Improved Compost [أثيوبيا]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
- المحررون: Noel Templer, Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Kompoosti Fooyya'a
technologies_6649 - أثيوبيا
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
الشخص (الأشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات
مستخدم الأرض:
Abdulqadir Mohammed
Farmer
أثيوبيا
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - كينيا1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
التعليقات:
The technology is very friendly to SLM since it restores soil fertility and improves the chemical, physical and biological properties of the soil.
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Soil Fertility Improvement Cluster [أثيوبيا]
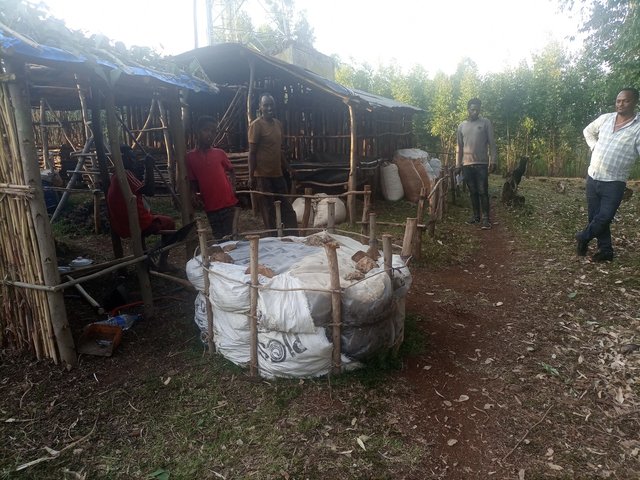
The Soil Fertility Improvement Cluster approach engages five or more farmers living in a village who share skills and labour to prepare and use improved compost as well as to demonstrate it to non-member of the group.
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
Improved compost making using “static pile” systems transforms organic material from plants and/or animals into high-value, rich organic compost. It demands less labour, and less time to reach maturity than conventional systems as it thoroughly mixes the ingredients at the beginning which precludes the need to turn the heap later.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
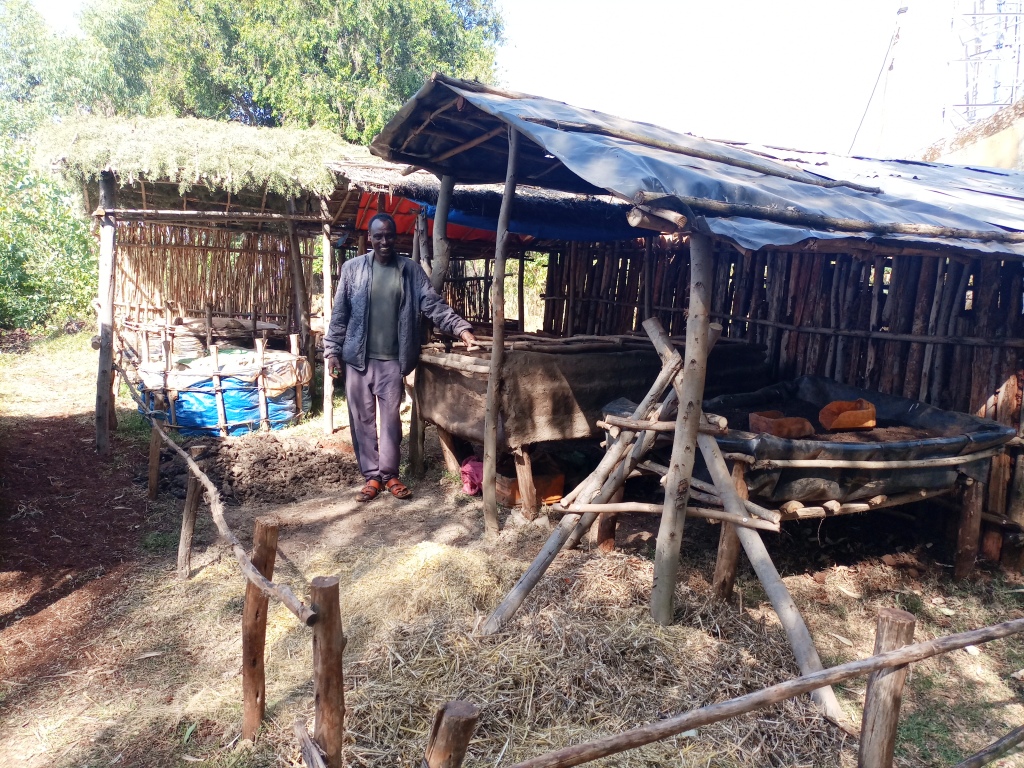
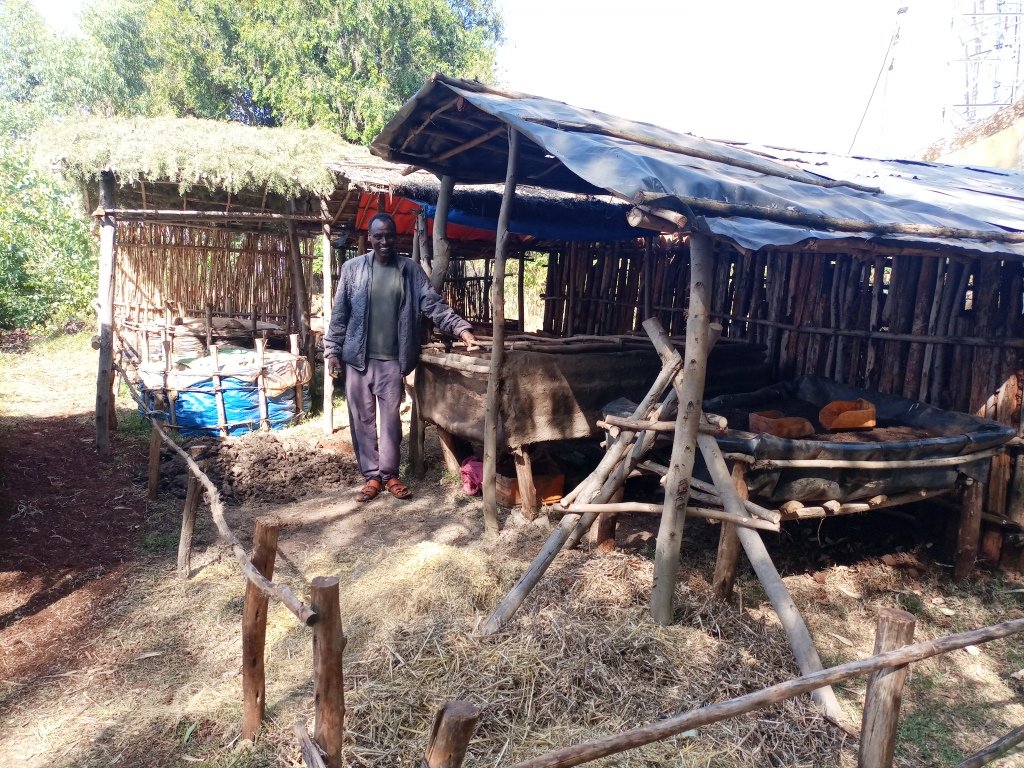
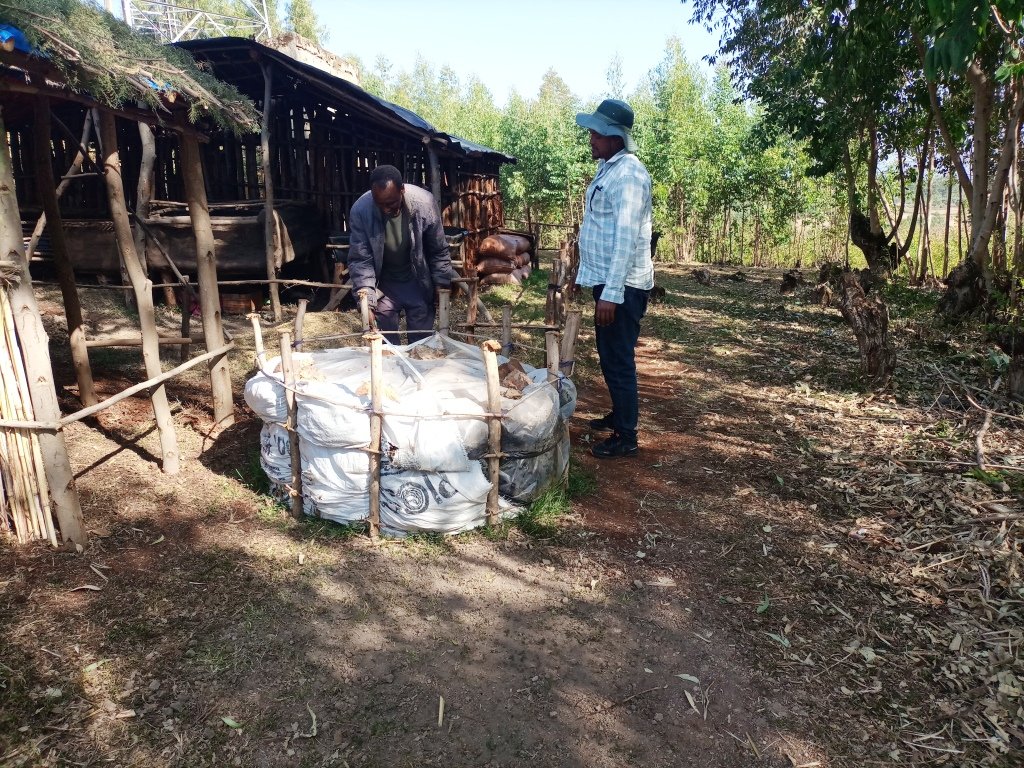
Improved composting using static pile systems transforms organic material from plants and/or animals into high-value, rich organic compost. This compost can be prepared in a heap form, where the ingredients are thoroughly mixed and wrapped within a polyethylene sheet. Notably, white polyethylene has the role of intercepting sunlight and improving the solarization effects on weed seeds or wild species arbitrarily used as biomass for improved compost production. This technique accelerates the breakdown of the organic materials faster because it heats up the compost as part of the decomposition process. Accordingly, the compost reaches maturity in 60-70 days. Compost provides the crop with balanced nutrients and helps to increase the soil's organic matter content. It has long‐term, and short‐term effects on plant nutrition as nutrients are continuously released. It is an organic matter resource with the unique ability to improve soils' chemical, physical and biological properties. Improved compost is applied in rows for vegetables and small cereal crops but spot application (planting holes) is employed for large cereal crops such as maize. The application is on an incremental basis year and again to reach out to the large size of lands. In principle, as the nutrients are slowly released, they may not need a continuous application like chemical fertilizers.
Improved compost-making requires 12-15 wooden pegs 1m high each supported by horizontal bars/string, to form a round structure. The interior is lined with plastic sheeting, then thoroughly mixed ingredients, including coffee hulls, ash, livestock manure, crop residues, livestock urine, water, and chaff are mixed and piled before being sealed in the structure. Unlike the mainstream heaps or pits types of composting, it doesn’t need turning. Therefore, this technique reduces labour requirement, and is liked by the users who have been piloting the technology. The relatively short maturity date also enables it to be produced at least twice a year during the offseason. Compost is prepared around the homestead – which allows closer attention - using livestock urine, manure, and house refuse.
In most of Ethiopia's central and western highlands, soil degradation is a severe issue. Soil acidity has become a growing problem challenging the livelihoods of smallholders. Thus, countering the negative effect of degradation and acidity through producing and using organic fertilizers is a key strategy. However, it is essential that the resources of biomass, family labour, skills and motivation, are combined to ensure sustainable land for crop production. From end users' observations and analysis, improved compost restores soil fertility. It increases yield as well as grain quality: this has been proved by testing the grain compared with the harvest where only chemical fertilizers have been applied. Farmers prefer the simplicity of preparing improved compost to the conventional method, and appreciate its role in improving yield and grain quality as well as reducing the labour demand.
2.3 صور التقنية
ملاحظات عامة بخصوص الصور:
The photo portrays the farmer measuring the total area (by cubic meters) where the improved compost is piled.
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
Video of the technology is not recorded.
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
أثيوبيا
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Oromia
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Babo kebele of Kersa district, Jimma zone
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
اذكر سنة التنفيذ:
2022
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال ابتكار مستخدمي الأراضي
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
Improved compost preparation was introduced by local NGOs known as FC Ethiopia that arranged experience exchange visits to a few farmers in the Arsi Zone of Oromia. A proactive farmer inspired by the technology outdid what he had observed during his visit. He continued inspiring the surrounding community by preparing improved compost with rich ingredients and early maturing capacity compared to conventional compost production.
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على النظام البيئي
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة سنوية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
الزراعة السنوية - حدد المحاصيل:
- الحبوب - قمح (ربيعي)
- الحبوب - الذرة
- الحبوب البقولية والبقول- الفاصوليا
- Hot pepper
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
- قصب السكر
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- الافوكادو
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد المحاصيل التي يتم زراعتها بشكل بيني:
Haricot beans with maize
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد:
Maize rotate by wheat and then faba beans.
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- لا (تابع مع السؤال 3.4)
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- بعلية
التعليقات:
Sources of water supply for improved compost making can be steams or groundwater. However, the compost can be applied to both the rainfed or irrigated agriculture.
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الإدارة المتكاملة للمحاصيل والثروة الحيوانية
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A3: معالجة سطح التربة
A3: التمييز بين أنظمة الحراثة:
A 3.3: Full tillage (< 30% soil cover)

التدابير الإدارية
- M2: تغيير في مستوى الإدارة/الكثافة
- M5: التحكم في/تغيير تركيبة الأنواع
التعليقات:
Applying organic fertilizer to the farm stimulates the regeneration of the lost wild species on the farm.
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Ca):التحمض

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Ps): هبوط التربة العضوية، استقرار التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة

تدهور المياه
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hp): تدهور نوعية المياه السطحية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
التعليقات:
The production and use of organic fertilizer improve soil fertility, regenerates lost species, and improve plant and animal biodiversity. Compost improves the vigorous growth of the crop, plant colour, and crop production. It also improves the rooting system, extends the grain filling period by about 20 days compared to the plot with chemical fertilizers, increases the number of ears/plants and seeds per ear in maize, etc.
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
Picture that clearly describe the technology is affixed. Detail description is available under the description.
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- لكل وحدة تقنية
حدد الوحدة:
Compost production structure
حدد أبعاد الوحدة (إذا كانت ذات صلة):
6-7m3
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
ETB
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
53,12
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
100
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select site and constructing the structure. | During the off-season particularly right after harvest when adequate biomass is available. |
| 2. | Collecting ingredients for compost making. | During crop harvest |
| 3. | Thoroughly combine the ingredients and seal. | After materials are ready to make the heap. |
| 4. | Harvest/open and dry the compost on open air. | Six to seven weeks after piling the compost. |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labor | PDs | 5,0 | 100,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Spade | number | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| معدات | Reck | number | 1,0 | 160,0 | 160,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Machete | number | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Sickle | number | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Posts for peg making | number | 2,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Horizontal bars | number | 5,0 | 10,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Strings | meter | 12,0 | 10,0 | 120,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Polyethylene sheet | meter | 14,0 | 50,0 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 3430,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 64,57 | |||||
إذا تحمل مستخدم الأرض أقل من 100% من التكاليف، حدد من قام بتغطية التكاليف المتبقية:
So far, the district/Woreda Office of Agriculture covered the cost of the spade for participating model farmers in the training as an incentive.
التعليقات:
Cost of making or producing the technology is largely covered by the land users themselves. District SLM experts provide technical support and monitoring the land users activities on irregular basis. It is only the labor cost and some expendable supplies that are demanded every other time. Otherwise, materials are reused for the perpetuation of compost production.
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
التعليقات:
Essentially, improved compost making does not need visible maintenance work. Rather it aspires collection of inputs or materials to perpetuate production of compost. Such activities can be considered as recurrent activities that ensure compost production on sustainable basis.
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Labor | PDs | 5,0 | 100,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Plastic sheet | meter | 14,0 | 50,0 | 700,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Posts | number | 2,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 1300,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 24,47 | |||||
التعليقات:
The estimated cost is only to construct one structure that allows the preparation of about 6-7 m3 of compost. If a farmer wants to produce as much compost as possible simultaneously, the material and labor demand can be doubled or quadrupled.
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
Material prices are also variable because of economic instability and price fluctuation. In general, the cost is inconsistent because of inflation.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
The site receives high rainfall in summer maximum (June to September). From January to May, it is the dry season with short showers in March/April.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Jimma
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- شبه رطبة
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التضاريس:
Topography (5.2) does not define improved compost as a practice/technology. The above questions are addressed merely to describe the site where the technology was applied. The technology can be applied in diverse landforms or slopes as long as necessary ingredients and issues that call for mitigation are experienced.
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- متوسط ( طميي، سلتي)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
The soil types is Nitosol and soil pH is about 5 on average.
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
جيد
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه السطحية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- متوسط
تنوع الموائل:
- متوسط
التعليقات والمواصفات الإضافية بشأن التنوع البيولوجي:
There is declining biodiversity because of the increasing degradation of the soil.
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- أقل من % 10من كامل الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- ثري
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- الجر الحيواني
الجنس:
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق صغير
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- دولة
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- وصول مفتوح (غير منظم)
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
كلا
حدد:
He accessed land redistribution through the local government.
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليقات:
As the farmland is closer to all-weather roads and the district town, the farmer can easily access almost all of the facilities in the area.
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2 tons/hectare
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
2.8 tons/hectare
التعليقات/ حدد:
Maize yield has immensely increased during the first harvest with compost as compared to the plot with NSP fertilizer at the rate of 100 kg/ha. As nutrients from organic fertilizers gradually available, it is expected to increase in the coming years.
جودة المحاصيل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Land users communicated the positive effects of using compost on grain size and overall quantity of production.
إنتاج الأعلاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
As biomass production is increasing, the part of crop residue that is used for livestock feed is also increasing.
تنوع المنتج
إدارة الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmlands where improved compost applied increases soil aggregate stability as compared to the farmland where only chemical fertilizers is applied.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Using organic fertilizer (improved compost) reduces land users investment on chemical fertilizers.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
It correlates with increasing production per unit of land.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The farmer also generate income from the sale of compost itself.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الأمن الغذائي / الاكتفاء الذاتي
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Convergent to food and nutrition security.
المؤسسات المجتمعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmer group formation is promoted for peer learning.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
كمية المياه
جودة المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Ground cover contributes to filtering the downslope runoff and siltation.
الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
The organic matter in the improved compost improve soil structure and simplify water drainage down in soil horizon.
التربة
رطوبة التربة
غطاء التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved compost increase biomass production and soil cover.
فقدان التربة
تراكم التربة
تكون قشرة التربة السطحية/انسداد مسام التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Improved compost promotes soil aggregate stability.
تراص التربة
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
التعليقات/ حدد:
Salinity is uncommon in the district.
الحموضة
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
Compost promotes the growth of wild species and/or promotes the succession of some lost species.
التنوع الحيواني
الأنواع المفيدة
تنوع الموائل
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
It increases surface and subsurface biomass production and sequester soil carbon.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Quantifying the positive or negative effects of technology demands the documentation of different facets of the technology which is virtually lacking. In most cases, farmer's responses and expert's opinions were used to addressing the comprehensive questions in the questionnaire.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
Slightly increases as it improves the soil infiltration potential.
تدفقات مائية موثوقة ومستقرة في موسم الجفاف
الفيضان في اتجاه مجرى النهر
تراكم الطمي باتجاه مصب النهر
التعليقات/ حدد:
It positively associate with reduction of the runoff due to good ground cover.
تلوث المياه الجوفية/الأنهار
آثار الغازات الدفيئة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Such impact can be achieved in the long-term.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
Improving soil fertility increases biodiversity and reduces multiple adverse effects of degradation on the environment.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | باعتدال | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | فصل جاف | زيادة | جيدة جدا |
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
العواقب الأخرى المتعلقة بالمناخ
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| فترة نمو ممتدة | جيدة جدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
إيجابي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
إيجابي
التعليقات:
The benefits accrued from the application of technology (improved compost) increases overtime as the rate of nutrient adsorption or release of the elements is on a gradual basis as compared to chemical fertilizers. The return remains positive despite variations in temporal and the degrees.
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بتحديد الكمية (عدد الأسر المعيشية و/أو المساحةالمغطاة):
About five farmers were adopted in one village. It is spreading in a similar manner over the other areas.
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 91-100%
التعليقات:
So far, the farmer is adopting through advisory services and familiarization with the technology via exchange visits. However, the visited farmer increased the number of ingredients used as feedstock for compost production compared to what he had seen during his visit to the Arsi zone of Oromia.
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Improve soil fertility and reduce acidity on gradual basis. |
| Increase grain and biomass yield and quality of the crop. |
| Generate income from the sale of compost. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| It reduces the investment cost on chemical fertilizers. |
| Shortly mature compared to conventional compost making, enabling more composts to be produced. |
| It reduces labor costs as an overturning operation is exempted. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Intensive labour during planting (transport to the farm and implement row or spot application) depending on the crop types. | Promote labour-sharing arrangements with neighboring peers, engage family labor, and use necessary farm tools such as wheelbarrows to transport to the nearby farms. |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| Introduction of the technology is steered by soil fertility improvement department of the district office on piecemeal basis. | Need popularization via the extension system. This demands institutionalizing the technology as the best technology/practice. |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
Two farmers
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
Only a farmer
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
Soil fertility improvement process owner.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
10/02/2023
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Soil Fertility Management: An introductory Fact-Sheet for Farmers and Projects.Organic Exchange. 2009
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
free online
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Making and Using Compost for Organic Farming
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://eorganic.org/node/2880
7.4 تعليقات عامة
The questionnaire is broad and often goes beyond the general feature of a technology. Of course, strict documentation of the different features of the technology are desirable.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Soil Fertility Improvement Cluster [أثيوبيا]
The Soil Fertility Improvement Cluster approach engages five or more farmers living in a village who share skills and labour to prepare and use improved compost as well as to demonstrate it to non-member of the group.
- جامع المعلومات: GERBA LETA
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية