Sustainable use of water [Greece]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Costas Kosmas
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2428 - Greece
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Agricultural University of Athens (AUA) - Greece1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies
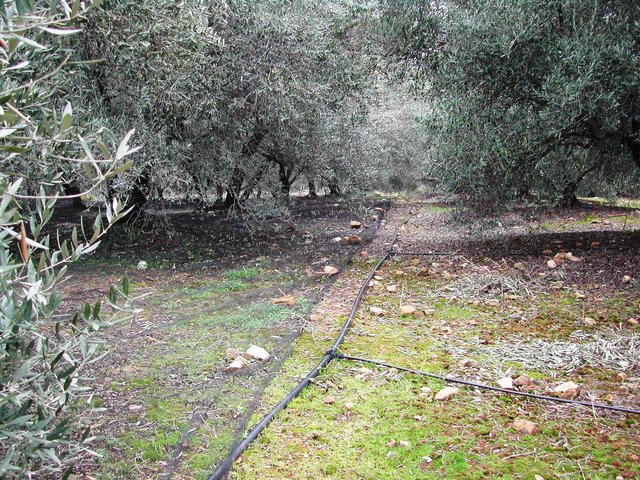

Application of water by drip irrigation [Greece]
Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation is a method which minimizes the use of water and fertilizer by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either onto the soil surface or directly onto the root zone, through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters.
- Compiler: Costas Kosmas
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
Sustainable use of water
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Greece
Region/ State/ Province:
Chania and Heraclion prefectures of Crete
Further specification of location:
Crete
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
20
2.7 Type of Approach
- recent local initiative/ innovative
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (prevention of soil erosion and water conservation)
to promote conservation of natural resources
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: significnat cost for the installation of the technology
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
increased cost for first installation
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- hindering
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly hindered the approach implementation if irrigation water is not available
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- hindering
planning the system requirements
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
The majority of land users are men
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | |
| planning | interactive | |
| implementation | external support | |
| monitoring/ evaluation | none | |
| Research | none |
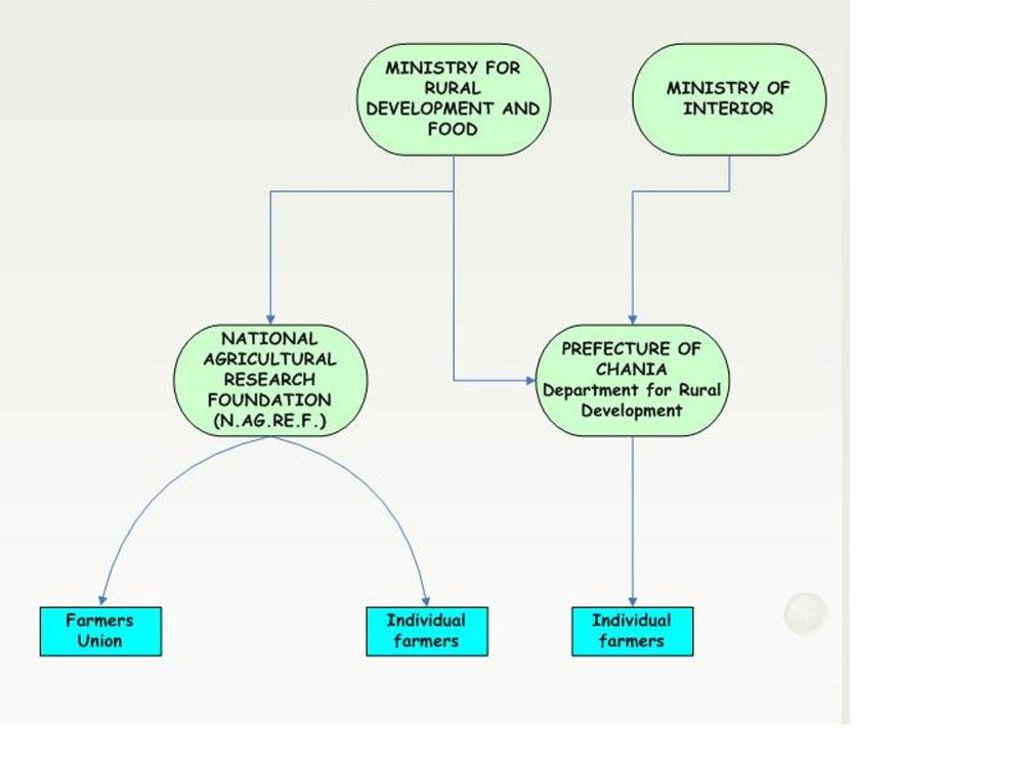
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- SLM specialists alone
Explain:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Yes
Specify who was trained:
- land users
If relevant, specify gender, age, status, ethnicity, etc.
Mainly men aged from twenties to sixties, Greeks
Form of training:
- public meetings
Subjects covered:
Conservation of natural resources
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- at permanent centres
Describe/ comments:
Name of method used for advisory service: analysis of production; Key elements: cost production, total production
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, a little
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Specify type of support:
- financial
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Comments:
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Yes
Specify topics:
- ecology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
ISPOT, AUA
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Financing and external material support
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Decrease in soil loss and increase in water conservation
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
mainly men, old aged Greeks
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Land users in Pelloponese
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Increase in farmers income
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
increasing income
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- increased production
- increased profit(ability), improved cost-benefit-ratio
- environmental consciousness
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- yes
If yes, describe how:
the cost resulting from the application of the technique is moderate
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Application of water by drip irrigation [Greece]
Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation is a method which minimizes the use of water and fertilizer by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either onto the soil surface or directly onto the root zone, through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters.
- Compiler: Costas Kosmas
Modules
No modules