Contour bunds for crops and forest/rangeland [النيجر]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Dieter Nill
- المحرر: –
- المراجعون: Deborah Niggli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Banquettes agricoles et sylvo-pastorales (French)
technologies_1652 - النيجر
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP)
النيجر
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
ألمانيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ألمانيااسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Misereor - ألمانيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Contour bunds, built with earth or stones, increase the amount of water available to crops and vegetation, thus contributing to the restoration of degraded land
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
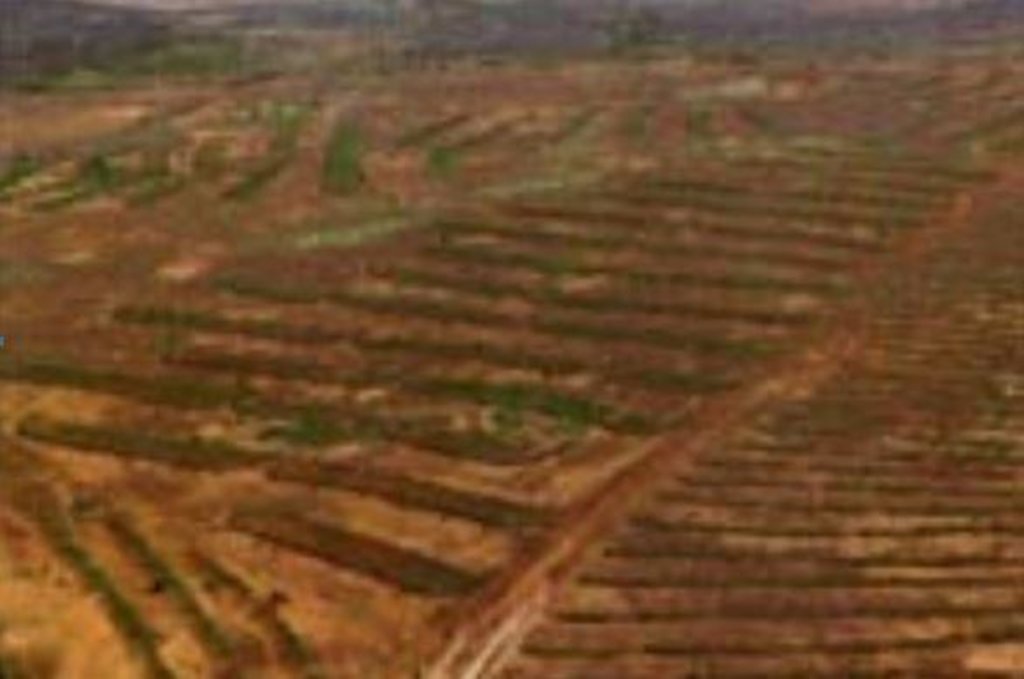
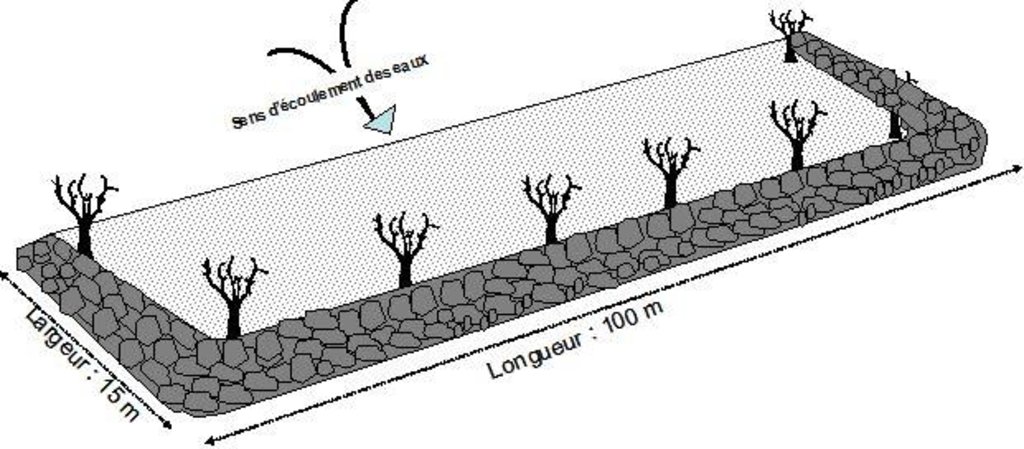
A contour bund is a rectangular structure consisting of bunds built with earth or stone or a combination of both, which can be permeable or impermeable. The bottom bund is up to 80 m long, and the wingwalls extend up to 15 m upslope. The contour bunds are built in staggered rows along the natural contour of the land with the open end facing uphill. Patches in the same row are spaced 6 m apart, and the rows are positioned about 25 m apart, depending of the gradient of the slope. Downslope of the structure, a water collection ditch 0.50 m wide and 0.30 m deep is dug. The earth excavated from the ditch is piled up and compacted to construct the main bund. When used for growing crops, a third of the total surface area inside the contour bunds is loosened by subsoiling. The remaining two thirds of the surface are left unworked and serve as a catchment area. This doubles or triples the volume of water available to crops. Trees are planted along the main bund to stabilise the structure.
Contour bunds for forest/rangeland work as contour bunds on cropland (described above), except that the sizing is slightly different. The main bund of patches used for this purpose is up to 100 m long and the rows are spaced up to 30 m apart.
In Niger, contour bunds for forest/rangeland are used to restore land in plateau areas which have been completely degraded and denuded by severe water and wind erosion. Contour bunds for growing crops are recommended for the restoration of pediments, particularly in areas where land use pressure is high. The technique is recommended for areas with a low gradient and rainfall of less than 600 mm.
The bunds capture and retain runoff for several days. Infiltration of the water into the soil increases, and there is a gradual build-up of sediment behind the bunds, creating favourable conditions for the establishment of vegetation. Contour bunds for crops increase the area of land that can be farmed and its productivity thanks to their capacity to retain runoff and the shelter provided by trees planted along the bottom bund, which protects the crops. An advantage from the perspective of watershed development is that contour bunds constructed on plateaux areas protect areas downstream against heavy runoff.
Before constructing the contour bunds, it is essential to clarify the ownership status of the land where the measures are to be implemented and who the users will be, with a view to avoiding disputes later on.
When constructing the contour bunds, it is important to mark out the contour lines correctly and ensure that the earth is firmly compacted.
With some upkeep, stone or stone-lined contour bunds last at least 20 years. Earthen bunds do not last as long. Good vegetation cover established along the bunds increases their lifetime.
The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events.
The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
النيجر
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Niger
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahoua
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- منتشرة بالتساوي على مساحة
إذا كانت المساحة الدقيقة غير معروفة، فيرجى الإشارة إلى المنطقة التقريبية المغطاة:
- 100-10 كم2
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- التكيف مع تغير المناخ/الظواهر المتطرفة وآثارها
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- المحاصيل الزيتية - الفول السوداني
- الحبوب - الدخن
- الحبوب - الذرة الرفيعة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- البازلاء
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- المانجو، المانغوستين، الجوافة
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
حدد:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

الغابات/ الأراضي الحرجية
- الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية
الغابات/الأراضي الحرجية (شبه) الطبيعية: حدد نوع الإدارة:
- قطع الأشجار الانتقائي
منتجات وخدمات:
- الخشب
- حطب الوقود
- الفواكه والمكسرات
- منتجات الغابات الأخرى
- الرعي/ رعي أطراف الأشجار الفتية (الجلح)
التعليقات:
major cash crop: Ground nut
major food crops: Millet
other: Sorghum, cow pea and mangoes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): crusting, surface runoff, water and wind erosion, unadapted land use methods, rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land, reduced or abandoned fallow periods, insecure access to land
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- التدابير المتقاطعة للمنحدرات
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- الحواجز والضفاف
التعليقات:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة
- (Pk)ظهور وتكون قشرة سطحية

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
التعليقات:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed common land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
المؤلف:
MDR, Niger, Recueil des fiches
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد العملة المستخدمة لحساب التكاليف:
- دولار أمريكي USD
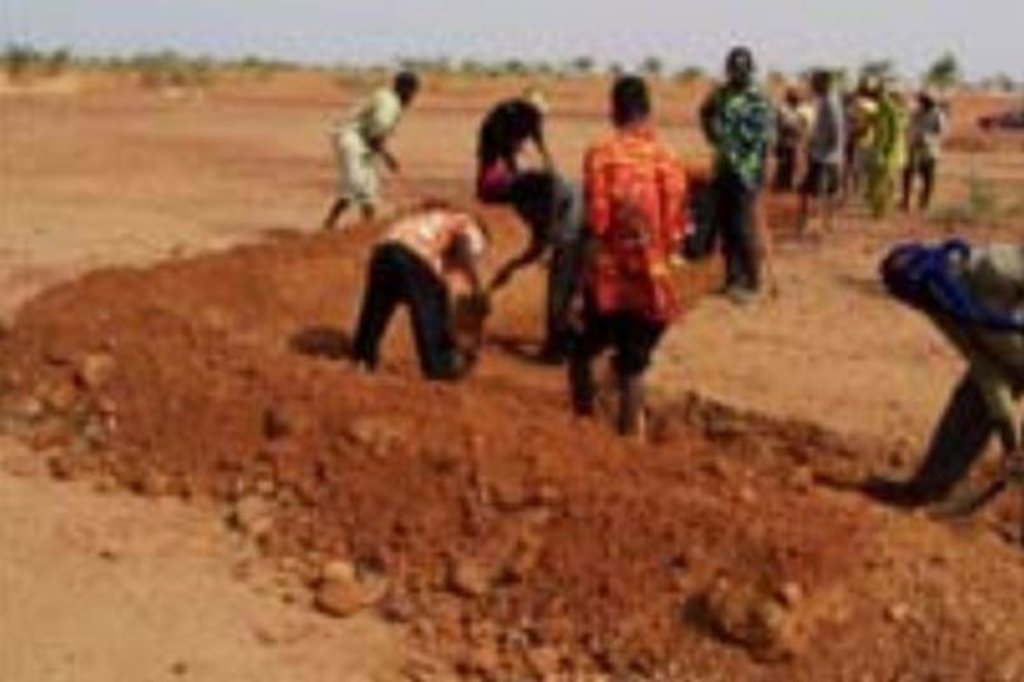
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The contour bunds are built in staggered rows along the natural contour of the land with the open end facing uphill. | |
| 2. | Downslope of the structure, a water collection ditch 0.50 m wide and 0.30 m deep is dug. | |
| 3. | The earth excavated from the ditch is piled up and compacted to construct the main bund | |
| 4. | When used for growing crops, a third of the total surface area inside the contour bunds is loosened by subsoiling | |
| 5. | Trees are planted along the main bund to stabilise the structure |
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Damages caused by excessive rainfall need to be repaired quickly |
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Labour: 54 man-days per ha.
Equipment: pickaxes, shovels, wheelbarrows, water-tube level.
Other costs: hire of machine for subsoiling (1 day per ha).
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه قاحلة
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil texture (topsoil): Fine to medium (sandy to clayey loams)
Soil fertility is very low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor - medium
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
متوسط
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
للاستخدام الزراعي فقط (الري)
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- شبه مرتحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- الكفاف (الإمداد الذاتي)
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- 10-50% من جميع الإيرادات
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ضعيف جدا
- ضعيف
مستوى المكننة:
- عمل يدوي
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- رجال
اذكر الخصائص الأخرى ذات الصلة لمستخدمي الأراضي:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: Most households crop for subsistence (mainly for small agropastoralists), but surplus is sold on market (medium agropastoralists). Commercial markets: some vegetable growing and pastoralists.
Level of mechanization: Ox and donkey for animal traction
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- مجتمعي/قروي
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
إنتاج الأعلاف
إنتاج حيواني
إنتاج الخشب
خطر فشل الإنتاج
منطقة الإنتاج
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
الطلب على مياه الري
الدخل والتكاليف
دخل المزرعة
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
livelihood and human well-being
التعليقات/ حدد:
Contour bunds for crops increase the area of land that can be farmed and its productivity thanks to their capacity to retain runoff and the shelter provided by trees planted along the bottom bund, which protects the crops
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
فقدان التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
سرعة الرياح
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | ليس جيدا |
| عاصفة هوائية محلية | جيدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث الهيدرولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فيضان عام (نهر) | ليس جيدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| انخفاض فترة النمو | غير معروف |
التعليقات:
Physical structures can be biologically stabilized through planting of grass, bushes or trees. Damages are generally small but need to be repaired quickly.
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 11-50%
التعليقات:
The techniques were implemented with food for work in the 1990s to 2000. At the end, the work provided by land users was not compensated. Only small equipment and transportation were provided for free.
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Some adoption (without support by the project) has been observed in some places. The level of replication is however limited to locations where stones are available nearby. Otherwise transportation becomes a problem. Potential for replication depends on the type of terrain, there being a nearby supply of the materials needed (stone). Subsoiling needs mechanical treatment by tractor.
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Contour bunds for crops increase the area of land that can be farmed and its productivity thanks to their capacity to retain runoff and the shelter provided by trees planted along the bottom bund, which protects the crops. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| In a low-rainfall scenario, the construction of contour bunds helps to restore vegetation cover on vast areas of denuded land from the first year after they are established. Infiltration of the water into the soil increases, and there is a gradual build-up of sediment behind the bunds, creating favourable conditions for the establishment of vegetation. |
| Good vegetation cover established along the bunds con- tributes to lowering soil temperature and providing pro- tection from wind erosion along the entire length of the patch. |
| The construction of contour bunds upstream of river basins reduces the risk of gully erosion and siltation downstream. |
| In Niger, it is mainly women who have benefitted from efforts to rehabilitate land on the plateaux. With the support of development projects, women were able to secure five-year leases from land owners. |
| This technique transforms unproductive land into land that is economically valuable. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| There are also disadvantages associated with subsoiling in the contour bunds. Although subsoiling permits rapid, relatively deep infiltration, the water is situated below the level where the roots of young crops or grasses are growing, which means that the infiltrated water is not used optimally in the initial stages. Furthermore, the surface of the subsoiled land becomes hard again after several years of cultivation, because the soil structure is broken down owing to a concentration of fine particles of earth in the grooves of the subsoil, which can clog up the pores of the soil. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Patches with impermeable bunds are not appropriate when there are heavy rains, as the flow of water can destroy the bunds. | The extensive work required to construct the contour bunds means that the community must be strongly motivated and well organised. |
| Contour bunds for growing crops can be used to restore land that has become unproductive. This technique is not, however, very cost-effective, because of the scale of the work involved. | When constructing the contour bunds, it is important to mark out the contour lines correctly and ensure that the earth is firmly compacted. |
| The distribution of water in the contour bunds is often uneven, because the terrain is not level, which means that production varies considerably from one area to another | |
| When there is heavy rain, runoff accumulates at the lowest point of the collection ditch, which can sometimes cause rilling | |
| There is a risk of the patches becoming waterlogged, which can damage the crops |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
01/07/2012
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط
لا يوجد روابط
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية