Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) [Philippines]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Deborah Niggli
approaches_1971 - Philippines
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
SLM specialist:
Castillo Forester Emma N.
emmancastillo2014@gmail.com
Department of Environment and Natural Resources-Forest Management Bureau (DENR-FMB)
Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Philippines
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Department of Agriculture-Region VIII (DA-8) - Philippines1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
25/01/2016
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Reference(s) to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Technologies
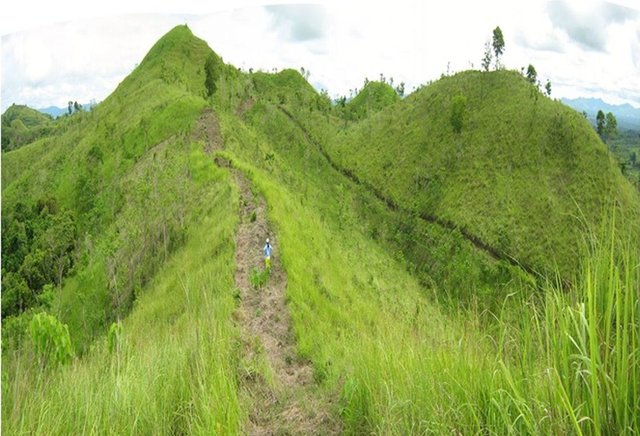

Firebreaks/ Greenbreaks [Philippines]
Gaps in vegetation or other combustible material that act as barriers to prevent and/ or control the spreading of forest fires to other areas.
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
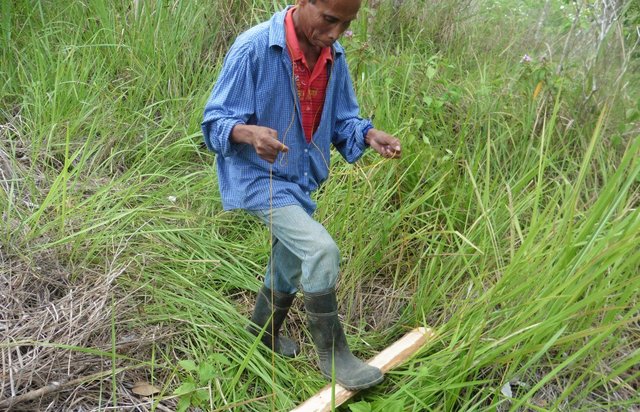

Pressing of Cogon Grass (Imperata cylindrica) [Philippines]
An indigenous technology of enhancing wildling growth by pressing of cogon grass.
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
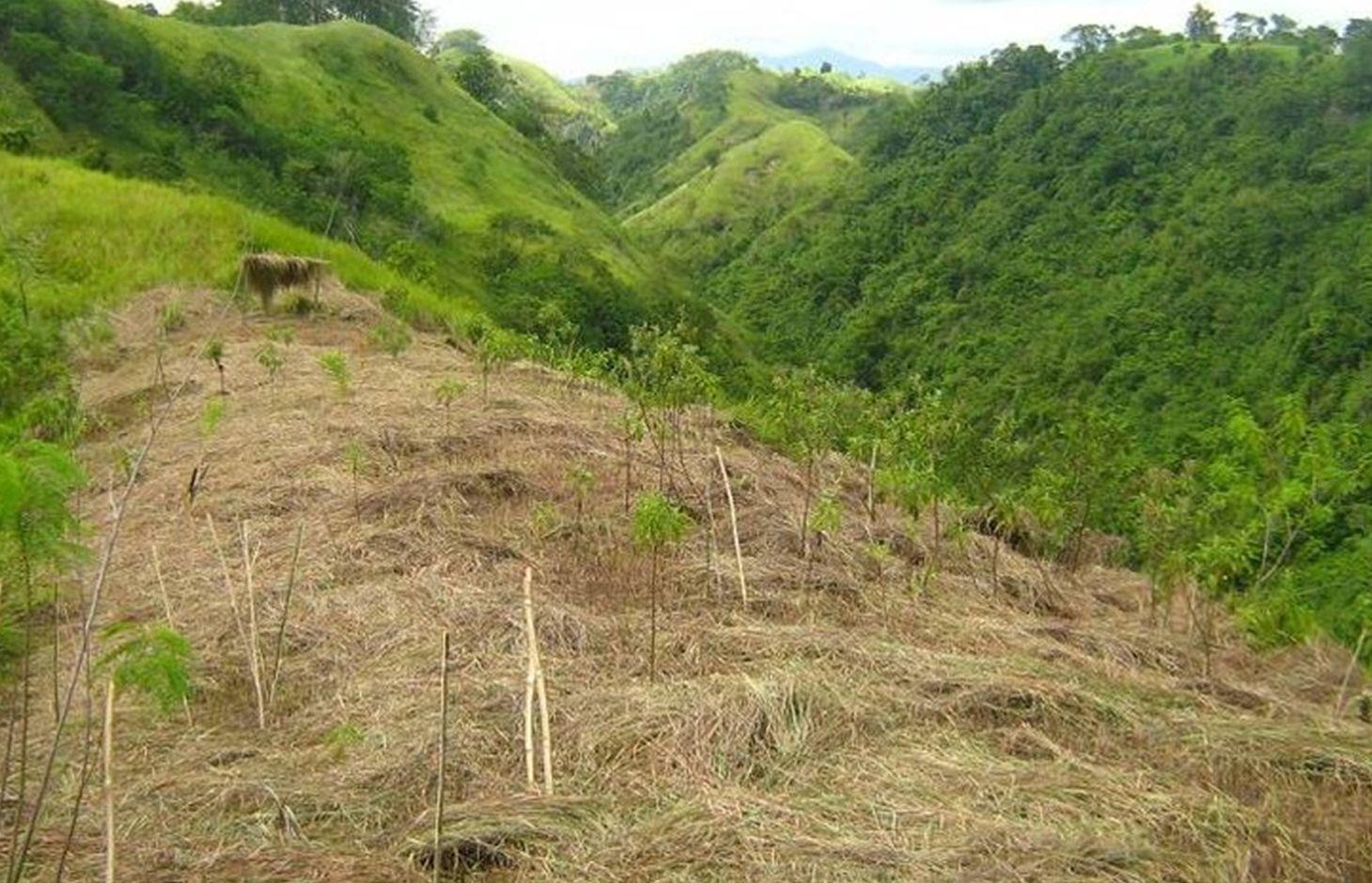
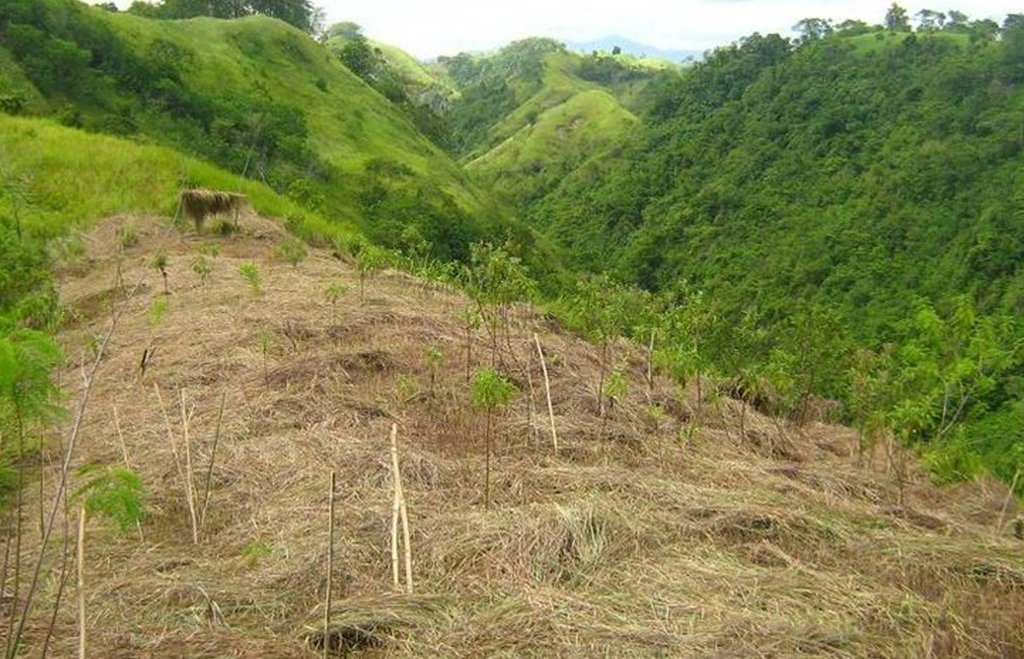
A process of rehabilitating degraded forest lands by taking advantage of trees already growing in the area.
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
The objectives of the Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) approach includes reduction of cost, speeding-up of forest restoration and enhancing plant diversity. It accelerates the succession process by removing or reducing barriers to natural regeneration such as competition with weedy species, soil degradation and recurring disturbances.
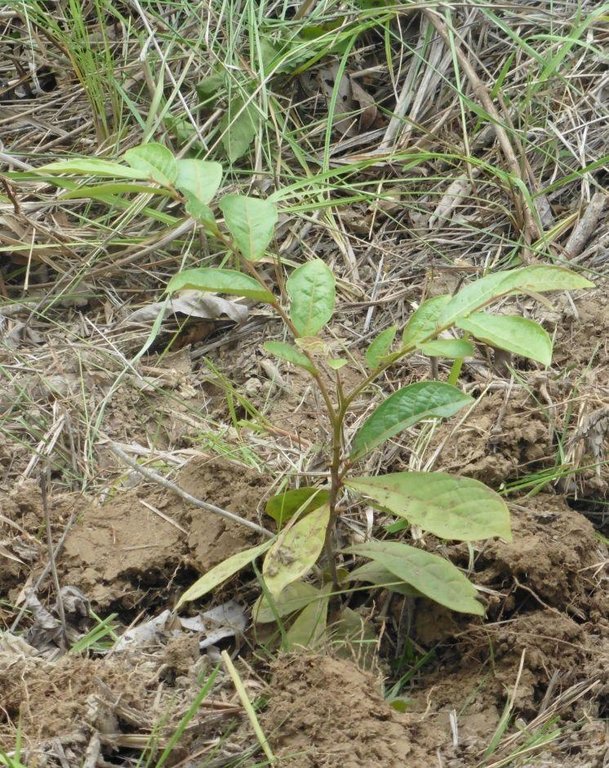
ANR is a method for enhancing the establishment of secondary forest from degraded grassland and shrub vegetation by protecting and nurturing mother trees and their wildlings inherently present in the area.
Stages of implementation: (a)Site identification wherein ideal sites for ANR implementation are those with 600-700 vigorous wildlings per hectare with 15-200 cm height of pioneer species, brush and other woody species relatively well spread on the area; (b) Survey, Mapping and Planning (SMP); (c)Locating and marking of wildlings which include tagging, measuring and identification for monitoring of growth and survival rates; (d) Liberation and tending of regenerants through ring weeding and placing of the cut grasses into the base of the wildlings to serve as mulch and protect them from direct exposure to sunlight and to serve as fertilizer overtime; (e) Suppressing the grass; and (f) Maintenance and protection of established ANR site.
The project of ANR in Barangay San Miguel, Danao, Bohol was initiated 2006 until 2009. Stakeholders involved are the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) including field counterparts in Region 7, Non-Government Organization, Local Government Unit (LGU) and the People's Organization (PO) in Danao, Bohol.
One of the important foci of the project is botanical inventory and vegetation study of site which deals only on the study of trees and other plant species in the site rather than biodiversity study of site which encompasses the study of both plant and animals in the site.
2.3 Photos of the Approach
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Philippines
Region/ State/ Province:
Danao, Bohol
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2006
Year of termination (if Approach is no longer applied):
2009
2.7 Type of Approach
- project/ programme based
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The main objective of the approach is to effectively convert deforested lands or degraded vegetation to a more productive forest.
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
institutional setting
- enabling
The unpopularity of the ANR approach was resolved through media mileage. Further, the adoption of LGU as well as its Declaration of Bohol as the country's first-ever ANR Municipality through Municipal Ordinance No. 2008-08-11 adopted by the Sangguniang Bayan on August 26, 2008 gained nationwide recognition of the approach.
knowledge about SLM, access to technical support
- enabling
Research, training, seminars were conducted
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- local land users/ local communities
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | passive | DENR |
| planning | passive | DENR |
| implementation | interactive | DENR, Bagong Pag-asa Foundation, People's Organization |
| monitoring/ evaluation | passive | DENR and the POs were involved in the establishment of firelines or firebreaks/ greenbreaks, conduct of patrol works, conduct ring weeding and augmentation planting. |
| research | passive |
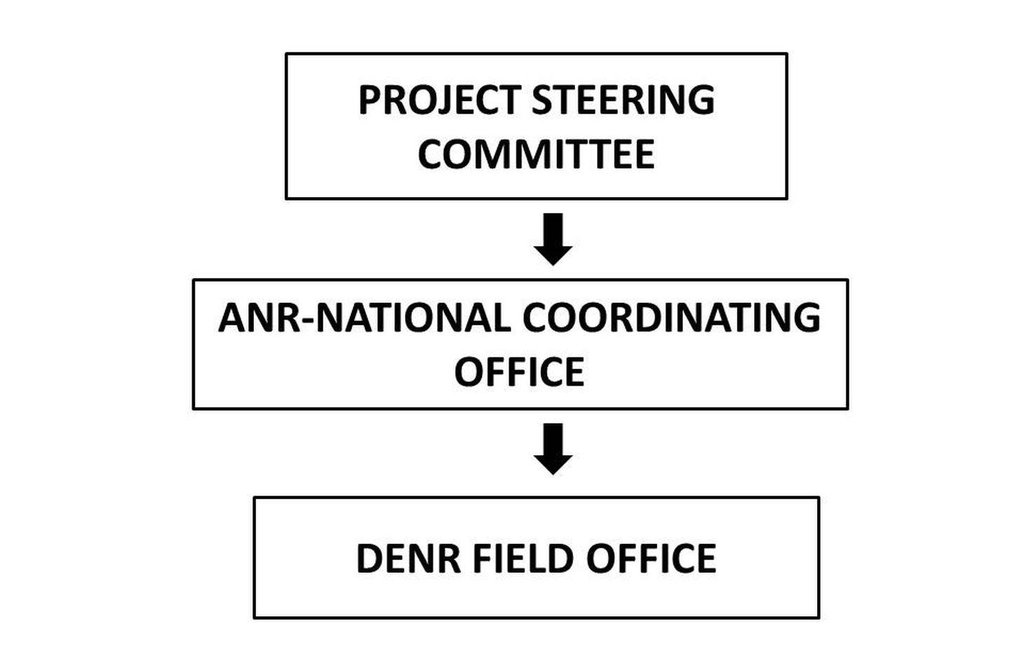
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
Description:
Functional Structure of ANR project
Author:
Forester Emma N. Castillo, Department of Environment and Natural Resources
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- mainly SLM specialists, following consultation with land users
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Yes
Specify who was trained:
- land users
- field staff/ advisers
If relevant, specify gender, age, status, ethnicity, etc.
Transfer of the technologies of ANR to forest officers, LGUs, NGOs, POs, community members, academe, research institutions, and civil society.
Form of training:
- on-the-job
- farmer-to-farmer
- demonstration areas
Subjects covered:
Management of site through the ANR technology
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
Specify whether advisory service is provided:
- on land users' fields
Describe/ comments:
DENR personnel were capacitated through trainings to ensure the continuation of the project.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, moderately
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
If yes, is this documentation intended to be used for monitoring and evaluation?
No
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Yes
Specify topics:
- ecology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
Biodiversity study through documentation of the vegetation status and notable changes in the biodiversity of the site with the application of the ANR techniques.
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- 10,000-100,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO-UN) 30%, DENR-FMB (in kind contributions) 70%
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
Yes
If yes, specify type(s) of support, conditions, and provider(s):
Activities undertaken under this approach was financed through the FAO-UN contribution.
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| tools | fully financed | tools, wooden board |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- paid in cash
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
5.5 Other incentives or instruments
Were other incentives or instruments used to promote implementation of SLM Technologies?
No
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Natural regeneration of the vegetation from grassland to forest is more apparent with the emergence of several reforestation species, natural secondary forest species and other indicator species. The growth of herbs and shrubs strongly indicates that the site is in early stage of development to a secondary forest.
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
not aimed by technology
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The town of Danao, Bohol was proclaimed as ANR municipality thus gaining the full support of the local government in terms of funding and other activities related to ANR.
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- environmental consciousness
improved biodiversity and restoration of the forest
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- yes
If yes, describe how:
The technology was transferred to various stakeholders that enabled them to continue the program.
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Strong support from various stakeholders including the LGU, DENR, international agencies and others. |
| Philippines was awarded and cited for forest restoration and UN forestry award. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| DENR issued a national policy wherein ANR is one of the major activities in forest restoration of tenurial instrument holder. ANR is also included as one of the major restoration technologies in several projects. |
| The techniques of ANR are simple which include the integration of economic and social values and forest reforestation. |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| The approach is underutilized due to lack of awareness and research results demonstrating its effectiveness | Research that could be used in determining potentials of a site for ANR techniques using soil and vegetation factors. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Firebreaks/ Greenbreaks [Philippines]
Gaps in vegetation or other combustible material that act as barriers to prevent and/ or control the spreading of forest fires to other areas.
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies

Pressing of Cogon Grass (Imperata cylindrica) [Philippines]
An indigenous technology of enhancing wildling growth by pressing of cogon grass.
- Compiler: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Modules
No modules