Transforming a coconut monocrop into a multi-storey food forest [الهند]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Praveena Sridhar
- المحررون: Rushabh Desadla, Aditya Tated, Dhyana Balasubramanian, Vishwesh Singh, Lu Yu
- المراجعون: William Critchley, Joana Eichenberger
Ottraipayir Thennai Sagubadi Muraiyai Pala Adukku Unavu Kaadaga Matruthal.
technologies_7366 - الهند
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المشاركة في تقييم وتوثيق التقنية
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
متخصص في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
اسم المشروع الذي سهّل توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Save Soil Movementاسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم التقنية (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Conscious Planet - Save Soil (Save Soil)1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 إعلان بشأن استدامة التقنية الموصوفة
هل التقنية الموصوفة هنا تمثل مشكلة فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي، بحيث لا يمكن إعلانها تقنية مستدامة لإدارة الأراضي؟:
كلا
1.5 الإشارة إلى الاستبيان (الاستبيانات) حول مناهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي (موثقة باستخدام WOCAT)

Conscious Planet - Save Soil’s Farmer Training and … [الهند]
The approach focuses on supporting farmers to increase productivity by increasing soil biology and organic matter content, primarily through plant residue and animal waste. Awareness and advocacy are followed by training programs and support for adopting regenerative agricultural practices.
- جامع المعلومات: Praveena Sridhar
2. وصف تقنيةالإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
2.1 وصف مختصر للتقنية
تعريف التقنية:
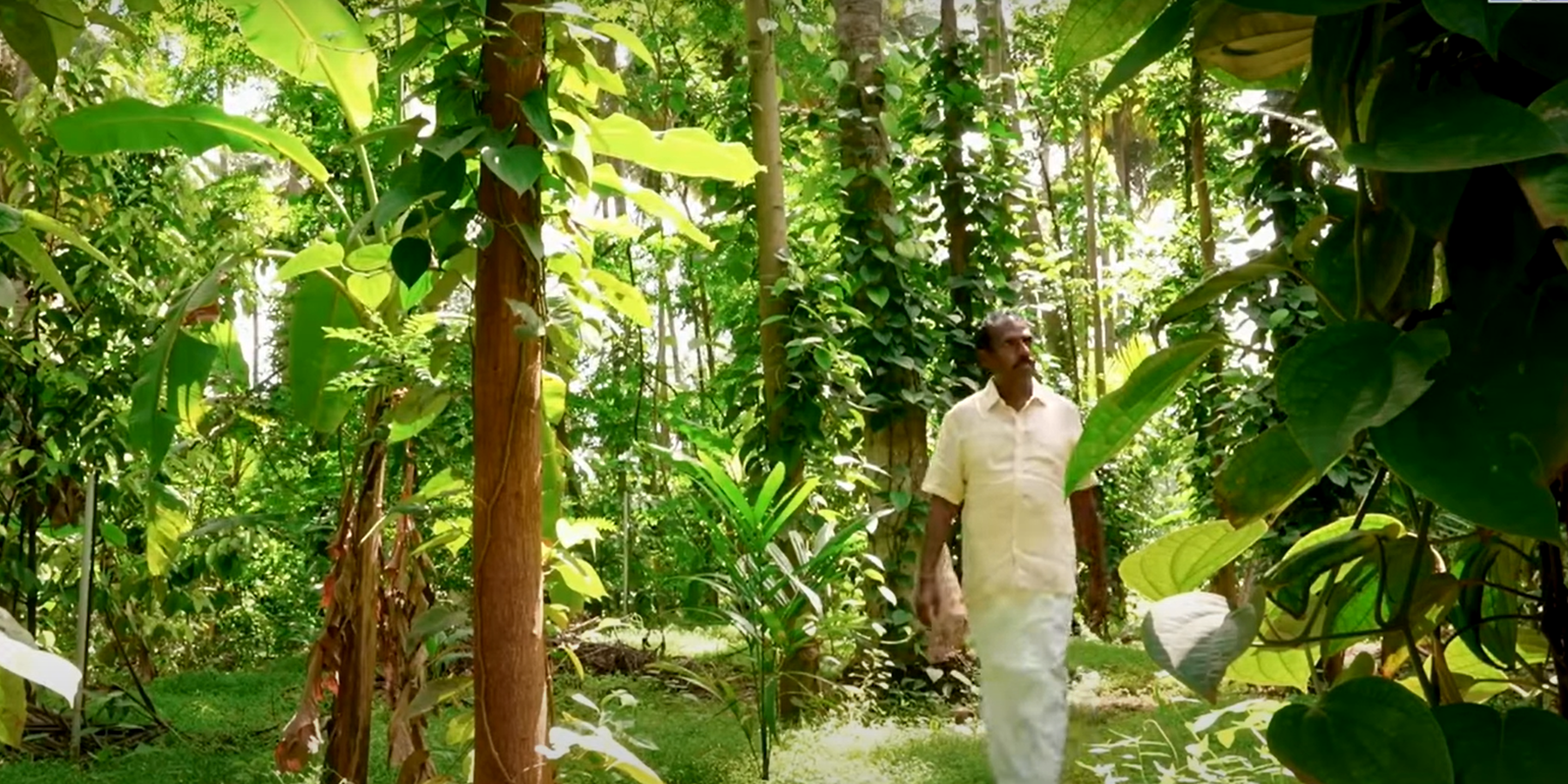
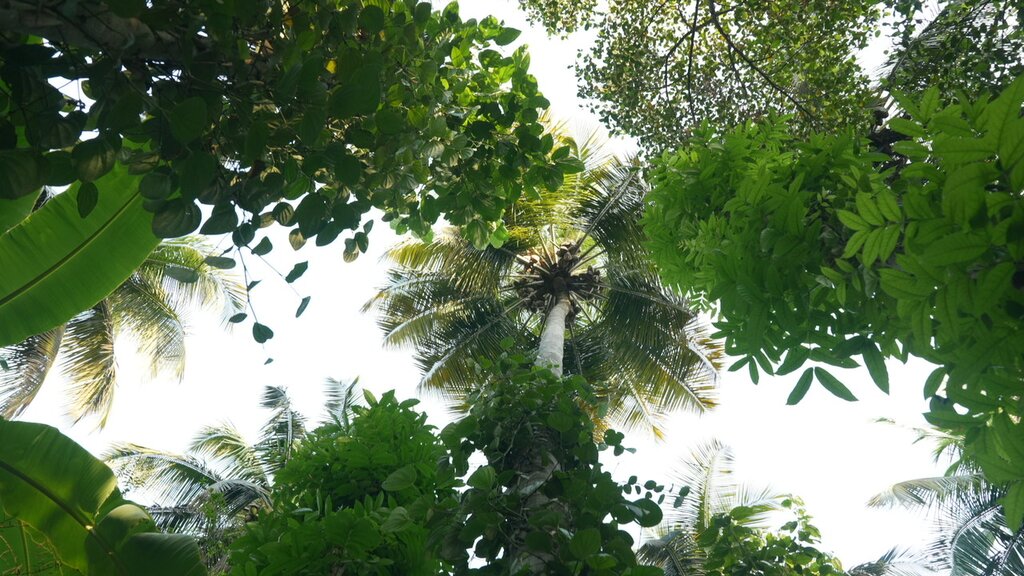
Transforming a monocrop coconut farm into a resilient food forest can sustainably enhance soil health, biodiversity and productivity while reducing labour and external input requirements. This demonstrates the potential to increase yields and provide long-term economic and ecological stability for farmers.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للتقنية
الوصف:
Transforming a monocrop coconut farm into a resilient food forest can sustainably enhance soil health, biodiversity, and productivity while reducing labour and external input requirements. This demonstrates the potential to increase yields and provide long-term economic and ecological stability for farmers. Experience was gained from implementation in 2008 on a monocrop coconut farm in Pollachi, Tamil Nadu. The stages were as follows:
1) Rainwater management: Trenches were dug throughout the farm to retain rainwater and prevent runoff, thus enhancing soil moisture. This was critical given the limited rainfall in the region. A drip irrigation system was installed for efficient watering.
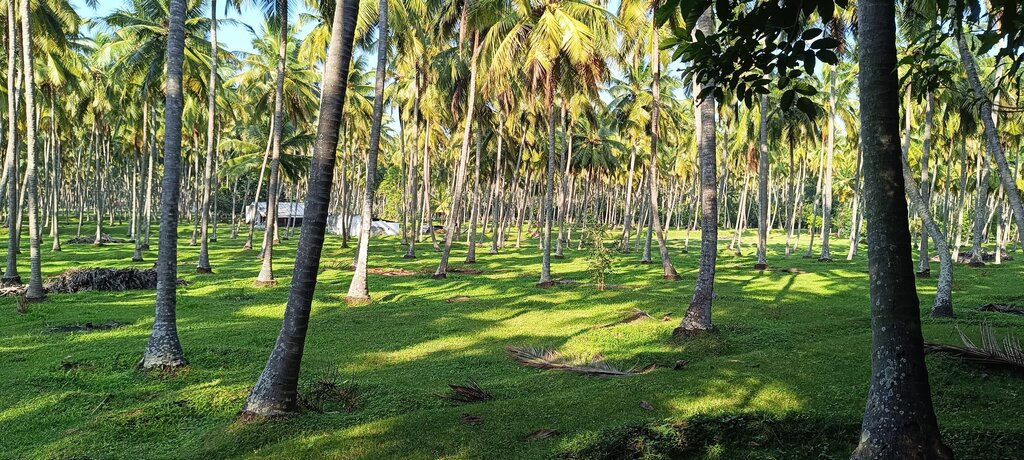
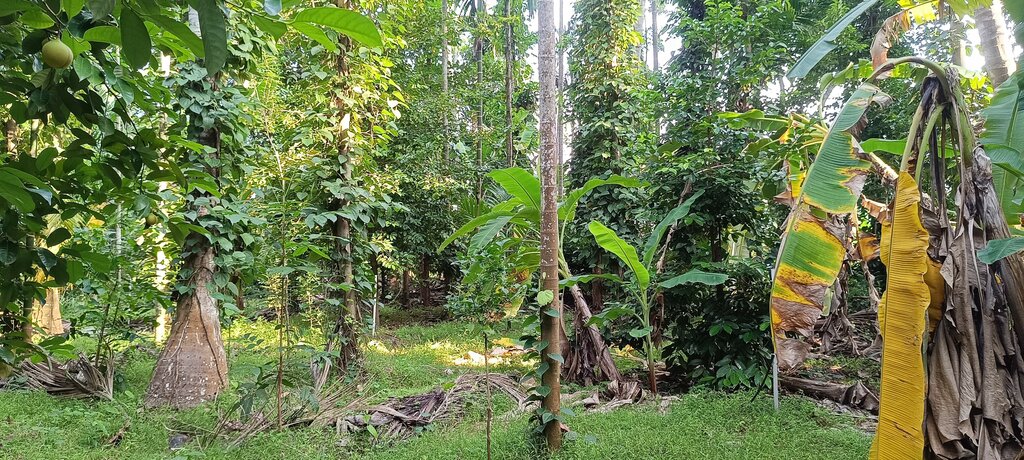
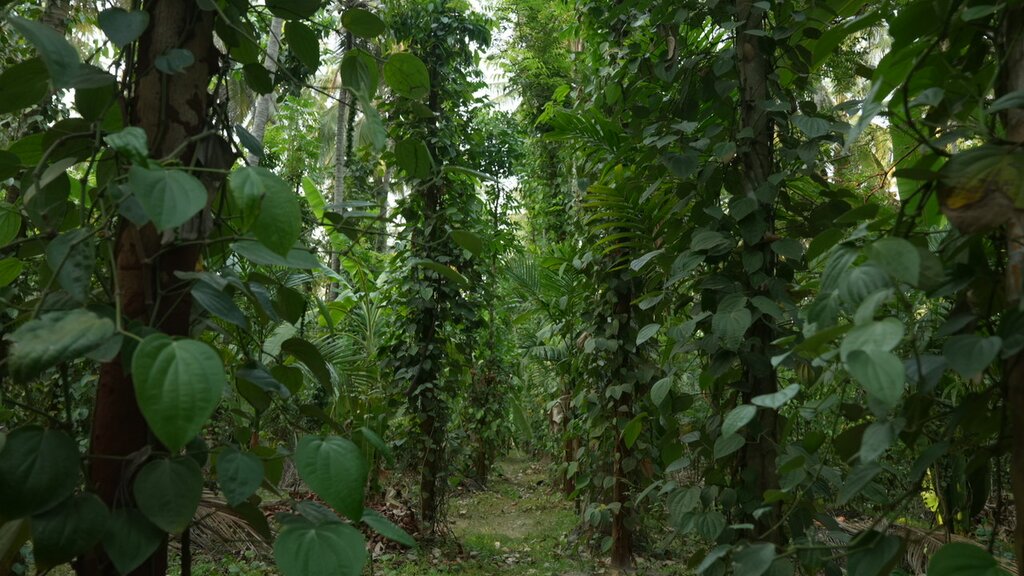
2) Plant diversity: Various crops were introduced. Nutmeg, intercropped among coconut trees, provides 3 - 4 times the income of coconuts after 15 to 20 years. Timber trees extract micronutrients from deeper soil layers via deep tap roots: micronutrients are concentrated in the leaves which are used as mulch to enrich the soil nutrient profile. Banana and papaya provided early income, shade for plants, and added biomass. This diversity also ensures a steady income, reducing dependency on external markets.
3) Biomass and soil fertility improvement: Fast-growing crops were planted to generate additional biomass. Leaves were pruned and added to the water-retaining trenches as mulch. Nitrogen-fixing plants were cultivated extensively to improve soil fertility, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers.
4) Mulch and bio-input application: Mulch in the trenches was decomposed by the bio-inputs from Cows (Earlier 2, now 1) applied via drip lines, which increased soil organic matter through enhanced microbial decomposition. The irrigation and sprinklers were used judiciously to achieve soil moisture rather than over-watering, as trees primarily needed stable moisture conditions.
5) Minimal maintenance approach: After establishing this system, the farm required minimal maintenance. There was no need for tilling, weeding, or other intensive practices, just monitoring of, and maintaining, moisture levels. This low-maintenance approach reduces farmers’ workloads and improves their quality of life.
6) Enhanced biodiversity and pest management: To further enhance biodiversity, flowering plants to attract pollinators and predatory insects can be planted along the farm's boundaries - though this was not done at this particular site. Nonetheless, the increased biodiversity already fostered here brought in earthworms, birds, and beneficial insects for natural pest management.
After 12 years of minimal maintenance, soil organic matter content increased from 0.5% to 3.36%, and both production quantity and quality increased. The farm retained high soil moisture despite periods of low rainfall. Land users liked the use of minimal inputs, crop diversification as a financial safety net, and the visible impact on soil health and yield, as well as the increase in land value. There was initial fear about time and money invested and doubts about the feasibility of a technology that challenged the status quo of the region. Digging trenches and planting saplings were physically demanding. The initial pest pressure was also a concern before a stable ecosystem was established. The transformation of this coconut monoculture into a diverse food forest has demonstrated a sustainable model of enhanced resilience, productivity, and biodiversity. This model can be replicated across similar regions to help minimize labor and improve farmers’ livelihoods while restoring land and ecosystems.
2.3 صور التقنية
2.4 فيديوهات عن التقنية
تعليقات، وصف موجز:
With a few simple interventions, soil that was infertile was brought back to life.
YouTube video link: https://youtu.be/Pt4AEXzgTfc?feature=shared
التاريخ:
10/06/2022
الموقع:
Pollachi, Tamil Nadu
اسم مصور الفيديو:
Save Soil Media team
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تنفيذ التقنية فيها والتي يغطيها هذا التقييم
البلد:
الهند
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Tamil Nadu
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Pollachi
حدد انتشار التقنية:
- يتم تطبيقها في نقاط محددة/ تتركز على مساحة صغيرة
هل يقع موقع/مواقع التقنية في منطقة محمية بشكل دائم؟:
كلا
Map
×2.6 تاريخ التنفيذ
في حالة عدم معرفة السنة بالتحديد، يرجى الإشارة إلى التاريخ التقريبي:
- منذ 10-50 سنة
2.7 إدخال التقنية
حدد كيف تم إدخال التقنية:
- من خلال المشاريع/ التدخلات الخارجية
التعليقات (نوع المشروع، الخ):
The key contributions to the project's technical knowledge include Ethirajalu R (Technical Expert), Anand Ethirajal (Operations Lead), and Dr. Poonyamurti (Ethnoveterinary Medicines Expert). Their expertise, along with the valuable insights shared by Indian stalwarts like Nammalwar, Sripad Davolkar, and Subhash Palekar
3. تصنيف تقنية الإدارة المستدامي للأراضي
3.1 الغرض الرئيسي ( الأغراض الرئيسية) للتقنية
- تحسين الإنتاج
- الحد من تدهور الأراضي ومنعه وعكسه
- الحفاظ على/تحسين التنوع البيولوجي
- التخفيف من تغير المناخ وآثاره
- خلق أثر اقتصادي مفيد
3.2 نوع (أنواع) استخدام الأراضي الحالية حيث يتم تطبيق التقنية
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
نعم
حدد استخدام الأراضي المختلطة (المحاصيل / الرعي / الأشجار):
- الحراجة الزراعية

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة معمرة (غير خشبية)
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
- Climbers : Pepper
الزراعات المعمرة (غير الخشبية) - حدد المحاصيل:
- الموز/موز الهند/الأباكا
- النباتات الطبية والعطرية والمبيدات الحشرية - المعمرة
- Curry Leaves, Lime, Turmeric, Papaya
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- جوز الهند (الفاكهة، والألياف، والأوراق، وما إلى ذلك)
- Nutmeg, Mahogany, Mountain Neem, Kino, Red Sandalwood, Blackwood, White Teak, Iron Wood
عدد مواسم الزراعة في السنة:
- 1
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
نعم
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا
3.3 هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟
هل تغير استخدام الأراضي نتيجة لتنفيذ التقنية؟:
- نعم (يرجى ملء الأسئلة أدناه فيما يتعلق باستخدام الأراضي قبل تنفيذ التقنية)
استخدامات الأراضي مختلطة ضمن نفس وحدة الأرض:
كلا

الأراضي الزراعية
- زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات
زراعة الأشجار والشجيرات -حدد المحاصيل:
- جوز الهند (الفاكهة، والألياف، والأوراق، وما إلى ذلك)
هل يتم ممارسة الزراعة البينية؟:
كلا
هل تتم ممارسة تناوب المحاصيل؟:
كلا
3.4 إمدادات المياه
إمدادات المياه للأرض التي يتم تنفيذ التقنية عليها:
- مختلط بعلي-مروي
3.5 مجموعةالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي التي تنتمي إليها هذه التقنية
- الحراجة الزراعية
- تحسين الغطاء الأرضي/النباتي
- الإدارة المتكاملة لخصوبة التربة
3.6 التدابير التقنية في مجال إلادارة المستدامة للأراضي

التدابير الزراعية
- A1: الغطاء النباتي/التربة
- A2: المادة العضوية/خصوبة التربة
- A6: إدارة المخلفات
A6:حدد إدارة المخلفات:
A 6.4:تم الاحتفاظ بها

التدابير النباتية
- V1: غطاء من الأشجار والشجيرات

التدابير البنيوية
- الحواجز والضفاف
- S4: تسوية الخنادق والحفر
- S6: الجدران والحواجز وسياجات القش، والسياجات
- S7: معدات حصاد المياه/الإمداد/الري
- منشآت المرافق الصحية/مياه الصرف
- S9: إنشاءات حماية النباتات وملاجىء الحيوانات
3.7 الأنواع الرئيسية من تدهور الأراضي التي تناولتها التقنية

تآكل التربة بالمياه
- الوزن(Wt): فقدان التربة السطحية/تآكل السطح

تآكل التربة الناتج عن الرياح
- (Et): فقدان التربة السطحية

التدهور الكيميائي للتربة
- (Cn): تراجع الخصوبة وانخفاض محتوى المادة العضوية (غير ناتج عن الانجراف)
- (Ca):التحمض
- (Cp): تلوث التربة
- (Cs): التملح/ القلونة

التدهور المادي أو الفيزيائي للتربة
- (Pc) : تراص التربة

التدهور البيولوجي
- (Bc): تناقص الغطاء النباتي
- (Bh): فقدان الموائل
- (Bq): انخفاض الكمية/الكتلة الحيوية
- (Bs): انخفاض جودة وتركيبة الأنواع/التنوع
- (Bl): فقدان الحياة بالتربة
- (Bp): زيادة الآفات/الأمراض، وفقدان الحيوانات المفترسة

تدهور المياه
- (Ha): التجفيف
- (Hs): التغيير في كمية المياه السطحية
- (Hg): التغير في مستوى المياه الجوفية/الطبقة المائية الجوفية
- (Hq): تدهور نوعية المياه الجوفية
3.8 منع أو حد أو عكس تدهور الأراضي
تحديد هدف التقنية فيما يتعلق بتدهور الأراضي:
- اصلاح/إعادة تأهيل الأراضي المتدهورة بشدة
4. المواصفات الفنية، وأنشطة التنفيذ، والمدخلات، والتكاليف
4.1 الرسم الفني للتقنية
المواصفات الفنية (المتعلقة بالرسم الفني):
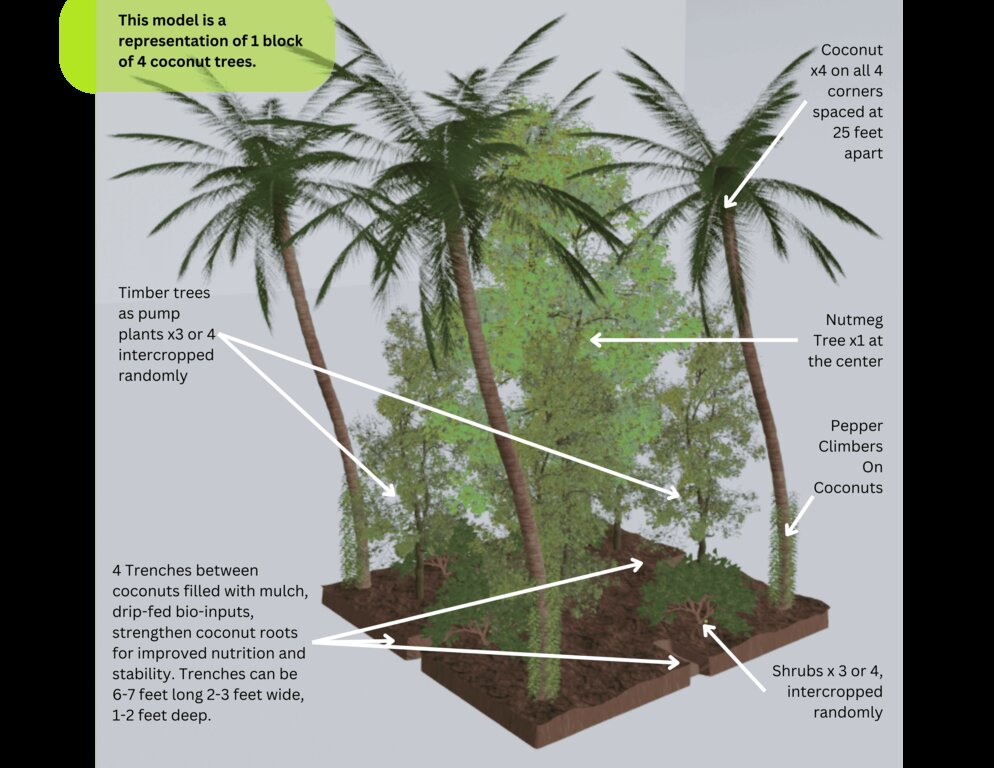
Area: 25 x 25 square feet.
Number of Coconut Trees: 4
Number of Nutmeg Trees: 1
Number of Pepper Climbers: 4
Number of Shrubs: 3-4 (Lime, Curry leaves, Medicinal herbs and Turmeric)
Number of Timber Trees : 3-4 (Mahogany, Mountain Neem, Kino, Red Sandalwood, Blackwood, White Teak and Ironwood)
Number of trenches : 4 ( 6x3x2 ft each, half in this block, half extended to the next block.
Irrigation System: Drip and a Center Fog Sprinkler for creating moisture in the atmosphere.
Input application: Cow dung and Cow urine mix flows to the trench covered with biomass. Decomposes it over time and creates humus for all the plants.
Initially biomass crops are planted, slowly transitioning to trees as the soil improves.
No maintenance after 3-4 years.
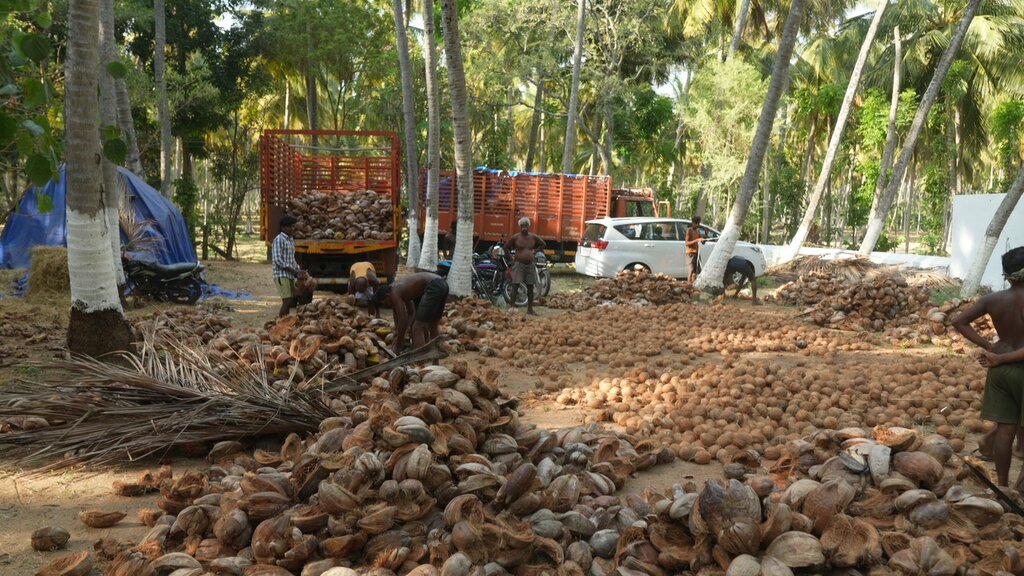
Coconut collected after it drops naturally.
Nutmeg and Pepper harvest happens in 3-4 years, gradually increasing yields.
Shrubs are harvested occasionally for self consumption and direct on farm sales.
المؤلف:
Aditya Tated
التاريخ:
29/10/2024
4.2 معلومات عامة بخصوص حساب المدخلات والتكاليف
حدد كيفية احتساب التكاليف والمدخلات:
- حسب مساحة تنفيذ التقنية
الإشارة إلى حجم ووحدة المساحة:
5.66 hectares
في حالة استخدام وحدة مساحة محلية، قم بالإشارة إلى عامل التحويل إلى هكتار واحد (على سبيل المثال، 1 هكتار = 2.47 فدان): 1 هكتار =:
1hectare = 2.47 acres
عملة أخرى/ عملة وطنية (حدد):
INR
إذا كان ذا صلة، وضح سعر الصرف من الدولار الأمريكي إلى العملة المحلية (على سبيل المثال، 1 دولار أمريكي = 79.9 ريال برازيلي): 1 دولار أمريكي =:
84,07
اذكر متوسط تكلفة أجر العمالة المستأجرة في اليوم الواحد:
600 INR
4.3 أنشطة التأسيس
| النشاط | التوقيت (الموسم) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plot assessment and planning | Before onset of rains |
| 2. | Digging trenches for rainwater harvesting | Before the rainy season |
| 3. | Setting up drip irrigation system | Before planting; dry season |
| 4. | Planting initial tree species (timber, fruit, nitrogen-fixing) | Early rainy season |
| 5. | Planting startup crops (e.g., banana, papaya) | Early rainy season |
| 6. | Mulching trenches with plant biomass | After trench creation, ongoing |
| 7. | Adding bio-inputs to mulch beds | Throughout growing seasons |
| 8. | Pruning trees and returning biomass | Regular intervals during dry seasons |
| 9. | Planting additional companion species | After initial species establishment |
| 10. | Setting up pest repellent measures | As needed, ongoing |
4.4 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للتأسيس
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Trench Digging | machine-hours | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Tree Planting | person-days | 75,0 | 600,0 | 45000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Farm Tools | lump sum | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Irrigation Setup | lump sum | 1,0 | 100000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Pruning Machine | units | 1,0 | 25000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Timber Saplings | units | 5500,0 | 3,0 | 16500,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Nutmeg Saplings | units | 1000,0 | 20,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Pepper Saplings | units | 1000,0 | 40,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Fruit Trees | units | 500,0 | 100,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Organic Manure | load | 10,0 | 1500,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Organic Pest Repellants | lump sum | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Fencing Irrigation | lump sum | 1,0 | 200000,0 | 200000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Bio-Input Preparation Unit | lump sum | 1,0 | 200000,0 | 200000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Pipes and Valves | lump sum | 1,0 | 530000,0 | 530000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Tool Shed | lump sum | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Worker Shed | lump sum | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Farm Animals | units | 5,0 | 20000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Fodder | annual | 1,0 | 25000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية | 1606500,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف إنشاء التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 19109,08 | |||||
التعليقات:
Land user bore all costs
4.5 الصيانة/الأنشطة المتكررة
| النشاط | التوقيت/الوتيرة | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning | Every 6 months |
| 2. | Irrigation system maintenance | Annually, before dry season |
| 3. | Mulching trenches | Twice a year, before onset of rains |
| 4. | Adding bio-inputs to mulch beds | Happens automatically with irrigation. |
| 5. | Harvesting fruits and biomass | As and when needed Coconut is collected after it falls by itself. |
| 6. | Replanting missing or damaged trees | Annually, before rainy season |
| 7. | Fencing and protection checks | Quarterly |
4.6 التكاليف والمدخلات اللازمة للصيانة/للأنشطة المتكررة (سنويًا)
| تحديد المدخلات | الوحدة | الكمية | التكاليف لكل وحدة | إجمالي التكاليف لكل مدخل | % من التكاليف التي يتحملها مستخدمو الأراضي | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| العمالة | Pruning, mulching, replanting | person-days | 100,0 | 600,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| العمالة | Harvesting | person-days | 300,0 | 600,0 | 180000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Tools for pruning fencing checks | lump sum | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Irrigation system maintenance | lump sum | 1,0 | 10000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| معدات | Fencing maintenance | lump sum | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | 100,0 |
| المواد النباتية | Replacement seedlings | pieces | 50,0 | 30,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| الأسمدة والمبيدات الحيوية | Preparing organic bio-inputs via irrigation system | lump sum | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| مواد البناء | Fencing materials for repair | lump sum | 1,0 | 8000,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 |
| غير ذلك | Cow Care and Fodder | kg | 5,0 | 5000,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية | 319500,0 | |||||
| إجمالي تكاليف صيانة التقنية بالدولار الأمريكي | 3800,4 | |||||
التعليقات:
Land users bore all costs
4.7 أهم العوامل المؤثرة على التكاليف
قدم وصفا لأهم العوامل التي تؤثر على التكاليف:
No factors significantly affected costs.
5. البيئة الطبيعية والبشرية
5.1 المناخ
هطول الأمطار السنوي
- < 250 مم
- 251- 500 ملم
- 501 - 750ملم
- 1,000-751 ملم
- 1,500-1,100 ملم
- 2,000-1,500 ملم
- 3,000-2,001 ملم
- 4,000-3,100 ملم
- > 4000 ملم
حدد متوسط هطول الأمطار السنوي (إذا كان معروفًا)، بالملليمتر:
865,00
المواصفات/التعليقات على هطول الأمطار:
Rainfall Distribution and Seasonality: Monsoon Seasons: Rainfall peaks during the southwest monsoon (June to September) and the northeast monsoon (October to November). August, October, and November are the rainiest months, each with an average precipitation between 167 to 214 mm.
Dry Periods: The driest months are January to March, with very low rainfall, averaging between 5 to 35 mm per month.
الإشارة إلى اسم محطة الأرصاد الجوية المرجعية المعنية:
Coimbatore Metrological station, India Meteorological Department’s (IMD) network.
المنطقة المناخية الزراعية
- رطبة
Generally warm, with an average annual temperature around 26–28°C (79–82°F). The hottest months tend to be March to May, where temperatures can reach up to 36–40°C (97–105°F), while the coolest months are December and January, with average daily temperatures ranging from 25–26°C (77–79°F)
5.2 طوبوغرافيا
متوسط الانحدارات:
- مسطح (0-2%)
- بسيط (3-5%)
- معتدل (6-10%)
- متدحرج (11-15%)
- تلال (16-30%)
- شديدة الانحدار(31-60%)
- فائقة الانحدار (>60%)
التضاريس:
- هضاب/سهول
- أثلام مرتفعة
- المنحدرات الجبلية
- منحدرات التلال
- منحدرات في السفوح
- قاع الوادي
المنطقة الارتفاعية:
- 100-0 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 500-101 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,000-501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 1,500-1,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,000-1,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 2,500-2,100 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 3,000-2,501 متر فوق سطح البحر
- 4,000-3,001 متر فوق سطح البحر
- > 4000 متر فوق سطح البحر
وضح ما إذا كانت التقنية مطبقة على وجه التحديد في:
- غير ذات صلة
5.3 التربة
متوسط عمق التربة:
- ضحل جدًا (0-20 سم)
- ضحلة (21-50 سم)
- متوسطة العمق (51-80 سم)
- عميقة (81-120 سم)
- عميقة جدًا (> 120 سم)
قوام التربة (التربة السطحية):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
قوام التربة (> 20 سم تحت السطح):
- ناعم/ثقيل (طيني)
المواد العضوية في التربة السطحية:
- منخفضة (<1%)
إذا كان متاحًا، قم بإرفاق وصف كامل للتربة أو تحديد المعلومات المتوفرة، على سبيل المثال نوع التربة، الرقم الهيدروجيني/ درجة حموضة التربة، قدرة التبادل الكاتيوني، النيتروجين، الملوحة وما إلى ذلك.
Soil type - Red sandy soil
5.4 توافر المياه ونوعيتها
منسوب المياه الجوفية:
50-5 م
توافر المياه السطحية:
ضعيف/ غير متوافر
نوعية المياه (غير المعالجة):
مياه شرب جيدة
تشير جودة المياه إلى:
المياه الجوفية
هل تعتبر ملوحة الماء مشكلة؟:
كلا
هل تحدث فيضانات في المنطقة؟:
كلا
تعليقات ومواصفات أخرى بشأن نوعية المياه وكميتها:
Pollachi, the place where the farm is located, water quality fluctuates throughout the year, particularly due to agricultural runoff and effluents from nearby industrial activities.
5.5 التنوع البيولوجي
تنوع الأنواع:
- منخفض
تنوع الموائل:
- منخفض
5.6 خصائص مستخدمي الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
مستقر أو مرتحل:
- غير المترحل
التوجه السوقي لنظام الإنتاج:
- مختلط (كفاف/ تجاري)
الدخل من خارج المزرعة:
- >50% من إجمالي الدخل
المستوى النسبي للثروة:
- متوسط
أفراداً أو مجموعات:
- فرد/أسرة معيشية
مستوى المكننة:
- ميكانيكية/ مزودة بمحرك
الجنس:
- نساء
- رجال
عمر مستخدمي الأرضي:
- متوسط العمر
5.7 متوسط مساحة الأرض التي يستخدمها مستخدمو الأراضي الذين يطبقون التقنية
- < 0.5 هكتارا
- 0.5 - 1 هكتار
- 1 -2 هكتار
- 2 - 5 هكتار
- 5 - 15 هكتار
- 15 - 50 هكتار
- 50 - 100هكتار
- 500-100 هكتار
- 1,000-500 هكتار
- 10,000-1,000 هكتار
- > 10,000 هكتار
هل يعتبر هذا نطاقًا صغيرًا أو متوسطًا أو واسعا (في إشارة إلى السياق المحلي)؟:
- على نطاق متوسط
5.8 ملكية الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام المياه
ملكية الارض:
- فردية، يوجد سند ملكية
حقوق استخدام الأراضي:
- فردي
حقوق استخدام المياه:
- فردي
هل تعتمد حقوق استخدام الأراضي على نظام قانوني تقليدي؟:
نعم
حدد:
Private Ownership
5.9 الوصول إلى الخدمات والبنية التحتية
الصحة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
التعليم:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
المساعدة التقنية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
العمل (على سبيل المثال خارج المزرعة):
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الأسواق:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطاقة:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الطرق والنقل:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
مياه الشرب وخدمات الصرف الصحي:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
الخدمات المالية:
- ضعيف
- معتدل
- جيد
6. الآثار والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية في الموقع
الآثار الاجتماعية والاقتصادية
الإنتاج
إنتاج المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
110
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
160
التعليقات/ حدد:
Coconuts were small in size and fewer in number when the farm was bought. After 6-7 years, the counts increased from 110 per tree per year to 160 and size increased 150% on average.
جودة المحاصيل
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Not so tasty
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
Taste is the best compared to surrounding many farms.
خطر فشل الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
50-60%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0%
التعليقات/ حدد:
The risk of production failure has come down to 0% as there is no pest and disease attack. The coconuts yield continuously throughout the year.
تنوع المنتج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3
التعليقات/ حدد:
From just one crop to 2 main crops, pepper as a sub-main crop and a variety of fruits for self consumption.
منطقة الإنتاج
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
60%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Coconuts occupied approximately 40% area in terms of canopy. Now in addition to that there is nutmeg which occupies another 20%. Rest of the area is for timber and other supporting crops not included here.
إدارة الأراضي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
24/7
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
1 Day a Week
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farmer before this owner spent hours in weeding, application of inputs and pesticide, burning of crop residue, harvesting coconuts. Now the whole farm needs 2 labour to collect fallen coconuts and turn on the irrigation switches and valves. The farmer comes to visit the farm once a week for monitoring.
توافر المياه ونوعيتها
نوعية مياه الشرب
توافر مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Earlier the bore wells would run only for a couple of hours and then the water would dry out. Now it fulfills the irrigation requirement without interruption.
الطلب على مياه الري
التعليقات/ حدد:
Demand for water has drastically come down as the SOC content in the soil has risen.
الدخل والتكاليف
النفقات على المدخلات الزراعية
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is no expense in any agricultural input apart from maintenance of 2-3 cows. The entire system is automatic. The slurry from the cowshed goes into the tank which supplies input through a venturi to the drip irrigaton system.
دخل المزرعة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Farm income has gone up significantly owing to the high yields, multiple crops, better prices, low cultivation and management costs.
تنوع مصادر الدخل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Incomes are coming from sale of coconuts, nutmeg and pepper. Coconut oil is also extracted now by the farmer and sold at a high premium price.
عبء العمل
التعليقات/ حدد:
The drudgery of mainting a monocrop and all the works associalted with conventional agriculture is eliminated by 95%. The only workload is to pick up the fallen coconuts and harvest nutmeg and pepper.
الآثار الاجتماعية والثقافية
الوضع الصحي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The health of the owner and the consumers is greatly benefitted owing to the absense of harmful chemicals and pesticides in the produce.
المعرفة بالإدارة المستدامة للأراضي/تدهور الأراضي
التعليقات/ حدد:
This model is a great source of wisdom about tree-based regenerative agriculture which can counter land degradation. It has all the necessary components of how to convert dirt into soil.
الآثار الايكولوجية
دورة المياه / الجريان السطحي
جودة المياه
حصاد / جمع المياه
الجريان السطحي
تصريف المياه الزائدة
مستوى المياه الجوفية/ الطبقة المائية الجوفية
التبخر
التربة
رطوبة التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil moisture is maintained as high levels except for summers when its a little low due to the intense heat this region faces.
غطاء التربة
تراص التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Soil compaction has reduced because of the heavy penetraton of tree roots, improved SOC and biological activity in the soil.
دورة المغذيات/إعادة الشحن
التعليقات/ حدد:
It is evident from the yields that there is a very resilient process of nutrient cycling happening in the farm compared to what was happening earlier.
المادة العضوية في التربة/تحت الطبقة c
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
0.5
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
3.36
التعليقات/ حدد:
The SOC level have increased continously and is still increasing because of the leaf litter that is added continuously throughout the year.
التنوع البيولوجي: الغطاء النباتي، الحيوانات
الغطاء النباتي
الكمية قبل الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
40%
الكمية بعد الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي:
90%
التعليقات/ حدد:
Vegetation cover in the form of trees, shrubs, perennial crops and pepper has shown dramatic increase.
الكتلة الحيوية/ طبقة الكربون فوق التربة
التعليقات/ حدد:
Addition of 3 times the number of trees has increased the above ground biomass multiple times.
التنوع النباتي
التعليقات/ حدد:
The farm is now a home for more than 100 species of plants compared to just one when it was bought.
الأنواع الدخيلة الغازية
التعليقات/ حدد:
There is an absolute balance in the farm ecosystem with no species going out of control. There are no significant weeds as the soil ecosystem and shade doesn't support the common invasive species found in the region.
التنوع الحيواني
التعليقات/ حدد:
Minor farm animals are seen. Since its not a large area, enough diversity has not been established.
الأنواع المفيدة
التعليقات/ حدد:
There are no harmful species for which the farmer needs to worry about. All species are beneficaial in some way or the other.
تنوع الموائل
التعليقات/ حدد:
Multi layer multi crop system allows various different habitat for a variety of species. Here from high coconut to rich soil undergrond has a habitat diversity of semi-forest which was not present earlier.
مكافحة الآفات/الأمراض
التعليقات/ حدد:
The farmer says he doesn't know what are pests now which was not the case earlier. Earlier his coconuts would be continously be harmed by something or the other.
الحد من مخاطر المناخ والكوارث
آثار الجفاف
التعليقات/ حدد:
The impact of drought is not significant in this farm because of the green cover, soil moisture, high water tables, year-round water availability and overall resiliance of the system. All other conventional farms face enormous hardship during droughts.
آثار السيكلون والعواصف المطرية
التعليقات/ حدد:
Impact of rain storms is also less as there is enough wind barriers because of the dense vegetation. The coconots have penetrated their roots towards the trenches and underground in search of nutrients making them strongly grounded and able to withstand storms easily.
انبعاث الكربون والغازات المسببة للاحتباس الحراري
التعليقات/ حدد:
This system is carbon negative as there is no use of chemicals or fossil fuels needed to run any operation except the transportation of coconuts to the markets.
سرعة الرياح
التعليقات/ حدد:
Wind velocity is hindered now due to the dense vegetation.
المناخ الموضعي (مايكرو)
التعليقات/ حدد:
The micro-climate is the most tangible change that anyone visiting the farm is able to relish. The coolness inside the farm is completely mood-changing for someone who is entering from outside. It leaves people wanting to live here or create such a place for themselves. Its an oasis in a desert.
حدد تقييم الآثار في الموقع (القياسات):
Soil Fertility: Initially, the soil was likely low in organic matter due to monoculture practices. Through the addition of nitrogen-fixing plants and mulching with biomass, the soil's nutrient levels improved naturally, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers.
Soil Organic Carbon: Soil organic carbon increased notably from 0.5% to 3.36% due to continuous mulching, the addition of bio-inputs, and water-retaining trenches. These practices enriched the soil with organic matter, improving its structure and capacity to hold moisture.
Erosion Control and Water Retention: Trenches and rainwater harvesting reduced runoff, preventing soil erosion and enhancing water retention, which helped maintain stable soil moisture levels, even in dry periods.
Microbial Health: The use of bio-inputs via drip irrigation boosted microbial activity in the soil, accelerating the decomposition of organic matter into humus, which further improved soil fertility and structure.
6.2 الآثار التي أظهرتها التقنية خارج الموقع
توافر المياه
التعليقات/ حدد:
It is assumed that as the groundwater table in the site has increased, it would definitely have some effect of the neighboring sites.
قيّم الآثار خارج الموقع (القياسات):
We have not conducted measurement of off-site ecological impacts for this farm as of now.
6.3 تعرض التقنية وحساسيتها لتغير المناخ التدريجي والظواهر المتطرفة/الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ (كما يراها مستخدمو الأراضي)
تغير مناخ تدريجي
تغير مناخ تدريجي
| الموسم | زيادة أو نقصان | كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| درجة الحرارة السنوية | زيادة | جيدة جدا | |
| درجة الحرارة الموسمية | فصل جاف | زيادة | جيدا |
| هطول الأمطار السنوي | جيدة جدا | ||
| هطول الأمطار الموسمية | موسم الرطوبة/ الأمطار | زيادة | جيدة جدا |
الظواهر المتطرفة / الكوارث المرتبطة بالمناخ
الكوارث الجوية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| عاصفة ممطرة محلية | جيدة جدا |
الكوارث المناخية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| موجة حر | جيدا |
| جفاف | جيدا |
الكوارث البيولوجية
| كيف تتعامل التقنية مع ذلك؟ | |
|---|---|
| الإصابة بالحشرات/الديدان | جيدة جدا |
6.4 تحليل التكلفة والعائد
كيف يمكن مقارنة العوائد نسبة لتكاليف الإنشاء (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
سلبي قليلا
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
كيف تتم مقارنة العوائدمع كلفة الصيانة/التكاليف المتكررة (من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي)؟
عوائد قصيرة الأجل:
محايد/متوازن
عوائد طويلة الأجل:
ايجابي جدا
6.5 اعتماد التقنية
- 1-10%
من بين جميع الذين تبنوا التقنية، كم عدد الذين فعلوا ذلك بشكل تلقائي، أي دون تلقي أي حوافز مادية/مدفوعات؟:
- 10-0%
6.6 التكيف
هل تم تعديل التقنية مؤخرًا لتتكيف مع الظروف المتغيرة؟:
كلا
6.7 نقاط القوة / المزايا / الفرص التي توفرها التقنية
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| 1) Efficient Rainwater Harvesting: Trenches prevent water runoff and retain moisture, helping farmers adapt to water-scarce conditions. Drip irrigation ensures efficient water use, reducing waste and improving moisture availability at plant roots. |
| 2) Nitrogen-fixing plants and bio-inputs build natural soil fertility, reducing or eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers. |
| 3) Income Stability: Diverse crops (timber, fruit, and cash crops like bananas and papayas) ensure year-round income and minimize dependency on a single crop. |
| 4) Pest and Disease Management: The natural ecosystem with pollinators and predatory insects reduces pest issues without needing chemical pesticides. |
| 5) Minimal Labor: Once established, the system requires less labor with minimal tilling or weeding, allowing farmers to save on labor costs. |
| 6) Increased Yield and Quality: Coconut yield has improved significantly, with larger and better-tasting coconuts, enhancing the crop’s market value. |
| 7) Ecological Balance: The increase in biodiversity supports natural pest control, improved pollination, and enriched soil. |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
|
1)Positive Environmental Impact: Enhanced Soil and Water Conservation: Rainwater harvesting and mulching contribute to soil health and sustainable water use, supporting resilient agricultural practices. Carbon Sequestration: The introduction of timber and fruit trees aids in carbon capture, helping to mitigate climate change. |
|
2)Increased Biodiversity and Natural Pest Management: Reduction in Chemical Usage: Biodiverse ecosystems reduce reliance on pesticides and chemical fertilizers, fostering healthier food systems. Positive Environmental Metrics: Biodiversity and natural pest control align with ecological sustainability, improving farm ecosystems. |
|
3)Model for Replication and Scaling: Technology Viability: A successful pilot farm serves as a model that other farmers can adopt, promoting tree-based agriculture and natural farming methods. Long-Term Sustainable Farming: This low-maintenance, high-diversity model provides a sustainable alternative to conventional farming, attracting interest from stakeholders focused on sustainable agriculture. |
|
4)Attracting Donor Support: Appeal to Donors: The project’s long-term sustainability and eco-friendly practices attract donors focused on climate resilience and food security. Potential for Diverse Funding: The combined focus on environmental sustainability, economic empowerment, and climate resilience appeals to various funding sources. |
6.8 نقاط ضعف / مساوىء / مخاطر التقنية وسبل التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| 1) Learning Curve: Farmers may need additional knowledge on tree-based agriculture and organic soil management, which could necessitate training and support. | 1) Training programs across the project region are conducted on various aspects of regenerative agriculture at minimal costs |
| 2) Consistency in Bio-input Application: The effectiveness of bio-inputs depends on regular application; skipping or improper application could hinder soil improvement. | 2) Farmer hand holding is available via farmer helpline for basic queries and farm visits are conducted if nature of query requires. |
| 3) Higher Pest Pressure in Early Stages: As biodiversity builds up gradually, farmers might initially encounter some pest pressure until a stable ecosystem is established. | 3) Pest and disease management trainings are quite frequent and also the training video is available on Save Soil youtube channel in regional languages for easy access for farmers |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| 1) Need for Technical Expertise and Training: Farmers may need intensive training in regenerative agriculture methods, necessitating resources for workshops, materials, and ongoing support staff, which may impact the organization’s budget and staffing. | 1) Major portion of funding goes into trainings and to create online and offline materials easily accessible to farmers. In mega training program where more than 1000s of farmers attend, free technical handbook is also provided to support them on a daily basis |
| 2) Difficulty in Immediate Impact Measurement: Due to the delayed returns, reporting immediate success and impact might be challenging, especially in a results-oriented funding environment. | 2) Need to implement milestone-based metrics, proxy indicators, and comparative reporting to showcase early progress. Farmer testimonials and case studies further illustrate positive outcomes, while data visualizations offer accessible insights into ecological improvements and economic stability. |
| 3) Risk of Low Farmer Adoption: Farmers may be hesitant about the model’s initial costs and labor, slowing adoption. | 3) Selective aspects of the technology can be taken up initially to see early success in order to manage finances |
| 4) Resource-Intensive Monitoring and Data Collection: Tracking soil health, biodiversity, and yields requires dedicated monitoring, which can be resource-intensive, especially across multiple farms. | 4) Success of few model farms will convince farmer community to take up this technology without having the need to monitor each and every farm |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
3-5 expert volunteers visited the farm for this survey.
- مقابلات مع مستخدمي الأراضي
1 person talked to the land user.
- مقابلات مع المتخصصين/الخبراء في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2 specialists were interviewed.
- التجميع من التقارير والوثائق الأخرى الموجودة
4 people were involved in documentation and reporting.
متى تم تجميع البيانات (ميدانيا)؟:
25/10/2024
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Cauvery Calling: Impact Assessment Report 2024: A global economic model for farmers with a significant ecological impact
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://drive.google.com/drive/u/1/search?q=UNCCD%20policy
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
SS-TKV Annual Report 2023-24
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1vvMD0kd-qWs4JtebbsBpOGBB-z_6CVr3ZcrK-1wV78Y/edit?tab=t.0
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Save Soil Movement - Model Farm, Proof of Concept
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://consciousplanet.org/en/save-soil/blog/save-soil-movement-model-farm-proof-of-concept
العنوان/الوصف:
A living example of Save Soil
عنوان الرابط URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QVis4gkcPIU&t=353s
7.4 تعليقات عامة
The farm is still undergoing transformation into a more efficient and profitable model with the technology implemented.
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Conscious Planet - Save Soil’s Farmer Training and … [الهند]
The approach focuses on supporting farmers to increase productivity by increasing soil biology and organic matter content, primarily through plant residue and animal waste. Awareness and advocacy are followed by training programs and support for adopting regenerative agricultural practices.
- جامع المعلومات: Praveena Sridhar
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية