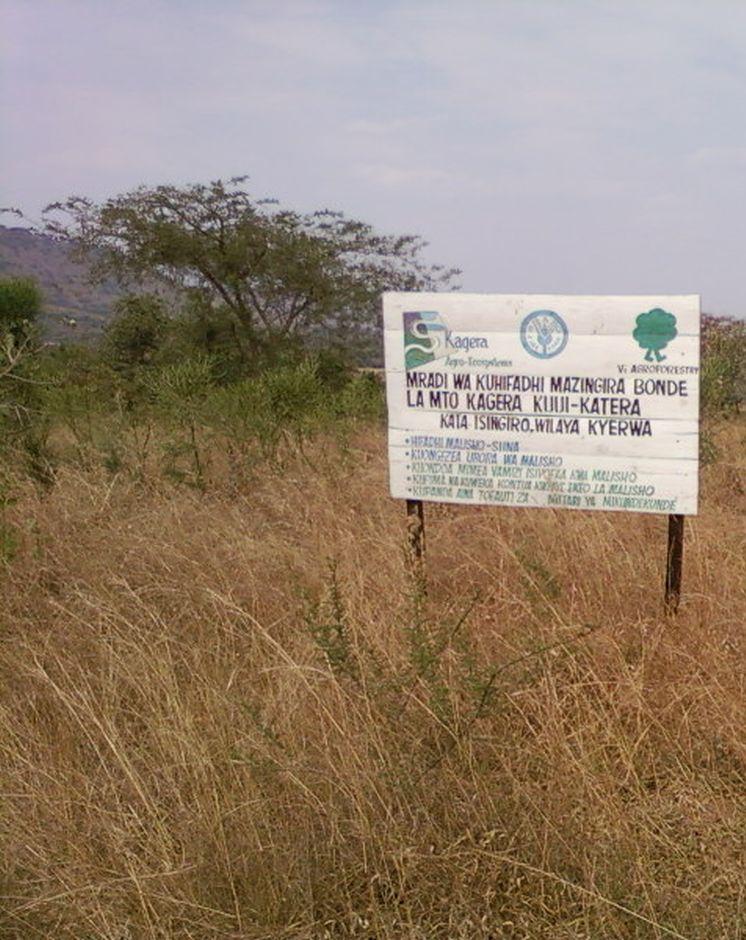
Range enclosures [تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Godfrey Baraba
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Hifadhi ya malisho
technologies_1612 - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Pesha Wambura
Kyerwa District Council
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Bubelwa Allani
Misenyi District Council
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدةاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدةاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Kyerwa District Council - تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Is the restriction, reseedling of desmodium decoloratum, stylothensis hamata and Stilozobium spps in the demarcated overgrazed land.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
The grazing land enclosure combined with quality pastures’ reseeding is the identification and demarcation of the degraded grazing land, reseeding palatable grass species and legumes with application of rotational grazing system. The technology is applied on the grazing land in the tropics, sub humid, gentle undulating upland, seasonal swamps to ensure SaLM with increased quantity and quality of pasture production. The land cultivation is done manually using hand hoes, in the mixed production system. The land ownership is communal and the land use right is organized (grazing land is demarcated) for all livestock keepers to graze their livestock. The establishment procedures includes planting of Euphobia spps along the borders, reseeding palatable grasses spps on the bare spots, plough and drill legume seeds intergraded with grasses. The maintenance procedures require range patrol, paddocks (fences and roads) maintenance. The average cost to establish one hector of the technology is US$ 122.11 while the maintenance of one hector is US$ 41.72 the technology was introduced by Kagera TAMP in 2012 using FFS methodology. Hay making is considered to be supportive technology that can add effectiveness to the main technology.
Purpose of the Technology: The major purpose is to restore soil vegetative cover, increase biomass, increase soil nutrient cycling, reduce soil moisture stress and diversify pasture species, for recommended carrying capacity attainments.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment activities include; first identification and demarcation of degraded grazing land done in June. Second is broadcasting improved pasture seeds (Chloris gayana and Congo signal) done in late August. Third is establishment of live fence (planting Euphobia spps, sisal seedling and mikwatango) done in September. Fourth is cultivation of bare land spots and drill legume seeds (Stylosthensis hamata, centocema pubences etc) or plant improved legume cuttings (Desmodium coloratum). The maintenance activities includes; first weeding invasive species (sida accuta, Duratura stromonium etc) done manually using hand hoes and machete in June and January. Second is fire break cleaning done manually using hand hoes in May and December. Last but not least to importance is range patrol done routinely.
Natural / human environment: The human environments includes wealthy stutus as 13% poor land user, 50% average land users and 37% rich land users owning the land ownership is communal. The land cultivation is done manually using hand hoes. The production system is mixed in the sense that, live cull cows and steers are for sale while small ruminants and milk are for both domestic consumption and sales of excess.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
تنزانيا، جمهورية تنزانيا المتحدة
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tanzania
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Kyerwa
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- < 0.1 كم2 (10 هكتار)
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ أقل من 10 سنوات (مؤخرًا)
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
FFS trained on land conservations in Katera hifadi ya malisho group using pasture improvemnt as indicor crop.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الرعي الزراعي (بما في ذلك الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية)

الأراضي الزراعية
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 2
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: November to February Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

أراضي الرعي
- Bovine, caprine and ovine
التعليقات:
Livestock density (if relevant):
> 100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem related to soil, water and vegetation in the area was loss of palatable spps, reduced vegetative cover and ....
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The major land use problem was poor/ inadequate pastures.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): bovine, caprine and ovine
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- إغلاق المنطقة (إيقاف الاستخدام، دعم الاصلاح)
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M5: التحكم في/تغيير تركيبة الأنواع
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bf): الآثار الضارة للحرائق
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Livestock holding density in the area is 116 per square km.), change of seasonal rainfall (dry spel tends to prolong in long rain seasons.), droughts (the area experiences a long drought period.), land tenure (difficult to control grazing regimes in the communal owned land.), governance / institutional (leizure fair on grazing land control resulted into cattle influxes in the area.)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Basic principles of pasture management is taught at colleges.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Leguminous spps re seedlings requires new knowledge.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of fires
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Instead of continuous grazing, rotational grazing is recommended to reduces the frequencies of livestock trumping the land.
Control / change of species composition: In the overgrazed land palatable spps had lost while unpalatable spps dominated. Furthermore, legumes for quality improvement had disappeared.
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
Tshs
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
1700,0
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
1.88
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | To identify the degraded grazing land. | |
| 2. | To plant Euphobia triculi | |
| 3. | To plat sisal | |
| 4. | To plat elephant grass | |
| 5. | To reseed legumes | |
| 6. | To clear fire break along the demarcated borders. |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 13,8 | 13,8 | |
| المواد النباتية | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 119,02 | 119,02 | |
| المواد النباتية | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 3,09 | 3,09 | |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 135,91 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,08 | |||||
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | To remove invasive spps (shrubs/weeds) | |
| 2. | To clean the fire break | June and December |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 41,73 | 41,73 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 41,73 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 0,02 | |||||
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
800mm bimodol (march to May and November to January)
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months has a temperature above 18°C. LGP is 180 to 210 days
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Landforms: Footslopes (ranked 1, UP), hillsopes (MS) and mountain slopes (EP, both ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Gentle (bordering the valley) and moderate (bordering the hill slopes)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (laying over ironstone gravel)
Soil texture: Medium (friable redish brown to brown, with fine to coarse sand)
Soil fertility: Low
Topsoil organic matter: Low (bare spots dominated)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
> 50 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Availability of surface water: Good (the range borders lake Kagenyi)
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water (available gravity tape water from .....sources)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
Dominated bare spots and dry soils.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- المجموعات/ المجتمع المحلي
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, poor
37% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
13% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: opportunity costs of technology application minimized the opportunity to invest and maintain off-farm activities.
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
التعليقات:
A communal grazing land is 152sqkm over 1040 house-holds
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
التعليقات:
A 3 hectare piece of communal grazing land alocated for a group of 35 members to undergo the SLM training.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج الأعلاف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1.5
التعليقات/ حدد:
DM yield improved after reducing trampling and bushfires.
جودة العلف
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
17
التعليقات/ حدد:
Legumes intercroping had fixed nitogen in the soil.
إنتاج حيواني
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
170
التعليقات/ حدد:
liveweight gain per anum improved due to optimum DM -intake and DCP availability. .
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
cost of desmodium, stylothensis hamata and Nappier grass
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
labour demanded for extra activities.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
المؤسسات المجتمعية
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
التعليقات/ حدد:
group members can organize themselves to conserve the rest of the overgrazed area
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
low
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
moderate
التعليقات/ حدد:
a training site shown positve results after six months of implimentation.
وضع الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا
التعليقات/ حدد:
FFF group members includes all genders.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
The effective duration of technology implimentation is too short to meet technology upscaling to suit the farming scale (medium scale ie. 100-300 cattle) herd size.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
الجريان السطحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
grasses impends water run -off
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
grasses covered soil surfaces
غطاء التربة
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
90
التعليقات/ حدد:
no bare spot found in the field.
فقدان التربة
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
cattle restrivted to tramp the soils.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
planted desmodium and stylothensis hamata
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
mixture of grasses and legumes.
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
snakes and rodents are hinding in tall grasses.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
خطر الحريق
التعليقات/ حدد:
firebreak constructed along the borders.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
The short term retuns compared with establishment is negative due to distocking requirement to suit the recommended carrying capacity. The long term return anticipated to be positive due to increased livestock density projecting increased off-take rates.
The short term return compared with maintenance is slightly negative as a result of increased costs of restriction. The long run return compared with maintenance is positve due to reduced costs of restriction while rotational grazing can simply suit the technology.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
التعليقات:
35% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
35 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: A total of 35 group members attended the FFS and applied the technology in a portion of communal grazing land.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The effective duration is to short for neither group members nor non group members to comply with the land policy requirement to acquire the land for technology implementation.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The communal land tenure applied in the area is a major obstacle for technology adoption. ie. the habit of open access rights for land use make it difficult to enclosure the require size of land in order to up scale the technology.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| It is simple to learn and understand. |
| In a short period of six months, the change was very distinct ie. grass covered the bare spot on soils, while in the dry spell the standing hay harvested to feed calves. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Difficult to transfer the knowledge into communal grazing land (overstocked >100LU/sqkm) without grazing land act enforcement. | Enforce grazing land and animal feed resources act. |
| The restriction of cattle to graze in the enclosure means twice as much land required for a significant short term returns. | Educate land users on carrying capacity importance. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
25/07/2014
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية