Firebreaks [السنغال]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Dieter Nill
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Pare-feux (French)
technologies_1615 - السنغال
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
ألمانيا
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Daniel André
Ministère des Eaux et Forêts, Senegal
السنغال
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Misereor - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Direction des Eaux et Forêts, Chasses et de la conservation des Sols - السنغال1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
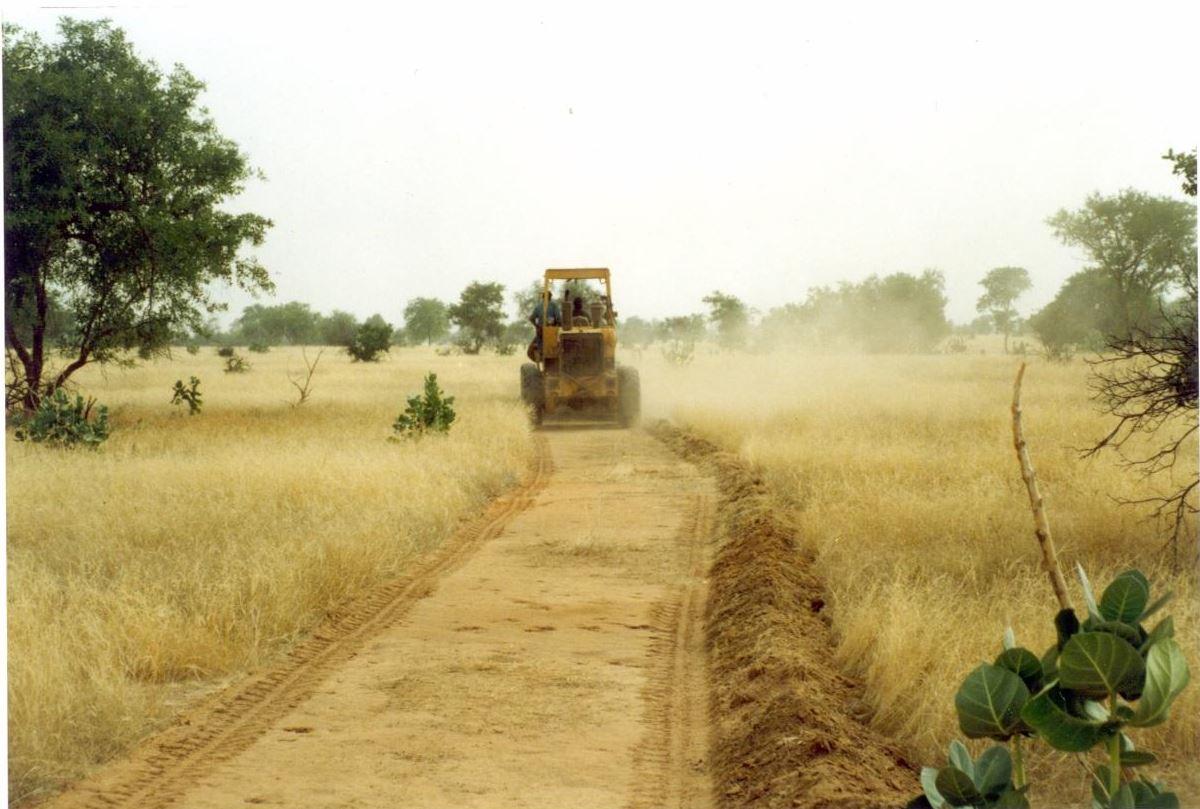
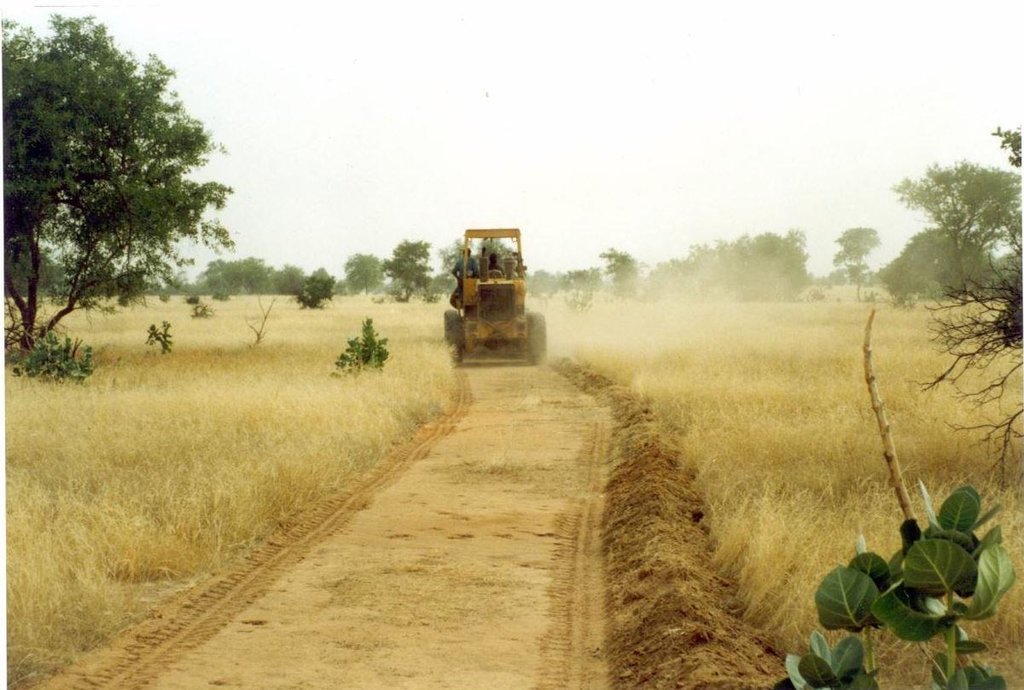
Firebreaks cut vast tracts of rangeland into smaller areas, with a view to limiting damage in the event of wildfire.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
This technique is used on rangeland with rainfall between 150 and 300 mm. Firebreaks are a precautionary measure designed to protect forage on rangelands during the dry season. Bushfires are frequent on good-quality rangeland with over 1t/ha of biomass.
Purpose of the Technology: Firebreaks cut vast tracts of rangeland into smaller areas, with a view to limiting damage in the event of wildfire. They can also be established along traditional tracks. The gap in the vegetation makes it easier to put fires out along the corridor, which facilitates rapid access. When the fire reaches the firebreak, there is no combustible material to fuel it and it burns itself out.
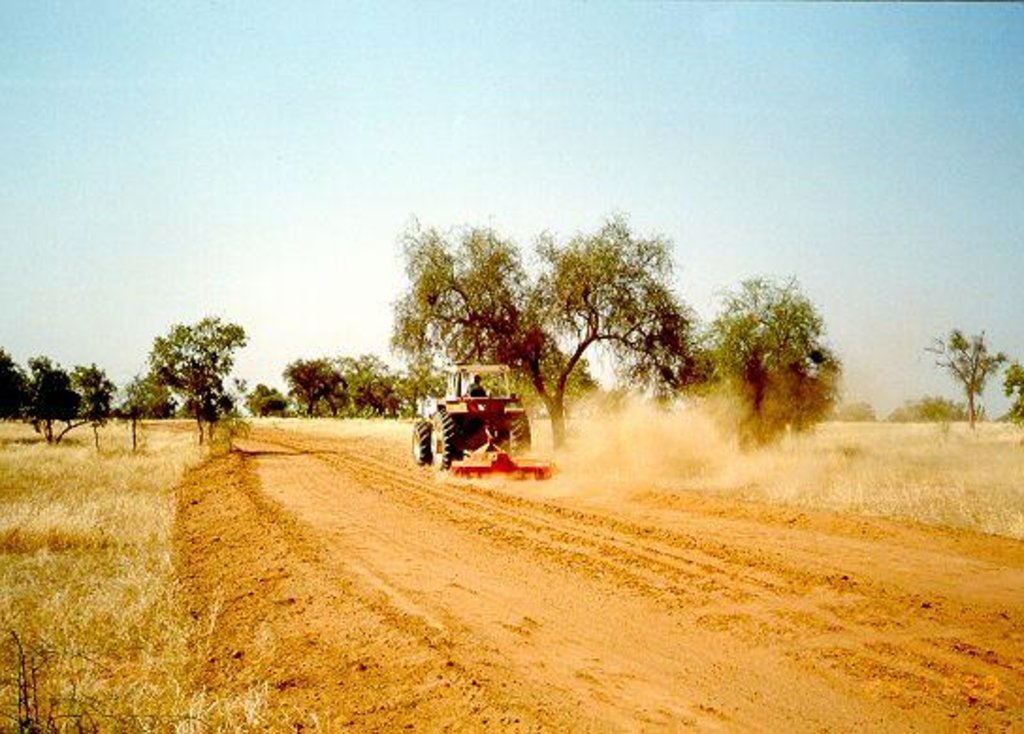
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are two techniques for creating firebreaks: (i) the manual method and (ii) the mechanised method. In both cases, a 10 to 15 m wide corridor is cleared perpendicular to the prevailing wind direction after the rainy season. Fires only poses a threat in the Sahel area in the dry season following a good rainy season when grass growth is good. The corridor is cleared of all herbaceous vegetation manually, using tools such as rakes, shovels and axes, or mechanically using a tractor pulling a large harrow, a four-wheel-drive vehicle pulling the blades behind it or graders. Trees are pruned, but left in place.
The sustainability of firebreaks depends on how well they are maintained. Once they have been created, they need to be cleared every year if grasses have grown over them again. If there is little vegetation growth, they can
be maintained once every two years or as required. If they are cleared manually, the communities or commune authorities must be well organised to ensure that the work is properly carried out. Good organisation is also required to ensure an effective response in the event of a fire (mobile unit).
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
السنغال
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Senegal
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Ferlo Region
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 1,000-100 كم2
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Developed in other countries. Implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation): Projet PASP (Projet d‘Autopromotion Pastorale dans le Ferlo - Project to Promote Self-Help of Pastoralists in the Ferlo Region) in Northern Senegal.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

أراضي الرعي
التعليقات:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Bushfires are frequent on good-quality rangeland with over 1t/ha of biomass; bushfire only poses a threat in the Sahel area in the dry season following a good rainy season when grass growth is good.
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحد من مخاطر الكوارث بالاستناد على النظام البيئي
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V3: إزالة الغطاء النباتي
التعليقات:
Main measures: vegetative measures
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bf): الآثار الضارة للحرائق
التعليقات:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bf: detrimental effects of fires
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (man made fires, natural flashes during thunderstorms), droughts
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- منع تدهور الأراضي
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of fires, reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires)
Vegetative measure: clearing of vegetation
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A 10 to 15 m wide corridor is cleared perpendicular to the prevailing wind direction after the rainy season of all herbaceous vegetation manually, using tools such as rakes, shovels and axes, or mechanically using a tractor pulling a large harrow, a four- wheel-drive vehicle pulling the blades behind it or graders. | |
| 2. | Trees are pruned, but left in place |
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Once they have been created, they need to be cleared every year if grasses have grown over them again. If there is little vegetation growth, they can be maintained once every two years or as required. |
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Manual method:
• equipment, such as rakes, shovels and axes
• labour.
Mechanised method:
• four-wheel-drive vehicle, tractor or land grader
• harrow
• labour to clear the corridor.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%)
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil fertility: Medium and low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium and poor
Soil water storage capacity: Medium and low
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Ground water table: 5-50m ( > 10 m)
Availability of surface water: Medium (surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
(mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- مجتمعي (منظم)
التعليقات:
traditional land use rights on fields, communal land on pasture and forest land
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الدخل والتكاليف
عبء العمل
آثار اجتماعية واقتصادية أخرى
Establishment and maintenance costs
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
التخفيف من حدة الصراع
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Preventing wildfire contributes to safeguarding the fauna and flora over vast tracts of rangeland, which would otherwise be destroyed. It also avoids enormous economic losses in terms of livestock and infrastructure (herding villages, forage). When rangelands remain intact, nomadic livestock keepers tend to stay within their area.
الآثار الايكولوجية
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
خطر الحريق
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | جيدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
التعليقات:
Both the short-term and the long-term benefits are very positive assuming that maintenance is done.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
100% of the area covered
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
التعليقات:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Fire breaks are economically viable but investment is high and generally asks for public investment. Cost sharing of beneficiaries has to be decided locally based on local conditions.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Asks for strong commitment of either beneficiaries and or local government.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
Preventing wildfire contributes to safeguarding the fauna and flora over vast tracts of rangeland, which would otherwise be destroyed. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The sustainability of firebreaks depends on how well they are maintained. Once they have been created, they need to be cleared every year if grasses have grown over them again. If there is little vegetation growth, they can be maintained once every two years or as required. If they are cleared manually, the communities or commune authorities must be well organised to ensure that the work is properly carried out. Good organisation is also required to ensure an effective response in the event of a fire (mobile unit). |
| It also avoids enormous economic losses in terms of livestock and infrastructure (herding villages, forage). When rangelands remain intact, nomadic livestock keepers tend to stay within their area. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| The lack of financial and logistic resources is a constraint on the creation of firebreaks, and it is often difficult to organise the beneficiaries (nomadic livestock keepers) asked to participate financially or physically in the work required to establish and maintain them. | Once the financing has been secured, considerable efforts are required to raise awareness about the need to prevent fires and mobilise the livestock keepers in a particular grazing area to become involved in the work. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية